Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 3
Assignment 3
Uploaded by
Smart WayOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 3
Assignment 3
Uploaded by
Smart WayCopyright:
Available Formats
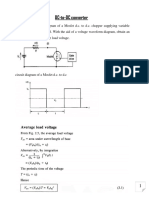
Assignment-3 Date: 21/09/2022
4EL01: Power Electronics
(1) Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s)
a) In a single phase fully controlled converter the _________ of an uncontrolled-converters are replaced by
____________.
b) In a fully controlled converter the load voltage is controlled by controlling the _________ of the converter.
c) A single-phase half wave-controlled converter always operates in the ________ conduction mode.
d) The voltage form factor of a single phase fully controlled half wave converter with a resistive inductive
load is _________ compared to the same converter with a resistive load.
e) The load current form factor of a single phase fully controlled half wave converter with a resistive
inductive load is _________ compared to the same converter with a resistive load.
f) A single phase fully controlled bridge converter can operate either in the _________ or ________
conduction mode.
g) In the continuous conduction mode at least _________ thyristors conduct at all times.
h) In the continuous conduction mode, the output voltage waveform does not depend on the ________
parameters.
i) The minimum frequency of the output voltage harmonic in a single phase fully controlled bridge
converter is _________ the input supply frequency.
j) The input displacement factor of a single phase fully controlled bridge converter in the continuous
conduction mode is equal to the cosine of the ________ angle.
k) In the discontinuous conduction mode the load current remains __________ for a part of the input cycle.
l) For the same firing angle the load voltage in the discontinuous conduction mode is __________ compared
to the continuous conduction mode of operation.
m) The load current ripple factor in the continuous conduction mode is _______ compared to the
discontinuous conduction mode.
n) In the inverter mode of operation electrical power flows from the ________ side to the __________side.
o) In the continuous conduction mode if the firing angle of the converter is increased beyond _________
degrees the converter operates in the _______ mode.
p) In a half-controlled converter two ________ of a fully controlled converter are replaced by two _________.
q) Depending on the positions of the ___________ the half-controlled converter can have ________different
circuit topologies.
r) The input/output waveforms of the two different circuit topologies of a half-controlled converter are
___________while the device ratings are __________.
Power electronics: 4EL01 M. P. Prajapati
s) A half-controlled converter has better output voltage ________ compared to a fully controlled converter.
t) A half-controlled converter has improved input _________ compared to a fully controlled converter.
u) In a half-controlled converter, the output voltage cannot become ___________ and hence it cannot operate
in the __________ mode.
v) For the same firing angle and input voltage the half-controlled converter gives _________ output voltage
form factor compared to a fully controlled converter.
w) For ripple-free continuous output current the input current displacement factor of a half-controlled
converter is given by ___________.
x) For the same supply and load parameters the output current form factor of a half-controlled converter is
_________ compared to a fully controlled converter.
y) The freewheeling operating mode of a half-controlled converter helps to make the output current _______.
(2) Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
1. At the boundary between continuous and discontinuous conduction the value of the output current at
ωt = α is _________.
2. The output voltage and current waveform of a single phase fully controlled and half controlled converter
will be same provided the extinction angle β is less than ________.
3. For the same value of the firing angle the average output voltage of a single-phase half-controlled converter
is _______ in the discontinuous conduction mode compared to the continuous conduction mode.
4. Single phase half-controlled converters are most suitable for loads requiring ________ voltage and current.
5. The three phase fully controlled bridge converter is obtained by replacing six _________ of an uncontrolled
converter by six __________.
6. The pulse number of a three phase fully controlled bridge converter is _________.
7. In a three phase fully controlled converter each device conducts for an interval of __________ degrees.
8. In a three phase fully controlled converter operating in continuous conduction there are ________ different
conduction modes.
9. The output voltage of a three phase fully controlled converter operating in the continuous conduction mode
consists of segments of the input ac ________ voltage.
