Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Part 8 Building Services: Section 1 Lighting and Natural Ventilation
Part 8 Building Services: Section 1 Lighting and Natural Ventilation
Uploaded by
Yashi GargCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Scavenger Hunt LightDocument10 pagesScavenger Hunt LightMs Ning0% (1)
- Orientation Buildings: Maximum Ventilation and Natural Light in All Climatic Conditions. ItDocument6 pagesOrientation Buildings: Maximum Ventilation and Natural Light in All Climatic Conditions. ItLo0oVve100% (1)
- Optometry PresentationDocument11 pagesOptometry PresentationEvelyn Tran100% (1)
- Landscape Design Site Planning ConsiderationsDocument9 pagesLandscape Design Site Planning ConsiderationsYcen SantiagoNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Passive Design ShadingDocument5 pages4.4 Passive Design Shadingrish kumarNo ratings yet
- Pptsangatharchitectsstudio 170517160447Document65 pagesPptsangatharchitectsstudio 170517160447Shreyas SasaparaNo ratings yet
- Orientation in ArchitectureDocument25 pagesOrientation in Architecture04 AneriiiNo ratings yet
- Perspective View With Out Boundary Wall: NotesDocument1 pagePerspective View With Out Boundary Wall: Notestuan mrNo ratings yet
- Evs 2 PDFDocument2 pagesEvs 2 PDFMahima palNo ratings yet
- Arch 605 Final PresentationDocument7 pagesArch 605 Final Presentationapi-467442145No ratings yet
- SOLAR SHADING, SHADOW ANGLES (Unit 2)Document18 pagesSOLAR SHADING, SHADOW ANGLES (Unit 2)SrehariNo ratings yet
- Building OrientationDocument5 pagesBuilding Orientationa_j_sanyal100% (2)
- Solar Shading, Shadow AnglesDocument18 pagesSolar Shading, Shadow AnglesSrehariNo ratings yet
- Hot and Dry Climate: Orientation of The Sun in SummerDocument3 pagesHot and Dry Climate: Orientation of The Sun in SummerShammi mauryaNo ratings yet
- 08Sp Daylighting Strategies That Maximize Benefits PDFDocument12 pages08Sp Daylighting Strategies That Maximize Benefits PDFSneha VohraNo ratings yet
- OrientationDocument29 pagesOrientationMadiha SalamNo ratings yet
- Stage 2Document28 pagesStage 2Riya VermaNo ratings yet
- Massing and Building Orientation: Click To Get Started!!Document25 pagesMassing and Building Orientation: Click To Get Started!!Rohit RazNo ratings yet
- Various Techniques of Shading To Reduce Heat GainDocument19 pagesVarious Techniques of Shading To Reduce Heat GainArslaan AlamNo ratings yet
- Team19 P1Document1 pageTeam19 P1Yifan ShenNo ratings yet
- Climate Responsive Architecture: Vernacular Architecture As The Source For Energy Efficiency and Thermal ComfortDocument8 pagesClimate Responsive Architecture: Vernacular Architecture As The Source For Energy Efficiency and Thermal ComfortKejalNo ratings yet
- TRD P6Document33 pagesTRD P6Charles Angelo AndradaNo ratings yet
- Facade Design StrategiesDocument6 pagesFacade Design StrategiesAnuja JadhavNo ratings yet
- Analysis For General Types of ClimateDocument14 pagesAnalysis For General Types of Climateupoppiety pooNo ratings yet
- Review Paper - Cold and Cloudy ClimateDocument4 pagesReview Paper - Cold and Cloudy ClimateOJASVI KHANDELWALNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Reviewer - TropdesDocument8 pagesModule 5 Reviewer - TropdesCTGPH 2021No ratings yet
- Unit - V - Design ConceptsDocument11 pagesUnit - V - Design ConceptsdaraNo ratings yet
- Technology ReportDocument47 pagesTechnology ReportAdriel PurbaNo ratings yet
- 2 OrientationDocument20 pages2 Orientationnnn mm100% (1)
