Professional Documents
Culture Documents
001.PG - Genset - Not Emission - El - Sys - Spec - Dec2017
001.PG - Genset - Not Emission - El - Sys - Spec - Dec2017
Uploaded by
bekheet222Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- New Holland Kobelco E385 Tier 3 Crawler Excavator Service Repair Workshop ManualDocument21 pagesNew Holland Kobelco E385 Tier 3 Crawler Excavator Service Repair Workshop ManualggjjjjotonesNo ratings yet
- EDC7UC31 CodesDocument22 pagesEDC7UC31 CodesFastcross Honda93% (15)
- IVECO EDC7 UC31 Diagrama ElectricoDocument4 pagesIVECO EDC7 UC31 Diagrama ElectricoLuis Ocampo100% (2)
- AP Supported Platforms v14.75 - PIQ - 12.0Document14 pagesAP Supported Platforms v14.75 - PIQ - 12.0Alessandro Costa100% (1)
- F4AFE411ADocument238 pagesF4AFE411Ajvega_534120No ratings yet
- Software Documentation EDC7UC31-CRS P - 340.9.1: P - 340 Ds-Cv/Eet Y445 S00 746-V91 Confidential - 1Document2,800 pagesSoftware Documentation EDC7UC31-CRS P - 340.9.1: P - 340 Ds-Cv/Eet Y445 S00 746-V91 Confidential - 1Arnaldo Ribeiro100% (3)
- Manual MuellerDocument36 pagesManual MuellerFabianoNo ratings yet
- NEF ECU Controller Tier 2 (EDC7) vs. Tier 3 (EDC7UC31) PinDocument8 pagesNEF ECU Controller Tier 2 (EDC7) vs. Tier 3 (EDC7UC31) PinMauricio GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Eletrica MF 9690 E 9790Document43 pagesEletrica MF 9690 E 9790PABLO DOS SANTOS100% (1)
- ECU ConnectorsDocument12 pagesECU ConnectorsWillian JefersonNo ratings yet
- EDC7 ECU Pin Assignments - pdf.2015Document4 pagesEDC7 ECU Pin Assignments - pdf.2015Didi Robles75% (4)
- Electronic Service ToolDocument199 pagesElectronic Service ToolEzequiel ZetaNo ratings yet
- Cursor Series Tier 4B: INDUSTRIAL Application (Tigercat)Document181 pagesCursor Series Tier 4B: INDUSTRIAL Application (Tigercat)Dmicalio Sim100% (2)
- Easy Iveco InstruccionesDocument174 pagesEasy Iveco InstruccionesAnonymous J1sELDp7100% (2)
- Connector Location Chart and Electrical Circuit Diagram by SystemDocument22 pagesConnector Location Chart and Electrical Circuit Diagram by SystemLucas Solon SolonNo ratings yet
- Diagrama PDFDocument1 pageDiagrama PDFeduardonemo100% (2)
- Ur620c To252 Mosfet SMDDocument4 pagesUr620c To252 Mosfet SMDBRUNONo ratings yet
- Fendt 1000 Vario ManualDocument19 pagesFendt 1000 Vario Manualgraig27No ratings yet
- Pages de F (WC) Wheel Loader Training Manual Rev3 082011Document142 pagesPages de F (WC) Wheel Loader Training Manual Rev3 082011Ahmed Kamal100% (4)
- Cursor and Nef Engine Edc7Uc31 Fme Tier3 Stageiiia Genset Industrial ApplicationDocument35 pagesCursor and Nef Engine Edc7Uc31 Fme Tier3 Stageiiia Genset Industrial ApplicationValeriy100% (1)
- NT Bosch Edc17cv41 Irom TC1797 Egpt Allbrand 1033Document3 pagesNT Bosch Edc17cv41 Irom TC1797 Egpt Allbrand 1033Daniel HallbergNo ratings yet
- 14 - SCRsystemInstallationGuideLineDNOx2 - V7.3Document103 pages14 - SCRsystemInstallationGuideLineDNOx2 - V7.3George Huarcaya Diaz100% (1)
- Bench MPC Iveco Edc7uc31 561Document1 pageBench MPC Iveco Edc7uc31 561apoludniak1982No ratings yet
- DPA5 User ManualDocument67 pagesDPA5 User ManualMaqpower EngenhariaNo ratings yet
- MET For Iveco Vehicles - List of SignalsDocument5 pagesMET For Iveco Vehicles - List of SignalsAmor Mansouri100% (1)
- RepairDiagnostics PT 01 C0G36Z008E 3MBDocument6 pagesRepairDiagnostics PT 01 C0G36Z008E 3MBJosé Da Silva MataNo ratings yet
- IVECO Electrical G13Document28 pagesIVECO Electrical G13Modise Thee Shepherd MofokengNo ratings yet
- DLPI Daf 1033Document3 pagesDLPI Daf 1033ddf_dedo100% (1)
- DW13294103Document72 pagesDW13294103p_jankoNo ratings yet
- DPA5 User Manual PDFDocument42 pagesDPA5 User Manual PDFcleverson ferreira100% (2)
- Diagrama Iveco Stralis PDFDocument104 pagesDiagrama Iveco Stralis PDFVini67% (3)
- Comparacion EDC7UC31 Vs EDC16UC40Document26 pagesComparacion EDC7UC31 Vs EDC16UC40Anonymous J1sELDp771% (7)
- DD4-3 Diagnostico Transmision DW63242001 - DD4 - 3Document48 pagesDD4-3 Diagnostico Transmision DW63242001 - DD4 - 3Fredy Roa100% (1)
- Bosch Edc7c3 ManDocument3 pagesBosch Edc7c3 ManEmi DNo ratings yet
- Cab Sensor and Actuator Module (SCA), Component DescriptionDocument1 pageCab Sensor and Actuator Module (SCA), Component DescriptionrudiNo ratings yet
- PDF Edc7uc31 Codes DDDocument10 pagesPDF Edc7uc31 Codes DDedgarNo ratings yet
- EDC16c8 PDFDocument4 pagesEDC16c8 PDFahmedco50% (2)
- F4HFE413KDocument358 pagesF4HFE413Kjvega_53412067% (3)
- Diagrama B7, B9, B12 BEA II PDFDocument98 pagesDiagrama B7, B9, B12 BEA II PDFjoseNo ratings yet
- Mid 185 - Pid 84 - Fmi 2Document3 pagesMid 185 - Pid 84 - Fmi 2AkbarNo ratings yet
- Tga GBDocument175 pagesTga GBMyo Min OoNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Buses: Wiring Diagram B9S, Els-Mux2Document84 pagesService Manual Buses: Wiring Diagram B9S, Els-Mux2Guillermo Guardia Guzman100% (1)
- CASE IH MAGNUM 235 - 260 - 290 - 315 - 340 - 370 Tractors Hydraulic Schematics - 47605412Document6 pagesCASE IH MAGNUM 235 - 260 - 290 - 315 - 340 - 370 Tractors Hydraulic Schematics - 47605412MilanNo ratings yet
- DDCRDocument3 pagesDDCRArmando CardosoNo ratings yet
- Bosch Edc7u31 Iveco 1033Document3 pagesBosch Edc7u31 Iveco 1033Diogo Silva Reis100% (1)
- Magnum Dxi13 Wiring ManualDocument149 pagesMagnum Dxi13 Wiring ManualВиктор Сабов100% (1)
- CNH Industrial: FPT Industrial AND IvecoDocument8 pagesCNH Industrial: FPT Industrial AND IvecoCLAUDIA MASININo ratings yet
- Autocom Delphi - Plug & Diagnose PDFDocument37 pagesAutocom Delphi - Plug & Diagnose PDFPaulo Ricardo MenezesNo ratings yet
- Engine CNH Trainee MPTS ™Document154 pagesEngine CNH Trainee MPTS ™Luis Miguel Echevarria Quispe100% (4)
- Tencreng0003 Ecu ControlDocument24 pagesTencreng0003 Ecu ControlAly AbdelhamedNo ratings yet
- BOSCH 40007 (U2 - Caterpilar D6K)Document84 pagesBOSCH 40007 (U2 - Caterpilar D6K)Joil AlvesNo ratings yet
- Fault Codes: Gearbox (Gearbox - Astronic ZF)Document2 pagesFault Codes: Gearbox (Gearbox - Astronic ZF)Стефан Тасиќ100% (1)
- (2020-0873) Marine EDC7C1 NEF Electronic System Specification Feb 2022Document18 pages(2020-0873) Marine EDC7C1 NEF Electronic System Specification Feb 2022KornNo ratings yet
- Detroit Transmissions Electronic ACRONYMSDocument4 pagesDetroit Transmissions Electronic ACRONYMScells-crosser0xNo ratings yet
- Technical Specifications AdaniDocument30 pagesTechnical Specifications Adanishahnawaz1709No ratings yet
- 2021 1208 Marine Commercial Pleasure NEF EDC7C1 CAN Spec Mar 2021Document50 pages2021 1208 Marine Commercial Pleasure NEF EDC7C1 CAN Spec Mar 2021KornNo ratings yet
