Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cheat ECG-2
Cheat ECG-2
Uploaded by
Neil Emman BotardoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- NUR3111 Post-Lecture QuizDocument28 pagesNUR3111 Post-Lecture QuizliNo ratings yet
- Defibrillation ChecklistDocument4 pagesDefibrillation ChecklistCzarina100% (1)
- EKG Study GuideDocument45 pagesEKG Study GuideBrawner100% (7)
- ECG SyllabusDocument27 pagesECG SyllabusSue HuangNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocument60 pagesCardiac ArrhythmiasMelissa Monique Peart-YatesNo ratings yet
- Basics of EcgDocument58 pagesBasics of Ecgbtalera100% (4)
- Heart Conduction 081627Document11 pagesHeart Conduction 081627chiemerieagana3No ratings yet
- Int9 ArrhythemiaDocument21 pagesInt9 ArrhythemiaOsama AlhumisiNo ratings yet
- Supraventricular TachycardiaDocument5 pagesSupraventricular TachycardialjubodragNo ratings yet
- 12 - Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocument12 pages12 - Cardiac ArrhythmiasYassine LaiymaniNo ratings yet
- 12 - Cardiac Arrhythmias - 0Document12 pages12 - Cardiac Arrhythmias - 0Ehtiram HuseynovNo ratings yet
- DefibrillatorDocument8 pagesDefibrillatorJisha JanardhanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac PeacemakerDocument19 pagesCardiac Peacemakerrana.said2018No ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram: Electrocardiogram EKG Heart Heart's Electrical Activity DiagnosisDocument38 pagesElectrocardiogram: Electrocardiogram EKG Heart Heart's Electrical Activity DiagnosislorhenzsoNo ratings yet
- Er Rotation - Ecg & BlsDocument39 pagesEr Rotation - Ecg & BlsJEDIDIAH ALOMBRONo ratings yet
- Pacemaker Learning Package: Paula Nekic CNE Liverpool Hospital ICU January 2016Document46 pagesPacemaker Learning Package: Paula Nekic CNE Liverpool Hospital ICU January 2016Deepak BhatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 125. CardioversionDocument21 pagesChapter 125. CardioversionZoe VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Pacemakers, Heart BlocksDocument31 pagesPacemakers, Heart BlockscindybevNo ratings yet
- ElectrocardiographyDocument11 pagesElectrocardiographysohan.ghosh23-25No ratings yet
- HEART SimplifiedDocument94 pagesHEART Simplifiedcloud kumoishNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmias - : Normal HeartbeatDocument4 pagesArrhythmias - : Normal HeartbeatToni Baskoro KristantoNo ratings yet
- DefibrillatorDocument10 pagesDefibrillatorMakhanVermaNo ratings yet
- PACEMAKERDocument5 pagesPACEMAKERPoonam ThakurNo ratings yet
- DefibrillatorsDocument54 pagesDefibrillatorsAli Al-AhmedyNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document53 pagesElectrocardiogram (ECG)eric100% (1)
- 6heart Sound PacemakerDocument28 pages6heart Sound PacemakerJack OneNo ratings yet
- Conduction SystemDocument2 pagesConduction SystemMalik Asif HussainNo ratings yet
- 7 DevicesDocument21 pages7 DevicesNazifa Tahsin014No ratings yet
- Dysrhythmias: Normal Electrical ActivityDocument32 pagesDysrhythmias: Normal Electrical ActivityLarisse de LeonNo ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument11 pagesECG InterpretationAndrea AndradaNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Dysrhythmias and Conduction Problems DysrhythmiasDocument15 pagesManagement of Patients With Dysrhythmias and Conduction Problems DysrhythmiasRoyce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation NursingDocument14 pagesEKG Interpretation NursingTanya ViarsNo ratings yet
- SVTDocument8 pagesSVTJulieNo ratings yet
- Ecg ProcedureDocument5 pagesEcg ProcedureLungu AdrianNo ratings yet
- Estimulação Transcutânea Não InvasivaDocument10 pagesEstimulação Transcutânea Não InvasivaMarcos AcioliNo ratings yet
- ECG Monitor and RhythmDocument9 pagesECG Monitor and Rhythmboxed juiceNo ratings yet
- Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) :: Name: Vincent Joshua B. Pangilinan BSN - IvDocument13 pagesSupraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) :: Name: Vincent Joshua B. Pangilinan BSN - Ivann aquinoNo ratings yet
