Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basis For Comparison Type I Error Type Ii Error: 22. Compare Type 1 Error and Type 2 Error in Sampling Plan. Answer
Basis For Comparison Type I Error Type Ii Error: 22. Compare Type 1 Error and Type 2 Error in Sampling Plan. Answer
Uploaded by
UDayOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basis For Comparison Type I Error Type Ii Error: 22. Compare Type 1 Error and Type 2 Error in Sampling Plan. Answer
Basis For Comparison Type I Error Type Ii Error: 22. Compare Type 1 Error and Type 2 Error in Sampling Plan. Answer
Uploaded by
UDayCopyright:
Available Formats
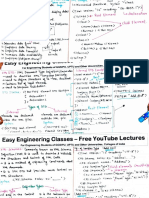
22. Compare Type 1 error and Type 2 error in sampling plan.
Answer.
BASIS FOR
TYPE I ERROR TYPE II ERROR
COMPARISON
Meaning Type I error refers to non- Type II error is the
acceptance of hypothesis acceptance of hypothesis
which ought to be accepted. which ought to be rejected.
Equivalent to False positive False negative
What is it? It is incorrect rejection of true It is incorrect acceptance of
null hypothesis. false null hypothesis.
Represents A false hit A miss
Probability of Equals the level of Equals the power of test.
committing error significance.
Indicated by Greek letter 'α' Greek letter 'β'
22. Explain fraction defective, percent defective and defect per unit.
Ans. Fraction Defective = It is define as the ratio of the number of nonconforming items in the population to the total number of items in that
population.
Percent defective = The percent defective is the number of values of a variable that fall outside of some user specified tolerance limits.
Defect per unit = A measure of quality that measures how many defects are associated with a single product or service unit.
23. Summarize statistical quality control and its advantages.
Ans. The use of the statistical method in the monitoring and maintaining of the quality of products and services.
For example: SQC serves as a medium allowing manufactures to attain maximum benefits by following contolled
testing of benefits by following controlled testing of manufactured products.
Advantages
Prevent recalls from happening.
Re-evaluate set production processes to increase efficiency.
Generate complete confidence in our product.
24. Distinguish between ‘variable charts’ and ‘attribute charts’.
Ans.
S.No. Variable Control Chart Attribute Control Chart
1 Measured Data Counted Data
Data is continuous like diameter, width, Data is discrete like go-no-go, good-not
2
length, etc. good, etc.
X bar and Range Chart, I (Individual)
3 p, np, c, u Chart
chart, MR (Moving Range) Chart, etc.
Quantitative value (Example: Diameter:
4 Qualitative Value (number of defects)
10.15 mm)
5 More costly Less costly
The decision takes time as the sample
6 Quick decision with small sample size
size is bigger
The time delay between the ‘out of
The time delay between ‘out of control’
7 control’ signal to corrective action
signal to corrective action is longer
is shorter
8 Improvement can be quantified Improvement can not be quantified
You might also like
- Machine Learning Business ReportDocument34 pagesMachine Learning Business ReportMITESH AGRAWAL100% (1)
- Guidelines For Validation Cooking InstructionsDocument39 pagesGuidelines For Validation Cooking InstructionsktigranNo ratings yet
- Hospitality Marketing Strategies and Implementation Among The Selected Restaurants of Butuan City During The PandemicDocument76 pagesHospitality Marketing Strategies and Implementation Among The Selected Restaurants of Butuan City During The PandemicJoannalou Talaugon50% (2)
- Uncertainty Estimation and CalculationDocument61 pagesUncertainty Estimation and CalculationOmar SaadiqNo ratings yet
- Multivariate Analysis – The Simplest Guide in the Universe: Bite-Size Stats, #6From EverandMultivariate Analysis – The Simplest Guide in the Universe: Bite-Size Stats, #6No ratings yet
