Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problems in Oxygenation
Problems in Oxygenation
Uploaded by
Camille Joy BaliliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problems in Oxygenation
Problems in Oxygenation
Uploaded by
Camille Joy BaliliCopyright:
Available Formats
SALES || October 21, 2022
Transcriber: EDMAR LORENZ C. LOLONG
Concepts on Oxygenation ▪ Diffusion - gas movement from an area of
Oxygen (O2) greater to lesser concentration thru a semi-
is a chemical element that is considered as permeable membrane
essential to survival it is a primary
requirement for cells to release energy during Important systems involved in oxygenation
chemical reactions. ▪ Cardiovascular
Nitrogen 78%, O2 20%, BCO2 1%, 1% other ▪ Nervous
gasses ▪ Musculoskeletal
▪ Respiratory
Oxygenation
is a combination of different processes that Basic requirements for good ventilation
contribute to bringing the oxygen from the 1. presence of patent passageway of air
environment into the cells of the body 2. Presence of elastic and expansive lungs and
tracheobronchial tree
Ventilation 3. Presence of adequate musculoskeletal
involves inspiration and exhalation. apparatuses
Air moves in and out of the lungs because 4. Presence of pressure gradient
intrathoracic pressure changes in relation to Presence of pressure gradient (change of
pressure and the airway opening. pressure per unit distance)
involves inspiration (movement of air into the
lungs) and out of the lungs thru exhalation. Normal protective mechanisms of the respiratory
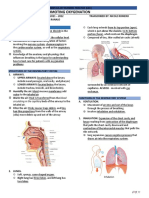
Respiration and ventilation are two different systems
things. Ventilation is mechanical and ▪ Nose-vibrissae - vibrissae (hairs of
involves the movement of air, Respiration is vestibules of the nose) When we breathe
physiologic and involves the exchange of through our noses, nose hair catches those
gases in the alveoli (external respiration) and particles. ... The second type of nose hair is
in the cells (internal respiration). called vibrissae. These longer hairs catch
RESPIRATION: The exchange of oxygen and large particles so they can't even get to our
carbon dioxide. cilia.
▪ Mucuciliary clearance - clearance is an
The cardiovascular, respiratory and part of innate defense mechanism that protects the
hematologic systems function to supply the pulmonary system from the harmful
body’s oxygen demands. consequences of inhaled agents, including
If these systems are dysfunctional → heart those of biological, chemical, and physical
failure, respiratory failure, hematologic system nature. Ciliated cells, which line the surface
problems → O2 deprivation epithelium of the airways, provide the force
necessary for mucociliary clearance by the
Respiration coordinated beating of their cilia.
A process in living organisms involving the ▪ Cough reflex - Cough, an expulsive reflex
production of energy, typically with the intake initiated when the respiratory tract is irritated
of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide by infection, noxious fumes, dust, or other
from the oxidation of complex organic types of foreign bodies. The reflex results in a
substances. sudden expulsion of air from the lungs that
carries with it excessive secretions or foreign
Processes needed to maintain adequate oxygenation material from the respiratory tract.
▪ Ventilation - movement of air in and out of ▪ Reflex bronchoconstriction - Cough is
the lungs. beneficial; pneumonia frequently results when
▪ Pulmonary perfusion - supplying the lungs an effective cough reflex is lost
with blood from the right side of the heart. Bronchoconstriction is an important and
Page 1 of 2
[SUB] 1.01 TITLE OF LECTURE – Dr. Professor
effective component of the airway defense If your heart rate is fast (over 100 beats per
reflexes protecting the lung and the rest of the minute), this is called tachycardia. A heart
body against inhaled irritants and airborne rate slower than 60 is called bradycardia. An
toxins such as cigarette smoke and acid occasional extra heartbeat is known as
aerosol. extrasystole. Palpitations are not serious most
▪ Macrophages - (large WBC, ingests foreign of the time. Palpitations are feelings or
materials) sensations that your heart is pounding or
▪ Surfactant - A fluid secreted by the cells of racing. They can be felt in your chest, throat,
the alveoli (the tiny air sacs in the lungs) that or neck. You may: Have an unpleasant
serves to reduce the surface tension of awareness of your own heartbeat. Feel like
pulmonary fluids; surfactant contributes to the your heart skipped or stopped beats.