- Defibrillation and CardioversionDocument28 pagesDefibrillation and CardioversionadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- ECG BasicsDocument15 pagesECG Basicsrohitmeena2889No ratings yet
- What Is A Defibrillator?Document8 pagesWhat Is A Defibrillator?Rajib RajuNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrhythmia 171209212142 2Document74 pagesCardiac Arrhythmia 171209212142 2Gunel Sadiqova100% (1)
- Supraventricular TachycardiaDocument2 pagesSupraventricular TachycardiaDevinder SinghNo ratings yet
- DefibrillatorDocument39 pagesDefibrillatorAhmad HassanNo ratings yet
- SPDX Electrocardiography-EcgDocument6 pagesSPDX Electrocardiography-Ecgdumppotato24No ratings yet
- Ventricular RhythmDocument3 pagesVentricular RhythmChristine StotomasNo ratings yet
- Aritmii EngDocument90 pagesAritmii EngAnna HaritonencoNo ratings yet
- Supraventricular TachycardiaDocument9 pagesSupraventricular TachycardiaclubsanatateNo ratings yet
- Defibrillation and Electrical CardioversionDocument27 pagesDefibrillation and Electrical CardioversionYui Hirasawa100% (1)
- 8C - Antiarrythmic DrugsDocument76 pages8C - Antiarrythmic DrugsShahpoor Ahmad ShirzadaNo ratings yet
- Basic ECG InterpretationDocument7 pagesBasic ECG InterpretationAprilJaedeeSanAgustinNo ratings yet
- Case Study On PacemakersDocument6 pagesCase Study On PacemakersBalamuruganNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Material 4.3 Cardiac Rhythm Disorders-2Document14 pagesSupplementary Material 4.3 Cardiac Rhythm Disorders-2Andrea Love PalomoNo ratings yet
- DC ShockDocument8 pagesDC Shockرافت العواضيNo ratings yet
- PMCC PF Support PermanentPacemakersDocument10 pagesPMCC PF Support PermanentPacemakersMonica TrifitrianaNo ratings yet
- Ecg 2Document38 pagesEcg 2noorazad1847No ratings yet
- Cardiac DysrythmiasDocument190 pagesCardiac DysrythmiasKoRnflakes100% (4)
- Catheter Ablation For AFDocument12 pagesCatheter Ablation For AFPeny Ruth Jessica DamanikNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Pacing For The SurgeonsDocument46 pagesCardiac Pacing For The SurgeonsRezwanul Hoque BulbulNo ratings yet
- ECG: Is A Recording of Electrical Activity of Heart Conducted Thru Ions in Body To SurfaceDocument24 pagesECG: Is A Recording of Electrical Activity of Heart Conducted Thru Ions in Body To Surfaceveenadivyakish100% (1)
- Indications: PurposeDocument13 pagesIndications: PurposeIRA ODETTE GATUSNo ratings yet
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideFrom EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- Clarificatory QDocument36 pagesClarificatory QNeil Emman BotardoNo ratings yet
- Clarificatory QDocument35 pagesClarificatory QNeil Emman BotardoNo ratings yet
- Cheat ECGDocument3 pagesCheat ECGNeil Emman BotardoNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument3 pagesUntitled DocumentNeil Emman BotardoNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in The Treatment of ArrhythmiasDocument37 pagesDrugs Used in The Treatment of ArrhythmiasChipego ChiyaamaNo ratings yet
- Post Operative HypotensionDocument7 pagesPost Operative HypotensionbbyesNo ratings yet
- Ekg Guidelines PDFDocument7 pagesEkg Guidelines PDFd.ramadhan100% (1)
- Common Terminology Criteria For Adverse Events Following Chemotherapy or Biological Antineoplastic Therapy in Dogs and Cats. VCOG. 2011Document30 pagesCommon Terminology Criteria For Adverse Events Following Chemotherapy or Biological Antineoplastic Therapy in Dogs and Cats. VCOG. 2011Mario GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Atrial-Rhythm 230518 191520-1Document2 pagesAtrial-Rhythm 230518 191520-1Maxinne GorospeNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmia Pharmacology MindmapDocument1 pageArrhythmia Pharmacology MindmapTesnikolaNo ratings yet
- ArrhythmiaDocument55 pagesArrhythmiaDonjeta AbaziNo ratings yet
- AACN Essentials of Progressive Care Nursing, Third Edition (Chulay, AACN Essentials of Progressive Care Nursing) 3rd Edition, (Ebook PDFDocument54 pagesAACN Essentials of Progressive Care Nursing, Third Edition (Chulay, AACN Essentials of Progressive Care Nursing) 3rd Edition, (Ebook PDFdoraziuntil68100% (10)