- Belimo BACnet Interface-Description Energy-Valve v4 01 En-Gb PDFDocument8 pagesBelimo BACnet Interface-Description Energy-Valve v4 01 En-Gb PDFBence BaloghNo ratings yet
- D25 User's GuideDocument191 pagesD25 User's GuideIlaiyaa RajaNo ratings yet
- Multiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...From EverandMultiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...No ratings yet
001.PG - Genset - Not Emission - El - Sys - Spec - Dec2017
001.PG - Genset - Not Emission - El - Sys - Spec - Dec2017
Uploaded by
bekheet222Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
001.PG - Genset - Not Emission - El - Sys - Spec - Dec2017
001.PG - Genset - Not Emission - El - Sys - Spec - Dec2017
Uploaded by
bekheet222Copyright:
Available Formats
NOT EMISSION
GENSET
POWER
GENERATION
EDC17CV41
Electronic System Specification
Revision 2.4 Dec 2017
Electronic System Specification
ELECTRONIC SYSTEM SPECIFICATION
EDC17CV41 Genset Application
NEF/Cursor Engines - Not Emissioned Engines
Valid for FPT and SAE ID CAN messages
INTRODUCTION
Symbols reference Abbreviations
DESCRIPTION Abbreviation Used for
Go to document cover page ATS After Treatment System
BC Body Computer
Go to main index
BDS Battery Disconnection Switch
Back to previous page CAN Controller Area Network
Go to external document CUC Clean Up Catalyst
DEF Diesel Exhaust Fluid (aqueous urea
Hyperlinked solution)
DOC Diesel Oxidation Catalyst
IMPORTANT!
DTC Diagnostic Trouble Code
This is a preliminary version of the document, some
content may not be active hyperlinks. ECM Engine Control Module
ECU Electronic Control Unit
EDC17CV41 BOSCH Electronic Diesel Control Unit
EOL End of Line
FMI Failure Mode Indicator
PCB Printed circuit board
PTO Power Take Off
SCR Selective Catalyst Reduction
SPN Suspect Parameter Number
TBC To be confirmed
TBD To be defined
TBU To be updated
VCM Vehicle Control Module
WC Worst Case
WH Wiring Harness
REVISION HISTORY
FPT Internal document reference
Version Date Modification Description Author Approval
TSC1-VE replaced by TSC1-PE;
1.4 06/07/2015 G. F. Di Graziano V. Palumbo
Added notes on TSC1s time out errors.
Document updating
Page Modification Description Date
- Updated document layout Dec 2017
Not emission - Genset All Rights Reserved
Revision 2.4_Dec 2017 FPT Confidential and Proprietary
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
Electronic System Specification 1
REFERENCE DOCUMENTS
Project Specific Documents
[A.1] CANSpec_Genset_Not_Emissioned v.1.1
[A.2] FPT electrical schematic diagrams: TBD
Standards Documents
SAE ISO
[B.1] SAE J1939/11 CAN Physical Layer [C.1] ISO 14229-1 UDS – Specifications and
[B.2] SAE J1939/21 CAN Data Link Layer Requirements
[B.3] SAE J1939/71 CAN Vehicle Application Layer [C.2] ISO 15765-1 Diagnostic on CAN – General
Information
[B.4] SAE J1939/73 CAN Diagnostic Application
Layer [C.3] ISO 15765-2 Diagnostic on CAN – Network
Layer Services
[C.4] ISO 11898 CAN Physical and Data Link
Specifications
THE DOCUMENT IS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE.
INDEX
1. ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM 2
2. ARCHITECTURE 4
3. ENGINE CONTROL MODULE 5
4. ELECTRICAL BALANCE FOR FPT COMPONENTS 13
5. VEHICLE FUNCTIONS 13
6. DIAGNOSIS 15
APPENDIX A. CALIBRATION SUMMARY AND HINT 15
APPENDIX B. CAN MATRIX 16
APPENDIX C. CAN INTERFACE AND FUNCTIONALITY 17
APPENDIX D. EDC17CV41 COMPONENT INTERFACE AND PIN LIST 17
APPENDIX E. LED CONNECTION CIRCUIT 21
All Rights Reserved Not emission - Genset
FPT Confidential and Proprietary Revision 2.4_Dec 2017
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
2 Electronic System Specification
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
The main parts of the Engine Management System are: The Figure 2.1 is referred to NEF 45 Not Emissioned
●● Engine Control Module (ECM) engine. It is valid also for 6 cylinders engine, except
only for number of cylinders and injectors.
●● Fuel Injection System (FIS) The Figure 2.2 is referred to Cursor 87 and 13 Not
●● Electrical and electronic components (sensors and Emissioned engines.
actuators)
NEF 4 CYL. TIER 2 (EDC17CV41)
1
2 7 8 9 10
4 6 11
5 12
Fuel
pre-filter
group
Vehicle CAN bus
23
13
Fuel tank 22
21
20 14
Vehicle perimeter
ECU
17 16 15
19 18 Vehicle perimeter
Figure 2.1. EMS scheme for NEF 4 cylinders not emissioned 260404
(v=vehicle mounted)
1. Engine Control Module w/fuel cooling pipe 13. Intake manifold pressure (P2) & temp sensor
2. Fuel filter delta switch 14. Cranckshaft speed sensor
3. Fuel filter with fuel T sensor 15. Air filter
4. Fuel pre-filter w/heater & water in fuel switch (v) 16. Air intercooler (v)
5. Over pressure valve 17. Intake air pressure & temperature sensor (v)
6. High pressure fuel pump 18. T/C compressor
7. Fuel filter deltaP switch (v) 19. T/C turbine
8. Fuel metering valve 20. Engine coolant temperature sensor
9. HP fuel rail 21. Engine oil pressure and temperature
10. HP rail pressure sensor 22. Camshaft speed sensor
11. Grid heater relay 23. HP puel injectores (4x)
12. Grid heater
Not emission - Genset All Rights Reserved
Revision 2.4_Dec 2017 FPT Confidential and Proprietary
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
Electronic System Specification 3
CURSOR 87/13 TIER 2
1 2 7 9 10
4 11
6
5 12
Fuel
pre-filter
group
23
13
Fuel tank 22
21
20 14
Vehicle perimeter
17 16 15
19 18 Vehicle perimeter
Figure 2.2. EMS scheme for Cursor 87 - 13 Not Emissioned 260403
(v=vehicle mounted)
1. Engine Control Module w/fuel cooling pipe 13. Intake manifold pressure (P2) & temp sensor
2. Fuel filter delta switch 14. Cranckshaft speed sensor
3. Fuel filter with fuel T sensor 15. Air filter
4. Fuel pre-filter w/heater & water in fuel switch (v) 16. Air intercooler (v)
5. Over pressure valve 17. Intake air pressure & temperature sensor (v)
6. High pressure fuel pump 18. T/C compressor
7. Fuel filter deltaP switch (v) 19. T/C turbine
8. Fuel metering valve 20. Engine coolant temperature sensor
9. HP fuel rail 21. Engine oil pressure and temperature
10. HP rail pressure sensor 22. Camshaft speed sensor
11. Grid heater relay 23. HP puel injectores (6x)
12. Grid heater
All Rights Reserved Not emission - Genset
FPT Confidential and Proprietary Revision 2.4_Dec 2017
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
4 Electronic System Specification
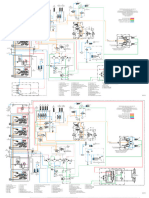
1. ARCHITECTURE
In the is shown the connection between EDC17CV41 and the other electrical and electronic devices installed on
the power generator.
