Professional Documents
Culture Documents
New Document 1
New Document 1
Uploaded by
James YangOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
New Document 1
New Document 1
Uploaded by
James YangCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: ________________________
MidtermASChem Class: ________________________
Date: ________________________
Time: 40 minutes
Marks: 50 marks
Comments:
The International Department of Zhangjiang Foreign Language School Page 1 of 7
This question is about atoms and ions.
1.
(a) Table 1 shows the relative charge and the relative mass for each of the fundamental
particles in an atom.
Complete Table 1.
Table 1
Relative charge Relative mass
Electron −1
Neutron
Proton 1
(2)
(b) Complete Table 2 to show the number of protons, electrons and neutrons in the selenium
atom and the selenium ion shown.
Table 2
Number of protons Number of electrons Number of neutrons
76Se 34
77Se2−
(2)
The International Department of Zhangjiang Foreign Language School Page 2 of 7
(c) A sample of selenium contains four isotopes.
Table 3 shows the relative abundances of the isotopes in this sample of selenium.
Table 3
76Se 77Se 78Se 80Se
Relative abundance 1.2 1.0 3.1 10.8
Calculate the relative atomic mass of this sample of selenium.
Give your answer to 1 decimal place.
Relative atomic mass ________________
(2)
A sample of selenium is analysed using a time of flight (TOF) mass spectrometer.
(d) The selenium atoms are ionised by electron impact.
Write an equation, including state symbols, to show this ionisation.
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
(e) Describe how the selenium ions are accelerated in the TOF mass spectrometer.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
The International Department of Zhangjiang Foreign Language School Page 3 of 7
A different sample of selenium contains a fifth isotope.
(f) After acceleration, the selenium ion has a kinetic energy of 4.742 × 10−14 J
The ion takes 2.572 × 10−6 s to travel 2.260 m along a flight tube.
Calculate the mass, in kg, of this ion.
v = velocity (m s−1)
KE = kinetic energy of the ion (J)
m = mass of the ion (kg)
Mass of ion ________________ kg
(3)
(g) Use your answer to part (f) to calculate the mass number of the ion.
(If you could not answer part (f) you should use the value 1.179 × 10−25 kg
This is not the correct answer.)
The Avogadro constant, L = 6.022 × 1023 mol−1
Mass number ________________
(2)
(Total 13 marks)
The International Department of Zhangjiang Foreign Language School Page 4 of 7
Zinc nitrate can be formed by the reaction
2.
ZnO(s) + 2 HNO3(aq) ⟶ Zn(NO3)2(aq) + H2O(l)
(a) An excess of zinc oxide is added to 150 cm3 of 1.25 mol dm−3 nitric acid.
Calculate the maximum mass, in g, of zinc nitrate (Mr = 189.4) formed.
Mass _________ g
(3)
(b) State how pure zinc nitrate can be obtained from the reaction mixture after the excess of
zinc oxide is removed.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
(c) Zinc nitrate decomposes when heated
2 Zn(NO3)2(s) ⟶ 2 ZnO(s) + 4 NO2(g) + O2(g)
Calculate the total volume, in m3, of gas formed when 1.20 g of zinc nitrate (Mr = 189.4) are
decomposed.
The volume of gas is measured at a temperature of 200 °C and a pressure of 100 kPa
The gas constant, R = 8.31 J K−1 mol−1
Total volume of gas ______________________ m3
(5)
The International Department of Zhangjiang Foreign Language School Page 5 of 7
(d) Complete the equation for the reaction of zinc with concentrated nitric acid.
_____ Zn + _____ HNO3 ⟶ _____Zn(NO3)2 + NH4NO3 + _____ H2O
(1)
(Total 10 marks)
This question is about structure and bonding.
3.
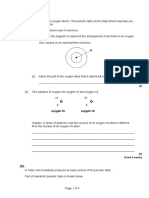
(a) The diagram below shows part of the structure of magnesium oxide.
Complete the diagram below by writing the formula of the appropriate ion in each circle.
(1)
(b) State why molten magnesium oxide conducts electricity.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
(c) Name and explain the shape of the nitrogen trichloride (NCl3) molecule.
Suggest the value of the bond angle.
Name of shape ______________________________________________________
Explanation of shape _________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
Bond angle ____________
(4)
The International Department of Zhangjiang Foreign Language School Page 6 of 7
(d) The table below gives some data about the F2 molecule and the CH3F molecule.