- Ecg Kiss 2022 HandoutDocument3 pagesEcg Kiss 2022 HandoutCiara EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For "DYSRHYTHMIAS"Document12 pagesNursing Care Plan For "DYSRHYTHMIAS"jhonroks79% (14)
- Drug ChartDocument40 pagesDrug ChartshabeebakpNo ratings yet
- ACLS AlgorithmsDocument4 pagesACLS Algorithmsmonickams100% (1)
- SeminorDocument6 pagesSeminorsherjin tintuNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology On ArrhythmiaDocument34 pagesPathophysiology On ArrhythmiaYhr Yh100% (1)
- Genxraver Girl Interrupted Usmle Step 2 Notes PDFDocument259 pagesGenxraver Girl Interrupted Usmle Step 2 Notes PDFughbuzzoffNo ratings yet
- FREE 2021 ACLS Study Guide - ACLS Made Easy!Document32 pagesFREE 2021 ACLS Study Guide - ACLS Made Easy!Alen ArguellesNo ratings yet
- Windkessel Model 1Document13 pagesWindkessel Model 1Emmanuel PrahNo ratings yet
- Sick Sinus Syndrom PDFDocument8 pagesSick Sinus Syndrom PDFSigit PratamaNo ratings yet
- Almostadoctor - co.Uk-Summary of ECG AbnormalitiesDocument8 pagesAlmostadoctor - co.Uk-Summary of ECG AbnormalitiesAnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tachycardia Complicated by Bradycardia Then Another Form of TachycardiaDocument7 pagesTachycardia Complicated by Bradycardia Then Another Form of TachycardiaLam Sin WingNo ratings yet
- Kuwait Pediatric GuideLinesDocument124 pagesKuwait Pediatric GuideLinesemicurudimov100% (1)
- DC ShockDocument8 pagesDC Shockرافت العواضيNo ratings yet
- Antidysrhythmic Drugs: Dr. SanoozDocument104 pagesAntidysrhythmic Drugs: Dr. SanoozsanoozarmNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrhythmias, Mechanisms of ArrhythmiasDocument74 pagesCardiac Arrhythmias, Mechanisms of Arrhythmiasyasahswi91No ratings yet
- 118 Skills Lab-Week 2-ECG TakingDocument8 pages118 Skills Lab-Week 2-ECG TakingKeisha BartolataNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Considerations in Chronic Lung Disease 2020Document276 pagesCardiac Considerations in Chronic Lung Disease 2020Dani CapiNo ratings yet
- Cara Membaca EKG Lengkap PAluDocument214 pagesCara Membaca EKG Lengkap PAluGiriNo ratings yet
- Ecg in DogsDocument107 pagesEcg in DogsPLABITA GOSWAMI100% (2)
- Albert Leon WaldoDocument69 pagesAlbert Leon WaldoViktor KaratanevNo ratings yet
Cheat ECG-2
Cheat ECG-2
Uploaded by
Neil Emman BotardoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cheat ECG-2
Cheat ECG-2
Uploaded by
Neil Emman BotardoCopyright:
Available Formats
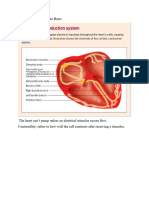
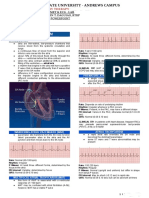
Vagal maneuver Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) refers to a cardiac
techniques used to increase vagal parasympathetic tone in an rhythm greater than 100 beats per minute, which originates
attempt to diagnose and treat various arrhythmias. above the bundle of His. SVT is characterized by rapid,
narrow (less than 0.12 seconds wide) QRS complexes.
Common vagal maneuvers include carotid sinus massage
(CSM), Valsalva maneuver (VM), and diving reflex. SVT is usually caused by the repetitive “re-entry“ of the
electrical impulse proximally, instead of propagating distally
transiently increase the arterial pressure in the carotid sinuses through the cardiac conduction system, due to blockages in the
and aortic arch. This action triggers the baroreceptor reflex, heart’s electrical conduction system.
which results in increased parasympathetic output to the heart
via the vagus nerve (cranial nerve X). Any tachycardic rhythm that does not originate in the
ventricles is referred to as SVT. This includes sinus
location of the carotid sinus is at the bifurcation of the internal tachycardia, junctional tachycardia, reentrant tachycardias,
and external carotid artery from the common carotid artery. multiple atrial tachycardia (MAT), atrial fibrillation, and atrial
The sinus contains baroceptors that sense changes in blood flutter.
pressure.