Multiple state switch
Engine
Control Speedometer
Engine
Module
hardwired Grid heater relay
components BOSCH Fuel filter relay
EDC17CV41
Engine CAN Bus (CAN 2) Engine CAN Bus (CAN 1)
Engine
Engine Control
and ATS
Interface Box Panel
components
Figure 3.1. Main connections between EDC17CV41 and the other electronic devices 242354
For further details on the engine interface box see paragraph 4.3.
Not emission - Genset All Rights Reserved
Revision 2.4_Dec 2017 FPT Confidential and Proprietary
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
Electronic System Specification 5
2. ENGINE CONTROL MODULE
2.1. Overview
The main features of the Engine Control Module are:
●● Hardware: BOSCH EDC17CV41. ●● Communication Protocols: SAE J1939 for engine
control, ISO14229 (UDS) for engine diagnosis.
●● Supply Voltage: used for 12/24 nominal voltage
applications. ●● Emission level software management:
Not Emissioned.
●● Communication Interfaces: High-Speed CAN.
2.2. Electrical Characteristics
●● Nominal voltage: ●● Battery wiring connection:
–– VBAT+ : 12 / 24V Recommended value resistance of the wiring
harness, between the VBAT+/ECM/VBAT- is ≤80mΩ.
–– VBAT- : connector pins: 0V
●● Battery reversal protection:
●● Supply voltage range for ECM operation:
The ECM has a reverse polarity protection within
–– VBAT+ : functional range: 9 – 32V Supply voltage range 9- 32V limits.
This protection is provided by an internal circuit.
●● Supply nominal voltage: During the phase when the supply voltage is
applied in reverse polarity to the ECM, the fuse of
–– 12V System: VBAT+ 14 +/- 0.5V the power supply lines will not be destroyed.
–– 24V System: VBAT+ 28 +/- 0.5V
●● ECM operation without battery: Not allowed.
●● Supply ripple:
–– Max value: 2 Arms @ 32V ●● The system cannot be powered on permanently
without engine running.
–– Min value : 1.5 Arms
●● Supply current in Key-Off condition (post after-run
phase), measured at room temperature:
–– IECM, K15=OFF: I < 500μA measured at VBAT+
power supply pins.
–– In Key-Off condition all the electrical loads,
managed by ECM relay, are disconnected.
All Rights Reserved Not emission - Genset
FPT Confidential and Proprietary Revision 2.4_Dec 2017
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
6 Electronic System Specification
2.2.1. Battery Disconnection Switch
The Battery Disconnection Switch (BDS) is not mandatory for FPT.
The BDS, if present, must be connected on the Battery+ pole.
The battery must remain connected to the ECM after Key-Off at least for the whole after-run time duration (315s).
Never disconnect battery with engine running. This operation may cause data loss in the ECM memory.
There are three allowed BDS electrical configurations:
●● The BDS is connected between the Battery+ pole and the ECM key switched supply (K15), but the ECM positive
supply is directly connected to the Battery+ pole. ECM is permanently powered, also after the after-run phase
conclusion (see Figure 4.1):
STARTER CONTROL RELAY ECM
STARTER RELAY 1.88
(necessary if not inluded in the starter)
1.19
ALTERNATOR
M
BODY CONTROLLER
STARTER INTERLOCK BODY
(Vehicle Safety) CONTROLLER
STARTER MOTOR
(+)
BATTERY
DISCONNECTION
BATTERY
SWITCH
k50
1.63
k15
(-) 1.69
TO VEHICLE/ KEY SWITCH
1.73
ENGINE LOADS 1.49
1.25 +BATT.
1.01
1.26
1.03
1.28
1.75 -BATT.
1.05
1.52
Figure 4.1. Battery Disconnection Switch 1st configuration 237830
Not emission - Genset All Rights Reserved
Revision 2.4_Dec 2017 FPT Confidential and Proprietary
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
Electronic System Specification 7
●● The BDS is connected between the Battery+ pole and the ECM positives supply, but it is controlled by external
logic, for example by Smart Fuse Box or Vehicle Control Module, that MUST supply the ECM for 315 seconds
after BDS opening (see Figure 4.2):
STARTER CONTROL RELAY ECM
STARTER RELAY 1.88
(necessary if not inluded in the starter)
1.19
ALTERNATOR
M
BODY CONTROLLER
STARTER INTERLOCK BODY
(Vehicle Safety) CONTROLLER
STARTER MOTOR
(+)
BATTERY
DISCONNECTION
BATTERY
SWITCH
k50
1.63
k15
(-) 1.69
TO VEHICLE/ KEY SWITCH
1.73
ENGINE LOADS 1.49
1.25 +BATT.
1.01
1.26
1.03
1.28
1.75 -BATT.
1.05
1.52
Figure 4.2. Battery Disconnection Switch 2nd configuration 237831
●● A Time Relay with a delay timer of 315 seconds is connected between the Battery+ pole and the ECM positive
supply. The Time Relay MUST guarantee the ECM supply for 315 seconds after BDS opening or key OFF (see
Figure 4.3):
STARTER CONTROL RELAY ECM
STARTER RELAY 1.88
(necessary if not inluded in the starter)
1.19
ALTERNATOR
M
BODY CONTROLLER
STARTER INTERLOCK BODY
(Vehicle Safety) CONTROLLER
STARTER MOTOR
(+)
BATTERY
DISCONNECTION
BATTERY
SWITCH
k50
1.63
(-) TIME RELAY k15
1.69
TO VEHICLE/ KEY SWITCH
1.73
ENGINE LOADS 1.49
1.25 +BATT.
1.01
1.26
INPUT ON
VOLTAGE OFF
N.O. RELAY ON
CONTACTS OFF DELAY TIMER ‘315 SEC. 1.03
1.28
1.75 -BATT.
1.05
1.52
Figure 4.3. Battery Disconnection Switch 3rd configuration 237832
All Rights Reserved Not emission - Genset
FPT Confidential and Proprietary Revision 2.4_Dec 2017
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
8 Electronic System Specification
●● Recommended ECM Ground paths and allowed/ ●● The ECM housing is internally not connected to
forbidden power supply connection set-ups. supply GND and it must not be connected separately
to ground.
–– The following ECM power supply/GND connection –– The following ECM power supply/GND connection
set-up is recommended (see Figure 4.4): set-ups are NOT allowed (see Figure 4.5):
+ - - + - + + - - + - +
Battery Starter Generator Battery Starter Generator
- -
+ +
Engine Engine
ECU ECU
case case
Ground Ground
ribbon ribbon
Chassis Chassis
Figure 4.4. Recommended ECM power supply / 237833
Figure 4.5. Wrong ECM power supply / 237834
GND connection set-up GND connection set-up
NOTE: IMPORTANT NOTE:
this figure shows a set-up having the internal supply the alternator used to recharge the vehicle battery must
GND connection to ECM housing. In this case, if the be protect against the load-dump, if not provided by FPT.
engine ground connection is faulty, an undesired
current can flow through the housing into the ECM
electronic circuits (PCB).
Not emission - Genset All Rights Reserved
Revision 2.4_Dec 2017 FPT Confidential and Proprietary
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
Electronic System Specification 9
2.2.2. Temperature limitations
●● Operating Temperature: -30°C to +95°C.