- IT 2 TQMDocument6 pagesIT 2 TQMUDayNo ratings yet
- IT 2 TQMDocument6 pagesIT 2 TQMUDayNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument3 pagesDocxyvonneberdosNo ratings yet
- Metrology Lecture 01Document31 pagesMetrology Lecture 01Getachew G/AmlakNo ratings yet
- Sample Size ConsiderationsDocument14 pagesSample Size ConsiderationsEDRUGNo ratings yet
- Inferential StatisticsDocument20 pagesInferential StatisticsNourhan KhattabNo ratings yet
- INferential StatisticsDocument34 pagesINferential StatisticsNhelia Santos BañagaNo ratings yet
- Practical Skills RetrievalDocument14 pagesPractical Skills Retrievalmariam saikNo ratings yet
- BSCHAPTER - 11 (Hypothesis Testing)Document67 pagesBSCHAPTER - 11 (Hypothesis Testing)kunal kabraNo ratings yet
- Lect 1Document29 pagesLect 1May FadlNo ratings yet
- Kelas 1 - Matrikulasi S-D Testing HypothesisDocument31 pagesKelas 1 - Matrikulasi S-D Testing Hypothesism nur rizkiNo ratings yet
- Type I and II ErrorsDocument11 pagesType I and II ErrorsPratik PachaniNo ratings yet
- Dr. KS - Errors in Chemical Analysis PDFDocument19 pagesDr. KS - Errors in Chemical Analysis PDFVijay Kumar VishvakarmaNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Hyphothesis Testing (Continuous)Document35 pages2.2 Hyphothesis Testing (Continuous)NS-Clean by SSCNo ratings yet
- Power of TestDocument3 pagesPower of TestEmy AL-AnaziNo ratings yet
- Research Hypothesis Type I and Type II Errors de La CruzDocument31 pagesResearch Hypothesis Type I and Type II Errors de La CruzLettynia Mellisze Famoso SorongonNo ratings yet
- Subject Measurement and Evaluation: Topic Degree of Freedom, Type 1and 2 Error and Level of SignificanceDocument23 pagesSubject Measurement and Evaluation: Topic Degree of Freedom, Type 1and 2 Error and Level of SignificanceAltaf UllahNo ratings yet
- Units 1.0Document8 pagesUnits 1.0AbhishekNo ratings yet
- QMMDocument54 pagesQMMgladwin thomasNo ratings yet
- Auditing Notes - Chapter 5Document14 pagesAuditing Notes - Chapter 5Future CPA75% (4)
- Biostatistics FinalDocument7 pagesBiostatistics Finalmohammad nomanNo ratings yet
- Mcqs of Measurement ThoeriesDocument5 pagesMcqs of Measurement ThoeriesZainab MehfoozNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Metrics:: Confusion MatrixDocument7 pagesEvaluation Metrics:: Confusion MatrixNithya PrasathNo ratings yet
- How To Read A Paper - The StatisticsDocument62 pagesHow To Read A Paper - The StatisticsMark KerrNo ratings yet
- MB 0034-1Document10 pagesMB 0034-1mehulctxNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Hypothesis TestingDocument9 pagesFundamentals of Hypothesis TestingLiana Monica LopezNo ratings yet
- PSY 240: Statistics in Psychology: One Sample Statistics: Calculating Significance For Paired MeansDocument41 pagesPSY 240: Statistics in Psychology: One Sample Statistics: Calculating Significance For Paired MeansFatmir MusliuNo ratings yet
- Introduction On Chi Square DistributionDocument13 pagesIntroduction On Chi Square DistributionMonil GandhiNo ratings yet
- 15EC35 - Electronic Instrumentation - Module 1 PDFDocument26 pages15EC35 - Electronic Instrumentation - Module 1 PDFNikhila NicksNo ratings yet
- Complemento Aula 8Document43 pagesComplemento Aula 8Hamsaveni ArulNo ratings yet
- How To Quantify ErrorDocument10 pagesHow To Quantify ErrorTunica Prince100% (1)
- Hypothesis TestingDocument17 pagesHypothesis TestingAdïtyã RäjpūtNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS STATISTICS - Chp6Document14 pagesBUSINESS STATISTICS - Chp6Allina PonganNo ratings yet
- Absite - Chapter 3 PresentationDocument12 pagesAbsite - Chapter 3 PresentationAlex ChenNo ratings yet
- Expt 1-10-2Document58 pagesExpt 1-10-2احمد غالبNo ratings yet
- Confidence Interval For Population VarianceDocument48 pagesConfidence Interval For Population VarianceNicholas BoampongNo ratings yet