During the procedure
Within the aortic arch, there are baroreceptors that sense
changes in aortic arterial pressure. These receptors send
afferent signals to the NTS via the vagus nerve. To avoid inducing cardiac arrest in a patient with a pulse,
synchronized cardioversion is performed instead of defibrillation
The result of the increased frequency of afferent signals due to when a patient is in an SVT with a pulse but is considered unstable
increased arterial pressure is the stimulation of vagal nuclei in according to the definition above. To perform synchronized
the medulla. These nuclei send efferent parasympathetic cardioversion, the defibrillator is placed into the “synchronize”
signals down the right and left vagus nerves to the heart. mode by pressing the appropriate button on the machine. This
causes the monitor to track the R wave of each QRS complex that
Within the heart, the right vagus nerve serves to stimulate the goes by. A synchronizing marker will appear above each QRS
sinoatrial (SA) node, the pacemaker of the healthy heart, in the complex, indicating that the synchronize feature is active.
right atrium; this causes slowed electrical activity within the
The appropriate energy level is then selected, and the
SA node. The left vagus nerve mostly innervates
discharge/shock button is pressed and held. The defibrillator does
atrioventricular (AV) node, which slows conduction between
not release the shock immediately. Instead, it waits for the next
the atria and the ventricles.
R-wave to appear and delivers the shock at the time of the R-wave.
This allows the shock to be provided safely away from the T wave,
The end product of vagal stimulation is a decrease in the speed
avoiding the R-on-T phenomenon.
and frequency of electrical impulses in the heart, which could
ultimately slow or terminate a tachydysrhythmia. The recommended energy levels used to perform synchronized
cardioversion vary from 50 to 200 joules. Recalling the specific
Diving Reflex –It gets triggered by breath-holding and cold energy level for a particular sub-type of unstable tachycardia is
water stimulus to the face. The prevailing theory is cold water difficult, especially in an emergent situation. The safest and easiest
exposure triggers the reflex by initiating afferent impulses recommendation is to start at the lowest energy level (50 joules),
from the trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve V), the predominant and if the shock is unsuccessful, double the amount of energy used.
sensory nerve of the face. The impulses then stimulate vagal In a refractory case, you will be at 200 joules after just three
nuclei in the brain, eventually resulting in the slowing of AV shocks.
nodal conduction.
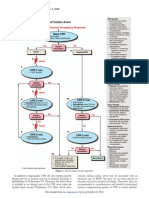
Cardioversion When a patient is defibrillated, the energy is released through the
paddles or hands-free pads immediately when the defibrillation
similar to electrical defibrillation in that a transthoracic button/s are pressed. The shock is delivered at whatever point the
electrical current is applied to the anterior chest to terminate a cardiac cycle happens to be in at that moment. If an electrical
life-threatening or unstable tachycardic arrhythmia. shock is provided during the relative refractory period
(corresponding to the latter part of the T wave), it is possible to
synchronized cardioversion is performed on patients that still induce VF (the so-called “R-on-T Phenomenon”). This would
have a pulse but are hemodynamically unstable. It is used to result in a patient who originally had a pulse being put into cardiac
treat both hemodynamically unstable ventricular and arrest.
supraventricular rhythms.
Cardioversion is usually done in the hospital. A care
placing a pair of manual paddles on the chest or through the provider will insert an IV into your forearm or hand and
application of adhesive “hands-free” pads.[5] Most current
give you medications called a sedative to help you sleep
defibrillators utilize a biphasic waveform that allows for a
lower energy level to be used to achieve effective cardioversion. during the procedure.
Because of their greater ability to terminate ventricular
dysrhythmias, defibrillators utilizing biphasic waveforms are
preferred to those utilizing the older, monophasic waveform. If you're having chemical cardioversion, you'll receive
medications through the IV to help restore your heart
The most common cause of sudden cardiac arrest in adults is
rhythm.
pulseless ventricular tachycardia (VT) or ventricular
fibrillation (VF). VT can also occur in the presence of a pulse;
often, it is the precursor to VF. VT is characterized by rapid,
If you're having electrical cardioversion, a care provider
wide (greater than 0.12 seconds) QRS complexes.
places several large patches (called sensors, or
electrodes) on your chest and sometimes your back.