●● The maximum temperature limit of the ECM which must never be exceeded during its active lifetime is 95°C.
This temperature is measured at a location at the bottom plate of the ECM housing which is defined in the
following drawing (see Figure 4.6).
173±2
110±2
1±2
-32
33.5±2
48.5±2
74±2
89±2
158±2
173±2
198.5±2
-92
213.5±2
232±1
260±3
Preparation
for selftapping screw M5
218±3
Figure 4.6. Bottom view of Bosch ECM 237835
Max. tolerable eveness of the customer contact survace less than or equal 0.5 to over the whole
contact surface.
Reference point to measure the temperature on the housing
●● Storage temperature:
oo Recommended: -30°C to +40°C;
oo For different values, please contact FPT.
●● The ECM is mounted on the engine and it is cooled by the Diesel fuel. Actually, it is checked during validation
measurement that ECM temperature does not exceed 95°C limit (measured at bottom plate).
●● The best cooling effect is reached when the fuel temperature is in a range from 50°C to 60°C.
In any case, the fuel temperature must not exceed 75°C.
All Rights Reserved Not emission - Genset
FPT Confidential and Proprietary Revision 2.4_Dec 2017
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
10 Electronic System Specification
2.3. Handling
●● Touching of connector pins of ECM is not allowed.
●● Opening of ECM housing is not allowed.
●● It has to be assured that no water can infiltrate through the wiring harness into the connector or the ECM
respectively. This can be achieved by using a siphon or a breathing hole (see Figure 4.7):
BOSCH
MIN 50
breathing hole on the wiring harness
Figure 4.7. Bosch ECM Connector 237836
2.3.1. Type of protection 2.4. Wiring Harness Architecture
●● The ECM has the standard DIN 40 050 and ISO The ECM input / output can be divided into engine and
20653 protection. vehicle connectors (see Figure 4.8).
●● In addition to this, it has IPX4K/6K/9K protections The wiring harness, carrying signals from these
against splash water at high pressures. sections to the other components, is composed by one/
two sections:
2.3.2. Coating of the Electronic Control ●● Engine Connector
Unit oo One section from the ECM connector to the
The coating process has to be discussed with FPT. engine components.
If the Electronic Control Module is coated, it must be
●● Vehicle Connector
ensured, that the Pressure Compensation Element
(PCE), the connector and the label are free of coating. oo One section from the ECM connector to some
not engine mounted components (filter heaters,
water in fuel sensor etc.).
BOSCH
EDC17C49
ENGINE CONNECTOR VEHICLE CONNECTOR
(A) (K)
ENGINE COMPONENTS ENGINE CAN BUS (CAN) EXTERNAL ENGINE
(HARDWIRED) COMPONENT
ATS COMPONENTS
CONTROL PANEL
(HARDWIRED)
Customer wiring VEHICLE WIRING INTERFACE
FPT wiring (FPT)
Figure 4.8. Wiring Harness Architecture 242355
Not emission - Genset All Rights Reserved
Revision 2.4_Dec 2017 FPT Confidential and Proprietary
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
Electronic System Specification 11
2.5. ECM Communication
In Figure 4.9 is shown the Power Generator architecture scheme:
FUEL TANK COOLANT NEF/CURSOR AC
SYSTEM ENGINE POWER GENERATION
AC LINE OUT
INJECTION SYSTEM AC LINE FEEDBACK
ECM CONTROL PANEL
EDC17CV41
Signal
#01
Signal ENGINE
#02 INTERFACE
BOX
Signal
#03
Figure 4.9. Power Generator architecture 260405
Signals #1 group: contains 3 type of signals: The engine interface box is an electronic equipment
●● Signals toward ECM that are driven by the engine connected between the power generator control panel
interface box, as the MSS circuitry for the engine and the engine ECM (EDC17CV41). Its purpose is to
speed selection. manage the following functions of the Power Generator:
●● Signals toward the engine interface box driven by ●● 50Hz or 60Hz generator operation, achieved through
the ECM, as the starter relay, the diagnostic lamp the selection of two fixed engine speed setpoint,
etc. respectively 1500rpm and 1800rpm. This is achieved
through the ECM MSS input or the vehicle Can line.
●● Signals toward the control panel driven by the
ECM, as the cold start lamp. These signals are ●● Display engine faults or alarms through a diagnostic
carried through the engine interface box for harness lamp.
simplification.
●● Provide actuation relays for some engine functions
Signals #2 group: contains the J1939 Vehicle Can
(engine starter, fuel heater) and dummy loads if one
line of the ECM used by both the engine interface box
or more of them are not mounted (for example if the
and the control panel.
engine has not the air heater system). This prevent
Signals #3 group: contains signals coming from the ECM to detect faults in case of missing electrical
additional sensors on the fuel tank (low fuel level), the loads on its output.
coolant system (high coolant temperature) and the The engine speed set point can be achieved in two
engine (low oil pressure). These signals are carried to ways:
the control panel for the alarm condition display and 1. Via MSS through a specific setup of the Engine
can be used in alternative to the same information Interface Box.
(except fuel level) provided by the ECM on the J1939
2. Via TSC1-PE/TE messages on the vehicle CAN
Can line.
sent to the ECM by the Control Panel.
All Rights Reserved Not emission - Genset
FPT Confidential and Proprietary Revision 2.4_Dec 2017
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
12 Electronic System Specification
The selection between the two configurations 2.5.1. Standard CAN lines
does not require a change in dataset. Called VEHICLE CAN, it is used to interface with other
CAN line is in fact configured in dataset as active by ECUs and Vehicle Control Module. This CAN bus is
default; to get this behaviour and in order to find a compliant to SAE J1939 standard.
compromise between logistic needs and eventual error Main characteristics are:
detection by the power generator user, the ECM error ●● Bit rate: 250kbit/s
relative to the timeout of CAN messages (TSC1-PE or
TSC1-TE) required to control engine speed is calibrated ●● Configuration: extended 29 bits identifier according
such in a way that diagnostic lamp is not switched on to CAN 2.0B
and no error is stored in the ECM fault memory. ●● A CAN termination resistance of 120 Ohm is inside
With the above described ECM dataset calibration, two the ECM; the other one must be situated at the other
possible situations can occur: end of the CAN bus.
●● Configurations without CAN line: if no errors are In order to avoid CAN interface malfunctions, the
active, diagnostic lamp is switched off and no TSC1 connections between the various ECUs should be
timeout error is present in the ECM fault memory. implemented by taking into account the guideline
●● Configurations with CAN line: to keep the CAN described in Appendix C and [B.1].
interface compliant with the Tier 4A family, two CAN
messages (TSC1-PE and TSC1-TE) are expected For Vehicle CAN matrix, see B a pagina 16
to be used, one as alternative to the other, to set 2.5.2. Special purpose CAN B line
and control the desired engine speed. Although this
(FPT only)
flexibility, no TSC1 timeout failure will be active into
For FPT only special operations (calibration verification/
the ECM failure memory. In the event of an actual
changes) on the ECM vehicle connector is available a
timeout of the TSC1 message used to control the
third CAN line with following characteristics:
engine speed, diagnostic lamp remains switched
off, but Genset user can however detect CAN fault ●● Bit rate: 1Mbit/s;
because engine speed drops down to the selected ●● Configuration: extended 29 bits identifier according
engine speed setpoint. to CAN 2.0B.
As shown in Figure 4.10, there are in total three CAN A K-line connection is available on the diagnostic
lines available on the ECM, which can be considered connector (see Figure 4.10) and is used only for
Standard CAN lines and Special Purpose CAN lines. FPT EOL purposes. It is not available for the engine
customer.
