Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Water Resources
Water Resources
Uploaded by
Gonzales, Erica Jeallean C.Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Water Resources
Water Resources
Uploaded by
Gonzales, Erica Jeallean C.Copyright:
Available Formats
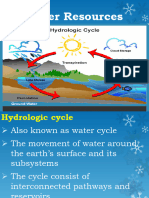
The water resources on earth.
There are two types or water, first is the fresh water the water that we
usually use, and the the water that people can drink, also Freshwater is defined as having a low salt
concentration — usually less than 1%.
and the second types of water is the salt water, the water in ocean, contains a higher concentration of
dissolved salts.
Salt water ocean, the majority of water in earth is salty, salt water or the ocean has a 97% water on earth.
Saltwater (ocean) is the fishes habitat, humans can only drink saltwater but there is a process so we can
drink saltwater and it's called desalination.
There are three major zone in the ocean 1st is the surface layer
The top surface layer is called the epipelagic zone, and is sometimes referred to as the "ocean skin" or
"sunlight zone.
2nd is the thermohaline These deep-ocean currents are driven by differences in the water's density, which
is controlled by temperature (thermo) and salinity (haline).
And lastly the deep zone, the lowest layer in the ocean.
Fresh water is vital to life and yet it is a finite resource. Of all the water on Earth, just 3% is fresh water.
Although critical to natural and human communities, fresh water is threatened by a myriad of forces
including overdevelopment, polluted runoff and global warming.
Ice caps and galciers is a thick layer of ice and snow and it is found at North and South pole,
approximately 90% of the ice in the earth is in Antarctica.
Fresh water-permafrost is a thick subsurface layer of soil that remains frozen throughout at least two
years straight occurring chiefly in polar regions.
Freshwater - groundwater
Makikita ito madalas sa mga balon, like on the picture, and also there are water on the ground underneath
your feet. An aquifer is a body of rock and/or sediment that holds groundwater.
Surface water and groundwater are reservoirs that can feed into each other. While surface water can seep
underground to become groundwater, groundwater can resurface on land to replenish surface water.
Springs are formed in these locations.
stream is a body of water that flows on Earth's surface. The word stream is often used interchangeably
with river, though rivers usually describe larger streams.
lake, any relatively large body of slowly moving or standing water that occupies an inland basin of
appreciable size. Definitions that precisely distinguish lakes, ponds, swamps, and even rivers and other
bodies of nonoceanic water are not well established.
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently or seasonally.
Flooding results in oxygen-free processes prevailing, especially in the soils.
There are 3 types of wetlands
Marsh- marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody plant species.
swamp is a forested wetland. Swamps are considered to be transition zones because both land and water
play a role in creating this environment. Swamps vary in size and are located all around the world.
Estuaries and their surrounding wetlands are bodies of water usually found where rivers meet the sea.
flood is an overflow of water (or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry.[1] In the
sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide.
There are many types of floods 1st one is
Riverine Flooding is when streams and rivers exceed the capacity of their natural or constructed channels
to accommodate water flow and water overflows the banks, spilling out into adjacent low-lying, dry land.
flash flood is a rapid flooding of low-lying areas: washes, rivers, dry lakes and depressions. It may be
caused by heavy rain associated with a severe thunderstorm, hurricane, or tropical storm, or by meltwater
from ice or snow flowing over ice sheets or snowfields.
Coastal flooding normally occurs when dry and low-lying land is submerged by seawater.
Surface water flooding is also known as pluvial flooding. It occurs when the volume of rainfall exceeds
the capacity of drains and surface water sewers and is unable to drain away through drainage systems or
soak into the land, and instead flows over the land.
River is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another
river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without
reaching another body of water.
