Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ASSESSMENT
ASSESSMENT
Uploaded by
Liza Soberano0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesThe document discusses the nursing process and different types of assessments. It begins by outlining the 5 phases of the nursing process - assessment, nursing diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. It then focuses on the assessment phase, describing the purpose and different types of assessments including initial, problem-focused, emergency, and time-lapsed reassessments. The key steps of assessment are described as data collection, organization, validation, and documentation. Data collection involves gathering both subjective and objective data through various methods such as observation, interviewing, and examination.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the nursing process and different types of assessments. It begins by outlining the 5 phases of the nursing process - assessment, nursing diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. It then focuses on the assessment phase, describing the purpose and different types of assessments including initial, problem-focused, emergency, and time-lapsed reassessments. The key steps of assessment are described as data collection, organization, validation, and documentation. Data collection involves gathering both subjective and objective data through various methods such as observation, interviewing, and examination.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesASSESSMENT
ASSESSMENT
Uploaded by
Liza SoberanoThe document discusses the nursing process and different types of assessments. It begins by outlining the 5 phases of the nursing process - assessment, nursing diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. It then focuses on the assessment phase, describing the purpose and different types of assessments including initial, problem-focused, emergency, and time-lapsed reassessments. The key steps of assessment are described as data collection, organization, validation, and documentation. Data collection involves gathering both subjective and objective data through various methods such as observation, interviewing, and examination.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
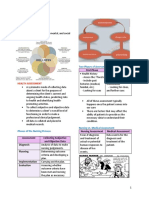
Nursing process comprise of 5 phases - It is performed within specified time
That includes: after admission
Assessment Purpose : is to complete database or
Nursing diagnosis problem identification and reference
Planning for future comparison
Implementation
Evaluation PROBLEM-FOCUSED ASSESSMENT
- It is an ongoing process integrated
ASSESSMENT with nursing care
- Is the systematic and continuous Purpose: is to determine the status
collection, organization, validation, of a specific problem identified in an
and documentation of data earlier assessment
- It is the first step in nursing process
EMERGENCY ASSESSMENT
Purpose = To gather information, collect - It is done during any physiologic or
data from different sources : physiologic crisis of the client
● Primary sources that are coming - Purpose : is to determine life-
from the client alone. threatening problems, identifying
● Secondary sources that are coming new or overlooked problems
from the results of physical exam,
nursing health history, laboratory or TIME-LAPSED REASSESSMENT
diagnostic test results. - It is done several months after initial
assessment
Data can be classified as: Purpose : is to compare the clients
➔ Subjective Data : from the client, status to baseline data previously
complains of symptoms that needs obtained
to be validated
➔ Objective data: can be observe from Assessment follows different process:
the client’s signs of illness A. Data collection
B. Organization
Assessment is done to establish a patients C. Validation
database which is a baseline data of the D. Documentation
client.
In doing assessment, we need to consider A. DATA COLLECTION - is the process of
what type of assessment we are going to gathering information about a client’s status.
do. Data is being defined as a set of information
or facts about a client.
Types of Assessment: - It focus on clients response to health
1. Initial Assessment problems or information about
2. Problem-focused assessment clients health status
3. Emergency assessment *Data collected should be relevant to the
4. Time-lapsed reassessment health problems.
- Consider the Time, Needs of client,
INITIAL ASSESSMENT developmental stage of the client,
physical surroundings, past and ★ Other description of data:
present coping patterns that are ○ Variable
being used by our client. ○ Constant
★ Data to be collected includes: ○ Variable - changes from day
○ Demographics to day or even our in needs
○ Medical history of updating from time to time
○ Health habits ○ Constant - unchanging
○ Education tikane
○ Allergies ★ Sources of Data:
○ Environmental and family ○ Primary - patient; statement
factors made
○ Potential for injury - Primary source
○ Ability to participate of care - Usually best source
○ Result of physical ○ Secondary - coming from
assessment other sources : Family or
Significant others, records or
reports of other healthcare
★ Data Characteristics: professionals and relevant
○ Complete literature.
○ Factual
○ Accurate ★ Data collection method:
○ Relevant 1. Observation/Observing
2. Interview/Interviewing
★ Types of Data: 3. Examination/Examining
○ Subjective - Symptoms or
covert data, which cannot be OBSERVATION - process of gathering
readily observed by another data, using the senses.
individual.