EDC17CV41
DIAGNOSTIC
CONNECTOR
ENGINE
CONTROL
INTERFACE
PANEL
BOX
Figure 4.10. CAN network 242357
Calibration CAN bus (CAN 2) SAE J1939
1Mbps (FPT only)
K-line flash programming UDS (FPT only)
Vehicle CAN bus (CAN 1) SAE J1939 259kbps
Not emission - Genset All Rights Reserved
Revision 2.4_Dec 2017 FPT Confidential and Proprietary
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
Electronic System Specification 13
3. ELECTRICAL BALANCE FOR FPT COMPONENTS
Engine control system components I average I peak
Low idle - 32 A (12/24V) *
ECM
High idle - 35 A (12/24V) *
12V System 180÷240A 180÷280A
Grid heater
24V System 120÷150A 160÷290A
12V System 25A
Fuel Filter Heater
24V System 12.5A
Table 1.1. Electrical Balance for FPT Components
* REMARK:
Peak current absorbed by ECM is calculated considering the worst case (anyhow a 30A fuse is present), but
average current could be far lower in normal conditions.
4. VEHICLE FUNCTIONS
4.1. Engine Torque and Speed Management
For engine controlling purposes the following TSC1 REMARK:
message is used (for details refer to [A.1]):
The Message Counter and Checksum should be
●● TSC1-PE/TE is used for engine speed control; this implemented in VCM as soon as possible, even if only
message is generated by the group controller. temporarily a default value can be acceptable (to set
A single isochronous governor is available (for the byte 8 for Message Counter/ Checksum to FFh).
details, please refer to [A.1])
In case of:
For safety reasons, a counter and a checksum must
be implemented in byte 8 of TSC1 messages (Message ●● Checksum failed, the affected TSC1 will be
Counter / Checksum). considered by engine control module as DISABLED
The Message Counter is used to detect situations and the relevant demand, engine speed control, has
where the sender repeats the same frame all the time not effect.
due to malfunction. The receiver of the information ●● Message Counter failed, after 5 consecutive
may use the counter parameter to detect this situation. message counter with the same value, the affected
The sender will increase the message counter in every TSC1 will be considered by engine control module as
cycle. The message counter will count from 0 to 7 and DISABLED and the relevant demand, engine speed
then wraps. control, has not effect.
The Message Checksum is used to verify the signal
●● CAN fault, engine speed moves to the engine speed
path from the sender to the receiver.
setpoint corresponding to the MSS position selected
The Message Checksum is calculated using the first 7 (for details, please refer to paragraph 4.1.1).
data bytes, the message counter and the bytes of the
message identifier.
It is calculated as follows:
●● Checksum = (Byte1 + Byte2 + Byte3 + Byte4 +
Byte5 + Byte6 + Byte7 + message counter & 0x0F +
message ID low byte + message ID mid low byte +
message ID mid high byte + message ID high byte)
●● Message Checksum = (((Checksum >> 6) & 0x03)
+ (Checksum >>3) + Checksum) & 0x07.
All Rights Reserved Not emission - Genset
FPT Confidential and Proprietary Revision 2.4_Dec 2017
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
14 Electronic System Specification
4.1.1. Multiple state switch 4.2. Water in Fuel Switch
MSS function of the EDC is used to select the operating The Water in Fuel Switch, installed in the fuel pre-
frequency of the Power Generator. In details, MSS can filter, indicates the presence of water in the fuel, over
be switched on three available positions: a fixed threshold dependent from the sensor physical
position 0: engine at low-idle (normally 800rpm); in construction.
this position, engine speed can be set by external CAN It is directly hardwired to the ECM vehicular connector
request via TSC1-PE/TE; (see E for connections). The state of the sensor is
position 1: engine at 1500rpm (for 50Hz power transmitted via CAN on WFI message (for details,
generator) isochronous; please refer to [A.1]).
position 2: engine at 1800rpm (for 60Hz power
generator) isochronous.
4.3. Engine Electrical heaters
Following is the schematic of the circuit connected
to the MSS input on the EDC, for the engine speed 4.3.1. Fuel Filter and pre-filter Heating
selection: Fuel filter and pre-filter heaters are used to limit the
forming of paraffin wax (in case of low temperatures)
1800rpm (2) inside the filtrating element which can stop the fuel
flow to the engine.
1500rpm (1)
Fuel filter and pre-filter heating is activated by ECM if
LOW IDLE (0)
fuel temperature is lower than FuelTHeatThrMin (and
4.97kΩ
1.2kΩ
battery voltage is in a proper range) and deactivated if
fuel temperature exceeds FuelTHeatThrMax.
5.6kΩ
In order to improve the engine cranking performances,
the heaters are switched off during the cranking phase.
MULTIPLE STATE SWITCH Fuel filter/pre-filter heating relay is directly hardwired
to ECM (see E for connections).
Figure 5.1. MSS circuit for engine speed selection 260700
If for some applications fuel filter/pre-filter heating
relay is not connected, the customer takes care of
The position is set at Power Generator installation,
connect to EDC17CV41 an equivalent impedance (R =
through proper dip-switches available inside the Engine
68Ω ± 10% and P=5W for 12V system, R=120Ω ±
Interface Box.
10% and P=5W for 24V system) to simulate the relay
REMARK: presence and to avoid diagnostic errors from the ECM
It’s recommended do not change the dip- switch (see Appendix D for connections).
configuration with the engine running, because this
4.3.2. Grid Heater
cause an immediate change in the engine speed and,
Grid heater is used in diesel applications that need a
thus, in the frequency of the generated AC.
quick and reliable start in cold conditions.
In all the three positions of MSS, if an external engine Grid heater is installed in the intake manifold and pre-
speed request via CAN becomes active, it has higher heat the combustion air to the required temperature
priority on the engine speed setpoint selected with for ignition of fuel.
MSS. It is switched on by ECM according to engine speed,
ambient temperature and intake temperature.
4.1.2. High-Idle setting Moreover, in its activation the battery status is taken
High-Idle speed is the maximum engine speed allowed into account.
in order to avoid engine over speed. When the grid heater is on, the ECM can command on
The normal working condition for Power Generator also a hardwired dedicated lamp (see paragraph 4.4.6)
application is engine speed control at 1500rpm or available in the Control Panel.
1800rpm (for 50Hz and 60Hz respectively); low-idle Grid heater is enabled in dataset and its status is
setting has a minor influence; however, if MSS is in also available via CAN. If for some applications grid
position 0 and no engine speed control via TSC1 CAN heater relay is not connected, the customer takes care
message is active, engine speed is set at low-idle of connect to EDC17CV41 an equivalent impedance
speed. (R=68Ω ± 10% and P=5W for 12V system, R=120Ω ±
High idle setting is useful only to protect the engine 10% and P=5W for 24V system) to simulate the relay
and the power generator in which the engine is presence and to avoid diagnostic errors from the ECM
mounted in the event of external CAN control; high- (see E for connections).
idle setpoint values, depending on the engine type and
displacement, they are set according to the following
table:
F2C (CURSOR 9) F3B (CURSOR 13) F4A (NEF)
High-Idle Set Point 1980rpm 1980rpm 1980rpm
Not emission - Genset All Rights Reserved
Revision 2.4_Dec 2017 FPT Confidential and Proprietary
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
Electronic System Specification 15
4.4. Lamps, Alarms and gauges 4.4.4. High Engine Oil Temperature
Lamp
4.4.1. Engine speed output This lamp warns that Engine oil temperature exceeded
Output signal enabled with standard square wave at higher limit threshold. Not hardwired to EDC.
6 pulse/rpm, 50% duty-cycle constant. The Engine Information via CAN by EDC2BC message (see [A.1]).
Speed is also available on the EEC1 CAN message.
4.4.5. Diagnostic Lamp
4.4.2. High Engine Coolant Temperature The diagnostic lamp can be driven by the ECM through
Lamp an hardwired connection (E) or managed via CAN
This lamp warns that Engine coolant temperature through the DM1 message (see [A.1]). It is mounted
exceeded higher limit threshold. Not hardwired to EDC. into the Engine Interface Box
Information via CAN by EDC2BC message. If the hardwired diagnostic lamp is not used, a dummy
Optionally, if required by the Customer, ECM can also resistor (R=1.2 kΩ ± 10%) must be connected to the
shut down the engine in order to protect it against ECM output, to avoid ghost errors.
over-heating.