You might also like
- Watercycle (Streams, Rivers, Lakes and Oceans): 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Earth Sciences Books EditionFrom EverandWatercycle (Streams, Rivers, Lakes and Oceans): 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Earth Sciences Books EditionNo ratings yet
- Short Notes On GeohydrologyDocument31 pagesShort Notes On GeohydrologyRavindr Kumar100% (2)
- Preboard 2 Sanitation DesignDocument7 pagesPreboard 2 Sanitation DesignMarvin KalnganNo ratings yet
- Earths WaterDocument13 pagesEarths WaterAna Marie Corales TabunarNo ratings yet
- LAS For Summative Assessment Identify The Various Water Resources On Earth (Document17 pagesLAS For Summative Assessment Identify The Various Water Resources On Earth (David Jonel RoceroNo ratings yet
- Mangroves Are Various Types of Trees Up To Medium Height and ShrubsDocument4 pagesMangroves Are Various Types of Trees Up To Medium Height and Shrubsdendi459No ratings yet
- Hydro SphereDocument33 pagesHydro SphereAlvinNo ratings yet
- Natsci HydrologyDocument3 pagesNatsci HydrologyDadula JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science (Fresh Water Reservoir)Document13 pagesEarth Science (Fresh Water Reservoir)FedNo ratings yet
- Sources of WaterDocument6 pagesSources of WaterAr Deepti ManojNo ratings yet
- ON Sources of Surface Water: Ganga Institute of Arch and Town Planning Kablana, H.R., IndiaDocument6 pagesON Sources of Surface Water: Ganga Institute of Arch and Town Planning Kablana, H.R., IndiaAr Deepti ManojNo ratings yet
- Water ResourcesDocument33 pagesWater ResourcesJolina RicoNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Water Resources The On EarthDocument16 pagesDistribution of Water Resources The On EarthKaizen ShoriNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Water On EarthDocument16 pagesDistribution of Water On EarthKaizen ShoriNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Water On EarthDocument16 pagesDistribution of Water On EarthKaizen ShoriNo ratings yet
- HYDROLOGICDocument27 pagesHYDROLOGICMarco Antonio MatanguihanNo ratings yet
- Movements of WaterDocument6 pagesMovements of WaterJhaJha AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Unit 7. EARTHS WATER RESOURCESDocument8 pagesUnit 7. EARTHS WATER RESOURCESproxima midnightxNo ratings yet
- Global Water Resources and Use Lecture 6Document9 pagesGlobal Water Resources and Use Lecture 6Mohamed WeyimiNo ratings yet
- Iv. The HydrosphereDocument43 pagesIv. The HydrosphereJohn Alfred FernandezNo ratings yet
- Water On EarthDocument3 pagesWater On Earthverito321No ratings yet
- 2 Bodies of WaterDocument1 page2 Bodies of WaterCristy Quirong SorialNo ratings yet
- WaterDocument8 pagesWatervihaanvrsNo ratings yet
- Earth Science MLG 4Document19 pagesEarth Science MLG 4Racquel BanaoNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument4 pagesNotesLokesh OriginalsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Notes Grade 8 ScienceDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Notes Grade 8 ScienceRachel Anne MaglinteNo ratings yet
- 10.1 - Earth's Supply of WaterDocument4 pages10.1 - Earth's Supply of Waterapi-251806635100% (1)
- Bodies of WaterDocument4 pagesBodies of WaterFhremond ApoleNo ratings yet
- Earth'S Water: - Started As A Combination of Gasses Which Were Carried by Meteor That Collided WithDocument5 pagesEarth'S Water: - Started As A Combination of Gasses Which Were Carried by Meteor That Collided WithEim NellaNo ratings yet