- Passive Design: Fundamentals ofDocument16 pagesPassive Design: Fundamentals ofEran NaierNo ratings yet
- SORAYA NABILLA PUTRI HIDAYAT - 20210210113702 - ARCH6003 - LB44 - FIN - ConfDocument6 pagesSORAYA NABILLA PUTRI HIDAYAT - 20210210113702 - ARCH6003 - LB44 - FIN - ConfSoraya Nabila PutriNo ratings yet
- ThermalDocument57 pagesThermalTesfuGebreslassieNo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation Through Site Selection and OrientationDocument40 pagesEnergy Conservation Through Site Selection and OrientationIna Rose100% (1)
- Microclimate: Site Planning ART - 436Document21 pagesMicroclimate: Site Planning ART - 436Aarushi BarnwalNo ratings yet
- Passive Solar Heating and CoolingDocument7 pagesPassive Solar Heating and Coolingsanchita sahuNo ratings yet
- N.Hiranya - Thrust AreaDocument15 pagesN.Hiranya - Thrust AreaGayathri KathiravanNo ratings yet
- 1867772461CBF SHADING DEVICES - Compressed PDFDocument14 pages1867772461CBF SHADING DEVICES - Compressed PDFAagney Alex RobinNo ratings yet
- Midtermproject342 ElifulucDocument12 pagesMidtermproject342 Elifulucelif uluçNo ratings yet
- 28.shading Devices BDocument5 pages28.shading Devices BmariyaNo ratings yet
- Part B DesignDocument2 pagesPart B DesignShammi mauryaNo ratings yet
- Design BDocument2 pagesDesign BShammi mauryaNo ratings yet
- Bruck House LadybugDocument19 pagesBruck House LadybugAdriel PurbaNo ratings yet
- Passive House OrientationDocument26 pagesPassive House OrientationSol Ai100% (1)
- Climate and Design ARC2030 Designing in Composite ClimateDocument39 pagesClimate and Design ARC2030 Designing in Composite ClimateAlisha KhanNo ratings yet
- Tropical ArchitectureDocument6 pagesTropical ArchitecturemNo ratings yet
- Urban Energy Technical Note: MARSABIT: Climate Analysis andDocument8 pagesUrban Energy Technical Note: MARSABIT: Climate Analysis andFABIUS IHINDULIZANo ratings yet
- Orientation of A BuildingDocument37 pagesOrientation of A BuildingYna Marie Gutierrez100% (1)
- Solar Geometry AND Sun ShadingDocument46 pagesSolar Geometry AND Sun ShadingBharathVenkatachalam50% (2)
- Tropical Design Lecture Pp. 35 42Document2 pagesTropical Design Lecture Pp. 35 42John Patrick ValinoNo ratings yet
- Climatology (AR-307) : Presented To: Miss STDocument59 pagesClimatology (AR-307) : Presented To: Miss STRitika RituNo ratings yet
- Orientation - YourHomeDocument24 pagesOrientation - YourHomeMelanie CabforoNo ratings yet
- Solar Passive Design Features For Hot & Dry ClimateDocument73 pagesSolar Passive Design Features For Hot & Dry ClimateSUHANI VERMANo ratings yet
- ECM1 Technical Information Hot-DryDocument30 pagesECM1 Technical Information Hot-DryUrviNo ratings yet
- Sustainability Plans Presentation Drawings Joshua HouseDocument3 pagesSustainability Plans Presentation Drawings Joshua HouseDiego DiazNo ratings yet
- Designing Spaces in Reinforced Concrete: Student NameDocument88 pagesDesigning Spaces in Reinforced Concrete: Student NameKinchit KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Importance of Orientation of BuildingDocument45 pagesImportance of Orientation of Buildingrgrid100% (1)
- Passive Cooling SystemDocument28 pagesPassive Cooling SystemJan Adrielle VeniceNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Passive Design IntroductionDocument2 pages4.1 Passive Design Introductionrish kumarNo ratings yet
- Principles of PlanningDocument40 pagesPrinciples of PlanningVarun Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Solar GeometryDocument46 pagesSolar GeometryNaGamani KanDan100% (1)