- Error MesurementDocument13 pagesError MesurementMubena HussainNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology and Biostatistics Part II 2Document45 pagesResearch Methodology and Biostatistics Part II 2Sohail SheikhNo ratings yet
- Some Discussions On Unit - 1Document11 pagesSome Discussions On Unit - 1kumbhalkarvalay8No ratings yet
- Errors in Hypothesis TestingDocument2 pagesErrors in Hypothesis TestingpaulNo ratings yet
- Statisticsprobability11 q4 Week1 v4Document10 pagesStatisticsprobability11 q4 Week1 v4Sheryn CredoNo ratings yet
- 3 - Test of Hypothesis (Part - 1) PDFDocument45 pages3 - Test of Hypothesis (Part - 1) PDFhijab100% (1)
- Acceptance Sampling SQCDocument41 pagesAcceptance Sampling SQCMahesh VaneNo ratings yet
- 6 ErrorAnalysisDocument9 pages6 ErrorAnalysisTonyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Data and Analysis - Notes 14Document9 pagesEngineering Data and Analysis - Notes 14Chou Xi MinNo ratings yet
- a78bde04-1efd-4ff1-9e48-b23104cd7c3b (1)Document10 pagesa78bde04-1efd-4ff1-9e48-b23104cd7c3b (1)veenahh314No ratings yet
- 2 Hypothesis Testing (Part 1)Document8 pages2 Hypothesis Testing (Part 1)Von Adrian Inociaan HernandezNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Sensitivity and Specificity in Relation To Two Types of Errors and Its Application in Medical ResearchDocument6 pagesThe Concept of Sensitivity and Specificity in Relation To Two Types of Errors and Its Application in Medical ResearchNurul FadliaNo ratings yet
- Math 140 Introductory Statistics: Types of ErrorDocument4 pagesMath 140 Introductory Statistics: Types of ErrorMichael Diptana Setiawan SutedjaNo ratings yet
- Testing HypothesisDocument14 pagesTesting HypothesisAbdul RafayNo ratings yet
- 8.5 One Tailed and Two Tailed TestsDocument2 pages8.5 One Tailed and Two Tailed TestsnithinNo ratings yet
- Business Research Methods: Prof - Radhika Kiran Kumar Indira Institute of Business ManagementDocument41 pagesBusiness Research Methods: Prof - Radhika Kiran Kumar Indira Institute of Business ManagementTanvi DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Unit 10-Experimental Physics - 1Document13 pagesUnit 10-Experimental Physics - 1PRABU VISHNUNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 2 Nihal RollNo-08Document2 pagesAssignment No. 2 Nihal RollNo-08krishna zanwarNo ratings yet
- Sample Size for Analytical Surveys, Using a Pretest-Posttest-Comparison-Group DesignFrom EverandSample Size for Analytical Surveys, Using a Pretest-Posttest-Comparison-Group DesignNo ratings yet
- IT 2 TQMDocument6 pagesIT 2 TQMUDayNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document1 pageProblem Set 2UDayNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document1 pageProblem Set 1UDayNo ratings yet
- PS5 (Semantic Web and Web Services) SolutionDocument3 pagesPS5 (Semantic Web and Web Services) SolutionUDayNo ratings yet
- Web Sementic It2Document6 pagesWeb Sementic It2UDayNo ratings yet
- Semantic Web Vision and TechnologiesDocument15 pagesSemantic Web Vision and TechnologiesUDayNo ratings yet
- StackDocument12 pagesStackUDayNo ratings yet
- Quick Revision Download C OOPs Slides Lec 1533 With AnnoDocument127 pagesQuick Revision Download C OOPs Slides Lec 1533 With AnnoUDayNo ratings yet
- Standard Template LibraryDocument18 pagesStandard Template LibraryUDayNo ratings yet
- Biology IT 1Document7 pagesBiology IT 1UDayNo ratings yet
- Quick Revision Download C Basics Slides Lec 114 With AnnoDocument267 pagesQuick Revision Download C Basics Slides Lec 114 With AnnoUDayNo ratings yet
- Biology TA 2Document3 pagesBiology TA 2UDayNo ratings yet