- Dokumen Geografi KelompokDocument16 pagesDokumen Geografi KelompokMario Pamdika Esvannado PutraNo ratings yet
- 1.3 The HydrosphereDocument5 pages1.3 The HydrosphereAnaNo ratings yet
- Rosalie Brillantes AsignmentDocument6 pagesRosalie Brillantes AsignmentTata Duero LachicaNo ratings yet
- Water Resources (Earth Science)Document13 pagesWater Resources (Earth Science)frenzaurelen pobeNo ratings yet
- Water ResourcesDocument52 pagesWater ResourcesJestelle DianaNo ratings yet
- Is Water That Exists in The Pore Spaces and Fractures inDocument12 pagesIs Water That Exists in The Pore Spaces and Fractures inAvy dela RosaNo ratings yet
- RiversDocument16 pagesRiversrihanna.chicotNo ratings yet
- Angel 5Document2 pagesAngel 5anon_874156217No ratings yet
- Chapter 15: Freshwater Resources: Natural Systems, Human Impacts, and ConservationDocument6 pagesChapter 15: Freshwater Resources: Natural Systems, Human Impacts, and ConservationEva WuNo ratings yet
- Assingnment No 1Document7 pagesAssingnment No 1AbhilashNo ratings yet
- Rivers (Drainage Basin and Hydrological Cycle)Document9 pagesRivers (Drainage Basin and Hydrological Cycle)zoeNo ratings yet
- Water in GeographyDocument5 pagesWater in Geographymaryam achakzaiNo ratings yet
- MathScieTech Report ModuleDocument3 pagesMathScieTech Report ModuleClarisse Allyza CabasanNo ratings yet
- Distribution of WaterDocument20 pagesDistribution of WaterVan IllaNo ratings yet
- 9th Class-TS-EM-Social Studies-3 - HydrosphereDocument9 pages9th Class-TS-EM-Social Studies-3 - HydrosphereSiddhenki StephenNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Fresh Water SystemsDocument5 pagesTopic 3 - Fresh Water SystemsjleodennisNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science: Unit 1 - Water Systems On The Earth's SurfaceDocument29 pagesGrade 8 Science: Unit 1 - Water Systems On The Earth's Surfacepanida SukkasemNo ratings yet
- Aquifers and Groundwater Movemen1Document8 pagesAquifers and Groundwater Movemen1patmarys247No ratings yet
- Hydrologic Cycle Ground Water Surface Water: Alawi, Arumpac, Cambongga, Emnace, LactuanDocument44 pagesHydrologic Cycle Ground Water Surface Water: Alawi, Arumpac, Cambongga, Emnace, LactuanMohammad Salic R. ArumpacNo ratings yet
- Bsce 5a - Hydrology - Assignment #1Document5 pagesBsce 5a - Hydrology - Assignment #1김태태No ratings yet
- Earth's Minerals and ResourcesDocument15 pagesEarth's Minerals and ResourcesLuisNo ratings yet
- Earth SciDocument20 pagesEarth SciClowohNo ratings yet
- E Flow ch1Document9 pagesE Flow ch1JMNo ratings yet
- Freshwater BiomesDocument8 pagesFreshwater BiomesMichael clyde LepasanaNo ratings yet
- GEORESEARCHDocument3 pagesGEORESEARCHJustin Menguan MerculioNo ratings yet
- Water Cycle With Google MapsDocument5 pagesWater Cycle With Google MapsGrayson Allensworth100% (1)
- Students Hydrosphere2Document54 pagesStudents Hydrosphere2Nikola MarinovNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Hidrosfera-ENDocument14 pages2.2 Hidrosfera-ENSERGIO ALEJANDRO SMITH GOMEZNo ratings yet
- Page 188-193Document7 pagesPage 188-19305 陳宗榮 RYAN GERALD CHUANo ratings yet
- Presented by 4th GroupDocument15 pagesPresented by 4th GroupsajNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 GeologyDocument5 pagesQuiz 2 Geologyhaha xdNo ratings yet
- Rain Water HarvestingDocument12 pagesRain Water HarvestingNabendu LodhNo ratings yet
- Phase II NPDES Storm Water Management Plan: March 2005Document35 pagesPhase II NPDES Storm Water Management Plan: March 2005Sean CrossNo ratings yet
