Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reflex Arc and Types of Neurones Notes
Reflex Arc and Types of Neurones Notes
Uploaded by
Jin LobahCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Nervous SystemDocument71 pagesThe Nervous SystemDennis Limosnero MayorNo ratings yet
- Sistem Saraf 2: Ida Ayu Eka Widiastuti Bagian Fisiologi FK UnramDocument63 pagesSistem Saraf 2: Ida Ayu Eka Widiastuti Bagian Fisiologi FK UnramUpuUt Putrhie MinchuuetNo ratings yet
- Nevous System NotesDocument7 pagesNevous System NotesSchool ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Biology - Coordination and ResponseDocument8 pagesBiology - Coordination and ResponseMiguel HallNo ratings yet
- Nervous Sys BiologyDocument6 pagesNervous Sys Biologyalviayaan807No ratings yet
- Coordination, Response and HomeostasisDocument31 pagesCoordination, Response and HomeostasisVenusCrazy 550No ratings yet
- Notes On Coordination - Response - Nervous System, Reflex Arc, Type of NeuronesDocument6 pagesNotes On Coordination - Response - Nervous System, Reflex Arc, Type of NeuronesamberNo ratings yet
- Topic 14 Coordination and Response: 14.1.1 Nervous Control in Humans The Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesTopic 14 Coordination and Response: 14.1.1 Nervous Control in Humans The Nervous SystemHassanNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesHuman Nervous Systemzainab umerNo ratings yet
- Nervous Coordination and ResponseDocument11 pagesNervous Coordination and ResponseJashya NoorNo ratings yet
- IX Coordination 2Document31 pagesIX Coordination 2Mohammed FahimNo ratings yet
- Coordination And: ResponseDocument29 pagesCoordination And: ResponseSolángé MirembeNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordiantionDocument25 pagesControl and CoordiantionnoNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument5 pagesCoordination and ResponseChal WijeNo ratings yet
- 4a1 Bio Notes (Coordination and Response 1)Document2 pages4a1 Bio Notes (Coordination and Response 1)charmainemakumbe60No ratings yet
- CAMBRIDGE IGCSE BIOLOGY Chapter 14 Coordination and ResponseDocument203 pagesCAMBRIDGE IGCSE BIOLOGY Chapter 14 Coordination and ResponseVentus Tan100% (2)
- Nervous System Notes #2Document7 pagesNervous System Notes #2LeoNo ratings yet
- 7 Sensitivity and CoordinationDocument19 pages7 Sensitivity and CoordinationVarun GoseinNo ratings yet
- 4a1 Bio Notes (Coordination and Response 2)Document1 page4a1 Bio Notes (Coordination and Response 2)charmainemakumbe60No ratings yet
- AP Psychology Module 9Document29 pagesAP Psychology Module 9Klein ZhangNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument69 pagesCoordination and ResponseRegis WachenukaNo ratings yet
- Nervous ControlDocument15 pagesNervous ControlzoeakatNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument12 pagesCoordination and ResponsemandonaldboikanyoNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Nervous System NotesDocument8 pages3.1 Nervous System NotesabaybezawitNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument16 pagesThe Nervous SystemMaia MohammedNo ratings yet
- 2 ReactionsDocument43 pages2 ReactionsTrixie Anne CordovaNo ratings yet
- Science-10 Q3 Module-3 Week-3Document5 pagesScience-10 Q3 Module-3 Week-3Marl Rina EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- G-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesG-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemYohannes NigussieNo ratings yet
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : The Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : The Nervous SystemGraceEstoleCalo100% (1)
- Introduction To The Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesIntroduction To The Nervous SystemRajesh DasariNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesHuman Nervous SystemI Kadek Adi Putra Suandana 2005No ratings yet
- NERVOUS - SYSTEM (Auto-Saved)Document52 pagesNERVOUS - SYSTEM (Auto-Saved)nadeemyakubu47No ratings yet
- The Neuromuscular System and ExerciseDocument20 pagesThe Neuromuscular System and ExercisenofriNo ratings yet
- Neurology Assignment 1Document9 pagesNeurology Assignment 1workupindia7No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesNervous SystemSatrioNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument31 pagesThe Nervous SystemceneveNo ratings yet