F2 CH3F
Relative molecular mass 38.0 34.0
Boiling point / °C −188 −78
Explain why the boiling point of CH3F is much higher than that of F2
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(3)
(e) Draw the structure of an AlCl3 molecule.
(1)
(f) Al2Cl6 is produced when co-ordinate bonds form between two molecules of AlCl3
Draw the structure of an Al2Cl6 molecule.
You should show covalent bonds as a line (—) and co-ordinate bonds as an arrow ⟶).
(
(2)
(Total 12 marks)
The International Department of Zhangjiang Foreign Language School Page 7 of 7
You might also like
- Enzyme Assays A Practical Approach by Robert Eisenthal, Michael DansonDocument304 pagesEnzyme Assays A Practical Approach by Robert Eisenthal, Michael DansonSara OchoaNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Electron Configuration: 8-27-2005 Joshua Perez-LunaDocument14 pagesStudent Exploration: Electron Configuration: 8-27-2005 Joshua Perez-LunaJoshua Perez-Luna67% (3)
- Week 3 Chemistry Paper 1Document14 pagesWeek 3 Chemistry Paper 1lesedimosarweNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Chemistry Paper 1Document13 pagesWeek 2 Chemistry Paper 19wgd495gqyNo ratings yet
- TOF Extra QuestionsDocument13 pagesTOF Extra Questionspoocooloocoo172No ratings yet
- Year 11 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursDocument12 pagesYear 11 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document6 pagesQuiz 1cikgu_aminNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Eoy Paper 2Document16 pagesGrade 10 Eoy Paper 2vuyelwa.mzileni2021No ratings yet
- Maths in Chemistry Exam Questions Booklet GULDocument44 pagesMaths in Chemistry Exam Questions Booklet GULXx Jasmine XxNo ratings yet
- 3.1.1.3 Electron Configuration: NameDocument81 pages3.1.1.3 Electron Configuration: NamesuccesshustlerclubNo ratings yet
- Energy ChangesDocument27 pagesEnergy Changesapi-422428700No ratings yet
- QuetsionsDocument26 pagesQuetsionssuccesshustlerclubNo ratings yet
- IE + Mass Spec Ex Q +msDocument15 pagesIE + Mass Spec Ex Q +msboobooNo ratings yet
- Bonding and StructureDocument30 pagesBonding and Structurei.naiduNo ratings yet
- TOF QuestionsDocument14 pagesTOF QuestionsremesanmeenakshiNo ratings yet
- Ujian Pengesanan T5 2021Document5 pagesUjian Pengesanan T5 2021mahfuzah sobriNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableDocument46 pagesAtomic Structure and The Periodic TableLiang LuNo ratings yet
- Redox Titration Questions 2Document11 pagesRedox Titration Questions 2Jaimi RosarioNo ratings yet
- 3 2 1 1constituentsoftheatomDocument32 pages3 2 1 1constituentsoftheatomRodriantonNo ratings yet
- OxfordAQA Chemistry Atomic StructureDocument86 pagesOxfordAQA Chemistry Atomic StructureNerisa Nurul BulanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry KS4 LZ 2.1Document21 pagesChemistry KS4 LZ 2.1Wreck RalphNo ratings yet
- 10-Topic-Test Atomic-Structure-And-The-Periodic-TableDocument16 pages10-Topic-Test Atomic-Structure-And-The-Periodic-Tableyuezhen wangNo ratings yet
- QuantitativeDocument29 pagesQuantitativeapi-422428700No ratings yet
- Bonding Exam Style Questions (Chemistry)Document30 pagesBonding Exam Style Questions (Chemistry)Temilola OwolabiNo ratings yet
- GR 9, Chem P-1Document23 pagesGR 9, Chem P-1kashif mohammedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 1 HacDocument16 pagesChemistry Paper 1 Hacdip-sta-06-22No ratings yet
- Topic Test Oxfordaqa Int A Level Chemistry A2 Physical Unit 3 ContentDocument22 pagesTopic Test Oxfordaqa Int A Level Chemistry A2 Physical Unit 3 ContentyinyixinNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Atomic StructureDocument9 pagesTopic 1 Atomic StructurearyanNo ratings yet