elastic properties of pulmonary tissue,
preventing the alveoli from collapsing. DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE FOR PROBLEMS IN
▪ HeringBreuer reflex - reflex (a reflex that OXYGENATION AG NEXT (LAIN NGA TRANS)
prevents overstretching and rupture of the
alveoli.
Risk factors
Modifiable:
• Smoking
• Sedentary lifestyle
• Obesity
• Diet
• Stress
• Substance abuse
• Environmental factors
Non modifiable:
• Age
• Gender
• Race
• Heredity/Genetics
Diagnostic Procedures/Tests
Common Problems
✓ Chest pain
✓ Dyspnea
✓ Fatigue
✓ Cough
✓ Wheezing
✓ Hoarseness
✓ Palpitation
✓ Body weakness
✓ Intermittent claudication
Angina is chest pain or discomfort caused
when your heart muscle doesn't get enough
oxygen-rich blood. It may feel like pressure or
squeezing in your chest. The discomfort also
can occur in your shoulders, arms, neck, jaw,
or back.
Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Body DressingDocument263 pagesBody Dressingvijaykumarmv100% (4)
- Template - BAIL APPLICATION-Ajay ReddyDocument16 pagesTemplate - BAIL APPLICATION-Ajay ReddySayan GhoshNo ratings yet
- Individual Ambidexterity in SMEs Towards A Typology Aligning The Concept, Antecedents and OutcomesDocument33 pagesIndividual Ambidexterity in SMEs Towards A Typology Aligning The Concept, Antecedents and OutcomesnorshamsiahibrahimNo ratings yet
- Physiological Changes in Elderly RespiDocument23 pagesPhysiological Changes in Elderly RespiIrwan M. IskoberNo ratings yet
- OXYGENATIONDocument8 pagesOXYGENATIONJo Marchianne Pigar0% (1)
- Obstructive Disease of Lung and Physiotherapy ManagementDocument76 pagesObstructive Disease of Lung and Physiotherapy Managementphysio43100% (1)
- Prologue 1.1 BackgroundDocument9 pagesPrologue 1.1 BackgroundWulan Yulia DintasariNo ratings yet
- 04 OxygenationDocument4 pages04 Oxygenationbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMzDocument12 pagesANATOMY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMzalthea jade villadongaNo ratings yet
- Apec Schools 1 Quarter S.Y. 2019 - 2020 Science 9 Lesson Handout #3: Coordinated Function - The Human Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesApec Schools 1 Quarter S.Y. 2019 - 2020 Science 9 Lesson Handout #3: Coordinated Function - The Human Respiratory SystemEy ChuaNo ratings yet
- Gas ExchangeDocument6 pagesGas Exchangerasha nadaNo ratings yet
- 2018 Respiratory System HandoutDocument10 pages2018 Respiratory System HandoutMr. DummyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Ppt.Document21 pagesRespiratory System Ppt.Tino MabhizaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.3 - Human Respiratory SystemDocument29 pagesTopic 2.3 - Human Respiratory Systembienfrancis.reyes.jhsNo ratings yet
- Life Processes (Respiration)Document2 pagesLife Processes (Respiration)Farid AhemadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMDocument48 pagesLecture 4 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMZara16No ratings yet
- Physiological Overview in Relation To PracticeDocument52 pagesPhysiological Overview in Relation To PracticedrkhaledassemNo ratings yet
- Respiration Grade 10 Biology - StudentDocument65 pagesRespiration Grade 10 Biology - StudentAsawni McDowellNo ratings yet
- Sains Tingkatan 3: Science Form 3Document27 pagesSains Tingkatan 3: Science Form 3Nadzirah RedzuanNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document40 pagesModule 2Sharanya BasakNo ratings yet
- Summary - The Respiratory SystemDocument1 pageSummary - The Respiratory SystemHannah NessNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument12 pagesRespiratory Systemab4943409No ratings yet
- Unit 6 Part 2Document23 pagesUnit 6 Part 2Ina NordsethNo ratings yet