Wires connect the sensors to a cardioversion machine. Transcutaneous cardiac pacing
The machine records your heart rhythm. It delivers
quick, low-energy shocks to the heart to restore a
regular heart rhythm. Attachment
Electric cardioversion usually takes only a few minutes
Before applying the patches, the skin site should be
to complete. cleansed with soap and water; alcohol and other
flammable liquids should be avoided. In patients with
excessive body hair, trimming rather than shaving is
After the procedure preferred to avoid tiny skin nicks that can increase pain
and skin irritation.
You'll spend an hour or so in a recovery room being
closely monitored for potential complications. Do cell phones interfere with pacemakers or ICDs?
Cell phones available in the U.S. (less than 3 watts) do
not appear to interfere with or damage pacemakers.
If electric cardioversion was a scheduled procedure, you
However, it's best to avoid keeping your cell phone in
can usually go home the same day. You'll need someone your breast pocket on the side of the device. And, use
to drive you home. After cardioversion, your ability to the phone on the opposite ear, as well.
make decisions may be affected for several hours.
Do pacemakers or ICDs need to be adjusted periodically?
Blood-thinning medications are usually taken for several Some devices may need to be adjusted if your medical
weeks after cardioversion to prevent clots from forming. condition or lifestyle changes. Most adjustments are
done using a device called a programmer. This is a
You'll need blood thinners even if no clots were found in
specialized computer that communicates with the
your heart before the procedure. pacemaker or ICD using magnetic signals via a "wand"
or loop placed over your chest where the device is
implanted. Your doctor will instruct you about the
Results schedule of follow-up visits you should keep based on
your condition and type of device. You may have an
assessment using a monitor and telephone line or an
For most people, cardioversion can quickly restore a
internet connection on a periodic basis. Most current
regular heartbeat. Some people need additional ICDs and some pacemakers can now be followed
procedures to keep a regular heart rhythm. remotely. This means the device can wirelessly transmit
data to your doctor.
Your health care provider may suggest lifestyle changes
to improve your heart health and prevent or treat When replacing a pacemaker or ICD, are the leads also replaced?
conditions — such as high blood pressure — that can If the original leads are working properly, in most cases,
cause irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias). they will be left in place and reattached to the new
device.
Try these heart-healthy lifestyle changes:
When do I have to replace my pacemaker or ICD?
Most device batteries will last at least 5 to 7 years,
● Limit or avoid alcohol depending on use. After that time, the battery or pulse
● Use less salt, which can help lower generator will need to be replaced. Replacing a
blood pressure pacemaker generator may be done on an outpatient
● Choose whole grains, lean meat, low-fat basis or may include an overnight stay in the hospital.
dairy, and fruits and vegetables
● Limit sugar and saturated fat and trans
Can I travel with my pacemaker or ICD?
fats
Yes, you can travel by air with your device and drive a
● Increase physical activity
car, if cleared by your doctor. Airport security detectors
● Maintain a healthy weight are generally safe, but let airport security staff know you
● Quit smoking have a pacemaker/ICD and discuss the appropriate
● Try to limit or manage stress and anger screening procedure. If selected to be screened by
handheld wand, politely remind the screener that these
Pacemaker wands should not be held over the device area for more
than a few seconds. You should be sure to always have
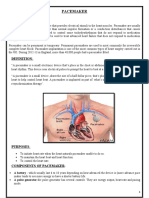
artificial electrical pulse generators that can be temporary or your identification card with you wherever you go. Some
permanent. They frequently emit a pulse lasting between 0.5 people with ICDs may not be allowed to drive unless
and 25 milliseconds with a voltage between 0.1 to 15 volts and cleared by their doctor. For your safety, and the safety of
at a frequency up to 300 per minute. others, your doctor may recommend that you do not
drive for 6 months after your ICD is implanted, or after
an ICD discharge. The life threatening heart arrhythmias
that these devices treat can cause you to lose
consciousness, which is dangerous if your are driving.
Can I exercise with a pacemaker?
You may be able to exercise with your pacemaker or
ICD, but check with your doctor first to make sure the
form of exercise you do will not damage the device.
Will I feel the pacemaker or ICD?
