Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Part 12 - Human Nervous System Anatomy
Part 12 - Human Nervous System Anatomy
Uploaded by
Amal Naeem JH0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views17 pagesThe nervous system comprises the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord and receives a large portion of the body's blood supply and oxygen due to its high metabolic needs. The CNS contains neurons for processing information and neuroglia for supporting neurons. Neuroglia make up 90% of the CNS and include astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and ependymal cells. The PNS contains nerves that connect the CNS to the rest of the body.
Original Description:
Original Title
Part 12- Human Nervous System Anatomy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe nervous system comprises the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord and receives a large portion of the body's blood supply and oxygen due to its high metabolic needs. The CNS contains neurons for processing information and neuroglia for supporting neurons. Neuroglia make up 90% of the CNS and include astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and ependymal cells. The PNS contains nerves that connect the CNS to the rest of the body.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views17 pagesPart 12 - Human Nervous System Anatomy
Part 12 - Human Nervous System Anatomy
Uploaded by
Amal Naeem JHThe nervous system comprises the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord and receives a large portion of the body's blood supply and oxygen due to its high metabolic needs. The CNS contains neurons for processing information and neuroglia for supporting neurons. Neuroglia make up 90% of the CNS and include astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and ependymal cells. The PNS contains nerves that connect the CNS to the rest of the body.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 17
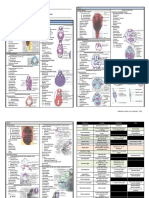
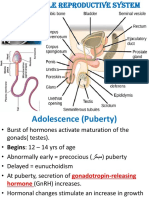
Part 12 – Nervous System Anatomy
– CNS comprises 2% of body weight (3–4
pounds).
• Receives 15% of blood supply
– High metabolic rate
• Brain uses 20% of oxygen consumed by
body at rest.
• Brain uses 50% of glucose consumed by
body at rest.
– Depends on blood flow for energy.
Central nervous system Components
• Two Anatomical Divisions
– Central nervous system (CNS)
• Brain
• Spinal cord
– Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
• All the neural tissue outside CNS
• Are nerves that go out to targets in body
• Two groups of neural cells in the nervous system:
• Neurons - For processing, transfer, and storage of
information. 30,000 neurons can fit on a pinhead.
Neuroglia: For support, regulation & protection of neurons
Neuroglia Cells
• 90% of CNS composed of glia
• CNS neuroglia:
• astrocytes
• oligodendrocytes
• microglia
• ependymal cells
• PNS neuroglia:
• Schwann cells (neurolemmocytes)
• satellite cells
Functional Classification of Neurons
• Sensory (afferent) neurons – transmit sensory information from
receptors of PNS towards the CNS
• most sensory neurons are unipolar, a few are bipolar
• Motor (efferent) neurons – transmit motor information from the
CNS to effectors (muscles/glands/adipose tissue) in the periphery of
the body
• all are multipolar
• Association (interneurons) – transmit information between neurons
within the CNS; analyze inputs, coordinate outputs
• are the most common type of neuron (20 billion)
• are all multipolar
Structure of Typical Synapse
Human Cerebral Cortex
The four lobes: occipital, parietal, temporal, and frontal
Amass of 100 billion neurons located inside the skull
Cerebrum : largest part
of human brain
The Brain
Human Brain Stem
CNS: Physical Support
Spinal Cord
-Cylinder of nerve tissue
- Continuous with brain
- Surrounded by vertebral
column
