Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EE201 - Tutorial 1
EE201 - Tutorial 1
Uploaded by
LIYANAGE S.N.Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EE201 - Tutorial 1
EE201 - Tutorial 1
Uploaded by
LIYANAGE S.N.Copyright:
Available Formats
EE201/282- Network Analysis
Tutorial – 1
DC Circuit Analysis and Two Terminal Resistors
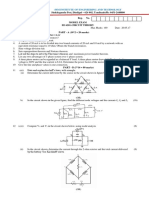
1. For the two-terminal resistors given by the v-i characteristics shown in Fig. Q-1, state
whether each one is
(i) linear or nonlinear.
(ii) voltage-controlled and/or current-controlled,
(iii) passive or active,
(iv) bilateral or nonbilateral.
i i
i i i i
v v v v v
non non non
v
non li li
vc cc vc nor cc vc
cc vc/cc
pa ac ac pa
ac ac
bi non non bi
non bi
Fig. Q1
2. The equations below specify the characteristics of some resistors. Indicate whether
they are
(i) linear or nonlinear,
(ii) time-varying or time-invariant,
(iii) voltage-controlled or current-controlled.
(iv) passive or active
(v) bilateral or nonbilateral.
a) v +10i = 0 (e) i = tanh v
b) v = (cos 2t)i + 3 (f) i -+ 3v = 10
c) i = exp(-v) (g) i = 2 +cos t
2
d) v = i (h) i= v + (cos2t)v/|v|
3. Suppose that the nonlinear resistor R has a characteristic specified by the equation
1
v=20i+ i2 + 2i3
a) Express v as a sum of sinusoids, given i(t) = cost + 2 cost
b) If = 22 what frequencies are present in v?
4. Use graphic series and parallel addition to find and plot the driving-point
characteristics of the one-port shown in Fig. Q-4.
KML 2020 - Dept. of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University of Peradeniya
Fig. Q-4
5. (a) Draw the driving-point characteristics for the two circuits shown in Fig. Q-5 a and
b. The two nonlinear resistors are described by the v-i characteristics shown in Fig.
Q-5 c and d respectively.
(b) Will the driving-point characteristic obtained in (a) change if the terminals of R1
turned around? Explain.
Fig. Q-5
6. Repeat Prob. 5(a) with the terminals of R2, turned around.
7. Use graphic addition to find the driving-point characteristic of the circuit shown in
Fig. Q-7
Fig. Q-7
8. Repeat Prob. 7 for the circuit shown in Fig. Q-8.
KML 2020 - Dept. of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University of Peradeniya
Fig. Q-8
9.
a) Draw the v-i characteristics of an ideal diode. Draw the i-v characteristics of its
dual. Hence draw the dual circuit of an ideal diode?
b) Draw the v-i characteristics of circuits shown in Fig. Q-9. What are their dual
circuits?
i
Fig. Q-9
10. Find the dual circuits for the circuits shown in Fig. Q-10.
Fig. Q-10
11. Plot the v-i characteristics for the circuits shown in Fig. Q-11 (a). Assume the zener
diodes are described by the v-i characteristic in Fig. Q-11 (b) with EZ = 10 V.
KML 2020 - Dept. of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University of Peradeniya
Fig. Q-11
(a) (b)
12. For the circuit shown in Fig. Q-12
a) Determine the driving-point characteristic of the one-port 1-1’, that is, the
equation describing the one-port in terms of the port voltage and the port
current.
b) Plot the characteristic in the v-i plane.
c) Determine an equivalent one-port which consists of one independent current
source and one linear resistor.
d) Determine the dual one-port of the above.
Fig. Q-12
13.
a) Plot the driving-point characteristic of the one-port shown in Fig, Q-13(a).
b) A current source i, is connected to the above one-port as shown in Fig. Q_13(b).
Determine the port voltage v for
(i) is=2A
(ii) is = 1 A
(iii) is = 1/2 A
Fig. Q-13
14. Use graphic series and parallel addition to find the driving-point characteristics of the
circuits shown in Fig. Q.14.
