Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aristotle
Aristotle
Uploaded by
Marjorie Canteras Tejano0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesAristotle believed monarchy was the ideal form of government if led by a virtuous "man of preeminent virtue, a god among men." Such a monarch would rule for the common good rather than selfish interests and their virtue would give them right to rule without being subject to laws. Aristotle also supported constitutional government and aristocracy, where the best men rule. He opposed democracy and oligarchy, seeing democracy as "rule of the poor" and oligarchy empowering only the wealthy. Aristotle advocated for a middle class and balancing the freedom of the poor with wealth of the rich.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAristotle believed monarchy was the ideal form of government if led by a virtuous "man of preeminent virtue, a god among men." Such a monarch would rule for the common good rather than selfish interests and their virtue would give them right to rule without being subject to laws. Aristotle also supported constitutional government and aristocracy, where the best men rule. He opposed democracy and oligarchy, seeing democracy as "rule of the poor" and oligarchy empowering only the wealthy. Aristotle advocated for a middle class and balancing the freedom of the poor with wealth of the rich.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesAristotle
Aristotle
Uploaded by
Marjorie Canteras TejanoAristotle believed monarchy was the ideal form of government if led by a virtuous "man of preeminent virtue, a god among men." Such a monarch would rule for the common good rather than selfish interests and their virtue would give them right to rule without being subject to laws. Aristotle also supported constitutional government and aristocracy, where the best men rule. He opposed democracy and oligarchy, seeing democracy as "rule of the poor" and oligarchy empowering only the wealthy. Aristotle advocated for a middle class and balancing the freedom of the poor with wealth of the rich.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
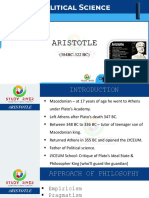
Aristotle’s Politics: -Aristotle holds monarchy to be the most
ideal kind of government.
Forms of Government
To determine whether a government is -Man of “preeminent in virtue” – “God
good or bad, Aristotle asked three among men”
basic questions:
Such man cannot be regarded as a part
1. Does the government serve the of the state, subject to the law like
common good or does it serve the everybody else.
selfish interests of those with
Since there is no law for men of
power?
preeminent virtue, monarchs are “law
2. Does the government rest on the themselves.
power at the ruler’s disposal or
Their superior virtue and political
does it rest on laws that have
capacity give them the right to “practice
been made in such a way that
compulsion and still live in harmony with
the ruled have agreed to them
their cities.
and have had a part in making?
A king is the resource of better classes
3. If the government is
against the people.
constitutional, is that
constitution just and are the laws The idea of a king is to be a protector of
made by that government just? the rich against unjust treatment; of the
people against insult and oppression.
Aristotle’s True Governments
Aristocracy
- Kingship
- Aristocracy -A government formed of the best men
absolutely (not relatively).
- Constitutional Government
Perversion of True Government -Based of merit and virtue
- Tyranny The deteriorated form of aristocracy that
form of aristocracy is oligarchy, in which
- Oligarchy government by the wealthy is carried on
for their own benefit rather than the
- Democracy
whole of the state.
Kingship
Constitutional Government Men think that is just is equal; that
equality is the supremacy of popular
-A state that the citizens at large will; and that freedom means the doing
administer for the common good. what a man likes. In such democracies,
everyone lives as he pleases
-”Unite the freedom of the poor and the
wealth of the rich.”
Democracy of the Poor
Thinking realistically of the stability of
the state, Aristotle holds that the freedom
-A state that the citizens at large
of the poor must be given consideration.
administer for the common good.
For a state in which many poor men are
excluded from office will necessarily be -”Unite the freedom of the poor and the
full of enemies wealth of the rich.”
For a state in which many poor men are
excluded from office will necessarily be
The role of the middle class
full of enemies.
“Poverty is the parent of revolution and Aristotle
crime.
“Happiness is good. But in
moderation.”
“Where there is no middle class, and the
poor greatly exceed in number, trouble Aristotle (384 BCE- 322 BCE)
arise, and the state soon comes to an
end.” Ancient Greek philosopher and scientist;
one of the greatest intellectual figures of
Aristotle was opposed to the selfish rule Western history.
by either an excessively wealthy
plutocracy or by a propertyless His father, Nicomachus, was the
proletariat. physician of Amyntas III, king of
Macedonia and grandfather of Alexander
Democracy the Great.