4.4.6. Cold Start Lamp
4.4.3. Low Engine Oil Pressure Lamp Cold start lamp is an hardwired to EDC lamp, indicating,
This lamp warns that Engine oil pressure is under lower when switched on, that you have to wait until pre-
limit threshold. Not hardwired to EDC. Information via heating cycle is completed before engine start (see
CAN by EDC2BC message. paragraph 4.3.2).
Optionally, if required by the Customer, ECM can also Cold start lamp is enabled in dataset; its status is
shut down the engine in order to protect it against low available via CAN on SHUTDN message (see [A.1]). It
pressure. is available (if used) in the Control Panel.
If the hardwired cold start lamp is not used, a dummy
resistor (R=1.2 kΩ ± 10%) must be connected to avoid
diagnostic errors from the ECM.
5. DIAGNOSIS
Diagnosis of the ECM and engine malfunctions can be executed in two ways, called on board and off board
diagnosis.
5.1. On board diagnosis 5.2. Off board diagnosis
The diagnostic information is sent by the ECM directly Diagnostic information can also be requested to the
on the CAN 1 bus through specific messages according ECM via the diagnostic connector depicted in Figure 13
to SAE J1939-73 (DM1, DM2, DM3, DM11), mainly with a diagnostic tool PT-BOX, that can send queries to
intended for diagnostic information to Instrument the ECM using the diagnostic protocol UDS (ISO 14229-
Cluster. 1 and ISO 15765-2), on CAN 1, and obtain information
regarding the engine status, operating conditions, and
engine sensors/actuators malfunctions.
ECM programming also possible via K-line (ISO 9141).
A. CALIBRATION SUMMARY AND HINT
The values shown in the following table are indicative and can be changed according to Application Department.
Function Parameter Value EOL programming
Limp home engine speed LimpHome 1200rpm No
Minimum fuel temperature threshold for
FuelTHeatThrMin 0°C No
fuel pre-filter heating control
Maximum fuel temperature threshold
FuelTHeatThrMax 5°C No
for fuel pre-filter heating control
Engine Speed set point for PTO 0 Pto0SetEngSpd 900rpm No
Engine Speed set point for PTO 1 Pto1SetEngSpd 1500rpm No
Engine Speed set point for PTO 2 Pto2SetEngSpd 1800rpm No
Engine Speed set point for PTO 3 Pto3SetEngSpd 900rpm No
PTO 0 Configuration Pto0ModeCfg 137 No
PTO 1 Configuration Pto1ModeCfg 137 No
PTO 2 Configuration Pto2ModeCfg 137 No
PTO 3 Configuration Pto3ModeCfg 137 No
Table A.1. Calibration values
(*)
configurable also via Diagnostic Tool, limited to predefined range.
All Rights Reserved Not emission - Genset
FPT Confidential and Proprietary Revision 2.4_Dec 2017
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
16 Electronic System Specification
B. CAN MATRIX
Sent messages (vehicle CAN Bus, pins 1.46 - 1.47)
Message name Cycle Time [ms] BUS LOAD [%] Worst Case
EEC1 10 6
EEC2 50 1.2
EEC3 50 1.2
EC1 5000(1) 0.012
ET1 1000 0.06
AMB 1000 0.06
IC1 500 0.12
EFL/P1 500 0.12
Messages transmitted by ECM
EFS 500 0.12
LFE 100 0.6
LFC On req -
VEP 1000 0.06
SHUTDN 1000 0.06
HOURS On req -
EDC2BC 50 1.2
DM1 1000 0.06
DM2 On req -
Diagnostic Message Ack On req -
STOD On req -
SOFT On req -
DIS On req -
WFI 1000 0.06
AAI 1000 0.06
UDS Response On req -
Table B.1. Transmitted messages greater than +/-10%.
(1) or in case of a change of speed and/or torque
Received messages (vehicle CAN Bus, pins 1.46 - 1.47)
Message name Cycle Time [ms] BUS LOAD [%] Worst Case
Messages received by ECM
TSC1-PE (1) 10 6
TSC1-TE (1) 10 6
PGN Request On req -
UDS Request On req -
Table B.2. Received messages
(1) when active, else 200ms
Not emission - Genset All Rights Reserved
Revision 2.4_Dec 2017 FPT Confidential and Proprietary
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
Electronic System Specification 17
C. CAN INTERFACE AND FUNCTIONALITY
Main cable parameters are: Referring to the network topology example in Figure
A.1, the connection wiring length are:
●● Cable type: twisted shielded cable ●● Max bus length (L): 40m
●● Specific resistance: 25 mOhm/m ●● Max cable stub length (S): 1m
●● Cable impedance (RL): 120 Ohm ●● Min node distance (d): 0.1m
●● Min distance from RL (d0): 0m
ECU 1 ECU 2 ECU n-1 ECU n
d0
RL RL
d
L
Figure A.1. CAN Network topology 237847
For other network topologies refer to [B.1].
D. EDC17CV41 COMPONENT INTERFACE AND PIN LIST
NEF Engines
Vehicle interface
Component Pin/Signal Note
Terminal K15 1.69 I_S_T15 Key switched supply
Terminal K50 1.63 I_S_T50 Start switch term. 50 input signal
1.01, 1.25, 1.26, 1.49, 1.73 V_V_
Vbat Supply ECM Positive Supply
BAT
1.03, 1.05, 1.28, 1.52, 1.75 G_G_
Vbat Ground ECM Ground Return
BAT
1.47 B_D_CANL0
CAN 1 interface Vehicle CAN
1.46 B_D_CANH0
1.95 B_D_CANL1
CAN 2 interface Calibration CAN (FPT only)
1.71 B_D_CANH1
ISO-K interface 1.70 B_D_ISOK K-line (FPT only)
1.27 O_V_RH31
Fuel filter/pre-filter heating relay Vbat voltage from heater
1.61 O_S_RL20
1.83 O_S_RL22
Grid heater relay Vbat voltagefrom heater