- This can be obtained: INTERVIEW - gathering of data by asking
Interview, sensation, questions
feelings, values, beliefs,
attitudes, perception of ❖ Types of interview:
personal health status, and ➢ Open-ended - non directive
life situation in nature, allows the clients
to express his feelings or
○ Objective - Signs or over thoughts, freedom to share
data. Can be observe, heard, their emotions.
seen, felt or smelled, can be ➢ Closed - directive, requires
measured or tested against short or factual answers
an acceptable standard ➢ Neutral - can be answer by
- Obtained : observation and the client without pressure
physical examination from nurse, open ended
questions and non directive
➢ Leading - usually close- - The nurse should have an
ended questions and excellent communication
directive in nature, which skills, active listening, good
directs the clients to answer eye contact
the questions asked by the - Open ended questions are
nurse, gives the client less usually
opportunity to decide 3. Working phase
whether the answer is true or 4. Termination phase - interview is
not. about to be end
- The gather information must
❖ We should consider 2 approaches: be kept confidential
1. Directive approach - usually elicits
and specific information which the
nurse controls the subject matter,
the client has little opportunity to ask EXAMINATION - physical examination/
question or discuss his/her concerns assessment
2. Non-directive approach - the nurse - Systematic data collection method
allows the client to control the that uses observation (sight,
purpose, subject matter and phase hearing, smell, touch) to detect
health problems
❖ Phases of interview:
1. Preparatory phase - the nurse ❖ Approaches of Examination
collects the background information Techniques
from previous charts, 1. Body system - investigates each
- the nurse ensures that the system individually
environment is conducive for 2. Cephalocaudal - head to toe
interview
- Seats are arranged 3-4 ft
apart ❖ Also :
- interviewer is at 45 degree ➢ Inspection - using sense
angle to the patient sight
- And the client given an ➢ Palpation - using sense of
adequate time to participate touch : finger pads because
in interview their concentration of nerve
ending make them highly
2. Introductory phase - the nurse sensitive to tactile
introduces his/herself, identify its dicrimination
purpose, ensures confidentiality, ➢ Percussion - strikes the body
provides patients need before surface to elicits sound that
starting an interview can be heard or vibration that
- During this phase the nurse can be felt
gathers info from client for ➢ Auscultation - listens through
the subjective data the use of stethoscope
B. ORGANIZATION - organizing related - Ask someone else to collect
cues into predetermined categories the same data to confirm
your findings
D. DOCUMENTATION - data should be
➔ Using 2 types of models: recorded in a factual manner & not as
◆ Nursing models: interpreted by the nurse
- Gordon’s 11 - Record Subjective data in the
Functional Health client’s own words, using quotation
Patterns marks
- NANDA Human - In documenting clients care, it
Response Pattern should be clear and concise --
◆ Non nursing model: - written in appropriate terminologies
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs - Avoid generalization, make it more
specific. Do not make summative
C. VALIDATION - “double checking” or statement regarding the client’s
verifying data status
*not all data should be validated especially
when the data is accepted, factual or
accurate
*validation process only done if there are
discrepancies
Purpose : to ensure its completeness,
accuracies and factual, Subjective and
Objective data may agrees, and to eliminate
errors, biases, and misperception, to avoid
jumping into conclusions
● Some ways to validate data:
1. Always compare S&O data to verify
the client’s statements with your
observations.
2. Be sure your data consist of cues,
not inferences. *inferences =
educated guesses
3. Double check data that are
extremely abnormal.
- Recheck your measurement
to be sure it is accurate
- Check to be sure your
measuring device is working
correctly, or use a different
piece of equipment.