At first, you may feel the weight of the device in your
chest. But, over time, most people get used to it. The
device generator is very small, about the size of two
small silver dollars stacked on top of each other, and
weighs about an ounce or less, depending on the make
and model of the device. ICDs are typically slightly
larger than a pacemaker. If the device feels loose or
wiggles in the pocket under the skin, report this to your
healthcare provider. Excessive movement can cause a
detachment of the generator from the wires, or the wires
from the heart muscle, and the device will not work
properly. If the ICD sends a shock to the heart or "fires,"
you will feel this as a jolt or kick in the chest.
Sometimes the placement of the ICD wires can stimulate
nerves that cause the diaphragm to twitch of the
diaphragm and nonstop hiccups or twitching of the
chest muscles. If this happens, call your healthcare
provider.
Can I have an MRI with my pacemaker or ICD?
When you have a pacemaker implanted, stay away from
devices with large magnets or magnetic fields that can
be created from motors of cars or boats. An MRI is a
diagnostic imaging tool used to take images of your
body using magnets. Some pacemaker and ICD devices
are approved to have an MRI but always talk with your
provider before having this test to make sure it is safe
for you. Magnetic fields can be created by other
machines which could affect the normal function of your
device. Avoid high-voltage radar machines, such as
radio or T.V. transmitters, electric arc welders,
high-tension wires, radar installations, or smelting
furnaces.
You might also like
- NUR3111 Post-Lecture QuizDocument28 pagesNUR3111 Post-Lecture QuizliNo ratings yet
- Defibrillation ChecklistDocument4 pagesDefibrillation ChecklistCzarina100% (1)
- EKG Study GuideDocument45 pagesEKG Study GuideBrawner100% (7)
- ECG SyllabusDocument27 pagesECG SyllabusSue HuangNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocument60 pagesCardiac ArrhythmiasMelissa Monique Peart-YatesNo ratings yet
- Basics of EcgDocument58 pagesBasics of Ecgbtalera100% (4)
- Heart Conduction 081627Document11 pagesHeart Conduction 081627chiemerieagana3No ratings yet
- Int9 ArrhythemiaDocument21 pagesInt9 ArrhythemiaOsama AlhumisiNo ratings yet
- Supraventricular TachycardiaDocument5 pagesSupraventricular TachycardialjubodragNo ratings yet
- 12 - Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocument12 pages12 - Cardiac ArrhythmiasYassine LaiymaniNo ratings yet
- 12 - Cardiac Arrhythmias - 0Document12 pages12 - Cardiac Arrhythmias - 0Ehtiram HuseynovNo ratings yet
- DefibrillatorDocument8 pagesDefibrillatorJisha JanardhanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac PeacemakerDocument19 pagesCardiac Peacemakerrana.said2018No ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram: Electrocardiogram EKG Heart Heart's Electrical Activity DiagnosisDocument38 pagesElectrocardiogram: Electrocardiogram EKG Heart Heart's Electrical Activity DiagnosislorhenzsoNo ratings yet
- Er Rotation - Ecg & BlsDocument39 pagesEr Rotation - Ecg & BlsJEDIDIAH ALOMBRONo ratings yet
- Pacemaker Learning Package: Paula Nekic CNE Liverpool Hospital ICU January 2016Document46 pagesPacemaker Learning Package: Paula Nekic CNE Liverpool Hospital ICU January 2016Deepak BhatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 125. CardioversionDocument21 pagesChapter 125. CardioversionZoe VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Pacemakers, Heart BlocksDocument31 pagesPacemakers, Heart BlockscindybevNo ratings yet
- ElectrocardiographyDocument11 pagesElectrocardiographysohan.ghosh23-25No ratings yet
- HEART SimplifiedDocument94 pagesHEART Simplifiedcloud kumoishNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmias - : Normal HeartbeatDocument4 pagesArrhythmias - : Normal HeartbeatToni Baskoro KristantoNo ratings yet
- DefibrillatorDocument10 pagesDefibrillatorMakhanVermaNo ratings yet