- Solar RadiationDocument40 pagesSolar RadiationMig TigNo ratings yet
- Eye DisorderDocument8 pagesEye DisorderNURSETOPNOTCHERNo ratings yet
- Sci 7 Summative Test 3Document2 pagesSci 7 Summative Test 3OSZEL JUNE BALANAY100% (1)
- KNX 4 DALI Gateway - Datasheet - EN - D0105Document19 pagesKNX 4 DALI Gateway - Datasheet - EN - D0105leng hoklayNo ratings yet
- Excimer Basics: An Overview of Excimer Laser TechnologyDocument3 pagesExcimer Basics: An Overview of Excimer Laser Technologypartha sarathi padhiNo ratings yet
- O W Grukul Science Most Likely CBSE Question Bank For Class 10 Exam-703-791Document89 pagesO W Grukul Science Most Likely CBSE Question Bank For Class 10 Exam-703-791S.P studiesNo ratings yet
- Polarization: Electromagnetic WavesDocument38 pagesPolarization: Electromagnetic WavesNikitaNo ratings yet
- Speed of Light - OdtDocument1 pageSpeed of Light - OdtFlorenz Pintero Del CastilloNo ratings yet
- Basic MCA-4300 - Technical Data Sheet - LLEDO GroupDocument3 pagesBasic MCA-4300 - Technical Data Sheet - LLEDO Groupjuan__davilaNo ratings yet
- 12th Class Physics Test Chapter 20Document1 page12th Class Physics Test Chapter 20ashfaq4985No ratings yet
- Influence of Fogging Lenses and Cycloplegia On Open-Field Automatic RefractionDocument20 pagesInfluence of Fogging Lenses and Cycloplegia On Open-Field Automatic RefractionMehrshad GhasemabadiNo ratings yet
- WY5W Basic: Product InformationDocument3 pagesWY5W Basic: Product InformationNicacio LucenaNo ratings yet
- Laser-to-Fiber Coupling: EE234 Photonics Laboratory, Lab 4Document8 pagesLaser-to-Fiber Coupling: EE234 Photonics Laboratory, Lab 4Bojan ZlatkovicNo ratings yet
- Class 8 - Chapter 16 - LightDocument30 pagesClass 8 - Chapter 16 - LightsanaNo ratings yet
- Polarization of LightDocument12 pagesPolarization of LightShrihari DholeNo ratings yet
- Wide-Lite Supra-Lyte Brochure 1993Document12 pagesWide-Lite Supra-Lyte Brochure 1993Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- Precision, Low Noise, CMOS, Rail-to-Rail, Input/Output Operational Amplifiers AD8605/AD8606/AD8608Document24 pagesPrecision, Low Noise, CMOS, Rail-to-Rail, Input/Output Operational Amplifiers AD8605/AD8606/AD8608cgmannerheimNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument25 pagesElectromagnetic WavesRobert LackeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The History and Limitations of Classical MechanicsDocument3 pagesChapter 1 The History and Limitations of Classical MechanicsBukhtawarNo ratings yet
- RelativityDocument378 pagesRelativitySaptarshi ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Igcse Phy 07Document2 pagesIgcse Phy 07Kamrul Hasan SagarNo ratings yet
- Studies in Occult Chemistry and PhysicsDocument161 pagesStudies in Occult Chemistry and Physicsjgvieira3751No ratings yet
- Sylvania Twist-Pak Post Top Refractor Models Spec SheetDocument2 pagesSylvania Twist-Pak Post Top Refractor Models Spec SheetAlan MastersNo ratings yet
- KPS-5130PD7C KingbrightDocument5 pagesKPS-5130PD7C KingbrightalanabdoNo ratings yet
- Photocell Sensor DatasheetDocument7 pagesPhotocell Sensor DatasheetRiya RoyNo ratings yet
- Bellalux CL A FIL 60 Non Dim 7W827 E27Document4 pagesBellalux CL A FIL 60 Non Dim 7W827 E27team37No ratings yet
- Validity of The Worth 4 Dot Test in Patients With Red-Green Color Vision DefectDocument4 pagesValidity of The Worth 4 Dot Test in Patients With Red-Green Color Vision DefectRaissaNo ratings yet