-Rule of the poor After his father’s death in 367, Aristotle
migrated to Athens, where he joined the
- Of the three degenerate forms, Academy of Plato. He remained there for
government of the poor for the benefit of 20 years as Plato’s pupil and colleague.
the poor is “the most tolerable.” Aristotle’s Ethical Philosophy:
1. The highest good and the end toward
which all human activity is directed is
happiness, which can be defined as
continuous contemplation of eternal and
universal truth.
2. One attains happiness by a virtuous
life and the development of reason and
the faculty of theoretical wisdom. For
this one requires sufficient external
goods to ensure health, leisure, and the
opportunity for virtuous action.
3. Moral virtue is a relative mean
between extremes of excess and
deficiency, and in general the moral life
is one of moderation in all things except
virtue. No human appetite or desire is
bad if it is controlled by reason according
to a moral principle. Moral virtue is
acquired by a combination of knowledge,
habituation, and self-discipline.
4. Virtuous acts require conscious choice
and moral purpose or motivation. Man
has personal moral responsibility for his
actions.
5. Moral virtue cannot be achieved
abstractly — it requires moral action in a
social environment. Ethics and politics
are closely related, for politics is the
science of creating a society in which
men can live the good life and develop
their full potential.
You might also like
- Public Corporations: General PrinciplesDocument23 pagesPublic Corporations: General PrinciplesMonefah Mulok100% (1)
- NHS Standard Application FormDocument17 pagesNHS Standard Application FormDanielaNo ratings yet
- BLS - 1st Yr (1) Plato Ideal StateDocument28 pagesBLS - 1st Yr (1) Plato Ideal StatePrisha Bauskar100% (2)
- Aristotle-By Riya GargDocument24 pagesAristotle-By Riya Gargkavy0% (1)
- Chapter 6 Kinds of GovernmentDocument4 pagesChapter 6 Kinds of GovernmentPaulAnthonyPascual100% (5)
- AristotleDocument7 pagesAristotleCharrise GellaNo ratings yet
- Aristotle Theory of Classification of GovernmentDocument2 pagesAristotle Theory of Classification of GovernmentSaad UllahNo ratings yet
- Political Regimes Q and ADocument8 pagesPolitical Regimes Q and ALivia FrunzaNo ratings yet
- Aristotelian Classification of ConstitutionDocument10 pagesAristotelian Classification of ConstitutionRda Renthlei100% (1)
- Lecture Aristotle Classification of GovernmentsDocument11 pagesLecture Aristotle Classification of GovernmentsBilal AkhterNo ratings yet
- Aristotle Politics: MONARCHY Page 21Document6 pagesAristotle Politics: MONARCHY Page 21arnaldpaguioNo ratings yet
- Plato's Ideal S-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesPlato's Ideal S-WPS OfficeGamli LoyiNo ratings yet
- Aristotle ConstitutionsDocument2 pagesAristotle ConstitutionsCodruța VârlanNo ratings yet
- PARAMITA - CHAKRABORTYAristotle and The Classification of Constitutions2020!05!03Aristotle and The Classification of The ConstitutionDocument3 pagesPARAMITA - CHAKRABORTYAristotle and The Classification of Constitutions2020!05!03Aristotle and The Classification of The ConstitutionArumugam mahalingamNo ratings yet
- Plato's The Republic: 2. Aristotle's Classification of GovernmentDocument3 pagesPlato's The Republic: 2. Aristotle's Classification of GovernmentDiola QuilingNo ratings yet
- AristotleDocument8 pagesAristotleAshley MathewNo ratings yet
- Aristotle Classification of JusticeDocument9 pagesAristotle Classification of JusticeAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- What Were Aristotle's Thoughts About The Government?Document2 pagesWhat Were Aristotle's Thoughts About The Government?prati pNo ratings yet
- Western PhilosophersDocument12 pagesWestern Philosophersifatima9852No ratings yet
- CiceroDocument5 pagesCiceroERICAH VILLACARLOSNo ratings yet
- The Contribution of The Greeks: Topic 1 - Political ThinkersDocument48 pagesThe Contribution of The Greeks: Topic 1 - Political ThinkersBlesdEmpressNo ratings yet
- Government ReviewerDocument10 pagesGovernment ReviewerFAUL MANGAYANo ratings yet