- PACEMAKERDocument5 pagesPACEMAKERPoonam ThakurNo ratings yet
- DefibrillatorsDocument54 pagesDefibrillatorsAli Al-AhmedyNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document53 pagesElectrocardiogram (ECG)eric100% (1)
- 6heart Sound PacemakerDocument28 pages6heart Sound PacemakerJack OneNo ratings yet
- Conduction SystemDocument2 pagesConduction SystemMalik Asif HussainNo ratings yet
- 7 DevicesDocument21 pages7 DevicesNazifa Tahsin014No ratings yet
- Dysrhythmias: Normal Electrical ActivityDocument32 pagesDysrhythmias: Normal Electrical ActivityLarisse de LeonNo ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument11 pagesECG InterpretationAndrea AndradaNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Dysrhythmias and Conduction Problems DysrhythmiasDocument15 pagesManagement of Patients With Dysrhythmias and Conduction Problems DysrhythmiasRoyce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation NursingDocument14 pagesEKG Interpretation NursingTanya ViarsNo ratings yet
- SVTDocument8 pagesSVTJulieNo ratings yet
- Ecg ProcedureDocument5 pagesEcg ProcedureLungu AdrianNo ratings yet
- Estimulação Transcutânea Não InvasivaDocument10 pagesEstimulação Transcutânea Não InvasivaMarcos AcioliNo ratings yet
- ECG Monitor and RhythmDocument9 pagesECG Monitor and Rhythmboxed juiceNo ratings yet
- Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) :: Name: Vincent Joshua B. Pangilinan BSN - IvDocument13 pagesSupraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) :: Name: Vincent Joshua B. Pangilinan BSN - Ivann aquinoNo ratings yet
- Defibrillation and CardioversionDocument28 pagesDefibrillation and CardioversionadnanreshunNo ratings yet
- ECG BasicsDocument15 pagesECG Basicsrohitmeena2889No ratings yet
- What Is A Defibrillator?Document8 pagesWhat Is A Defibrillator?Rajib RajuNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrhythmia 171209212142 2Document74 pagesCardiac Arrhythmia 171209212142 2Gunel Sadiqova100% (1)
- Supraventricular TachycardiaDocument2 pagesSupraventricular TachycardiaDevinder SinghNo ratings yet
- DefibrillatorDocument39 pagesDefibrillatorAhmad HassanNo ratings yet
- SPDX Electrocardiography-EcgDocument6 pagesSPDX Electrocardiography-Ecgdumppotato24No ratings yet
- Ventricular RhythmDocument3 pagesVentricular RhythmChristine StotomasNo ratings yet
- Aritmii EngDocument90 pagesAritmii EngAnna HaritonencoNo ratings yet
- Supraventricular TachycardiaDocument9 pagesSupraventricular TachycardiaclubsanatateNo ratings yet
- Defibrillation and Electrical CardioversionDocument27 pagesDefibrillation and Electrical CardioversionYui Hirasawa100% (1)
- 8C - Antiarrythmic DrugsDocument76 pages8C - Antiarrythmic DrugsShahpoor Ahmad ShirzadaNo ratings yet
- Basic ECG InterpretationDocument7 pagesBasic ECG InterpretationAprilJaedeeSanAgustinNo ratings yet
- Case Study On PacemakersDocument6 pagesCase Study On PacemakersBalamuruganNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Material 4.3 Cardiac Rhythm Disorders-2Document14 pagesSupplementary Material 4.3 Cardiac Rhythm Disorders-2Andrea Love PalomoNo ratings yet
- DC ShockDocument8 pagesDC Shockرافت العواضيNo ratings yet
- PMCC PF Support PermanentPacemakersDocument10 pagesPMCC PF Support PermanentPacemakersMonica TrifitrianaNo ratings yet
- Ecg 2Document38 pagesEcg 2noorazad1847No ratings yet
- Cardiac DysrythmiasDocument190 pagesCardiac DysrythmiasKoRnflakes100% (4)
- Catheter Ablation For AFDocument12 pagesCatheter Ablation For AFPeny Ruth Jessica DamanikNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Pacing For The SurgeonsDocument46 pagesCardiac Pacing For The SurgeonsRezwanul Hoque BulbulNo ratings yet
- ECG: Is A Recording of Electrical Activity of Heart Conducted Thru Ions in Body To SurfaceDocument24 pagesECG: Is A Recording of Electrical Activity of Heart Conducted Thru Ions in Body To Surfaceveenadivyakish100% (1)
- Indications: PurposeDocument13 pagesIndications: PurposeIRA ODETTE GATUSNo ratings yet