10. The peak voltage appearing across any device of a three phase fully controlled converter is equal to the
________ input ac ________ voltage.
11. The input ac current of a three phase fully controlled converter has a ________ step waveform.
12. The input ac current of a three phase fully controlled converter contains only _________ harmonics but
no _________ harmonic.
13. A three phase fully controlled converter can also operate in the _________ mode.
14. Discontinuous conduction in a three phase fully controlled converter is _________.
Power electronics: 4EL01 M. P. Prajapati
(3) Attend the Following Questions in details:
Q1. Is it possible to operate a single phase fully controlled half wave converter in the inverting mode?
Explain.
Q.2 Explain with the help of neat power-diagram and associated waveforms, the operation of a single-
phase half-wave controlled converters with (i) Resistive load (ii) Inductive load..
Q.3 Give any two differences single phase full and semi converter?
Q.4 Derive an expression for (i) Average load voltage (iii) RMS load voltage (ii) Average load current
for a M-2 configuration with resistive and inductive load.
Q.5 Explain the effect of freewheeling diode in details. Also, justify the statement “Freewheeling diode
improves the power factor of the system.
Q.6 What are the advantages of six-pulse converter?
Q.7 What is mean by full converter?
Q.8 State the difference between semi converter and full converter.
Q.9 What is the difference between half controlled & fully controlled bridge rectifier?
Q.10 Explain the working of a three-phase full converter with ‘R’ load for the firing angles of 60°, 90°
and 150°.
Q.11 Explain the operation of three-phase, half-wave-controlled converter with resistive load, and
inductive load. Sketch the associated waveforms also
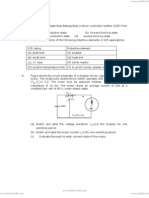
(4) Solve the following:
Q.1 A single phase fully controlled thyristor bridge converter supplies a load consisting of R, L and V c.
The inductance L in the circuit is so large that the output current may be considered to be virtually
constant. Assume the SCR to be ideal with following data: RMS supply voltage = 220 V, load resistance
R= 0.5 W, output current I dc = 10 A. Determine: (a) Firing angle a if EC = 135 V (b) a if EC = -145.
Q.2 If the half-wave-controlled rectifier has a purely resistive load of R and the delay angle is a = π/3.
Determine:
(a) Rectification efficiency (b) Form factor (c) Ripple factor (d) Transformer utilization factor (e) Peak
inverse voltage for SCR T1
Q.3 A single-phase semi converter is operated from 120 V, 50 Hz ac supply. The load resistance is 10 Ω.
If the average output voltage is 25% of the maximum possible average output voltage, determine:
(a) firing angle (b) rms and average output current (c) rms and average thyristor current.
Q.4 A three-phase half-wave-controlled rectifier has a supply of 200 V/phase. Determine the average
load voltage for firing angle of 0°, 30°, 60°, assuming a thyristor volt drop of 1.5 V and continuous load
current.