- AQA A Level Physics: 7 MinutesDocument18 pagesAQA A Level Physics: 7 Minutesrzkrn7kq44No ratings yet
- EQ's TRIPLE AND SEPARATE TFDocument5 pagesEQ's TRIPLE AND SEPARATE TFvikramrolex96No ratings yet
- 3.1.3.5 Shapes of Simple Molecules + IonsDocument89 pages3.1.3.5 Shapes of Simple Molecules + IonsTobiNo ratings yet
- Autumn Pathway ABDocument42 pagesAutumn Pathway ABH ChowdreyNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Fundamentals Particles QsDocument10 pagesAtomic Structure Fundamentals Particles QsJesulayomi BolajiNo ratings yet
- CCC 2015 PTC ENDocument12 pagesCCC 2015 PTC ENmarcusmaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Oxygen-16 Oxygen-18Document9 pagesOxygen-16 Oxygen-18Mohammed Rabee alzaabiNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument24 pagesBondingapi-422428700No ratings yet
- Winter 2009Document16 pagesWinter 2009rahil.kakkadNo ratings yet
- 3.1.8.1 Born-Haber Cycles (A-Level Only)Document73 pages3.1.8.1 Born-Haber Cycles (A-Level Only)jaisisantosh2007No ratings yet
- Class Test (Atomic Structure) : Academic Session: 2019-2020Document5 pagesClass Test (Atomic Structure) : Academic Session: 2019-2020GM Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Quantititive Chemistry - Paper 1 TES - 4Document37 pagesQuantititive Chemistry - Paper 1 TES - 4KshitijNo ratings yet
- ALevel Physical Chemistry Past PapersDocument24 pagesALevel Physical Chemistry Past PaperssabihagailaniNo ratings yet
- T1W4 (Revision)Document4 pagesT1W4 (Revision)John LebizNo ratings yet
- 4 Atomic Structure: TrilogyDocument13 pages4 Atomic Structure: TrilogyAsmik LogianNo ratings yet
- CH - 03 - Prac - Test-Web RDocument8 pagesCH - 03 - Prac - Test-Web RMartria EhabNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Quiz 3 Practice Name - KEY - : Ti and ODocument2 pagesUnit 3 Quiz 3 Practice Name - KEY - : Ti and OZara ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 9620 CH02 International A Level Chemistry Specimen Paper 2016 v1Document19 pages9620 CH02 International A Level Chemistry Specimen Paper 2016 v1boledey653No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Test 2 300920Document11 pagesUnit 1 Test 2 300920ibrahim ahmedNo ratings yet
- Chem 209A Pre-Test 2 Semester, AY 2021-2022Document3 pagesChem 209A Pre-Test 2 Semester, AY 2021-2022JEZELLE KAYE BOCONo ratings yet
- Topic 2: Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableDocument4 pagesTopic 2: Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableLoh Jun Xian100% (1)
- Topic 2: Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableDocument4 pagesTopic 2: Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableAnshu MovvaNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 3Document5 pagesPractice Test 3bln19aNo ratings yet
- Topic Test Oxfordaqa Int A Level Chemistry As Level InorganicDocument21 pagesTopic Test Oxfordaqa Int A Level Chemistry As Level InorganicdissaoctafianellisNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Group 1Document2 pagesPeriodic Table Group 1rudi_zNo ratings yet
- Level IGCSE (9-1)Document17 pagesLevel IGCSE (9-1)RaishmaNo ratings yet
- GeneralpropertiesDocument31 pagesGeneralproperties/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- Paper 1 AQA 2023 ASDocument27 pagesPaper 1 AQA 2023 AS2024a.saeedNo ratings yet
- 11th Full Length (1)[1]Document6 pages11th Full Length (1)[1]Kushagra Parijat LahirNo ratings yet
- New Document 1: 162 MinutesDocument40 pagesNew Document 1: 162 MinutesDigola WillsNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Structure and Bonding HDocument14 pages4.2 Structure and Bonding HMagd OsamaNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Chemistry 1140A Fall 2019 Name - (1pt)Document6 pagesExam 1 Chemistry 1140A Fall 2019 Name - (1pt)hamiltonj_866440No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Perdiodic Table Paper 1 With AnswersDocument26 pagesAtomic Structure Perdiodic Table Paper 1 With Answersnikhitasingh15No ratings yet
