Professional Documents
Culture Documents
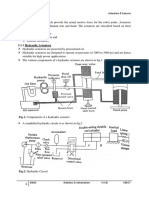
Special Electrical Machines Unit 1
Special Electrical Machines Unit 1
Uploaded by
ilenjeeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- EE1001 Special Electrical Machines Two Mark Questions and AnswersDocument23 pagesEE1001 Special Electrical Machines Two Mark Questions and Answersmohamedfahims64% (11)
- 2 Marks Special Machines.Document26 pages2 Marks Special Machines.Samraj MahalingamNo ratings yet
- Special Electrical MachinesDocument5 pagesSpecial Electrical MachinesEswaran0% (1)
- EE2403 Special Electrical MachinesDocument19 pagesEE2403 Special Electrical MachinesvasanthavananNo ratings yet
- SPECIAL ELECTRICAL MACHINES - Questions & AnswersDocument38 pagesSPECIAL ELECTRICAL MACHINES - Questions & AnswersMuhammad JunaidNo ratings yet
- Advant and Disadvantages of Induction MotorDocument2 pagesAdvant and Disadvantages of Induction MotorAnonymous iqwlnYPRGTNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor AdvantagesDocument2 pagesInduction Motor AdvantagesAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1-Synchronous Reluctance MotorDocument14 pagesUNIT 1-Synchronous Reluctance MotornirmalpseNo ratings yet
- What Are The Basic Parts of An Induction Motor?Document6 pagesWhat Are The Basic Parts of An Induction Motor?purbasha kanchan ghoshNo ratings yet
- Ee2403 (Special Electrical Machines Question BankDocument20 pagesEe2403 (Special Electrical Machines Question Bankkrish_skumar6302No ratings yet
- Special - Electrical - Machines QBDocument25 pagesSpecial - Electrical - Machines QBVel MuruganNo ratings yet
- Ac MotorDocument44 pagesAc MotorAbra AbraNo ratings yet
- Low Voltage Non Motor Industrial Feeder Calculating Ampacity Ratings of Feeders Conductors Factors Affecting Ampacity RatingsDocument3 pagesLow Voltage Non Motor Industrial Feeder Calculating Ampacity Ratings of Feeders Conductors Factors Affecting Ampacity RatingsRance FloresNo ratings yet
- Hamadaseceppt 180422122103Document11 pagesHamadaseceppt 180422122103sUmangal GHoshNo ratings yet
- Ev Engine ResearchDocument15 pagesEv Engine ResearchAnshul YadavNo ratings yet
- Electrical Science-2: Term Paper of Ele102Document7 pagesElectrical Science-2: Term Paper of Ele102shailesh singhNo ratings yet
- SEM 2 Marks With AnsDocument15 pagesSEM 2 Marks With AnsRevathy KannanNo ratings yet
- Electtrical Motors: Figures 4.1Document11 pagesElecttrical Motors: Figures 4.1Cholan PillaiNo ratings yet
- Universal Motor A Simple Guide To Construction Types and WorkingDocument7 pagesUniversal Motor A Simple Guide To Construction Types and Workingmireyo1488No ratings yet
- A-Complete-Guide-to-Repulsion-Motor (Use For Repulsion Motor Article)Document5 pagesA-Complete-Guide-to-Repulsion-Motor (Use For Repulsion Motor Article)vishalNo ratings yet
- Direct Current (DC) Motors: OperationDocument6 pagesDirect Current (DC) Motors: OperationckyprianouNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document33 pagesUnit 2kssrao13No ratings yet
- Task 4Document33 pagesTask 4Vishnu SasidharanNo ratings yet
- Motor Start TheoryDocument30 pagesMotor Start TheoryMaskbassNo ratings yet
- Types of Ac GeneratorDocument10 pagesTypes of Ac GeneratorJherel BerinNo ratings yet