-------------------
Power electronics: 4EL01 M. P. Prajapati
You might also like
- Unlock BiosDocument38 pagesUnlock BiosIgor Pamplona100% (2)
- VSC-Based HVDC Link: To Allow Further Modifications To The Original System. This Model ShownDocument38 pagesVSC-Based HVDC Link: To Allow Further Modifications To The Original System. This Model Shownlesly100% (1)
- PX5202 - SSDC Question BankDocument21 pagesPX5202 - SSDC Question BankRoja50% (2)
- ELCT 92 - Transformer Assignment 1 - Fall 2018Document6 pagesELCT 92 - Transformer Assignment 1 - Fall 2018Edwin TomNo ratings yet
- myDAQ and myRIO DocumentationDocument22 pagesmyDAQ and myRIO DocumentationMani BalaNo ratings yet
- Australian HiFi-May - June 2018Document85 pagesAustralian HiFi-May - June 2018Phan Bình100% (1)
- ECE Library Books PDFDocument25 pagesECE Library Books PDFvijay cvijayNo ratings yet
- Multi-Modular Multi-Level Pulse Width Modulated Inverters: Mon W LDocument6 pagesMulti-Modular Multi-Level Pulse Width Modulated Inverters: Mon W LveguruprasadNo ratings yet
- Operation and Analysis of The Three Phase Fully Controlled Bridge ConverterDocument24 pagesOperation and Analysis of The Three Phase Fully Controlled Bridge Convertermohammed aliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07Document38 pagesChapter 07Umair Hassan100% (2)
- Power Electronics Book Part 2 PDFDocument379 pagesPower Electronics Book Part 2 PDFHorch Mohamed50% (2)
- Problem Set 3Document2 pagesProblem Set 3John Wanyoike MakauNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Converter: Four Switches V V 2, Capacitive Turn-Off Snubbing, ZV Turn-OnDocument10 pagesDC-DC Converter: Four Switches V V 2, Capacitive Turn-Off Snubbing, ZV Turn-OnRomitan AlexandraNo ratings yet
- CYCLOCONVERTERDocument17 pagesCYCLOCONVERTERRachmat Guntur Dwi Putra100% (1)
- A Design of Single Phase Bridge Full-Wave Rectifier: Sitaram Mahato, Naina Mohanty, Ipsita Pahi, Romeo JenaDocument7 pagesA Design of Single Phase Bridge Full-Wave Rectifier: Sitaram Mahato, Naina Mohanty, Ipsita Pahi, Romeo JenaKelvin MusyokiNo ratings yet
- Pe Course File 9 198Document190 pagesPe Course File 9 198Dr ADITYA VORANo ratings yet
- Phase-Controlled Converters: Unit IiDocument29 pagesPhase-Controlled Converters: Unit IiChinnaGurappaNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument11 pagesQuestion BankRohini MukunthanNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Inverters: Experiment 9Document8 pagesSingle Phase Inverters: Experiment 9AmeerMuaviaNo ratings yet
- Single Phase To Three Phase ConverterDocument5 pagesSingle Phase To Three Phase ConverterGabriel MejiaNo ratings yet
- Cycloconverters: Fig.1 Block Diagram of A CycloconverterDocument17 pagesCycloconverters: Fig.1 Block Diagram of A Cycloconvertersagar jaiswal100% (3)
- CYCLOCONVERTERSDocument8 pagesCYCLOCONVERTERSBabu EvanceNo ratings yet
- Phase-Controlled Converter: ObjectivesDocument8 pagesPhase-Controlled Converter: Objectiveskafle_yrsNo ratings yet
- Dual ConvertersDocument10 pagesDual ConvertersAlexNo ratings yet
- DesignFeatures 3-1110Document10 pagesDesignFeatures 3-1110khaled1512No ratings yet
- In Industrial ApplicationsDocument10 pagesIn Industrial ApplicationsEddy Santiago Neira SisaNo ratings yet
- CyclocovertersDocument4 pagesCyclocovertersAlfredNo ratings yet
- Ac Motor ADocument83 pagesAc Motor Alvb123No ratings yet
- Test Emc1Document2 pagesTest Emc1Omkar SheteNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics 2 MarkDocument5 pagesPower Electronics 2 MarkPrakash Mahendran100% (2)
- Energy Conversion and Management: K.M. Tsang, W.L. ChanDocument9 pagesEnergy Conversion and Management: K.M. Tsang, W.L. Chanroy9940198838No ratings yet