KML 2020 - Dept. of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University of Peradeniya
Fig. Q-14
15. Using only concave resistors. convex resistors. and at most one linear resistor and
one dc source. synthesize the driving-pint characteristics shown in Fig. Q-15
Fig. Q-15
16.
a) The piecewise-linear v-i characteristic in Fig. Q-16(a) can be described by
Specify the coefficients ao, a1, b1, b2, I1, and I2.
b) Specify the parameters R,, R,, R,, I,, and I, in Fig. Q-16(b) so that the driving-point
characteristic of the one-port N is given by Fig. Q-16(a)
Fig. Q-16
KML 2020 - Dept. of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University of Peradeniya
17. The zener-diode circuit shown in Fig. Q-17 functions as an inexpensive voltage
regulator which maintains a constant output voltage when the load resistance R,
andlor power supply voltage E change within a prescribed range.
a) Assuming an ideal zener-diode v-i characteristic with E, = 5 V (see Fig. Q-11), find
(by the graphic method) the driving-point characteristic of the one-port N.
b) Using the driving-point characteristic from (a), find the output voltage v, when RL
= 2 k and RL = 500 , respectively.
c) If E can vary by 25 percent, specify the allowable range of RL in order to maintain
a constant 5 V output voltage.
Fig. Q-17
18. Consider the circuit shoun in Fig. Q-18(a) . where the tunnel diode and the pn-
junction diode are modeled by the piecewise-linear characteristics in Fig. Q-18(b)
and (c). respectively. Use the load-line method to find the voltage v1 and the current
i2 at each operating point of the circuit.
Fig. Q-18
(b)
KML 2020 - Dept. of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University of Peradeniya
19. For the circuit shown in Fig. Q-19 plot the transfer characttristic v2 as a function of is.
is
Fig. Q-19
KML 2020 - Dept. of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University of Peradeniya
You might also like
- EE201 - Tutorial 2Document4 pagesEE201 - Tutorial 2LIYANAGE S.N.No ratings yet
- Lab 9Document4 pagesLab 9Dhruvesh AsnaniNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Summative 202 SaturdayDocument3 pagesPower Electronics Summative 202 SaturdayTấn Long Đoàn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Applications of Diode CircuitsDocument3 pagesApplications of Diode CircuitsIonutNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Pyq 2023Document11 pagesSemiconductor Pyq 2023AyushNo ratings yet
- Multilevel Topologies. Josep PauDocument32 pagesMultilevel Topologies. Josep PauJose ManuelNo ratings yet
- Basics of Network Theory - Practice Sheet 01Document11 pagesBasics of Network Theory - Practice Sheet 01Pratik AdhikaryNo ratings yet
- E2001 Circuit Analysis: Academic Year 2020-2021Document15 pagesE2001 Circuit Analysis: Academic Year 2020-2021Eunice GohNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2Document5 pagesSheet 2Amr HatemNo ratings yet
- Eee205 TermDocument25 pagesEee205 TermMuhammad Imran HossainNo ratings yet
- Department of E Ectrical Electronic Engineering Bangladesh Unive Sity of Engineering TechnologyDocument3 pagesDepartment of E Ectrical Electronic Engineering Bangladesh Unive Sity of Engineering TechnologyMeowNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For ExaminationDocument4 pagesImportant Questions For ExaminationSaurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Problems Chapter 1 ContentsDocument6 pagesProblems Chapter 1 ContentsĐức ThànhNo ratings yet