- Man and The StateDocument3 pagesMan and The StateAnonymous K286lBXothNo ratings yet
- Aristotle NotesDocument10 pagesAristotle NotesShailja SehrawatNo ratings yet
- Aristotle Notes For CSSDocument7 pagesAristotle Notes For CSSHina AwanNo ratings yet
- A Comparison Between Ancient Greek and Chinese Philosophy On PoliticsDocument5 pagesA Comparison Between Ancient Greek and Chinese Philosophy On PoliticsChi HàNo ratings yet
- Would Aristotle System Be Able To Create A Good Society/State in Pakistan?Document13 pagesWould Aristotle System Be Able To Create A Good Society/State in Pakistan?Shafaq BilalNo ratings yet
- AristotleDocument3 pagesAristotleSardar Ramzan DogarNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument3 pagesIntroductionLiving WoodNo ratings yet
- Montesquieu-The Spirit of The LawsDocument6 pagesMontesquieu-The Spirit of The LawsTaylor HinojosaNo ratings yet
- Plato PDFDocument13 pagesPlato PDFMuneer Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Aristotle's Classification of GovernmentDocument5 pagesAristotle's Classification of Governmentshreya mathane0% (1)
- Plato's 3 RegimesDocument5 pagesPlato's 3 RegimesOmar DiazNo ratings yet
- Aristotle Views On Constitution PDFDocument4 pagesAristotle Views On Constitution PDFGaurav PandeyNo ratings yet
- Aristotle - Law and StatecraftDocument5 pagesAristotle - Law and StatecraftDania ChNo ratings yet
- CSS Solved Political Science Past PapersDocument4 pagesCSS Solved Political Science Past PapersAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Forms of Government by Associated Attributes: by Elements of Where Decision-Making Power Is HeldDocument2 pagesForms of Government by Associated Attributes: by Elements of Where Decision-Making Power Is Heldankitabhat93No ratings yet
- Week 5 Aristotle Political ThoughtDocument22 pagesWeek 5 Aristotle Political ThoughtHazel GasconNo ratings yet
- Name: Marwa Riaz Roll No: 25 Assignment: Political Science Semester: 2nd Department: Political Science & IR Government College Women University FaislabadDocument11 pagesName: Marwa Riaz Roll No: 25 Assignment: Political Science Semester: 2nd Department: Political Science & IR Government College Women University FaislabadZain RiazNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of ARISTOTLEDocument17 pagesPhilosophy of ARISTOTLEYousuf KhanNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - The StateDocument5 pagesWeek 2 - The StateANGELICA ROMAWAKNo ratings yet
- Classification-Of-States Mid Term AssignmentDocument18 pagesClassification-Of-States Mid Term AssignmentNadeem MalikNo ratings yet
- Sociology 1Document8 pagesSociology 1Raheela MughalNo ratings yet
- The StateDocument23 pagesThe Statehamzakha1296No ratings yet
- Political Science Paper 1 (2019)Document35 pagesPolitical Science Paper 1 (2019)Afia NazirNo ratings yet
- 1 Social and Political Philosophy-1Document55 pages1 Social and Political Philosophy-1api-278252759No ratings yet
- Aristotle: From Politics, C. 340 BCE: Ideas To ConsiderDocument5 pagesAristotle: From Politics, C. 340 BCE: Ideas To ConsiderKatie ChenNo ratings yet
- Aristotle: From Politics, C. 340 BCE: Ideas To ConsiderDocument5 pagesAristotle: From Politics, C. 340 BCE: Ideas To ConsiderKatie ChenNo ratings yet
- Comparative Government ReportDocument19 pagesComparative Government ReportDonna GaelaNo ratings yet
- Biographical Briefing On Plato1 2Document2 pagesBiographical Briefing On Plato1 2api-38237833No ratings yet
- Aristotal Political Theory Distinctive NotesDocument2 pagesAristotal Political Theory Distinctive NotesOsama GillNo ratings yet
- Aristotle PowerPointToPdfDocument15 pagesAristotle PowerPointToPdfAkash EhmedNo ratings yet
- POLS 110 Political Philosophers ReadingsDocument27 pagesPOLS 110 Political Philosophers ReadingsNgeleka kalalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04: Main Currents of Western Political ThoughtsDocument5 pagesChapter 04: Main Currents of Western Political ThoughtsAqib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 8a. Theories of SoverreigntyDocument27 pages8a. Theories of SoverreigntyRohit Mohan0% (1)