- Origin of spinal nerves
(31 pairs)
Spinal Cord Structure
CNS Gray and White Matter
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
– Extracellular fluid of the CNS
– Secreted by ependymal cells of the
choroid plexus
• Circulates to subarachnoid space and ventricles
• Reabsorbed by arachnoid villi
– Functions
• Cushions brain
• Maintains stable interstitial fluid environment
– Total volume of CSF = 125–150 mL
– Choroid plexus produces 400–500 mL/day
– Recycled three times a day
You might also like
- Living With DysarthriaDocument9 pagesLiving With DysarthriaJessiNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Head To Toe AssessmentDocument22 pagesComprehensive Head To Toe Assessmentqueenzk80% (30)
- Ex4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoDocument14 pagesEx4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoNexie100% (1)
- BalneotherapyDocument27 pagesBalneotherapyDwinda RizaryNo ratings yet
- Lec2 Sem2 Cnsweek1 20110630Document10 pagesLec2 Sem2 Cnsweek1 20110630arhamsalahuddinNo ratings yet
- NervoussysteDocument55 pagesNervoussysteaishabahaa03No ratings yet
- Tisu Neural Neurofisiologi Neuron Neuroglia Terminologi SarafDocument141 pagesTisu Neural Neurofisiologi Neuron Neuroglia Terminologi SarafRainne LeeNo ratings yet
- CNS 1Document13 pagesCNS 1Jeff ParkNo ratings yet
- NERVOUSDocument78 pagesNERVOUSsarathnta9No ratings yet
- Neuro 1Document28 pagesNeuro 1Cosmina CorbeanuNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesNervous SystemCatalina CortesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Nervous Tissue - Chap 13Document25 pagesAnatomy Nervous Tissue - Chap 13Angelica RicoNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesNervous SystemDarryl CalimlimNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Nervous TissueDocument29 pagesAnatomy Nervous TissuePaapa MorrisNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives 1. Brain and Spinal Cord.: Dr. Claudia M. Diaz Brain Lectures SummaryDocument12 pagesLearning Objectives 1. Brain and Spinal Cord.: Dr. Claudia M. Diaz Brain Lectures SummaryCarleta StanNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: April Joy A. TalasDocument24 pagesThe Nervous System: April Joy A. TalasPoy Alis100% (1)
- 10.nervous TissueDocument70 pages10.nervous TissueGenard Neil Credo Barrios100% (1)
- Central Nervous SystemDocument110 pagesCentral Nervous SystemAnonymous hYMWbANo ratings yet
- 8 Nervous SystemDocument104 pages8 Nervous SystemDiana Jean Cabiente100% (1)
- Histology of Nervous Tissue and Medulla SpinalisDocument32 pagesHistology of Nervous Tissue and Medulla SpinalisSuhas Kapse100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument60 pagesNervous Systemmewtiny31No ratings yet
- Anatomy Lecture 19,20,21: 1 Hour 04,06,08-11-2013Document64 pagesAnatomy Lecture 19,20,21: 1 Hour 04,06,08-11-2013Batot EvaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesNervous SystemHenry ValerioNo ratings yet
- Nervous and Special SensesDocument137 pagesNervous and Special Sensesprincessfarah hussinNo ratings yet
- NURS1108 Lecture 8 - Nervous System Intro ENHANCEDDocument50 pagesNURS1108 Lecture 8 - Nervous System Intro ENHANCEDJacia’s SpaceshipNo ratings yet
- Biological Neural SystemsDocument20 pagesBiological Neural SystemsRoots999No ratings yet
- Cental Nerves SystemDocument28 pagesCental Nerves Systemsureshchander.bNo ratings yet
- Nervous TissueDocument29 pagesNervous TissueKaruna PrabhuNo ratings yet
- UNIT 7 Nervous System Sept 2023Document94 pagesUNIT 7 Nervous System Sept 2023ndamanomhataabisai7No ratings yet
- Sistem SarafDocument141 pagesSistem SarafPei YiingNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Intro NERVESDocument19 pagesNervous System Intro NERVESJeromeNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 8 - Sistem Saraf MinDocument43 pagesPertemuan 8 - Sistem Saraf MinErsha PutriNo ratings yet