- Varilux X Extended Ranges of Vision White PaperDocument7 pagesVarilux X Extended Ranges of Vision White PaperRadpilot PilotNo ratings yet
- Article 28 - Search LightsDocument2 pagesArticle 28 - Search Lightsreynold deepakNo ratings yet
Part 8 Building Services: Section 1 Lighting and Natural Ventilation
Part 8 Building Services: Section 1 Lighting and Natural Ventilation
Uploaded by
Yashi GargOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Part 8 Building Services: Section 1 Lighting and Natural Ventilation
Part 8 Building Services: Section 1 Lighting and Natural Ventilation
Uploaded by
Yashi GargCopyright:
Available Formats
PART 8 BUILDING SERVICES
SECTION 1 LIGHTING AND NATURAL VENTILATION
Scope
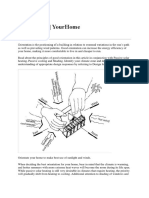
Orientation of a Building
Orientating the buildings along with the micro climate General Climatic Zones
is what helps to make a building sustainable enough
and not a burden on the environment around.
Orienting buildings is an important criteria but another
aspect to keep the interiors also climate friendly is the
orientation of the voids that are the fenestrations and HOT AND DRY WARM AND HUMID MODERATE COLD
openings on the structure.
Winter Midday Shadow
The larger building face The planning & orientation Design should be well Orient houses on top of
should face N– S. mustn’t absorb more of thought to reduce heat gain slope & not at the bottom to
Orientation along the west warm radiations from E-W & maintain thermal comfort. avoid the katabatic flow of
is never preferred. slope. air.
Summer Midday Shadow
Solar Radiations Prevailing Wind Orientation Planting of Trees
Orient longer facades along the north. This will provide glare
free light in summer from north without shading and winter sun Evergreens block winter wind
penetration from the south. Not helpful for cooling
45 or 30
N
degree
If a site has multiple buildings, they should be Place buildings at a 30 or 45 degree angle to the direction
arranged in ascending order of their heights of wind for enhanced ventilation. Form can be staggered in W E
and be built on stilts to allow ventilation the wind facing direction also to achieve the same result.
Block direct sunlight Block direct sunlight
Best for cooling Good for cooling
negative pressure S
Deciduous trees block summer sun
and allow winter sun.
Taller forms in the wind direction of prevailing
May interfere with passive or active
wind can alter the wind movement pattern for
solar design
low lying buildings behind them Staggered layout helps in accentuating wind movement
Principles of Lighting Daylighting
Realizations: Daylight
Using Controlling Careful
Complementing Static Overcast
Directional Glare Planning of Sunlight Skylight
Interiors and Exteriors Sky Condition
Lighting Brightness &
Colours
Promoting Activities Variable Sky
Minimizing Correlate Installing & Practical Conditions
Lighting throughout Emergency Functionality Direct Indirect
Flickering in
Building to Lightings Overcast Overcast
Artificial lighting
Reduce Risk of Accidents Skylight Skylight
Controlling Degrees Direct Indirect Direct Indirect
of Visibility Sunlight Sunlight Skylight Skylight
‘Direct Light’ ‘Diffuse’ Light ‘Diffuse Light’
Aesthetic Appeal
Climate-based daylight modeling- absolute values (luminance and Daylight factor- relative values
Influencing illuminance) founded on real climate data intensive to climate and orientation.