- بور الكترونيكDocument20 pagesبور الكترونيكawabNo ratings yet
- Qpaper 2019Document4 pagesQpaper 2019OmkarNo ratings yet
- Two-Stage H-Bridge Transformer Coupled DC-DC Converter With Zero Voltage SwitchingDocument8 pagesTwo-Stage H-Bridge Transformer Coupled DC-DC Converter With Zero Voltage SwitchingRakeshconclaveNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Matrix Over CycloconvertersDocument46 pagesAdvantages of Matrix Over CycloconvertersnazaahaNo ratings yet
- Maharaja Institute of Technology Mysore Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument2 pagesMaharaja Institute of Technology Mysore Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDhanush Gowda D TNo ratings yet
- Simulation and Experimental Results of 7-Level Inverter SystemDocument8 pagesSimulation and Experimental Results of 7-Level Inverter Systembacuoc.nguyen356No ratings yet
- Pe Unit 5 PDFDocument8 pagesPe Unit 5 PDFmjrsudhakarNo ratings yet
- Parative Analysis of Cascade H-Bridge Multilevel PDFDocument6 pagesParative Analysis of Cascade H-Bridge Multilevel PDFnadeemq_0786No ratings yet
- Power ConverterDocument11 pagesPower ConverterNaga Sai KiranNo ratings yet
- Ee 6503Document2 pagesEe 6503Attagasam ArjunNo ratings yet
- Statespace Model FWD ConverterDocument4 pagesStatespace Model FWD ConverterrogerozNo ratings yet
- Mac Int J.Power ElectronicsDocument14 pagesMac Int J.Power Electronicssandeepbabu28No ratings yet
- LECTURE 28 (Ch. 11) Ac Voltage Controllers: ECE 452 Power ElectronicsDocument18 pagesLECTURE 28 (Ch. 11) Ac Voltage Controllers: ECE 452 Power ElectronicsNishant ParikhNo ratings yet
- Lab 8 Single Phase InvertersDocument8 pagesLab 8 Single Phase InvertersM Hassan BashirNo ratings yet
- Conv DC-DC Paper ENglishDocument5 pagesConv DC-DC Paper ENglishpepe890305No ratings yet
- Analysis of The Performance of A Flying-Capacitor Three Level Buck Converter TopologyDocument5 pagesAnalysis of The Performance of A Flying-Capacitor Three Level Buck Converter TopologyInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Modelling and Control of A Flying-Capacitor Inverter: AbstractDocument9 pagesModelling and Control of A Flying-Capacitor Inverter: AbstractMariem KammounNo ratings yet
- A Three Phase Induction Motor Is Basically A Constant Speed Motor So ItDocument39 pagesA Three Phase Induction Motor Is Basically A Constant Speed Motor So ItManish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- New Type Single-Stage DC Ac InverterDocument5 pagesNew Type Single-Stage DC Ac InverterqiwatingNo ratings yet
- 9A02504 Power ElectronicsDocument4 pages9A02504 Power ElectronicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Power ConverterDocument9 pagesPower ConverterSrini VasuluNo ratings yet
- Third Year Question Bank POWER ELECTRONICSDocument11 pagesThird Year Question Bank POWER ELECTRONICSvenkatesh_paboluNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual 8 Inverters PDFDocument8 pagesLab Manual 8 Inverters PDFMuhammad AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Parallel Reasonance ConverterDocument43 pagesParallel Reasonance Converterchong151190No ratings yet
- Gate Ee 1991Document7 pagesGate Ee 1991Bhavani Chandra UniqueNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of Frequency Converter Used in Speed Control of Asynchronous MotorDocument6 pagesModeling and Simulation of Frequency Converter Used in Speed Control of Asynchronous MotorLelosPinelos123No ratings yet