- IT 2 TQMDocument6 pagesIT 2 TQMUDayNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Technique: Subject Code: IMT-24Document7 pagesQuantitative Technique: Subject Code: IMT-24Asis LaskarNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Model Uncertainty of An Spt-Based Simplified Method For Reliability Analysis For Probability of LiquefactionDocument18 pagesEvaluating Model Uncertainty of An Spt-Based Simplified Method For Reliability Analysis For Probability of LiquefactionDeviprasad B SNo ratings yet
- mgt202 ForecastingDocument4 pagesmgt202 ForecastingKathleen MarcialNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Hypothesis TestingDocument118 pagesChapter 7 Hypothesis Testingadhit46100% (1)
- Josh Fagan Mentor: Dr. Arthur Charlesworth Department Mathematics and of Computer Science, University of Richmond, VA 23173Document1 pageJosh Fagan Mentor: Dr. Arthur Charlesworth Department Mathematics and of Computer Science, University of Richmond, VA 23173Anh TranNo ratings yet
- Math 403 Quiz 1 - Answer Key v1.0Document9 pagesMath 403 Quiz 1 - Answer Key v1.0Grace HolgadoNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Statistics For Business and Economics 8th Edition Newbold Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument48 pagesInstant Download PDF Statistics For Business and Economics 8th Edition Newbold Solutions Manual Full Chapterteczliforio100% (4)
- The Normal Distribution - IBDP Mathematics: Analysis and Approaches SL - KognityDocument8 pagesThe Normal Distribution - IBDP Mathematics: Analysis and Approaches SL - KognityShreya LukhwaniNo ratings yet
- Hossein Tavakoli: Research Method 2012 TehranDocument9 pagesHossein Tavakoli: Research Method 2012 TehranFaith FulNo ratings yet
- Ebook Discovering The Scientist Within Research Methods in Psychology 1St Edition Lewandowski Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument47 pagesEbook Discovering The Scientist Within Research Methods in Psychology 1St Edition Lewandowski Test Bank Full Chapter PDFrowanbridgetuls3100% (14)
- 05 Permutation PDFDocument22 pages05 Permutation PDFMarcelinus AlfasisuryaNo ratings yet
- Igcse Geography Alternative To Coursework NotesDocument6 pagesIgcse Geography Alternative To Coursework Notesafaydoter100% (2)
- Relation Between Math Self-Efficacy and Mathematics Achievement With Control of Math Attitude - Soleymani 2016Document4 pagesRelation Between Math Self-Efficacy and Mathematics Achievement With Control of Math Attitude - Soleymani 2016Mary KatogianniNo ratings yet
- Ucd Method PDFDocument24 pagesUcd Method PDFRonald GenNo ratings yet
- 6026-Article Text-16886-1-10-20201201Document12 pages6026-Article Text-16886-1-10-20201201Nuriel AguilarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document36 pagesChapter 6Amroz AfzalNo ratings yet
- BS 6-8Document60 pagesBS 6-8AnshumanNo ratings yet
- A Training Workshop On Statistical and Presentational System Software (SPSS) 18.0 WindowsDocument32 pagesA Training Workshop On Statistical and Presentational System Software (SPSS) 18.0 WindowsMuhammad haseebNo ratings yet
- True/False: Chapter 10: Determining How Costs BehaveDocument35 pagesTrue/False: Chapter 10: Determining How Costs BehaveKelvin John Ramos100% (1)
- Modelling Recurrent EventsDocument10 pagesModelling Recurrent Eventsmasudul9islamNo ratings yet
- Exercise ProbabilityDocument5 pagesExercise ProbabilityAhmad MalakNo ratings yet
- Statistical Hypothesis TestingDocument21 pagesStatistical Hypothesis TestingAjit KarnikNo ratings yet
- MATH 524 Nonparametric StatisticsDocument16 pagesMATH 524 Nonparametric StatisticsPatrick LeungNo ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Business Analytics 4th Edition by Jeffrey D. Camm All ChapterDocument43 pagesFull Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Business Analytics 4th Edition by Jeffrey D. Camm All Chapterkhojeconxa100% (4)
- 1 SMDocument8 pages1 SMKhautsarNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity 2.1-2.5Document5 pagesLearning Activity 2.1-2.5ADRIAN FRAGATANo ratings yet
- Minitab-Brochure ENDocument7 pagesMinitab-Brochure ENEmmanuel AladroNo ratings yet