- Cargo Hold Cleaning Quick Guide A4 062021Document4 pagesCargo Hold Cleaning Quick Guide A4 062021EmmaNo ratings yet
- Trace Impurities in Monocyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons by Gas Chromatography and Effective Carbon NumberDocument13 pagesTrace Impurities in Monocyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons by Gas Chromatography and Effective Carbon NumberAngel Cambero100% (1)
- 16 Fire and Welding BlanketDocument9 pages16 Fire and Welding BlanketpradipNo ratings yet
- Module 2 BioGeoChemical CyclesDocument25 pagesModule 2 BioGeoChemical CyclesPonce GuerreroNo ratings yet
- SheetDocument108 pagesSheetPinkyNo ratings yet
- Ersoy2014Document7 pagesErsoy2014Roxana LencinaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 5 PDFDocument4 pagesWorksheet 5 PDFThant Zin HtunNo ratings yet
- Manual Caldera FultonDocument69 pagesManual Caldera FultonMaria Gabriela Sosa100% (1)
- 112 Bridging Topic 3 4pDocument6 pages112 Bridging Topic 3 4pAlyssa MacaraigNo ratings yet
- Installation Procedure Kamos RTJ GasketDocument16 pagesInstallation Procedure Kamos RTJ Gasketekhwanhakim100% (3)
- Organic Reactions PPT AlcoholsDocument43 pagesOrganic Reactions PPT Alcoholssmithsashay74No ratings yet
- White Topping As A Rehabilitation Method On PavementsDocument30 pagesWhite Topping As A Rehabilitation Method On PavementsShahir ShrNo ratings yet
- Fire ExtinguishersafetytrainingDocument28 pagesFire ExtinguishersafetytrainingAishwarya NaiduNo ratings yet
- 3 LAB ACTIVITY SHEET 3 Precipitation and Solubility 1Document3 pages3 LAB ACTIVITY SHEET 3 Precipitation and Solubility 1Jurel JohnNo ratings yet
- BIO 204 Current Final Term Fall 2020 by Amaan KhanDocument38 pagesBIO 204 Current Final Term Fall 2020 by Amaan KhanSharqaNo ratings yet
- Steripen Classic EnglishDocument4 pagesSteripen Classic Englishben123456789benNo ratings yet
- Crl-Soil Sampling-Pcapi R4a 2022Document40 pagesCrl-Soil Sampling-Pcapi R4a 2022Marc ChristianNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 10.3: AlcoholsDocument2 pagesWorksheet 10.3: AlcoholsseungminNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - Chemistry - Diagnostic ExamDocument2 pagesAnswer Key - Chemistry - Diagnostic ExamNiño Edrianne Nimo100% (2)
- Klbersynth - UH1 - 6-460Document6 pagesKlbersynth - UH1 - 6-460Chiranjeevi VijayaraghavanNo ratings yet
- Modern Construction Building Methods Techniques MST Connect With Design and Construciton of Pool MANUALDocument86 pagesModern Construction Building Methods Techniques MST Connect With Design and Construciton of Pool MANUALAe R ONNo ratings yet
- MCAT Organic Chemistry ReviewDocument43 pagesMCAT Organic Chemistry ReviewVetina LirioNo ratings yet
- Tle 7 - Cookery Week 3Document9 pagesTle 7 - Cookery Week 3Dominic Camacho RotaNo ratings yet
- Chandeep Singh XI-A PhysicsDocument16 pagesChandeep Singh XI-A Physicschandeep singhNo ratings yet
- QNBN Vendor List For MaterialsDocument1 pageQNBN Vendor List For Materialshatem hamaidiNo ratings yet
- Food-PackagingDocument48 pagesFood-PackagingTrishitman DasNo ratings yet
- T300 Technical Data Sheet 1 PDFDocument2 pagesT300 Technical Data Sheet 1 PDFmaraNo ratings yet
- Utilization of Achuete For DyeDocument19 pagesUtilization of Achuete For DyeReina Charis Panaligan-AgbayaniNo ratings yet





















































![11th Full Length (1)[1]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/748328360/149x198/bb22d69df4/1720260370?v=1)
