Perceptions, Creating
Visual Effects
Creating Pleasing
Aura
Recommended Values of Luminance
Components Of Daylight Factor
Colour Rendering
KANCHAN SINGH, SAMRIDHI, YASHI GARG
You might also like
- Scavenger Hunt LightDocument10 pagesScavenger Hunt LightMs Ning0% (1)
- Orientation Buildings: Maximum Ventilation and Natural Light in All Climatic Conditions. ItDocument6 pagesOrientation Buildings: Maximum Ventilation and Natural Light in All Climatic Conditions. ItLo0oVve100% (1)
- Optometry PresentationDocument11 pagesOptometry PresentationEvelyn Tran100% (1)
- Landscape Design Site Planning ConsiderationsDocument9 pagesLandscape Design Site Planning ConsiderationsYcen SantiagoNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Passive Design ShadingDocument5 pages4.4 Passive Design Shadingrish kumarNo ratings yet
- Pptsangatharchitectsstudio 170517160447Document65 pagesPptsangatharchitectsstudio 170517160447Shreyas SasaparaNo ratings yet
- Orientation in ArchitectureDocument25 pagesOrientation in Architecture04 AneriiiNo ratings yet
- Perspective View With Out Boundary Wall: NotesDocument1 pagePerspective View With Out Boundary Wall: Notestuan mrNo ratings yet
- Evs 2 PDFDocument2 pagesEvs 2 PDFMahima palNo ratings yet
- Arch 605 Final PresentationDocument7 pagesArch 605 Final Presentationapi-467442145No ratings yet
- SOLAR SHADING, SHADOW ANGLES (Unit 2)Document18 pagesSOLAR SHADING, SHADOW ANGLES (Unit 2)SrehariNo ratings yet
- Building OrientationDocument5 pagesBuilding Orientationa_j_sanyal100% (2)
- Solar Shading, Shadow AnglesDocument18 pagesSolar Shading, Shadow AnglesSrehariNo ratings yet
- Hot and Dry Climate: Orientation of The Sun in SummerDocument3 pagesHot and Dry Climate: Orientation of The Sun in SummerShammi mauryaNo ratings yet
- 08Sp Daylighting Strategies That Maximize Benefits PDFDocument12 pages08Sp Daylighting Strategies That Maximize Benefits PDFSneha VohraNo ratings yet
- OrientationDocument29 pagesOrientationMadiha SalamNo ratings yet
- Stage 2Document28 pagesStage 2Riya VermaNo ratings yet
- Massing and Building Orientation: Click To Get Started!!Document25 pagesMassing and Building Orientation: Click To Get Started!!Rohit RazNo ratings yet
- Various Techniques of Shading To Reduce Heat GainDocument19 pagesVarious Techniques of Shading To Reduce Heat GainArslaan AlamNo ratings yet
- Team19 P1Document1 pageTeam19 P1Yifan ShenNo ratings yet
- Climate Responsive Architecture: Vernacular Architecture As The Source For Energy Efficiency and Thermal ComfortDocument8 pagesClimate Responsive Architecture: Vernacular Architecture As The Source For Energy Efficiency and Thermal ComfortKejalNo ratings yet
- TRD P6Document33 pagesTRD P6Charles Angelo AndradaNo ratings yet
- Facade Design StrategiesDocument6 pagesFacade Design StrategiesAnuja JadhavNo ratings yet
- Analysis For General Types of ClimateDocument14 pagesAnalysis For General Types of Climateupoppiety pooNo ratings yet
- Review Paper - Cold and Cloudy ClimateDocument4 pagesReview Paper - Cold and Cloudy ClimateOJASVI KHANDELWALNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Reviewer - TropdesDocument8 pagesModule 5 Reviewer - TropdesCTGPH 2021No ratings yet
- Unit - V - Design ConceptsDocument11 pagesUnit - V - Design ConceptsdaraNo ratings yet
- Technology ReportDocument47 pagesTechnology ReportAdriel PurbaNo ratings yet
- 2 OrientationDocument20 pages2 Orientationnnn mm100% (1)
- Passive Design: Fundamentals ofDocument16 pagesPassive Design: Fundamentals ofEran NaierNo ratings yet