You might also like
- 4 Essential Keys To Effective CommunicationDocument95 pages4 Essential Keys To Effective CommunicationAitor Sevillano Chapartegui100% (10)
- Housecalls 101: Policy and Procedure Manual for Medical Home VisitsFrom EverandHousecalls 101: Policy and Procedure Manual for Medical Home VisitsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process ApproachDocument16 pagesNursing Process ApproachHUSSAINA BANO67% (3)
- Nursing ProcessDocument134 pagesNursing Processkennedy14344100% (4)
- Health Assessment - Lecture: Definition of NursingDocument6 pagesHealth Assessment - Lecture: Definition of NursingEthel May AlabastroNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment 1.0Document11 pagesHealth Assessment 1.0Nathalie CaracaNo ratings yet
- Module 1-Nursing ProcessDocument12 pagesModule 1-Nursing ProcessrishellemaepilonesNo ratings yet
- FON-LEC Chapter 4Document9 pagesFON-LEC Chapter 4Harry AglugobNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process: Ns. Nuning Khurotul Af'ida, S.Kep.,M.KepDocument91 pagesNursing Process: Ns. Nuning Khurotul Af'ida, S.Kep.,M.KepDindaaNo ratings yet
- NCM103 the Nursing ProcessDocument10 pagesNCM103 the Nursing ProcessJude RiveraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process ModuleDocument21 pagesNursing Process ModuledocgioreNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Health AssessmentDocument2 pagesIntroduction of Health AssessmentKrishna Faith P. DelaraNo ratings yet
- Ncma121 LecDocument30 pagesNcma121 LecAlyanna TiglaoNo ratings yet
- Nursing ProcessDocument5 pagesNursing Processchnllh19No ratings yet
- Reviewer Final 1Document6 pagesReviewer Final 1zabalaiiirogeliopaclibarNo ratings yet
- Week3-5Nursing Process-OUTLINEDocument4 pagesWeek3-5Nursing Process-OUTLINEemman.magtibayNo ratings yet
- Ha Lesson 1 and 2Document2 pagesHa Lesson 1 and 2JhayneNo ratings yet
- ASSESSINGDocument3 pagesASSESSINGCrazy StrangerNo ratings yet
- The Nursing ProcessDocument9 pagesThe Nursing Processiannello100% (2)
- M1 - Nursing Process, Critical Thinking, Intro To HaDocument40 pagesM1 - Nursing Process, Critical Thinking, Intro To HaRomalyn MoralesNo ratings yet
- HA LEC ReviewerDocument12 pagesHA LEC ReviewerKyungmin OñaNo ratings yet
- Nursing ProcessDocument21 pagesNursing Processrubycorazon_edizaNo ratings yet
- Assess PDFDocument5 pagesAssess PDFLouis UranoNo ratings yet
- NCM 101 - Health Assessment: Topic OutlineDocument8 pagesNCM 101 - Health Assessment: Topic OutlineJohannaNo ratings yet
- NSG Process NEWDocument135 pagesNSG Process NEWRhea Lyn LamosteNo ratings yet
- Nursing ProcessDocument131 pagesNursing ProcessYochabel BorjeNo ratings yet
- First Part MaternalDocument53 pagesFirst Part Maternalkennedy14344No ratings yet
- Health Assessment PrelimDocument10 pagesHealth Assessment Prelimpsyche.ladicaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process 2Document90 pagesNursing Process 2rerenrahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Remember: Goals and Plan of Care Should Be Base According To Client's Problems/needs NOT According To Your OwnDocument11 pagesRemember: Goals and Plan of Care Should Be Base According To Client's Problems/needs NOT According To Your Ownavinash dhameriyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Introduction: The Nursing ProcessDocument7 pagesUnit 1: Introduction: The Nursing ProcessMeyden PringNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument24 pagesAssessmentAswathyNo ratings yet
- Funda NotesDocument13 pagesFunda NotesMa. Christina Jane OmambacNo ratings yet
- Ho Complete Nursing Process 2024Document21 pagesHo Complete Nursing Process 2024Jasmine DamianNo ratings yet
- Health AssessmentDocument77 pagesHealth AssessmentDawn RallosNo ratings yet
- Group 1 AssessingDocument19 pagesGroup 1 AssessingFaith De los santosNo ratings yet
- Prelim Lec Health AssessmentDocument26 pagesPrelim Lec Health AssessmentJade Buri100% (1)
- A MergedDocument246 pagesA MergedJude Rhandy CorroNo ratings yet
- Part A - AssessmentDocument38 pagesPart A - AssessmentJaya PriyaNo ratings yet