- Cns - Iii: DR Muhammad Ressam NazirDocument36 pagesCns - Iii: DR Muhammad Ressam NazirRessam NazirNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Intro NERVESDocument22 pagesNervous System Intro NERVESJoshdave cuambotNo ratings yet
- 2.nervous SystemDocument25 pages2.nervous SystemEka PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Session 4 - Nervous SystemDocument153 pagesSession 4 - Nervous SystemLezyl Mae CabogNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Manusia: DR Mellova Amir MSCDocument52 pagesFisiologi Manusia: DR Mellova Amir MSCRizal adhitya100% (1)
- Introduction To NeuroanatomyDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Neuroanatomybelete abyuNo ratings yet
- 3-17 Nervous HandoutDocument12 pages3-17 Nervous Handoutopthalmology 18No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument27 pagesNervous Systemdty2257202010031No ratings yet
- Overview of The Nervous System & Neurotransmission: Assoc. Prof Peter ShortlandDocument58 pagesOverview of The Nervous System & Neurotransmission: Assoc. Prof Peter Shortlandkenny013No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesNervous SystemJewel Angeline MartinezNo ratings yet
- Nervous (Doc Notes)Document8 pagesNervous (Doc Notes)besinioaleahjaneNo ratings yet
- Biopsychology-Reviewer PDFDocument12 pagesBiopsychology-Reviewer PDFsherlynmaytiglaoNo ratings yet
- Introduction Into The Nervous System 2017-18Document58 pagesIntroduction Into The Nervous System 2017-18maodNo ratings yet
- Topic 7. Nervous System Anatomy and Physiology 1Document29 pagesTopic 7. Nervous System Anatomy and Physiology 1Janine Jerica JontilanoNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesThe Nervous Systemhamako02No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument112 pagesNervous Systemolaya.xyzanigaia.bsnNo ratings yet
- 11 NsDocument29 pages11 NsWakanda ForeverNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Manusia: DR Mellova Amir MSCDocument52 pagesFisiologi Manusia: DR Mellova Amir MSCRizal AdhityaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesNervous SystemAltaf Hussain Khan50% (2)
- L1 SBM Neuro 1Document88 pagesL1 SBM Neuro 1Sohil PatelNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 4 PDF FreeDocument15 pagesNervous System 4 PDF FreeZedy GullesNo ratings yet
- Nervous System I: Essentials of Human AnatomyDocument40 pagesNervous System I: Essentials of Human Anatomyأمال داودNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of BrainstemDocument30 pagesAnatomy of BrainstemAliyah Tofani PawelloiNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Nervous System: OutlineDocument15 pagesOverview of The Nervous System: OutlineYasir Qadhi's Complete Seerah SeriesNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - IDocument43 pagesNervous System - IChandni PNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial NervesDocument57 pagesChapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nervesgabbs_123No ratings yet
- Brain Anatomy: Diencephalon, Brain Stem and Medulla SpinalisDocument36 pagesBrain Anatomy: Diencephalon, Brain Stem and Medulla SpinalisAngela FovinaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument30 pagesNervous SystemkenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Functional Units of The NS 1Document15 pagesLecture 5 - Functional Units of The NS 1A KNo ratings yet
- Bme 1 PDFDocument51 pagesBme 1 PDFSoumen Biswas48No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument46 pagesNervous Systemrabia khalidNo ratings yet
- Part 1 - Types of Anatomy and Basic Anatomical TermsDocument24 pagesPart 1 - Types of Anatomy and Basic Anatomical TermsAmal Naeem JH100% (1)
- Part 5 - Human Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesPart 5 - Human Respiratory SystemAmal Naeem JHNo ratings yet
- Part 8 - Human Male Reproductive SystemDocument19 pagesPart 8 - Human Male Reproductive SystemAmal Naeem JHNo ratings yet