- Ee6009 PeresDocument89 pagesEe6009 PeresparthibanNo ratings yet
- Special Electrical Machines FULL PART A &B Question BankDocument220 pagesSpecial Electrical Machines FULL PART A &B Question BankSanjeevKumarKNo ratings yet
- Motor AppplicationDocument17 pagesMotor Appplicationtajul tonoyNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: Working Principle, TypesDocument3 pagesInduction Motor: Working Principle, TypesFARAZ UL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- Electric Traction - ReferenceDocument19 pagesElectric Traction - ReferenceShrestha SanjuNo ratings yet
- Robotics Unit-2 QBDocument7 pagesRobotics Unit-2 QBveerapandianNo ratings yet
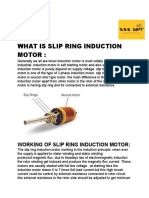
- Slip Ring and Squirrel Cage Induction MotorsDocument13 pagesSlip Ring and Squirrel Cage Induction MotorsPrem SagarNo ratings yet
- Motors TypesDocument6 pagesMotors TypesSoham DesaiNo ratings yet
- Which Motor Has High Starting Torque and Staring Current DC Motor, Induction Motor or Synchronous Motor?Document26 pagesWhich Motor Has High Starting Torque and Staring Current DC Motor, Induction Motor or Synchronous Motor?NavdeepNo ratings yet
- Dr. BK Singh's Mechatronics Chap-3Document52 pagesDr. BK Singh's Mechatronics Chap-3Mekibib EmawayihNo ratings yet
- Infant Monitoring System Using Co2 Sensor-Project ReportDocument59 pagesInfant Monitoring System Using Co2 Sensor-Project ReportRajesh Kumar0% (1)
- Drives in Mechatronics1Document14 pagesDrives in Mechatronics1Durga PrasadNo ratings yet
- Synchronous - Induction MotorsDocument1 pageSynchronous - Induction Motorsselraj0708No ratings yet
- Kaizen - Motor Selection GuideDocument11 pagesKaizen - Motor Selection GuideAmory Sabri AsmaroNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Induction MotorsDocument11 pagesSingle Phase Induction MotorsSafnas KariapperNo ratings yet
- A Self-Study Report On "Servo Motors": Rathan Kumar SM USN:1JS17ME433Document6 pagesA Self-Study Report On "Servo Motors": Rathan Kumar SM USN:1JS17ME433Rathan Kumar SMNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument20 pagesInduction MotorC V VIJAY KUMASRNo ratings yet
- Ee6703 Sem Small and Big NotesDocument107 pagesEe6703 Sem Small and Big NotesSANGEETHA JAYAMURUGANNo ratings yet
- A Universal Motor Is UniversalDocument6 pagesA Universal Motor Is UniversalrodinooNo ratings yet
- Ac and DC MotorDocument6 pagesAc and DC MotorKhairunnisa ZakiriNo ratings yet
- Universal Motor - PPSXDocument29 pagesUniversal Motor - PPSXPerfil Web JdcortestwebNo ratings yet
- Gutierrez - Synchronous MotorsDocument3 pagesGutierrez - Synchronous MotorsJohn Michael MarianoNo ratings yet
- Iam PPT FHD MotorsDocument25 pagesIam PPT FHD MotorsShreeNo ratings yet
- Universal MotorDocument4 pagesUniversal MotorBobNo ratings yet
- Reluctance MotorDocument27 pagesReluctance MotorMax Sedric L LaylayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Phase Induction MachinesDocument101 pagesChapter 3 Phase Induction Machineskelemyas ayalewNo ratings yet
- 4.1 DC Motor SpecificationDocument6 pages4.1 DC Motor SpecificationAsgher KhattakNo ratings yet
- Ev & HVDocument9 pagesEv & HVsuhas2002kulkarniNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics and EDDocument45 pagesPower Electronics and EDtefe yabatuNo ratings yet