- Nervous System-Double AwardDocument4 pagesNervous System-Double AwardTumisang PitiroseNo ratings yet
- Neuron NotesDocument10 pagesNeuron Notesapi-263230840No ratings yet
- 1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDocument7 pages1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDiya MehtaNo ratings yet
- C14.1 Nervous Control in Humans 4Document36 pagesC14.1 Nervous Control in Humans 4thomasaquinasrevannoNo ratings yet
- Week 10 BioDocument7 pagesWeek 10 BioTaze UtoroNo ratings yet
- Coordination HDocument9 pagesCoordination HmatinNo ratings yet
- Science Vi-Quarter 2 Module (Week 1-2 Nervous System)Document21 pagesScience Vi-Quarter 2 Module (Week 1-2 Nervous System)Denver TamayoNo ratings yet
- The NeuronsDocument3 pagesThe NeuronsAsim ZafarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Nervous SystemDocument32 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Nervous SystemLouise Murphy100% (1)
- Control and Coordination: Stick Progression Sheet and Pre-Assessment Sheet in Two Different PagesDocument45 pagesControl and Coordination: Stick Progression Sheet and Pre-Assessment Sheet in Two Different PagesPriyanshu ManwaniNo ratings yet
- Document 10Document23 pagesDocument 10haashniNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Control (IGCSE and O Level Biology 2023-2025)Document65 pagesCoordination and Control (IGCSE and O Level Biology 2023-2025)Tashwaar TamimNo ratings yet
- Neuron SystemDocument17 pagesNeuron Systemdibya patraNo ratings yet
- NeuronsDocument9 pagesNeuronsMuhammad Junaid SialNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Nervous TissueDocument8 pagesModule 5 Nervous TissueHermione MalfoyNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Week 1b Term 2 The Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesGrade 10 Week 1b Term 2 The Nervous SystemEsther KissoonNo ratings yet
- Volume 10Document26 pagesVolume 10sequeirachris24No ratings yet
- MARCH 19, 2024 The Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesMARCH 19, 2024 The Nervous SystemAlmira ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemBryan Bries100% (2)
- 7.reflex Regulation of Physiological Function PDFDocument2 pages7.reflex Regulation of Physiological Function PDFNektarios TsakalosNo ratings yet
- 14.1 The Nervous SystemDocument15 pages14.1 The Nervous SystemNathan TeferaNo ratings yet
- BIOPSYCHOLOGYDocument11 pagesBIOPSYCHOLOGYArunima RoyNo ratings yet
- Reflex LabDocument4 pagesReflex Labapi-340991045No ratings yet
Reflex Arc and Types of Neurones Notes
Reflex Arc and Types of Neurones Notes
Uploaded by
Jin LobahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reflex Arc and Types of Neurones Notes
Reflex Arc and Types of Neurones Notes
Uploaded by
Jin LobahCopyright:
Available Formats
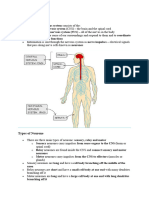
Types of Neurone
There are three main types of neurone: sensory, relay and motor
Sensory neurones carry impulses from sense organs to the CNS (brain or
spinal cord)
Relay neurones are found inside the CNS and connect sensory and motor
neurones
Motor neurones carry impulses from the CNS to effectors (muscles or
glands)
Neurones have a long fibre (axon)
This means that less time is wasted transferring the impulse from one cell to
another
The axon is insulated by a fatty sheath with small uninsulated sections along it
(called nodes)
This means that the electrical impulse does not travel down the whole axon,
but jumps from one node to the next
Their cell body contains many extensions called dendrites
This means they can connect to many other neurones and receive
impulses from them, forming a network for easy communication
The three types of neurone
Sensory neurones are long and have a cell body branching off the
middle of the axon
Relay neurones are short and have a small cell body at one end with
many dendrites branching off it
Motor neurones are long and have a large cell body at one end with long
dendrites branching off it
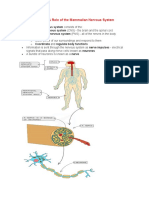
The Reflex Arc
An involuntary (or reflex) response does not involve the brain as the
coordinator of the reaction and you are not aware you have completed it until
after you have carried it out
This is an automatic and rapid response to a stimulus such as touching
something sharp or hot
As it does not involve the brain, a reflex response is quicker than any other
type of nervous response
This helps to minimise the damage to the body
Reflex actions are:
1.