1.74 O_V_RH21 (V2)
1.77 O_S_RH07
Diagnostic LED Ground from lamp
1.51 G_G_RL07
1.13 I_S_DIG01 Ground from
Water In Fuel Switch
1.43 G_R_AN14 sensor
Engine speed output 1.34 O_F_ENGN 6 Pulse/Rev. open-collector Signal
1.19 O_S_RH04
Starter relay
1.88 O_S_RL21
1.41 I_A_AN26
Multi State Switch
1.43 G_R_AN14
1.06 O_S_RL25
Cold Start LED
1.74 O_V_RH21
Table D.1. I/O interface for EDC17CV41 – NEF Engines
All Rights Reserved Not emission - Genset
FPT Confidential and Proprietary Revision 2.4_Dec 2017
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
18 Electronic System Specification
NEF Engines
Engine interface
Component Pin/Signal Note
2.90 G_R_AN05
2.07 V_V_5VSS1A
Boost pressure and temperature
2.37 I_A_AN16
sensor
2.86 I_A_AN05
2.39 I_A_AN17
Coolant temperature sensor
2.59 G_R_AN18
2.12 I_A_AN18
Fuel temperature sensor
2.59 G_R_AN18
2.06 G_R_DF03
Oil pressure and temperature 2.35 I_A_AN01
sensor 2.13 I_A_AN15
2.31 V_V_5VSS1F
2.66 I_F_CRSPOS
Increment speed sensor
2.65 I_F_CRSNEG
(crankshaft)
2.69 SHIELD
2.68 I_F_CASPOS
Segment speed sensor (camshaft) 2.67 G_R_CASNEG
2.69 SHIELD
2.60 G_R_RAILPS
Rail pressure sensor 2.11 V_V_5VSS3B
2.36 I_A_RAILPS
Cylinder 1 Injector 2.49 O_P_SVH11 2.73 O_P_SVL11
Cylinder 2 Injector 2.26 O_P_SVH22 2.02 O_P_SVL22
for NEF 4 cyl engine only
Cylinder 3 Injector 2.25 O_P_SVH21 2.01 O_P_SVL21
Cylinder 4 Injector 2.50 O_P_SVH12 2.74 O_P_SVL12
Cylinder 1 Injector 2.49 O_P_SVH11 2.73 O_P_SVL11
Cylinder 2 Injector 2.51 O_P_SVH13 2.75 O_P_SVL13
Cylinder 3 Injector 2.50 O_P_SVH12 2.74 O_P_SVL12
for NEF 6 cyl engine only
Cylinder 4 Injector 2.27 O_P_SVH23 2.03 O_P_SVL23
Cylinder 5 Injector 2.25 O_P_SVH21 2.01 O_P_SVL21
Cylinder 6 Injector 2.26 O_P_SVH22 2.02 O_P_SVL22
Table D.2. I/O interface for EDC17CV41 – NEF Engines
Not emission - Genset All Rights Reserved
Revision 2.4_Dec 2017 FPT Confidential and Proprietary
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
Electronic System Specification 19
CURSOR Engines
Vehicle interface
Component Pin/Signal Note
Terminal K15 1.69 I_S_T15 Key switched supply
Terminal K50 1.63 I_S_T50 Start switch term.50 input signal
Vbat Supply 1.01, 1.25, 1.26, 1.49, 1.73 V_V_BAT ECM Positive Supply
Vbat Ground 1.03, 1.05, 1.28, 1.52, 1.75 G_G_BAT ECM Ground Return
1.47 B_D_CANL0
CAN 1 interface Vehicle CAN
1.46 B_D_CANH0
1.95 B_D_CANL1 Calibration CAN
CAN 2 interface
1.71 B_D_CANH1 (FPT ONLY)
ISO-K interface 1.70 B_D_ISOK K-line (FPT ONLY)
Fuel filter/pre-filter heating 1.27 O_V_RH31
Vbat voltage from heater
relay 1.61 O_S_RL20
1.83 O_S_RL22
Grid heater relay Vbat voltage from heater
1.74 O_V_RH21 (V2)
1.77 O_S_RH07
Diagnostic LED Ground from lamp
1.51 G_G_RL07
1.13 I_S_DIG01
Water In Fuel Switch Ground from sensor
1.43 G_R_AN14
Engine speed output 1.34 O_F_ENGN 6 Pulse/Rev. open-collector Signal
1.19 O_S_RH04
Starter relay
1.88 O_S_RL21
1.41 I_A_AN26
Multi State Switch
1.43 G_R_AN14
1.06 O_S_RL25
Cold Start LED
1.74 O_V_RH21
Table D.3. I/O interface for EDC17CV41 – CURSOR Engines
All Rights Reserved Not emission - Genset
FPT Confidential and Proprietary Revision 2.4_Dec 2017
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
20 Electronic System Specification
CURSOR Engines
Engine interface
Component Pin/Signal Note
2.90 G_R_AN05
Boost pressure and temperature 2.07 V_V_5VSS1A
sensor 2.37 I_A_AN16
2.86 I_A_AN05
2.39 I_A_AN17
Coolant temperature sensor
2.59 G_R_AN18
2.12 I_A_AN18
Fuel temperature sensor
2.59 G_R_AN18
2.06 G_R_DF03
Oil pressure and temperature 2.35 I_A_AN01
sensor 2.13 I_A_AN15
2.31 V_V_5VSS1F
2.66 I_F_CRSPOS
Increment speed sensor
2.65 I_F_CRSNEG
(crankshaft)
2.69 SHIELD
2.68 I_F_CASPOS
Segment speed sensor
2.67 G_R_CASNEG
(camshaft)
2.69 SHIELD
2.60 G_R_RAILPS
Rail pressure sensor 2.11 V_V_5VSS3B Analog sensor
2.36 I_A_RAILPS
Cylinder 1 Injector 2.49 O_P_SVH11 2.73 O_P_SVL11 Dedicated high voltage drivers
Cylinder 2 Injector 2.50 O_P_SVH12 2.74 O_P_SVL12
Cylinder 3 Injector 2.51 O_P_SVH13 2.75 O_P_SVL13
Cylinder 4 Injector 2.25 O_P_SVH21 2.01 O_P_SVL21
Cylinder 5 Injector 2.27 O_P_SVH23 2.03 O_P_SVL23
Cylinder 6 Injector 2.26 O_P_SVH22 2.02 O_P_SVL22
2.58 O_V_MEU
Fuel Metering Unit (ZME)
2.83 O_T_MEU
2.32 V_V_5VSS1E Analog sensor
Crankcase Pressure Sensor 2.42 G_R_AN20
2.61 I_A_AN03
2.33 V_V5VSS2B Analog sensor
Exhaust gas absolute pressure
2.16 I_A_AN02
sensor
2.19 G_R_AN02
G_R_DF02 Fixed threshold pressure switch
Fuel Filter Clogging Switch
I_F_DF02
2.19 G_R_AN02 Analog sensor
Fuel Pre-Filter Clogging Pressure
2.08 V_V_5VSS2C
Sensor (C13 ONLY)
2.62 I_A_AN07
Table D.4. I/O interface for EDC17CV41 – CURSOR Engines
Not emission - Genset All Rights Reserved
Revision 2.4_Dec 2017 FPT Confidential and Proprietary
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
Electronic System Specification 21
E. LED CONNECTION CIRCUIT
In the following scheme is shown the circuit for connecting LED lamps to the ECM outputs, for 12V and 24V
applications.