- Short Type Questions of Three Phase Induction Motor - 01.04.2020Document5 pagesShort Type Questions of Three Phase Induction Motor - 01.04.2020Amit DebnathNo ratings yet
- DRIVES NotesDocument44 pagesDRIVES NotesChase GarciaNo ratings yet
- AC Electric Motors Control: Advanced Design Techniques and ApplicationsFrom EverandAC Electric Motors Control: Advanced Design Techniques and ApplicationsFouad GiriNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Electrical Engineering: For Practitioners in the Oil, Gas and Petrochemical IndustryFrom EverandHandbook of Electrical Engineering: For Practitioners in the Oil, Gas and Petrochemical IndustryNo ratings yet
- Dynamometer: Theory and Application to Engine TestingFrom EverandDynamometer: Theory and Application to Engine TestingNo ratings yet
Special Electrical Machines Unit 1
Special Electrical Machines Unit 1
Uploaded by
ilenjeeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Special Electrical Machines Unit 1
Special Electrical Machines Unit 1
Uploaded by
ilenjeeCopyright:
Available Formats
EE1001 SPECIAL ELECTRICAL MACHINES VII SEMESTER ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING Two Mark Questions and Answers
UNIT I 1. What is a synchronous reluctance motor? A reluctance motor that utilizes an ac rotating field, which allows for the possibility of extremely smooth torque and good operation to low speeds. 2. What are the types of rotor in synchronous reluctance motor? 1: Salient rotor 2. Radially laminated rotor 3. Axially laminated rotor 3. Mention some applications of synchronous reluctance motor. 1. Fiber-spinning mills 2. Industrial process equipment 3. Metering pumps 4. Wrapping and folding machines 5. What are the advantages of increasing LdILq ratio in synchronous reluctance motor? 1. Motor power factor increases. 2. 12R losses reduced. 3. Reduced volt-ampere ratings of the inverter driving the machine. 6. Compare synchronous reluctance motor and induction motor. Synchronous reluctance motor Induction motor
Better efficiency Highcost Low power factor. Used for low and medium power application. Efficiency is low compared with synchronous reluctance motor. Lowcost High power factor. Used for high power application.
7. Write down the torque equation of synchronous reluctance motor.
8. Draw the torque-angle characteristics of synchronous reluctance motor. 9. Draw the speed-torque characteristics of synchronous reluctance motor. 10. Draw the steady-state phasor diagram of synchronous reluctance motor.
11. What is Vernier motor? Vernier motor is a permanent magnet motor and has a high torque at low speed. It operates on the principles of a Vernier. 12. What is the application of Vernier motor? The Vernier motor is mainly used where require low speed and high torque. 13. Mention some advantages and disadvantages of synchronous reluctance Motor Advantages 1. There is no concern with demagnetization, hence synchronous reluctance. 2. There need be no excitation field at zero torque, thus eliminating electromagnetic spinning losses. 3. Synchronous reluctance machine rotors can be constructed entirely from high strength, low-cost materials.