1. Automatic
2. Fast
3. Protective
A reflex
1. The pin (the stimulus) is detected by a pain/pressure/touch receptor in the
skin
2. Sensory neurone sends electrical impulses to the spinal cord (the coordinator)
3. Electrical impulse is passed on to relay neurone in the spinal cord
4. Relay neurone connects to motor neurone and passes the impulse on
5. Motor neurone carries impulse to a muscle in the leg (the effector)
6. The muscle will contract and pull the foot up and away from the sharp object
(the response)
You might also like
- The Nervous SystemDocument71 pagesThe Nervous SystemDennis Limosnero MayorNo ratings yet
- Sistem Saraf 2: Ida Ayu Eka Widiastuti Bagian Fisiologi FK UnramDocument63 pagesSistem Saraf 2: Ida Ayu Eka Widiastuti Bagian Fisiologi FK UnramUpuUt Putrhie MinchuuetNo ratings yet
- Nevous System NotesDocument7 pagesNevous System NotesSchool ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Biology - Coordination and ResponseDocument8 pagesBiology - Coordination and ResponseMiguel HallNo ratings yet
- Nervous Sys BiologyDocument6 pagesNervous Sys Biologyalviayaan807No ratings yet
- Coordination, Response and HomeostasisDocument31 pagesCoordination, Response and HomeostasisVenusCrazy 550No ratings yet
- Notes On Coordination - Response - Nervous System, Reflex Arc, Type of NeuronesDocument6 pagesNotes On Coordination - Response - Nervous System, Reflex Arc, Type of NeuronesamberNo ratings yet
- Topic 14 Coordination and Response: 14.1.1 Nervous Control in Humans The Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesTopic 14 Coordination and Response: 14.1.1 Nervous Control in Humans The Nervous SystemHassanNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesHuman Nervous Systemzainab umerNo ratings yet
- Nervous Coordination and ResponseDocument11 pagesNervous Coordination and ResponseJashya NoorNo ratings yet
- IX Coordination 2Document31 pagesIX Coordination 2Mohammed FahimNo ratings yet
- Coordination And: ResponseDocument29 pagesCoordination And: ResponseSolángé MirembeNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordiantionDocument25 pagesControl and CoordiantionnoNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument5 pagesCoordination and ResponseChal WijeNo ratings yet
- 4a1 Bio Notes (Coordination and Response 1)Document2 pages4a1 Bio Notes (Coordination and Response 1)charmainemakumbe60No ratings yet
- CAMBRIDGE IGCSE BIOLOGY Chapter 14 Coordination and ResponseDocument203 pagesCAMBRIDGE IGCSE BIOLOGY Chapter 14 Coordination and ResponseVentus Tan100% (2)
- Nervous System Notes #2Document7 pagesNervous System Notes #2LeoNo ratings yet
- 7 Sensitivity and CoordinationDocument19 pages7 Sensitivity and CoordinationVarun GoseinNo ratings yet
- 4a1 Bio Notes (Coordination and Response 2)Document1 page4a1 Bio Notes (Coordination and Response 2)charmainemakumbe60No ratings yet
- AP Psychology Module 9Document29 pagesAP Psychology Module 9Klein ZhangNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument69 pagesCoordination and ResponseRegis WachenukaNo ratings yet
- Nervous ControlDocument15 pagesNervous ControlzoeakatNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument12 pagesCoordination and ResponsemandonaldboikanyoNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Nervous System NotesDocument8 pages3.1 Nervous System NotesabaybezawitNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument16 pagesThe Nervous SystemMaia MohammedNo ratings yet
- 2 ReactionsDocument43 pages2 ReactionsTrixie Anne CordovaNo ratings yet