- ECE 8830 - Electric Drives: Topic 9: Current-Fed InvertersDocument60 pagesECE 8830 - Electric Drives: Topic 9: Current-Fed InvertersKelvin LiewNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Advanced Multilevel Converters and Applications in Grid IntegrationFrom EverandAdvanced Multilevel Converters and Applications in Grid IntegrationAli Iftekhar MaswoodNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 3: Switching Power SuppliesFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 3: Switching Power SuppliesNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Smart WayNo ratings yet
- Real Time Monitoring of 3 Axis Accelerometer UsingDocument7 pagesReal Time Monitoring of 3 Axis Accelerometer UsingSmart WayNo ratings yet
- Mid1 SyallabusDocument1 pageMid1 SyallabusSmart WayNo ratings yet
- 4EL01 Winter - 2021 Exam Section IIDocument2 pages4EL01 Winter - 2021 Exam Section IISmart WayNo ratings yet
- Birla Vishvakarma Mahavidyalaya (Engineering College)Document2 pagesBirla Vishvakarma Mahavidyalaya (Engineering College)Smart WayNo ratings yet
- LG Color TV Service ManualDocument29 pagesLG Color TV Service ManualbojanicicNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6: Ac Fundamentals (Network) : DV DTDocument12 pagesChapter - 6: Ac Fundamentals (Network) : DV DTHassan SayedNo ratings yet
- View Topic - Boss - Metal Zone MT2 ModsDocument10 pagesView Topic - Boss - Metal Zone MT2 ModsDavide CastagnoneNo ratings yet
- Msi Geforce GTX 1060 6gt Ocv1Document1 pageMsi Geforce GTX 1060 6gt Ocv1Saul CardozaNo ratings yet
- Edc U-2 Scr&ujtDocument18 pagesEdc U-2 Scr&ujtRAVEE396No ratings yet
- Cobra CA-73 Microphone WiringDocument1 pageCobra CA-73 Microphone WiringrftekNo ratings yet
- 2-Phase Stepping Motor Driver: Thick-Film Hybrid ICDocument23 pages2-Phase Stepping Motor Driver: Thick-Film Hybrid ICKaland RoboNo ratings yet
- Series 8523/8: Circuit-Breakers For Motor ProtectionDocument2 pagesSeries 8523/8: Circuit-Breakers For Motor ProtectionKumarNo ratings yet
- Yaskawa Parameter 702191Document8 pagesYaskawa Parameter 702191Neo RossiNo ratings yet
- QN3107M6N: General Description Product SummaryDocument5 pagesQN3107M6N: General Description Product SummarylalukurniawanNo ratings yet
- Basic GatesDocument7 pagesBasic GatesMAMTA KUMARINo ratings yet
- MOSO SPD10KA DatasheetDocument2 pagesMOSO SPD10KA DatasheetMarcelo EspecheNo ratings yet
- PHILIPS LCD 2K7 S50HW-YD05 - Plasma Panel TroubleshootingDocument4 pagesPHILIPS LCD 2K7 S50HW-YD05 - Plasma Panel TroubleshootingalephzeroNo ratings yet
- MT5388GFMG/A: Details PDFDocument1 pageMT5388GFMG/A: Details PDFSamaro RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Informacion Tecnica Modulo de Entrada PLC Horner Modelo He559dim710Document3 pagesInformacion Tecnica Modulo de Entrada PLC Horner Modelo He559dim710Rodolfo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Handling Out of PQIDocument21 pagesHandling Out of PQIShandi Cah YuhuiNo ratings yet
- PCB Design - Schematic DiagramDocument29 pagesPCB Design - Schematic DiagramFrancesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To VLSIDocument60 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To VLSIsadia santaNo ratings yet
- Ele App MechDocument7 pagesEle App Mechanon_683483930No ratings yet
- 1.1 Flapper Nozzle AmplifierDocument1 page1.1 Flapper Nozzle AmplifierAndi KurniaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines IDocument15 pagesElectrical Machines Imepco10050% (4)
- EE20L Exp1Document5 pagesEE20L Exp1Patrick HernandezNo ratings yet
- TR16 Battery Tester InstructionDocument2 pagesTR16 Battery Tester InstructionJoe SmithNo ratings yet
- Signal Processing FirstDocument6 pagesSignal Processing Firstnickswap100% (1)
- ABB Brochure AC 800PEC FinalDocument12 pagesABB Brochure AC 800PEC FinalintoisrNo ratings yet
- FM Receiver in GNU RadioDocument6 pagesFM Receiver in GNU RadioRakesh S KNo ratings yet