Disadvantages 1. Compared to induction motor it is slightly heavier and has low power factor. But Increasing the saliency ratio , the power factor can be improved. 2. High cost than induction motor. 3. Need speed synchronization to inverter output frequency by using rotor position sensor and sensor less control. 14. Write down any two properties of synchronous reluctance motor. 1. High output power capability. 2. Ability of the rotor to withstand high speeds. 3. Negligible zero-torque spinning losses. 4. High reliability. 15. What is reluctance torque is synchronous reluctance motor? The torque exerted by the reluctance motor because of the tendency of the salient poles to align themselves in the minimum reluctance position. This torque is called reluctance torque. 16. What arc the design considerations in synchronous reluctance motor? 1. Power factor 2. Copper loss and core loss 3. Cost 4. Efficiency
You might also like
- EE1001 Special Electrical Machines Two Mark Questions and AnswersDocument23 pagesEE1001 Special Electrical Machines Two Mark Questions and Answersmohamedfahims64% (11)
- 2 Marks Special Machines.Document26 pages2 Marks Special Machines.Samraj MahalingamNo ratings yet
- Special Electrical MachinesDocument5 pagesSpecial Electrical MachinesEswaran0% (1)
- EE2403 Special Electrical MachinesDocument19 pagesEE2403 Special Electrical MachinesvasanthavananNo ratings yet
- SPECIAL ELECTRICAL MACHINES - Questions & AnswersDocument38 pagesSPECIAL ELECTRICAL MACHINES - Questions & AnswersMuhammad JunaidNo ratings yet
- Advant and Disadvantages of Induction MotorDocument2 pagesAdvant and Disadvantages of Induction MotorAnonymous iqwlnYPRGTNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor AdvantagesDocument2 pagesInduction Motor AdvantagesAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1-Synchronous Reluctance MotorDocument14 pagesUNIT 1-Synchronous Reluctance MotornirmalpseNo ratings yet
- What Are The Basic Parts of An Induction Motor?Document6 pagesWhat Are The Basic Parts of An Induction Motor?purbasha kanchan ghoshNo ratings yet
- Ee2403 (Special Electrical Machines Question BankDocument20 pagesEe2403 (Special Electrical Machines Question Bankkrish_skumar6302No ratings yet
- Special - Electrical - Machines QBDocument25 pagesSpecial - Electrical - Machines QBVel MuruganNo ratings yet
- Ac MotorDocument44 pagesAc MotorAbra AbraNo ratings yet
- Low Voltage Non Motor Industrial Feeder Calculating Ampacity Ratings of Feeders Conductors Factors Affecting Ampacity RatingsDocument3 pagesLow Voltage Non Motor Industrial Feeder Calculating Ampacity Ratings of Feeders Conductors Factors Affecting Ampacity RatingsRance FloresNo ratings yet
- Hamadaseceppt 180422122103Document11 pagesHamadaseceppt 180422122103sUmangal GHoshNo ratings yet
- Ev Engine ResearchDocument15 pagesEv Engine ResearchAnshul YadavNo ratings yet
- Electrical Science-2: Term Paper of Ele102Document7 pagesElectrical Science-2: Term Paper of Ele102shailesh singhNo ratings yet
- SEM 2 Marks With AnsDocument15 pagesSEM 2 Marks With AnsRevathy KannanNo ratings yet
- Electtrical Motors: Figures 4.1Document11 pagesElecttrical Motors: Figures 4.1Cholan PillaiNo ratings yet
- Universal Motor A Simple Guide To Construction Types and WorkingDocument7 pagesUniversal Motor A Simple Guide To Construction Types and Workingmireyo1488No ratings yet
- A-Complete-Guide-to-Repulsion-Motor (Use For Repulsion Motor Article)Document5 pagesA-Complete-Guide-to-Repulsion-Motor (Use For Repulsion Motor Article)vishalNo ratings yet
- Direct Current (DC) Motors: OperationDocument6 pagesDirect Current (DC) Motors: OperationckyprianouNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document33 pagesUnit 2kssrao13No ratings yet
- Task 4Document33 pagesTask 4Vishnu SasidharanNo ratings yet
- Motor Start TheoryDocument30 pagesMotor Start TheoryMaskbassNo ratings yet
- Types of Ac GeneratorDocument10 pagesTypes of Ac GeneratorJherel BerinNo ratings yet
- Ee6009 PeresDocument89 pagesEe6009 PeresparthibanNo ratings yet