- Historical Development of Nursing ProcessDocument150 pagesHistorical Development of Nursing ProcessSalale FiicheeNo ratings yet
- 2019 5framework of Health AssessmentDocument31 pages2019 5framework of Health Assessmentharley dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Funda Nursing ProcessDocument9 pagesFunda Nursing Processj UNo ratings yet
- FundaDocument41 pagesFundashawdino03No ratings yet
- TFN Review 1Document5 pagesTFN Review 1Anthony RiggsNo ratings yet
- The Nursing ProcessDocument3 pagesThe Nursing ProcessBianca Marithè RejanoNo ratings yet
- Notes Encoded in ClinicalDocument24 pagesNotes Encoded in Clinicaljane pletaNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment AssignmentDocument15 pagesHealth Assessment Assignmentpslokesha84No ratings yet
- Health: Health Assessment Lecture ReviewerDocument22 pagesHealth: Health Assessment Lecture RevieweryanNo ratings yet
- Concepts, Process, and Practice Kozier & Erb's 9 Edition: Fundamentals of NursingDocument7 pagesConcepts, Process, and Practice Kozier & Erb's 9 Edition: Fundamentals of NursingLester Paul SivilaNo ratings yet
- Nursing AssesmentDocument39 pagesNursing AssesmentRed Jimeno100% (1)
- 01 Proses Keperawatan JiwaDocument18 pages01 Proses Keperawatan JiwaMuzay YanaNo ratings yet
- Midwifery Skills Clinical Laboratory: The Midwives ProcessDocument26 pagesMidwifery Skills Clinical Laboratory: The Midwives ProcessNano KaNo ratings yet
- Health AssessmentDocument12 pagesHealth Assessmenthtagulao.nsgNo ratings yet
- 01 Proses Keperawatan JiwaDocument18 pages01 Proses Keperawatan JiwaastriNo ratings yet
- Ncma: Health AssessmentDocument25 pagesNcma: Health AssessmentBb PrintsNo ratings yet
- 6 Steps / Phases OF Nursing ProcessDocument24 pages6 Steps / Phases OF Nursing ProcessMary Anthonette Arenas EstradaNo ratings yet
- FundaaaDocument13 pagesFundaaaLorna Mae MontanezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Health AssessmentDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Health AssessmentAngela SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Health AssessmentDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Health AssessmentMa. Lou Danielle VallanoNo ratings yet
- NCLEX-RN Exam Prep 2024-2025: 500 NCLEX-RN Test Prep Questions and Answers with ExplanationsFrom EverandNCLEX-RN Exam Prep 2024-2025: 500 NCLEX-RN Test Prep Questions and Answers with ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- Hns Nclex-Rn Prep: Bilingual Prep for the Bilingual NurseFrom EverandHns Nclex-Rn Prep: Bilingual Prep for the Bilingual NurseNo ratings yet
- Administration of Iv FluidsDocument3 pagesAdministration of Iv FluidsLiza SoberanoNo ratings yet
- NDH - Nurses NotesDocument1 pageNDH - Nurses NotesLiza SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Assisting in Blood TransfusionDocument2 pagesAssisting in Blood TransfusionLiza SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Prelim PagesDocument3 pagesPrelim PagesLiza SoberanoNo ratings yet
- NDH - Vital Signs Monitoring SheetDocument1 pageNDH - Vital Signs Monitoring SheetLiza SoberanoNo ratings yet
- July 12 UpdateDocument73 pagesJuly 12 UpdateLiza SoberanoNo ratings yet
- MENTAL STATUS ASSESSMENT FormDocument6 pagesMENTAL STATUS ASSESSMENT FormLiza SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Tracking of ChangesDocument1 pageTracking of ChangesLiza SoberanoNo ratings yet
- DIAGNOSISDocument4 pagesDIAGNOSISLiza SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Rle Week3Document6 pagesRle Week3Liza SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Overview of A Nursing Process The Nursing Process: Steps in Critical ThinkingDocument2 pagesOverview of A Nursing Process The Nursing Process: Steps in Critical ThinkingLiza SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Rle NCM 116 Day 2: Be It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledDocument5 pagesRle NCM 116 Day 2: Be It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledLiza SoberanoNo ratings yet
- RUBRIC in Conducting An MSA (Interview) Criteria 4 3 2 1Document1 pageRUBRIC in Conducting An MSA (Interview) Criteria 4 3 2 1Liza SoberanoNo ratings yet