- Assignment NO 1: Name:Adeel Afzal Section: C Sap I'd: 70126263 Assignment: Physiology Submitted To: DR Urfah ZaighamDocument6 pagesAssignment NO 1: Name:Adeel Afzal Section: C Sap I'd: 70126263 Assignment: Physiology Submitted To: DR Urfah ZaighamAdeel AfzalNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases-HumansDocument14 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gases-Humansnihalbolla2023No ratings yet
- BORATA FUNDA OxyDocument15 pagesBORATA FUNDA Oxyfiel borataNo ratings yet
- Igcse Biology Revision Booklet - Term 2Document69 pagesIgcse Biology Revision Booklet - Term 2Raahil MohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working With The Other Organ SystemsDocument60 pagesChapter 1 - Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working With The Other Organ SystemsPatricia Sofia DizonNo ratings yet
- BreathingDocument5 pagesBreathingvictory IsaacNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange in Plants and AnimalsDocument51 pagesGaseous Exchange in Plants and AnimalsJesimie OriasNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 5 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture - 5 PDFDavid JokerNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Oxygenation Orpeza Cezar 1 7Document8 pages3.1 Oxygenation Orpeza Cezar 1 7Mika Marielle TrincheraNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesThe Respiratory SystemAbhi LiteNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 PTDocument12 pagesLec 3 PTBassam AlgalalyNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesPhysiology of Respiratory SystemAngelica Joan SorianoNo ratings yet
- Ncma113 Finals-ReviewerDocument53 pagesNcma113 Finals-ReviewerAB AlmazoraNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument74 pagesThe Respiratory SystemRaghu NadhNo ratings yet
- MTPX Care SemiDocument7 pagesMTPX Care SemirusselpageNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesRespiratory SystemAdit KumarNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: The Organs That Help To Get Oxygen From The Air Into Your Blood, and To Get Rid of Carbon DioxideDocument22 pagesRespiratory System: The Organs That Help To Get Oxygen From The Air Into Your Blood, and To Get Rid of Carbon DioxideTravel UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- Ch-11 and Ch-12 Gas-Exchange in Humans and RespirationDocument12 pagesCh-11 and Ch-12 Gas-Exchange in Humans and Respirationdaveymilan36No ratings yet
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument16 pagesHuman Respiratory SystemJohn marcus ViadoNo ratings yet
- System ThinkingDocument18 pagesSystem Thinkingzayana kadeejaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Respiratory Systemxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System Notes (1) ChangesDocument25 pagesThe Respiratory System Notes (1) ChangesAisha BrownNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange: Short Question AnswersDocument5 pagesGaseous Exchange: Short Question AnswersNadeem ArainNo ratings yet
- 16 RespirationDocument62 pages16 RespirationqingxuguNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Insufficiency.Document54 pagesOxygen Insufficiency.Josephine George JojoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesRespiratory SystemCraigNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Strcuture and Function of Ventilatory SystemDocument36 pages2.1 Strcuture and Function of Ventilatory SystemchaaarrNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 LEC Topic 2 Oxygenation Current Health History Physical Examination Normal Abnormal Breath Sounds Breathing PatternsDocument7 pagesNCM 112 LEC Topic 2 Oxygenation Current Health History Physical Examination Normal Abnormal Breath Sounds Breathing PatternsViviene Faye FombuenaNo ratings yet
- Hand Note - Session-1 2Document12 pagesHand Note - Session-1 2Abod AbodNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 1st Grading Week 3Document2 pagesSCIENCE 9 1st Grading Week 3tin AmuraoNo ratings yet