- Jntuh Previous Year PaperDocument2 pagesJntuh Previous Year Paper20BA693 KmitNo ratings yet
- Sankalp Phaseiv El 8 Lecture-8Document5 pagesSankalp Phaseiv El 8 Lecture-8aggnaman009No ratings yet
- NK C SI R: Electrostatics, Home Work Sheet-4Document2 pagesNK C SI R: Electrostatics, Home Work Sheet-4AishwaryNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 1 Breadboards & DC MeasurementsDocument12 pagesLaboratory 1 Breadboards & DC MeasurementsRaza HyderNo ratings yet
- R.D. Enggineering College, Duhai, GZB: Deptt. of Electronics & Communication EnggDocument3 pagesR.D. Enggineering College, Duhai, GZB: Deptt. of Electronics & Communication EnggMohan SinghNo ratings yet
- Xone Port NetworksDocument53 pagesXone Port NetworksjayxcellNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Practice QuestionsDocument19 pagesAnalog Electronics Practice Questionssharma_rockstarNo ratings yet
- Network Practice Sheet 1 & 2 CHDocument23 pagesNetwork Practice Sheet 1 & 2 CHPAWAN KUMAR MAURYANo ratings yet
- Nas MCQDocument7 pagesNas MCQPankaj KaleNo ratings yet
- Current electricity f1Document4 pagesCurrent electricity f1Ashwary SethNo ratings yet
- اسئلة تحليلات الدوائر الكهربائية (شبكات كهربائية)Document3 pagesاسئلة تحليلات الدوائر الكهربائية (شبكات كهربائية)لقلثلثلثقNo ratings yet
- Transformer TestsDocument5 pagesTransformer TestsBerentoNo ratings yet
- 4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetDocument19 pages4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetmntykrNo ratings yet
- Técnicas Digitales y Analógicas - 27124 Ejercicios DiodosDocument2 pagesTécnicas Digitales y Analógicas - 27124 Ejercicios DiodosAndrés Muñoz AcostaNo ratings yet
- Buku DiodaDocument8 pagesBuku Diodanaru_chan1003No ratings yet
- Sheet 4-1Document4 pagesSheet 4-1bodesaid2002No ratings yet
- Example 4 1 Circuits IntroductionDocument4 pagesExample 4 1 Circuits IntroductionDiego Escobar MoncadaNo ratings yet
- 750913A02101 Electrical CircuitsDocument2 pages750913A02101 Electrical CircuitsKURAKULA VIMAL KUMARNo ratings yet
- L' m-lIEEE: Cox W VDocument16 pagesL' m-lIEEE: Cox W VSumaiya Binte YousufNo ratings yet
- MCQ Gate by RK KanodiaecDocument440 pagesMCQ Gate by RK KanodiaecViswakarma ChakravarthyNo ratings yet
- Training Questions in Electronics/F 6, Gths K'Bo Paper Two: January 2010Document6 pagesTraining Questions in Electronics/F 6, Gths K'Bo Paper Two: January 2010NGOUNENo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Power AmplifiersDocument11 pagesChapter 7 Power Amplifierstolesa 2020No ratings yet
- Eee 312 6Document3 pagesEee 312 6sabitavabiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6: 1 2 C CE BEDocument4 pagesTutorial 6: 1 2 C CE BEAadarshPotluruNo ratings yet
- Electrical Systems EC1021Document5 pagesElectrical Systems EC1021Sulaksha WimalasenaNo ratings yet
- Ee Electrical and Electronic MeasurementsDocument33 pagesEe Electrical and Electronic MeasurementsNilamani Umashankar JenaNo ratings yet
- EE1000 DC Networks Problem SetDocument7 pagesEE1000 DC Networks Problem SetAmit DipankarNo ratings yet
- Elec-275 Final Examination Winter 2013Document6 pagesElec-275 Final Examination Winter 2013Kowe100% (1)
- Multisim Activity 3 BXX LastName FirstName Copy 040546Document9 pagesMultisim Activity 3 BXX LastName FirstName Copy 040546feihtwollip3No ratings yet