VBATT
D1
R2
GND
R1
D2
Figure A.3. CAN Network topology 237848
Parameter Condition Min Typ Max
Operating Range Ta-40°C to +85°C 9V 28.8V 36V
R1 1.2 kΩ
R2 1.2 kΩ
Resistor Tolerance 5%
Table E.1. Component values for 12/24V application
In case of diagnostic lamp:
●● Vbatt is connected to pin 1.77
●● GND is connected to pin 1.51
REMARK:
The Diode D1 shall be inserted to decouple all light indicators
All Rights Reserved Not emission - Genset
FPT Confidential and Proprietary Revision 2.4_Dec 2017
Controlled copy is located on fptindustrial.com
BACK TO OUR ROOTS
WHILE ANTICIPATING THE FUTURE
FPT Industrial S.P.A. a brand of CNH Industrial
Via Puglia, 15 10156 Turin - Italy . P.IVA. IT09397710014
You might also like
- New Holland Kobelco E385 Tier 3 Crawler Excavator Service Repair Workshop ManualDocument21 pagesNew Holland Kobelco E385 Tier 3 Crawler Excavator Service Repair Workshop ManualggjjjjotonesNo ratings yet
- EDC7UC31 CodesDocument22 pagesEDC7UC31 CodesFastcross Honda93% (15)
- IVECO EDC7 UC31 Diagrama ElectricoDocument4 pagesIVECO EDC7 UC31 Diagrama ElectricoLuis Ocampo100% (2)
- AP Supported Platforms v14.75 - PIQ - 12.0Document14 pagesAP Supported Platforms v14.75 - PIQ - 12.0Alessandro Costa100% (1)
- F4AFE411ADocument238 pagesF4AFE411Ajvega_534120No ratings yet
- Software Documentation EDC7UC31-CRS P - 340.9.1: P - 340 Ds-Cv/Eet Y445 S00 746-V91 Confidential - 1Document2,800 pagesSoftware Documentation EDC7UC31-CRS P - 340.9.1: P - 340 Ds-Cv/Eet Y445 S00 746-V91 Confidential - 1Arnaldo Ribeiro100% (3)
- Manual MuellerDocument36 pagesManual MuellerFabianoNo ratings yet
- NEF ECU Controller Tier 2 (EDC7) vs. Tier 3 (EDC7UC31) PinDocument8 pagesNEF ECU Controller Tier 2 (EDC7) vs. Tier 3 (EDC7UC31) PinMauricio GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Eletrica MF 9690 E 9790Document43 pagesEletrica MF 9690 E 9790PABLO DOS SANTOS100% (1)
- ECU ConnectorsDocument12 pagesECU ConnectorsWillian JefersonNo ratings yet
- EDC7 ECU Pin Assignments - pdf.2015Document4 pagesEDC7 ECU Pin Assignments - pdf.2015Didi Robles75% (4)
- Electronic Service ToolDocument199 pagesElectronic Service ToolEzequiel ZetaNo ratings yet
- Cursor Series Tier 4B: INDUSTRIAL Application (Tigercat)Document181 pagesCursor Series Tier 4B: INDUSTRIAL Application (Tigercat)Dmicalio Sim100% (2)
- Easy Iveco InstruccionesDocument174 pagesEasy Iveco InstruccionesAnonymous J1sELDp7100% (2)
- Connector Location Chart and Electrical Circuit Diagram by SystemDocument22 pagesConnector Location Chart and Electrical Circuit Diagram by SystemLucas Solon SolonNo ratings yet
- Diagrama PDFDocument1 pageDiagrama PDFeduardonemo100% (2)
- Ur620c To252 Mosfet SMDDocument4 pagesUr620c To252 Mosfet SMDBRUNONo ratings yet
- Fendt 1000 Vario ManualDocument19 pagesFendt 1000 Vario Manualgraig27No ratings yet
- Pages de F (WC) Wheel Loader Training Manual Rev3 082011Document142 pagesPages de F (WC) Wheel Loader Training Manual Rev3 082011Ahmed Kamal100% (4)
- Cursor and Nef Engine Edc7Uc31 Fme Tier3 Stageiiia Genset Industrial ApplicationDocument35 pagesCursor and Nef Engine Edc7Uc31 Fme Tier3 Stageiiia Genset Industrial ApplicationValeriy100% (1)
- NT Bosch Edc17cv41 Irom TC1797 Egpt Allbrand 1033Document3 pagesNT Bosch Edc17cv41 Irom TC1797 Egpt Allbrand 1033Daniel HallbergNo ratings yet
- 14 - SCRsystemInstallationGuideLineDNOx2 - V7.3Document103 pages14 - SCRsystemInstallationGuideLineDNOx2 - V7.3George Huarcaya Diaz100% (1)
- Bench MPC Iveco Edc7uc31 561Document1 pageBench MPC Iveco Edc7uc31 561apoludniak1982No ratings yet
- DPA5 User ManualDocument67 pagesDPA5 User ManualMaqpower EngenhariaNo ratings yet
- MET For Iveco Vehicles - List of SignalsDocument5 pagesMET For Iveco Vehicles - List of SignalsAmor Mansouri100% (1)
- RepairDiagnostics PT 01 C0G36Z008E 3MBDocument6 pagesRepairDiagnostics PT 01 C0G36Z008E 3MBJosé Da Silva MataNo ratings yet
- IVECO Electrical G13Document28 pagesIVECO Electrical G13Modise Thee Shepherd MofokengNo ratings yet
- DLPI Daf 1033Document3 pagesDLPI Daf 1033ddf_dedo100% (1)
- DW13294103Document72 pagesDW13294103p_jankoNo ratings yet
- DPA5 User Manual PDFDocument42 pagesDPA5 User Manual PDFcleverson ferreira100% (2)
- Diagrama Iveco Stralis PDFDocument104 pagesDiagrama Iveco Stralis PDFVini67% (3)
- Comparacion EDC7UC31 Vs EDC16UC40Document26 pagesComparacion EDC7UC31 Vs EDC16UC40Anonymous J1sELDp771% (7)
- DD4-3 Diagnostico Transmision DW63242001 - DD4 - 3Document48 pagesDD4-3 Diagnostico Transmision DW63242001 - DD4 - 3Fredy Roa100% (1)
- Bosch Edc7c3 ManDocument3 pagesBosch Edc7c3 ManEmi DNo ratings yet
- Cab Sensor and Actuator Module (SCA), Component DescriptionDocument1 pageCab Sensor and Actuator Module (SCA), Component DescriptionrudiNo ratings yet
- PDF Edc7uc31 Codes DDDocument10 pagesPDF Edc7uc31 Codes DDedgarNo ratings yet
- EDC16c8 PDFDocument4 pagesEDC16c8 PDFahmedco50% (2)
- F4HFE413KDocument358 pagesF4HFE413Kjvega_53412067% (3)
- Diagrama B7, B9, B12 BEA II PDFDocument98 pagesDiagrama B7, B9, B12 BEA II PDFjoseNo ratings yet
- Mid 185 - Pid 84 - Fmi 2Document3 pagesMid 185 - Pid 84 - Fmi 2AkbarNo ratings yet
- Tga GBDocument175 pagesTga GBMyo Min OoNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Buses: Wiring Diagram B9S, Els-Mux2Document84 pagesService Manual Buses: Wiring Diagram B9S, Els-Mux2Guillermo Guardia Guzman100% (1)
- CASE IH MAGNUM 235 - 260 - 290 - 315 - 340 - 370 Tractors Hydraulic Schematics - 47605412Document6 pagesCASE IH MAGNUM 235 - 260 - 290 - 315 - 340 - 370 Tractors Hydraulic Schematics - 47605412MilanNo ratings yet
- DDCRDocument3 pagesDDCRArmando CardosoNo ratings yet
- Bosch Edc7u31 Iveco 1033Document3 pagesBosch Edc7u31 Iveco 1033Diogo Silva Reis100% (1)
- Magnum Dxi13 Wiring ManualDocument149 pagesMagnum Dxi13 Wiring ManualВиктор Сабов100% (1)
- CNH Industrial: FPT Industrial AND IvecoDocument8 pagesCNH Industrial: FPT Industrial AND IvecoCLAUDIA MASININo ratings yet
- Autocom Delphi - Plug & Diagnose PDFDocument37 pagesAutocom Delphi - Plug & Diagnose PDFPaulo Ricardo MenezesNo ratings yet
- Engine CNH Trainee MPTS ™Document154 pagesEngine CNH Trainee MPTS ™Luis Miguel Echevarria Quispe100% (4)
- Tencreng0003 Ecu ControlDocument24 pagesTencreng0003 Ecu ControlAly AbdelhamedNo ratings yet
- BOSCH 40007 (U2 - Caterpilar D6K)Document84 pagesBOSCH 40007 (U2 - Caterpilar D6K)Joil AlvesNo ratings yet
- Fault Codes: Gearbox (Gearbox - Astronic ZF)Document2 pagesFault Codes: Gearbox (Gearbox - Astronic ZF)Стефан Тасиќ100% (1)
- (2020-0873) Marine EDC7C1 NEF Electronic System Specification Feb 2022Document18 pages(2020-0873) Marine EDC7C1 NEF Electronic System Specification Feb 2022KornNo ratings yet
- Detroit Transmissions Electronic ACRONYMSDocument4 pagesDetroit Transmissions Electronic ACRONYMScells-crosser0xNo ratings yet
- Technical Specifications AdaniDocument30 pagesTechnical Specifications Adanishahnawaz1709No ratings yet
- 2021 1208 Marine Commercial Pleasure NEF EDC7C1 CAN Spec Mar 2021Document50 pages2021 1208 Marine Commercial Pleasure NEF EDC7C1 CAN Spec Mar 2021KornNo ratings yet
- Belimo BACnet Interface-Description Energy-Valve v4 01 En-Gb PDFDocument8 pagesBelimo BACnet Interface-Description Energy-Valve v4 01 En-Gb PDFBence BaloghNo ratings yet
- D25 User's GuideDocument191 pagesD25 User's GuideIlaiyaa RajaNo ratings yet
- Multiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...From EverandMultiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...No ratings yet