- Part 4 - Human Skeletal SystemDocument25 pagesPart 4 - Human Skeletal SystemAmal Naeem JHNo ratings yet
- Part 7 - Human Urinary SystemDocument18 pagesPart 7 - Human Urinary SystemAmal Naeem JHNo ratings yet
- Part 13 - Human Sensory Organs AnatomyDocument21 pagesPart 13 - Human Sensory Organs AnatomyAmal Naeem JHNo ratings yet
- Part 3 - Anatomy of The SkinDocument23 pagesPart 3 - Anatomy of The SkinAmal Naeem JHNo ratings yet
- Part 6 - Anatomy of Human Digestive SystemDocument29 pagesPart 6 - Anatomy of Human Digestive SystemAmal Naeem JHNo ratings yet
- Part 9 - Human Female Reproductive SystemDocument16 pagesPart 9 - Human Female Reproductive SystemAmal Naeem JHNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Interventions For Physical Therapy Third Edition Kessler Full ChapterDocument67 pagesNeurologic Interventions For Physical Therapy Third Edition Kessler Full Chaptermary.scriven487100% (15)
- The Cns Portfolio EditionDocument9 pagesThe Cns Portfolio Editionapi-438492450No ratings yet
- Clinical Aspects of IVHDocument11 pagesClinical Aspects of IVHsteffiwpNo ratings yet
- The Incidence of Absence Seizures Is Between 0Document3 pagesThe Incidence of Absence Seizures Is Between 0Citra AntaNo ratings yet
- AP Psych Unit 4 VocabDocument3 pagesAP Psych Unit 4 Vocabdittman1430No ratings yet
- Humane Science Frog Anatomy Student WorkbookDocument69 pagesHumane Science Frog Anatomy Student WorkbookisekaidbreadNo ratings yet
- Eye IgcseDocument4 pagesEye IgcseLavanya TheviNo ratings yet
- DNB Emergency Medicine Paper2Document2 pagesDNB Emergency Medicine Paper2lakshminivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument6 pages1 PBQia TafaNo ratings yet
- Learning and MemoryDocument32 pagesLearning and MemoryPhoebeDrewNo ratings yet
- Psychology Reference BooksDocument1 pagePsychology Reference BooksrichieerishiNo ratings yet
- Spinal CordDocument4 pagesSpinal CordMabel LynNo ratings yet
- KEY MED 2 Updated 2021 Feb Unit 81Document10 pagesKEY MED 2 Updated 2021 Feb Unit 81huyenhungho5892No ratings yet
- Barsalou - 1999 - Perceptual Symbol SystemsDocument84 pagesBarsalou - 1999 - Perceptual Symbol SystemsAlexandru RoșuNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System, NotesDocument6 pagesThe Nervous System, NotesnadshinkNo ratings yet
- Soviet Psychologart An Life Y - The Psychology of Art. Vygotsky 1925Document18 pagesSoviet Psychologart An Life Y - The Psychology of Art. Vygotsky 1925Daniel Stain FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Bio 5.2Document6 pagesBio 5.2zwindows123456789No ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainPrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- Understanding Neurology - A Problem-Orientated Approach PDFDocument241 pagesUnderstanding Neurology - A Problem-Orientated Approach PDFAshabul AnharNo ratings yet
- R. Angeline Prabha & J.Lavina Mary: Jacsi College of Engg. NazarethDocument17 pagesR. Angeline Prabha & J.Lavina Mary: Jacsi College of Engg. NazarethRose EdwardNo ratings yet
- Nerve Conduction Studies: Australian Family Physician September 2011Document6 pagesNerve Conduction Studies: Australian Family Physician September 2011anjelikaNo ratings yet
- G10 Sci CM 22-23Document20 pagesG10 Sci CM 22-23Earn cruzNo ratings yet
- 1718 - BInggris XI K13Document13 pages1718 - BInggris XI K13Cin Poenya Ta100% (1)
- Voices and Pseudo-Voices in Psychosis and OCD Differential DiagnosisDocument5 pagesVoices and Pseudo-Voices in Psychosis and OCD Differential DiagnosisRobert A. LindsayNo ratings yet
- Manual of Nervous DiseasesDocument342 pagesManual of Nervous DiseasesAnonymous HDOLl9No ratings yet
- Clinical Applied Psychophysiology - Carlson, J., Seifert, R. & Birbaumer, NDocument284 pagesClinical Applied Psychophysiology - Carlson, J., Seifert, R. & Birbaumer, NJuan Esteban100% (1)