- SORAYA NABILLA PUTRI HIDAYAT - 20210210113702 - ARCH6003 - LB44 - FIN - ConfDocument6 pagesSORAYA NABILLA PUTRI HIDAYAT - 20210210113702 - ARCH6003 - LB44 - FIN - ConfSoraya Nabila PutriNo ratings yet
- ThermalDocument57 pagesThermalTesfuGebreslassieNo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation Through Site Selection and OrientationDocument40 pagesEnergy Conservation Through Site Selection and OrientationIna Rose100% (1)
- Microclimate: Site Planning ART - 436Document21 pagesMicroclimate: Site Planning ART - 436Aarushi BarnwalNo ratings yet
- Passive Solar Heating and CoolingDocument7 pagesPassive Solar Heating and Coolingsanchita sahuNo ratings yet
- N.Hiranya - Thrust AreaDocument15 pagesN.Hiranya - Thrust AreaGayathri KathiravanNo ratings yet
- 1867772461CBF SHADING DEVICES - Compressed PDFDocument14 pages1867772461CBF SHADING DEVICES - Compressed PDFAagney Alex RobinNo ratings yet
- Midtermproject342 ElifulucDocument12 pagesMidtermproject342 Elifulucelif uluçNo ratings yet
- 28.shading Devices BDocument5 pages28.shading Devices BmariyaNo ratings yet
- Part B DesignDocument2 pagesPart B DesignShammi mauryaNo ratings yet
- Design BDocument2 pagesDesign BShammi mauryaNo ratings yet
- Bruck House LadybugDocument19 pagesBruck House LadybugAdriel PurbaNo ratings yet
- Passive House OrientationDocument26 pagesPassive House OrientationSol Ai100% (1)
- Climate and Design ARC2030 Designing in Composite ClimateDocument39 pagesClimate and Design ARC2030 Designing in Composite ClimateAlisha KhanNo ratings yet
- Tropical ArchitectureDocument6 pagesTropical ArchitecturemNo ratings yet
- Urban Energy Technical Note: MARSABIT: Climate Analysis andDocument8 pagesUrban Energy Technical Note: MARSABIT: Climate Analysis andFABIUS IHINDULIZANo ratings yet
- Orientation of A BuildingDocument37 pagesOrientation of A BuildingYna Marie Gutierrez100% (1)
- Solar Geometry AND Sun ShadingDocument46 pagesSolar Geometry AND Sun ShadingBharathVenkatachalam50% (2)
- Tropical Design Lecture Pp. 35 42Document2 pagesTropical Design Lecture Pp. 35 42John Patrick ValinoNo ratings yet
- Climatology (AR-307) : Presented To: Miss STDocument59 pagesClimatology (AR-307) : Presented To: Miss STRitika RituNo ratings yet
- Orientation - YourHomeDocument24 pagesOrientation - YourHomeMelanie CabforoNo ratings yet
- Solar Passive Design Features For Hot & Dry ClimateDocument73 pagesSolar Passive Design Features For Hot & Dry ClimateSUHANI VERMANo ratings yet
- ECM1 Technical Information Hot-DryDocument30 pagesECM1 Technical Information Hot-DryUrviNo ratings yet
- Sustainability Plans Presentation Drawings Joshua HouseDocument3 pagesSustainability Plans Presentation Drawings Joshua HouseDiego DiazNo ratings yet
- Designing Spaces in Reinforced Concrete: Student NameDocument88 pagesDesigning Spaces in Reinforced Concrete: Student NameKinchit KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Importance of Orientation of BuildingDocument45 pagesImportance of Orientation of Buildingrgrid100% (1)
- Passive Cooling SystemDocument28 pagesPassive Cooling SystemJan Adrielle VeniceNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Passive Design IntroductionDocument2 pages4.1 Passive Design Introductionrish kumarNo ratings yet
- Principles of PlanningDocument40 pagesPrinciples of PlanningVarun Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Solar GeometryDocument46 pagesSolar GeometryNaGamani KanDan100% (1)
- Solar RadiationDocument40 pagesSolar RadiationMig TigNo ratings yet
- Eye DisorderDocument8 pagesEye DisorderNURSETOPNOTCHERNo ratings yet