- NCM 103 PlanningDocument2 pagesNCM 103 PlanningLiza SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Aspects / Activites of Rehabilitation ProgramDocument2 pagesAspects / Activites of Rehabilitation ProgramLiza SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Transcribing Doctors OrderDocument6 pagesTranscribing Doctors OrderLiza SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz in Introduction To PhilosophyDocument2 pagesLong Quiz in Introduction To PhilosophyAlzen GalaponNo ratings yet
- Tao Te Ching Reflection BethersDocument2 pagesTao Te Ching Reflection Bethersapi-562628548No ratings yet
- Bloom's Revised TaxonomyDocument34 pagesBloom's Revised TaxonomyCATHERINE CAMACHONo ratings yet
- 1.1 - SEP - MetaethicsDocument34 pages1.1 - SEP - MetaethicsvexahNo ratings yet
- 1st Module 2 in HealthDocument14 pages1st Module 2 in HealthAlbert Ian CasugaNo ratings yet
- The Good LifeDocument23 pagesThe Good LifenicaNo ratings yet
- Educational Psychology: An International Journal of Experimental Educational PsychologyDocument13 pagesEducational Psychology: An International Journal of Experimental Educational PsychologyFahimeh MoafianNo ratings yet
- Komitmen Pemenuhan Hak Asasi Manusia (Ham) Serta Pengaruhnya Terhadap Pertumbuhan Ekonomi Di IndonesiaDocument26 pagesKomitmen Pemenuhan Hak Asasi Manusia (Ham) Serta Pengaruhnya Terhadap Pertumbuhan Ekonomi Di Indonesiaumi marwiyahNo ratings yet
- S. Waterlow - Nature, Change and Agency in Aristotle's PhysicsDocument16 pagesS. Waterlow - Nature, Change and Agency in Aristotle's PhysicsPatrizia LaspiaNo ratings yet
- Intro Phil 4TH Summative ExamDocument3 pagesIntro Phil 4TH Summative ExamLOID JAY KadileNo ratings yet
- Instructional Barriers of Classroom CommunicationDocument4 pagesInstructional Barriers of Classroom CommunicationKen ChepkwonyNo ratings yet
- (Ed 105 - Facilitating Learner-Centered Teaching) December 7, 2020 - January 15, 2021 Focus On LearningDocument18 pages(Ed 105 - Facilitating Learner-Centered Teaching) December 7, 2020 - January 15, 2021 Focus On LearningMa. Arnelyn AniNo ratings yet
- PracticalResearch1 Q3 Week1 v4Document15 pagesPracticalResearch1 Q3 Week1 v4RAEJEHL TIMCANGNo ratings yet
- EsssayDocument5 pagesEsssayNuman FarooqiNo ratings yet
- Is Morality Relative - The Philosophers' MagazineDocument4 pagesIs Morality Relative - The Philosophers' MagazinepambarrosoNo ratings yet
- Freud Origins of Psychoanalysis Letters To Fliess Part 1Document16 pagesFreud Origins of Psychoanalysis Letters To Fliess Part 1skjfldsfdsdfiojsdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 The Art of ListeningDocument6 pagesChapter 10 The Art of ListeningButch PicardalNo ratings yet
- Format For A Literature ReviewDocument2 pagesFormat For A Literature ReviewshishankisNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 3 ResearchDocument5 pagesWorksheet 2 3 ResearchCj FestinNo ratings yet
- Planning Through Debate-The Communicative Turn in Planning Theory-Patsy HealyDocument21 pagesPlanning Through Debate-The Communicative Turn in Planning Theory-Patsy HealyBagas SatyaNo ratings yet
- ELT 523 - Professionalism in TeachingDocument35 pagesELT 523 - Professionalism in TeachingSucy GipintsNo ratings yet
- Eesl 5200 Final Project Part 3 05Document9 pagesEesl 5200 Final Project Part 3 05api-582648042No ratings yet
- Many Forms of Culture: American Psychologist May 2009Document12 pagesMany Forms of Culture: American Psychologist May 2009Melgie Ann AmbatNo ratings yet
- Psychology Knowledge OrganisersDocument12 pagesPsychology Knowledge OrganisersRema BoualdjaNo ratings yet
- Human Development TheoryDocument3 pagesHuman Development TheoryMaribel Pascual FloresNo ratings yet
- Types of Perception (OB)Document10 pagesTypes of Perception (OB)Ankita GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - Module 4: Mental Health & StressDocument19 pagesQuarter 1 - Module 4: Mental Health & StressAlyssa Marie Dela Cruz100% (1)
- SN 12.2 - Vibhaṅgasutta-Bhikkhu SujatoDocument3 pagesSN 12.2 - Vibhaṅgasutta-Bhikkhu SujatoRyan BurtonNo ratings yet
- 1997 Thurlow Reading Writing QuartDocument19 pages1997 Thurlow Reading Writing QuartElsya RahmiNo ratings yet