- Special Electrical Machines FULL PART A &B Question BankDocument220 pagesSpecial Electrical Machines FULL PART A &B Question BankSanjeevKumarKNo ratings yet
- Motor AppplicationDocument17 pagesMotor Appplicationtajul tonoyNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: Working Principle, TypesDocument3 pagesInduction Motor: Working Principle, TypesFARAZ UL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- Electric Traction - ReferenceDocument19 pagesElectric Traction - ReferenceShrestha SanjuNo ratings yet
- Robotics Unit-2 QBDocument7 pagesRobotics Unit-2 QBveerapandianNo ratings yet
- Slip Ring and Squirrel Cage Induction MotorsDocument13 pagesSlip Ring and Squirrel Cage Induction MotorsPrem SagarNo ratings yet
- Motors TypesDocument6 pagesMotors TypesSoham DesaiNo ratings yet
- Which Motor Has High Starting Torque and Staring Current DC Motor, Induction Motor or Synchronous Motor?Document26 pagesWhich Motor Has High Starting Torque and Staring Current DC Motor, Induction Motor or Synchronous Motor?NavdeepNo ratings yet
- Dr. BK Singh's Mechatronics Chap-3Document52 pagesDr. BK Singh's Mechatronics Chap-3Mekibib EmawayihNo ratings yet
- Infant Monitoring System Using Co2 Sensor-Project ReportDocument59 pagesInfant Monitoring System Using Co2 Sensor-Project ReportRajesh Kumar0% (1)
- Drives in Mechatronics1Document14 pagesDrives in Mechatronics1Durga PrasadNo ratings yet
- Synchronous - Induction MotorsDocument1 pageSynchronous - Induction Motorsselraj0708No ratings yet
- Kaizen - Motor Selection GuideDocument11 pagesKaizen - Motor Selection GuideAmory Sabri AsmaroNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Induction MotorsDocument11 pagesSingle Phase Induction MotorsSafnas KariapperNo ratings yet
- A Self-Study Report On "Servo Motors": Rathan Kumar SM USN:1JS17ME433Document6 pagesA Self-Study Report On "Servo Motors": Rathan Kumar SM USN:1JS17ME433Rathan Kumar SMNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument20 pagesInduction MotorC V VIJAY KUMASRNo ratings yet
- Ee6703 Sem Small and Big NotesDocument107 pagesEe6703 Sem Small and Big NotesSANGEETHA JAYAMURUGANNo ratings yet
- A Universal Motor Is UniversalDocument6 pagesA Universal Motor Is UniversalrodinooNo ratings yet
- Ac and DC MotorDocument6 pagesAc and DC MotorKhairunnisa ZakiriNo ratings yet
- Universal Motor - PPSXDocument29 pagesUniversal Motor - PPSXPerfil Web JdcortestwebNo ratings yet
- Gutierrez - Synchronous MotorsDocument3 pagesGutierrez - Synchronous MotorsJohn Michael MarianoNo ratings yet
- Iam PPT FHD MotorsDocument25 pagesIam PPT FHD MotorsShreeNo ratings yet
- Universal MotorDocument4 pagesUniversal MotorBobNo ratings yet
- Reluctance MotorDocument27 pagesReluctance MotorMax Sedric L LaylayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Phase Induction MachinesDocument101 pagesChapter 3 Phase Induction Machineskelemyas ayalewNo ratings yet
- 4.1 DC Motor SpecificationDocument6 pages4.1 DC Motor SpecificationAsgher KhattakNo ratings yet
- Ev & HVDocument9 pagesEv & HVsuhas2002kulkarniNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics and EDDocument45 pagesPower Electronics and EDtefe yabatuNo ratings yet
- Short Type Questions of Three Phase Induction Motor - 01.04.2020Document5 pagesShort Type Questions of Three Phase Induction Motor - 01.04.2020Amit DebnathNo ratings yet
- DRIVES NotesDocument44 pagesDRIVES NotesChase GarciaNo ratings yet
- AC Electric Motors Control: Advanced Design Techniques and ApplicationsFrom EverandAC Electric Motors Control: Advanced Design Techniques and ApplicationsFouad GiriNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Electrical Engineering: For Practitioners in the Oil, Gas and Petrochemical IndustryFrom EverandHandbook of Electrical Engineering: For Practitioners in the Oil, Gas and Petrochemical IndustryNo ratings yet
- Dynamometer: Theory and Application to Engine TestingFrom EverandDynamometer: Theory and Application to Engine TestingNo ratings yet