- DA AnalysisDocument5 pagesDA AnalysisraineymjNo ratings yet
- ESE Questions Bank EE NetworkDocument12 pagesESE Questions Bank EE NetworkgregNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Dr. Balraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Laboratory - PHY 120xcxcDocument63 pagesLaboratory - PHY 120xcxchwuhwuheNo ratings yet
- Test 2 Electronics Code: DDWK 2002 Answer All Questions Time: 1 HourDocument2 pagesTest 2 Electronics Code: DDWK 2002 Answer All Questions Time: 1 HourRAZMAN BIN RAMEDANNo ratings yet
- Final Question - ECE1312 - Sem1 - 14-15Document9 pagesFinal Question - ECE1312 - Sem1 - 14-15FARAZ ABDUL BASITNo ratings yet
- EE31594 Quiz 4 Dec 14, 2019Document8 pagesEE31594 Quiz 4 Dec 14, 2019Hyunsog ChoiNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Manual With LogoDocument69 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manual With LogoPunith Gowda M BNo ratings yet
- EC6411 Circuit & Devices Lab ManualDocument93 pagesEC6411 Circuit & Devices Lab ManualKALAIMATHINo ratings yet
- 7.electric Current & Circuits-1Document12 pages7.electric Current & Circuits-1sri ramNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document8 pagesTutorial 5Muhammad FauziNo ratings yet
- 201 Lab Experiment2Document5 pages201 Lab Experiment2Fatih TokgözNo ratings yet
- Analogue ElectronicsDocument7 pagesAnalogue ElectronicsrizwanahbNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Sem 2 2014 - 2015Document10 pagesMid Term Sem 2 2014 - 2015FARAZ ABDUL BASITNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - Principles of ElectronicsDocument13 pagesQuestion Bank - Principles of ElectronicsADDELYN CYNTHIA ANAK TONYNo ratings yet
- ET1006 - 1820 - Exam With AnswersDocument12 pagesET1006 - 1820 - Exam With AnswersfastNo ratings yet
- Mark. Un-Attempted Questions Will Be Counted As Wrong Answers. No Question Will Be Entertained During The Exam. Time Allowed: 30 MinutesDocument4 pagesMark. Un-Attempted Questions Will Be Counted As Wrong Answers. No Question Will Be Entertained During The Exam. Time Allowed: 30 MinutesMuhammad ShafiqNo ratings yet
- EE201 - Tutorial 2Document4 pagesEE201 - Tutorial 2LIYANAGE S.N.No ratings yet
- Lesson1 1Document8 pagesLesson1 1LIYANAGE S.N.No ratings yet
- Lesson1 2Document3 pagesLesson1 2LIYANAGE S.N.No ratings yet
- EF501 Assignment 4Document1 pageEF501 Assignment 4LIYANAGE S.N.No ratings yet
- EF501 Assignment 2Document1 pageEF501 Assignment 2LIYANAGE S.N.No ratings yet
- Sindalagundu Post, Dindigul - 624 002, Tamilnaduph: 0451-2448800 Reg. No. Model Exam Ee 6201-Circuit TheoryDocument2 pagesSindalagundu Post, Dindigul - 624 002, Tamilnaduph: 0451-2448800 Reg. No. Model Exam Ee 6201-Circuit Theoryboomadev6321No ratings yet
- Expt. No.4 555timer DAC ADCDocument3 pagesExpt. No.4 555timer DAC ADCsachin1391No ratings yet
- 4 - Diode ClippersDocument3 pages4 - Diode ClippersHello WorldNo ratings yet
- Low Power Low Dropout Middle Current Voltage Regulators: General Description FeaturesDocument10 pagesLow Power Low Dropout Middle Current Voltage Regulators: General Description Features171 171No ratings yet
- Modern QRP Rigs and The Development of The QCX CW Transceiver KitDocument36 pagesModern QRP Rigs and The Development of The QCX CW Transceiver KitChandrashekhar KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Module 5 (Radio Receivers)Document13 pagesModule 5 (Radio Receivers)Sarah J SinfuegoNo ratings yet