- Evolution of Political IdeologiesDocument40 pagesEvolution of Political Ideologiesblah blah 56743No ratings yet
- Political PhilosophyDocument14 pagesPolitical PhilosophySajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- History of Political ThoughtDocument44 pagesHistory of Political ThoughtHarryNoharaNo ratings yet
- PhilosphyDocument8 pagesPhilosphyZara Khan100% (1)
- Mahmud MIdtermDocument6 pagesMahmud MIdtermMumtahina MahmudNo ratings yet
- ADMINISTRATIVE ACCOUNTABILITY of Public OfficersDocument9 pagesADMINISTRATIVE ACCOUNTABILITY of Public OfficersMarjorie Canteras TejanoNo ratings yet
- Thucydides TrapDocument2 pagesThucydides TrapMarjorie Canteras TejanoNo ratings yet
- Grave Threat - Case DigestDocument4 pagesGrave Threat - Case DigestMarjorie Canteras TejanoNo ratings yet
- Case Digest in GR No. 123045Document5 pagesCase Digest in GR No. 123045Marjorie Canteras TejanoNo ratings yet
- Sumacab NorteDocument146 pagesSumacab NorteZoilo PaynorNo ratings yet
- Roxas Versus Binay BailiwicksDocument126 pagesRoxas Versus Binay BailiwicksManuel L. Quezon IIINo ratings yet
- DowryDocument67 pagesDowryVaibhav Singh0% (1)
- HMT 431 Dedoroy Dieza Final OutputDocument17 pagesHMT 431 Dedoroy Dieza Final OutputPaul John DedoroyNo ratings yet
- Application 27060000022091067345 1663078554Document2 pagesApplication 27060000022091067345 1663078554Afzal NavedNo ratings yet
- Barbaza, AntiqueDocument2 pagesBarbaza, AntiqueSunStar Philippine NewsNo ratings yet
- Ujian Praktek Bhs Inggris WajibDocument4 pagesUjian Praktek Bhs Inggris WajibMikael TitoNo ratings yet
- Printable List of Countries and Capitals by ContinentDocument5 pagesPrintable List of Countries and Capitals by ContinentBabis MpamiasNo ratings yet
- Polder: Polders and The NetherlandsDocument5 pagesPolder: Polders and The NetherlandsTrySoeNo ratings yet
- 201335694Document80 pages201335694The Myanmar Times100% (1)
- African Beauty EssayDocument6 pagesAfrican Beauty EssayTaylorRosemaryNo ratings yet
- The African Roots of The Celtish Clans # 2 - Black Celts, Black Britons - by - Jamani - Rasta LivewireDocument10 pagesThe African Roots of The Celtish Clans # 2 - Black Celts, Black Britons - by - Jamani - Rasta LivewireYorubaGyal GrownWoman50% (2)
- Elementary Spanish Grammar PDFDocument377 pagesElementary Spanish Grammar PDFUtku KepcenNo ratings yet
- Theatrical Arts Guild Constitution and BylawsDocument4 pagesTheatrical Arts Guild Constitution and Bylawsbigblacknope is hereNo ratings yet
- Proposal For Model Nursery2Document10 pagesProposal For Model Nursery2Satish Bhat100% (1)
- Krishna Menon On KashmirDocument620 pagesKrishna Menon On KashmirEnuga S. Reddy100% (4)
- Cambridge University Press The Historical JournalDocument32 pagesCambridge University Press The Historical JournalPablo TorresNo ratings yet
- A Tale of Two Cities PDFDocument56 pagesA Tale of Two Cities PDFSudiptoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Public AdministrationDocument4 pagesChapter 5 Public AdministrationjustinejamesjoseNo ratings yet
- 17 Great Books About American Presidents For Presidents' Day Weekend - The New York TimesDocument11 pages17 Great Books About American Presidents For Presidents' Day Weekend - The New York TimesAnonymous j6r5KRtrH2No ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris X SemuaDocument17 pagesBahasa Inggris X Semuacandu kenariNo ratings yet
- Marriage Encounter Pamphlet For WebsiteDocument2 pagesMarriage Encounter Pamphlet For Websiteapi-236277001No ratings yet
- Ir 2Document15 pagesIr 2Kuthubudeen T MNo ratings yet
- Commoner Issue 15Document447 pagesCommoner Issue 15Alice CorbleNo ratings yet
- Nationalism in IndiaDocument18 pagesNationalism in Indiasurajyadav210No ratings yet
- PRESSMAN Jefrey y Aaron WILDAVSKY - Implementation en Shafritz - Classics of Public AdministratioDocument4 pagesPRESSMAN Jefrey y Aaron WILDAVSKY - Implementation en Shafritz - Classics of Public AdministratioAngela Quillatupa MoralesNo ratings yet
- The Secular City (Cox, Stewart)Document2 pagesThe Secular City (Cox, Stewart)zagarin_madalina2685No ratings yet
- 41st Common CSPsDocument13 pages41st Common CSPsMuhammad Mohkam Ud DinNo ratings yet