- Sci 7 Summative Test 3Document2 pagesSci 7 Summative Test 3OSZEL JUNE BALANAY100% (1)
- KNX 4 DALI Gateway - Datasheet - EN - D0105Document19 pagesKNX 4 DALI Gateway - Datasheet - EN - D0105leng hoklayNo ratings yet
- Excimer Basics: An Overview of Excimer Laser TechnologyDocument3 pagesExcimer Basics: An Overview of Excimer Laser Technologypartha sarathi padhiNo ratings yet
- O W Grukul Science Most Likely CBSE Question Bank For Class 10 Exam-703-791Document89 pagesO W Grukul Science Most Likely CBSE Question Bank For Class 10 Exam-703-791S.P studiesNo ratings yet
- Polarization: Electromagnetic WavesDocument38 pagesPolarization: Electromagnetic WavesNikitaNo ratings yet
- Speed of Light - OdtDocument1 pageSpeed of Light - OdtFlorenz Pintero Del CastilloNo ratings yet
- Basic MCA-4300 - Technical Data Sheet - LLEDO GroupDocument3 pagesBasic MCA-4300 - Technical Data Sheet - LLEDO Groupjuan__davilaNo ratings yet
- 12th Class Physics Test Chapter 20Document1 page12th Class Physics Test Chapter 20ashfaq4985No ratings yet
- Influence of Fogging Lenses and Cycloplegia On Open-Field Automatic RefractionDocument20 pagesInfluence of Fogging Lenses and Cycloplegia On Open-Field Automatic RefractionMehrshad GhasemabadiNo ratings yet
- WY5W Basic: Product InformationDocument3 pagesWY5W Basic: Product InformationNicacio LucenaNo ratings yet
- Laser-to-Fiber Coupling: EE234 Photonics Laboratory, Lab 4Document8 pagesLaser-to-Fiber Coupling: EE234 Photonics Laboratory, Lab 4Bojan ZlatkovicNo ratings yet
- Class 8 - Chapter 16 - LightDocument30 pagesClass 8 - Chapter 16 - LightsanaNo ratings yet
- Polarization of LightDocument12 pagesPolarization of LightShrihari DholeNo ratings yet
- Wide-Lite Supra-Lyte Brochure 1993Document12 pagesWide-Lite Supra-Lyte Brochure 1993Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- Precision, Low Noise, CMOS, Rail-to-Rail, Input/Output Operational Amplifiers AD8605/AD8606/AD8608Document24 pagesPrecision, Low Noise, CMOS, Rail-to-Rail, Input/Output Operational Amplifiers AD8605/AD8606/AD8608cgmannerheimNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument25 pagesElectromagnetic WavesRobert LackeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The History and Limitations of Classical MechanicsDocument3 pagesChapter 1 The History and Limitations of Classical MechanicsBukhtawarNo ratings yet
- RelativityDocument378 pagesRelativitySaptarshi ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Igcse Phy 07Document2 pagesIgcse Phy 07Kamrul Hasan SagarNo ratings yet
- Studies in Occult Chemistry and PhysicsDocument161 pagesStudies in Occult Chemistry and Physicsjgvieira3751No ratings yet
- Sylvania Twist-Pak Post Top Refractor Models Spec SheetDocument2 pagesSylvania Twist-Pak Post Top Refractor Models Spec SheetAlan MastersNo ratings yet
- KPS-5130PD7C KingbrightDocument5 pagesKPS-5130PD7C KingbrightalanabdoNo ratings yet
- Photocell Sensor DatasheetDocument7 pagesPhotocell Sensor DatasheetRiya RoyNo ratings yet
- Bellalux CL A FIL 60 Non Dim 7W827 E27Document4 pagesBellalux CL A FIL 60 Non Dim 7W827 E27team37No ratings yet
- Validity of The Worth 4 Dot Test in Patients With Red-Green Color Vision DefectDocument4 pagesValidity of The Worth 4 Dot Test in Patients With Red-Green Color Vision DefectRaissaNo ratings yet
- Varilux X Extended Ranges of Vision White PaperDocument7 pagesVarilux X Extended Ranges of Vision White PaperRadpilot PilotNo ratings yet
- Article 28 - Search LightsDocument2 pagesArticle 28 - Search Lightsreynold deepakNo ratings yet