- G7 - Respiration - NotesDocument6 pagesG7 - Respiration - NotesSahithi PNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument20 pagesRespiration in OrganismsAdityaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Patients With Respiratory Disorders Basic Respiratory Care ModalitiesDocument15 pagesAssessment of Patients With Respiratory Disorders Basic Respiratory Care ModalitiesJhosita Flora LarocoNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System PDFDocument25 pagesThe Respiratory System PDFbilly sauraNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument33 pagesRespiratory Systemamulyajadhav119No ratings yet
- FU-M3-CU11 Respiratory Function and Nursing CareDocument17 pagesFU-M3-CU11 Respiratory Function and Nursing CareHERLIN HOBAYANNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Chapter 3Document49 pagesUnit 2 - Chapter 3Zin Min KhantNo ratings yet
- Ila College of Health: Respiratory PhysiologyDocument29 pagesIla College of Health: Respiratory PhysiologyDaniel DendaNo ratings yet
- Worksheets: Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesWorksheets: Respiratory SystemAbigailBarrionGutierrezNo ratings yet
- Pecha KuchaDocument3 pagesPecha KuchaCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Disorders PPT 3 1Document9 pagesNervous System Disorders PPT 3 1Camille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Disorders PPT 1Document4 pagesNervous System Disorders PPT 1Camille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- SOAP Bible Study Pages 1 PDFDocument1 pageSOAP Bible Study Pages 1 PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- February 2023 Little Bible Plan PDFDocument1 pageFebruary 2023 Little Bible Plan PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument3 pagesAnxiety DisordersCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- SOAP Bible Study Printable PDFDocument2 pagesSOAP Bible Study Printable PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- TOP 10 LEADING CAUSE OF MATERNAL AND INFANT MORBIDITY in The Philippines and WOH PDFDocument7 pagesTOP 10 LEADING CAUSE OF MATERNAL AND INFANT MORBIDITY in The Philippines and WOH PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- A 3.1 Sudden Pregnancy Complications PDFDocument47 pagesA 3.1 Sudden Pregnancy Complications PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- NSH1 Preterm Labour and Pemature Rupture of Membranes 1 New PDFDocument35 pagesNSH1 Preterm Labour and Pemature Rupture of Membranes 1 New PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Maternal Mortality PDFDocument101 pagesMaternal Mortality PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Jerish Verania Laboratory Activity 1 PDFDocument5 pagesJerish Verania Laboratory Activity 1 PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document - Edited 8 PDFDocument2 pagesUntitled Document - Edited 8 PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Disorder 1 QuizletDocument12 pagesCognitive Disorder 1 QuizletCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics of Efficiencies and Outcomes of The Patients - Edited PDFDocument5 pagesNursing Informatics of Efficiencies and Outcomes of The Patients - Edited PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics in Health Car1 PDFDocument9 pagesNursing Informatics in Health Car1 PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- U2A3 Hero Definition Essay Draft PDFDocument4 pagesU2A3 Hero Definition Essay Draft PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- C304 Task 1 Word A PDFDocument33 pagesC304 Task 1 Word A PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Disorders in Childhood and AdolescenceDocument7 pagesDisorders in Childhood and AdolescenceCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Disorder 2 QuizletDocument5 pagesCognitive Disorder 2 QuizletCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Cognitive DisordersDocument5 pagesCognitive DisordersCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument4 pagesAnxiety DisordersCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Cancer of The ThyroidDocument1 pageCancer of The ThyroidCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Endocrine AssessmentDocument16 pagesEndocrine AssessmentCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Cancer of The LungsDocument4 pagesCancer of The LungsCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Cancer of The Stomach Stomach CancerDocument2 pagesCancer of The Stomach Stomach CancerCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Aids HivDocument2 pagesAids HivCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Giltendez Prelim Activity International Arrivals PDFDocument2 pagesGiltendez Prelim Activity International Arrivals PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Cancer of The ProstateDocument3 pagesCancer of The ProstateCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- NUR2226 AT2 Part ADocument7 pagesNUR2226 AT2 Part ACamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Sydney Opera HouseDocument7 pagesSydney Opera HouseakosileeNo ratings yet
- DL-6101 - Criminal Procedure CodeDocument257 pagesDL-6101 - Criminal Procedure CodeTiki TakaNo ratings yet
- Blood SugarDocument18 pagesBlood Sugarlaloo01No ratings yet
- Susantha CV - NewDocument4 pagesSusantha CV - NewsusanthaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 LiteratureDocument15 pagesChapter 5 LiteratureNiña Erica PaladoNo ratings yet
- Dka AlgorithmDocument1 pageDka AlgorithmAbhinav AggarwalNo ratings yet
- 10 8 FrenchenlightenmentDocument10 pages10 8 FrenchenlightenmentNicholas ColemanNo ratings yet
- Theory of ProfitDocument10 pagesTheory of ProfitKajal Patil100% (1)
- Villareal Vs AligaDocument12 pagesVillareal Vs AligaIrang Gandia0% (1)
- Introduction To Metric SpacesDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Metric Spaceshyd arnes100% (1)
- Algebraic ExpressionsDocument24 pagesAlgebraic Expressionsmanahilnasir67No ratings yet
- Revised Neurophysiology of Pain QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesRevised Neurophysiology of Pain QuestionnaireivanNo ratings yet
- Guadines v. SandiganbayanDocument13 pagesGuadines v. SandiganbayanDenise CuizonNo ratings yet
- 14 25 1 SMDocument10 pages14 25 1 SMShindy Hamidah ManteuNo ratings yet
- Boniao .Emmersion PaperDocument24 pagesBoniao .Emmersion PaperNathaniel AlobaNo ratings yet
- The Vietnam War: Pre-ReadingDocument8 pagesThe Vietnam War: Pre-ReadingLinh Thuy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Viveka Chudamani Lesson One123Document5 pagesViveka Chudamani Lesson One123Lakshman WhiteNo ratings yet
- Distillation of Formaldehyde Containing MixturesDocument8 pagesDistillation of Formaldehyde Containing MixturesasudeyhNo ratings yet
- 8 Steps To Perfect English AccentDocument5 pages8 Steps To Perfect English Accentadhe hildaNo ratings yet
- My First Writing - Workbook 2 - Answer Key (E-Future)Document26 pagesMy First Writing - Workbook 2 - Answer Key (E-Future)Mona MohamedelsayedNo ratings yet
- Appointment, Removal and Resignation of AuditorsDocument3 pagesAppointment, Removal and Resignation of AuditorsAsad Ehsan Warraich100% (1)
- An Analytical Model For The Strength Prediction of Hybrid (Boltedbonded) Composite JointsDocument9 pagesAn Analytical Model For The Strength Prediction of Hybrid (Boltedbonded) Composite Jointskhudhayer1970No ratings yet
- 8 LOZANO Vs BALLESTEROSDocument3 pages8 LOZANO Vs BALLESTEROSmark anthony mansuetoNo ratings yet
- Pangasinan State UniveristyDocument8 pagesPangasinan State UniveristyCha ChaNo ratings yet
- I Wonder PoemDocument9 pagesI Wonder PoemPaakkialetchumi NarainasamyNo ratings yet
- Crim Law II ReviewerDocument157 pagesCrim Law II ReviewerJierah ManahanNo ratings yet
- NLL Adv ExtraPracticeKeyDocument2 pagesNLL Adv ExtraPracticeKeybeatrizplp90No ratings yet