- NE149 TH Street NTCDocument2 pagesNE149 TH Street NTCAkoKhalediNo ratings yet
- British Standard: A Single Copy of This British Standard Is Licensed ToDocument13 pagesBritish Standard: A Single Copy of This British Standard Is Licensed ToYaser ShabasyNo ratings yet
- Quiz No. 02 Sanitation, Design & Installation (40%)Document19 pagesQuiz No. 02 Sanitation, Design & Installation (40%)Shadow0% (1)
- Is 10446 1983 PDFDocument60 pagesIs 10446 1983 PDFJothimanikkam SomasundaramNo ratings yet
- Stormwater PDFDocument39 pagesStormwater PDFernestnsabimana74No ratings yet
- R K CashewsDocument5 pagesR K CashewsVijay SethupathiNo ratings yet
- Manufacture, Construction, Operation, and Maintenance of Aquatic Play EquipmentDocument13 pagesManufacture, Construction, Operation, and Maintenance of Aquatic Play EquipmentAhmad Zubair RasulyNo ratings yet
- Astm Specifications With Reference To Aashto SpecificationsDocument3 pagesAstm Specifications With Reference To Aashto SpecificationsHermann PankowNo ratings yet
- Operations and Maintenance Stormwater Drainage Requirements - GuidelineDocument14 pagesOperations and Maintenance Stormwater Drainage Requirements - GuidelineBarrasons Engineers Team0% (1)
- What Tool Is Used To Open Plugged or Sluggish Drain Piping? A. Drain Auger B. Force Cup C. Hand-Spinner Drain Cable D. PlungerDocument100 pagesWhat Tool Is Used To Open Plugged or Sluggish Drain Piping? A. Drain Auger B. Force Cup C. Hand-Spinner Drain Cable D. Plungergeraint phaeton100% (1)
- Chapter - 2Document39 pagesChapter - 2ልደቱ ገብረየስNo ratings yet
- DD - 20 - Circular Precast Concrete ManholesDocument5 pagesDD - 20 - Circular Precast Concrete ManholesVJ GeoNo ratings yet
- Building Over Drainage Easements PolicyDocument10 pagesBuilding Over Drainage Easements PolicyTanmay VegadNo ratings yet
- Abbreviations Plumbing Symbols: Fort Worth DistrictDocument21 pagesAbbreviations Plumbing Symbols: Fort Worth DistrictDenzel NgNo ratings yet
- Blu BrochureDocument8 pagesBlu BrochureElvi PapajNo ratings yet
- Calculation Storm PipeDocument10 pagesCalculation Storm PipesenghouNo ratings yet
- 2 M.tech INfrastructure 19-11-2011 FINALDocument57 pages2 M.tech INfrastructure 19-11-2011 FINALfandhiejavanov2009No ratings yet
- Gutter Flow and Inlet Design - 2Document11 pagesGutter Flow and Inlet Design - 2Tin VillalbaNo ratings yet
- Adoption of Sewers Section 104 of The Water Industry Act 1991Document26 pagesAdoption of Sewers Section 104 of The Water Industry Act 1991Hamzah NordinNo ratings yet
- Working Drawing GuidelinesDocument24 pagesWorking Drawing GuidelinesChristian Paul SiguaNo ratings yet
- Weao SDC Scope Document 2017 FinalDocument14 pagesWeao SDC Scope Document 2017 FinalDikshant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Weekly Progress Review Meeting-EPCC-02 - 10.04.2024 - MOM - 95Document47 pagesWeekly Progress Review Meeting-EPCC-02 - 10.04.2024 - MOM - 95phanikrishnabNo ratings yet
- Msu BoqDocument3 pagesMsu BoqAlmher RemolloNo ratings yet
- ES WD DeadLevel PDocument2 pagesES WD DeadLevel PWattsNo ratings yet
- Topic Outline Flood ControlDocument6 pagesTopic Outline Flood ControlCathy AnchetaNo ratings yet
- REF - DA181066 General Building Specifications - (A5463689)Document43 pagesREF - DA181066 General Building Specifications - (A5463689)Rafael Yap G.No ratings yet
- Cameron Highlands Presentation Slides PDFDocument76 pagesCameron Highlands Presentation Slides PDFAbdul Hayyi bin AwangNo ratings yet