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideFrom EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- Clarificatory QDocument36 pagesClarificatory QNeil Emman BotardoNo ratings yet
- Clarificatory QDocument35 pagesClarificatory QNeil Emman BotardoNo ratings yet
- Cheat ECGDocument3 pagesCheat ECGNeil Emman BotardoNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument3 pagesUntitled DocumentNeil Emman BotardoNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in The Treatment of ArrhythmiasDocument37 pagesDrugs Used in The Treatment of ArrhythmiasChipego ChiyaamaNo ratings yet
- Post Operative HypotensionDocument7 pagesPost Operative HypotensionbbyesNo ratings yet
- Ekg Guidelines PDFDocument7 pagesEkg Guidelines PDFd.ramadhan100% (1)
- Common Terminology Criteria For Adverse Events Following Chemotherapy or Biological Antineoplastic Therapy in Dogs and Cats. VCOG. 2011Document30 pagesCommon Terminology Criteria For Adverse Events Following Chemotherapy or Biological Antineoplastic Therapy in Dogs and Cats. VCOG. 2011Mario GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Atrial-Rhythm 230518 191520-1Document2 pagesAtrial-Rhythm 230518 191520-1Maxinne GorospeNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmia Pharmacology MindmapDocument1 pageArrhythmia Pharmacology MindmapTesnikolaNo ratings yet
- ArrhythmiaDocument55 pagesArrhythmiaDonjeta AbaziNo ratings yet
- AACN Essentials of Progressive Care Nursing, Third Edition (Chulay, AACN Essentials of Progressive Care Nursing) 3rd Edition, (Ebook PDFDocument54 pagesAACN Essentials of Progressive Care Nursing, Third Edition (Chulay, AACN Essentials of Progressive Care Nursing) 3rd Edition, (Ebook PDFdoraziuntil68100% (10)
- Ecg Kiss 2022 HandoutDocument3 pagesEcg Kiss 2022 HandoutCiara EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For "DYSRHYTHMIAS"Document12 pagesNursing Care Plan For "DYSRHYTHMIAS"jhonroks79% (14)
- Drug ChartDocument40 pagesDrug ChartshabeebakpNo ratings yet
- ACLS AlgorithmsDocument4 pagesACLS Algorithmsmonickams100% (1)
- SeminorDocument6 pagesSeminorsherjin tintuNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology On ArrhythmiaDocument34 pagesPathophysiology On ArrhythmiaYhr Yh100% (1)
- Genxraver Girl Interrupted Usmle Step 2 Notes PDFDocument259 pagesGenxraver Girl Interrupted Usmle Step 2 Notes PDFughbuzzoffNo ratings yet
- FREE 2021 ACLS Study Guide - ACLS Made Easy!Document32 pagesFREE 2021 ACLS Study Guide - ACLS Made Easy!Alen ArguellesNo ratings yet
- Windkessel Model 1Document13 pagesWindkessel Model 1Emmanuel PrahNo ratings yet
- Sick Sinus Syndrom PDFDocument8 pagesSick Sinus Syndrom PDFSigit PratamaNo ratings yet
- Almostadoctor - co.Uk-Summary of ECG AbnormalitiesDocument8 pagesAlmostadoctor - co.Uk-Summary of ECG AbnormalitiesAnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tachycardia Complicated by Bradycardia Then Another Form of TachycardiaDocument7 pagesTachycardia Complicated by Bradycardia Then Another Form of TachycardiaLam Sin WingNo ratings yet
- Kuwait Pediatric GuideLinesDocument124 pagesKuwait Pediatric GuideLinesemicurudimov100% (1)
- DC ShockDocument8 pagesDC Shockرافت العواضيNo ratings yet
- Antidysrhythmic Drugs: Dr. SanoozDocument104 pagesAntidysrhythmic Drugs: Dr. SanoozsanoozarmNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrhythmias, Mechanisms of ArrhythmiasDocument74 pagesCardiac Arrhythmias, Mechanisms of Arrhythmiasyasahswi91No ratings yet
- 118 Skills Lab-Week 2-ECG TakingDocument8 pages118 Skills Lab-Week 2-ECG TakingKeisha BartolataNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Considerations in Chronic Lung Disease 2020Document276 pagesCardiac Considerations in Chronic Lung Disease 2020Dani CapiNo ratings yet
- Cara Membaca EKG Lengkap PAluDocument214 pagesCara Membaca EKG Lengkap PAluGiriNo ratings yet
- Ecg in DogsDocument107 pagesEcg in DogsPLABITA GOSWAMI100% (2)
- Albert Leon WaldoDocument69 pagesAlbert Leon WaldoViktor KaratanevNo ratings yet