- Science-10 Q3 Module-3 Week-3Document5 pagesScience-10 Q3 Module-3 Week-3Marl Rina EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- G-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesG-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemYohannes NigussieNo ratings yet
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : The Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : The Nervous SystemGraceEstoleCalo100% (1)
- Introduction To The Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesIntroduction To The Nervous SystemRajesh DasariNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesHuman Nervous SystemI Kadek Adi Putra Suandana 2005No ratings yet
- NERVOUS - SYSTEM (Auto-Saved)Document52 pagesNERVOUS - SYSTEM (Auto-Saved)nadeemyakubu47No ratings yet
- The Neuromuscular System and ExerciseDocument20 pagesThe Neuromuscular System and ExercisenofriNo ratings yet
- Neurology Assignment 1Document9 pagesNeurology Assignment 1workupindia7No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesNervous SystemSatrioNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument31 pagesThe Nervous SystemceneveNo ratings yet
- Nervous System-Double AwardDocument4 pagesNervous System-Double AwardTumisang PitiroseNo ratings yet
- Neuron NotesDocument10 pagesNeuron Notesapi-263230840No ratings yet
- 1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDocument7 pages1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDiya MehtaNo ratings yet
- C14.1 Nervous Control in Humans 4Document36 pagesC14.1 Nervous Control in Humans 4thomasaquinasrevannoNo ratings yet
- Week 10 BioDocument7 pagesWeek 10 BioTaze UtoroNo ratings yet
- Coordination HDocument9 pagesCoordination HmatinNo ratings yet
- Science Vi-Quarter 2 Module (Week 1-2 Nervous System)Document21 pagesScience Vi-Quarter 2 Module (Week 1-2 Nervous System)Denver TamayoNo ratings yet
- The NeuronsDocument3 pagesThe NeuronsAsim ZafarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Nervous SystemDocument32 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Nervous SystemLouise Murphy100% (1)
- Control and Coordination: Stick Progression Sheet and Pre-Assessment Sheet in Two Different PagesDocument45 pagesControl and Coordination: Stick Progression Sheet and Pre-Assessment Sheet in Two Different PagesPriyanshu ManwaniNo ratings yet
- Document 10Document23 pagesDocument 10haashniNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Control (IGCSE and O Level Biology 2023-2025)Document65 pagesCoordination and Control (IGCSE and O Level Biology 2023-2025)Tashwaar TamimNo ratings yet
- Neuron SystemDocument17 pagesNeuron Systemdibya patraNo ratings yet
- NeuronsDocument9 pagesNeuronsMuhammad Junaid SialNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Nervous TissueDocument8 pagesModule 5 Nervous TissueHermione MalfoyNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Week 1b Term 2 The Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesGrade 10 Week 1b Term 2 The Nervous SystemEsther KissoonNo ratings yet
- Volume 10Document26 pagesVolume 10sequeirachris24No ratings yet
- MARCH 19, 2024 The Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesMARCH 19, 2024 The Nervous SystemAlmira ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemBryan Bries100% (2)
- 7.reflex Regulation of Physiological Function PDFDocument2 pages7.reflex Regulation of Physiological Function PDFNektarios TsakalosNo ratings yet
- 14.1 The Nervous SystemDocument15 pages14.1 The Nervous SystemNathan TeferaNo ratings yet
- BIOPSYCHOLOGYDocument11 pagesBIOPSYCHOLOGYArunima RoyNo ratings yet
- Reflex LabDocument4 pagesReflex Labapi-340991045No ratings yet