- Logic Design Styles: Dinesh SharmaDocument6 pagesLogic Design Styles: Dinesh Sharmachandan choudharyNo ratings yet
- Charlieplexed Display With 12 Led'S: (FSM With Datapath and Control Path)Document5 pagesCharlieplexed Display With 12 Led'S: (FSM With Datapath and Control Path)prem kumarNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering Technology: Lecture PlanDocument4 pagesFaculty of Engineering Technology: Lecture PlanNorhafizah Bt SallehNo ratings yet
- A3144 Hall Effect Sensor: 3 January 2018 - 0 CommentsDocument5 pagesA3144 Hall Effect Sensor: 3 January 2018 - 0 CommentsSorin NemesNo ratings yet
- Ee 3101 Electronics I Laboratory Experiment 9 Lab Manual Applications of Ic Building BlocksDocument5 pagesEe 3101 Electronics I Laboratory Experiment 9 Lab Manual Applications of Ic Building BlocksPriyanshu KumawatNo ratings yet
- AC-DC BridgesDocument4 pagesAC-DC BridgesManan DesaiNo ratings yet
- Design of High Gain Folded-Cascode Operational Amplifier Using 1.25 Um CMOSDocument9 pagesDesign of High Gain Folded-Cascode Operational Amplifier Using 1.25 Um CMOSHassan El-kholyNo ratings yet
- Sequential CircuitsDocument19 pagesSequential CircuitsSalil TimalsinaNo ratings yet
- PLDDocument10 pagesPLDDr Ravi Kumar A.VNo ratings yet
- VLSI Module 3 PDFDocument34 pagesVLSI Module 3 PDFGovind M RoddannavarNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument338 pagesElectronicsTahuu Ahmed100% (1)
- A733 PDFDocument2 pagesA733 PDFBahram4321No ratings yet
- Figure 4-1 It Is Often Possible To Simplify A Logic Circuit Such As That in Part (A) To Produce A More Efficient Implementation, Shown in (B)Document72 pagesFigure 4-1 It Is Often Possible To Simplify A Logic Circuit Such As That in Part (A) To Produce A More Efficient Implementation, Shown in (B)Fx HardsonNo ratings yet
- 8-To-1 MUXDocument3 pages8-To-1 MUXMahijaNo ratings yet
- High Power Switching Audio Power Amplifier With Symmetrical Topology and Digital ControlDocument3 pagesHigh Power Switching Audio Power Amplifier With Symmetrical Topology and Digital ControlPéter PAPPNo ratings yet
- EE305 - Telecommunications I: Rsc. Ast. Dr. Mustafa Anıl REŞATDocument25 pagesEE305 - Telecommunications I: Rsc. Ast. Dr. Mustafa Anıl REŞATLütfi Alper AydoğanNo ratings yet
- 74 Series Logic ICsDocument9 pages74 Series Logic ICsshahidali6No ratings yet
- Thevinin and NortonDocument44 pagesThevinin and NortonfareenfarzanawahedNo ratings yet
- Resonant Converters: Problems With Switching DevicesDocument18 pagesResonant Converters: Problems With Switching Devicesmanoj kumarNo ratings yet
- PJ1117CM-2 5VDocument6 pagesPJ1117CM-2 5VАлексей ГомоновNo ratings yet
- Voltage Controlled OscillatorDocument7 pagesVoltage Controlled OscillatorHemantha DalugamaNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Model of Class e Amplifier Based On The Harmonic Balance MethodDocument5 pagesMathematical Model of Class e Amplifier Based On The Harmonic Balance MethodahsoopkNo ratings yet
- Dc-To-Dc Converter Control Circuits: Features Functional Block DiagramDocument2 pagesDc-To-Dc Converter Control Circuits: Features Functional Block DiagramAnkitNo ratings yet
- Preparatory Guidebook For Comprehensive Examination: Question Bank DsdaDocument14 pagesPreparatory Guidebook For Comprehensive Examination: Question Bank DsdaMisbah Sajid ChaudhryNo ratings yet