Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 5 - 7
Module 5 - 7
Uploaded by
Elaine Grace BaylosisOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 5 - 7
Module 5 - 7
Uploaded by
Elaine Grace BaylosisCopyright:
Available Formats
Continued Lecture Part 5 (from MODULE 2) operations worldwide.
International Chamber Of Commerce (ICC)? For a standard delivery between established
trade partners, neighboring countries or
What is International Chamber Of
countries belonging to a common trading
Commerce (ICC)?
area, these TERMS are often easily agreed
- The ICC is the world’s only truly global upon as a matter of standard practice with
business organization and is recognized as only an adjustment related to the actual
the voice of international business. Based in freight and insurance charges, often in
Paris. connection with open account trading. In
such cases, the buyer often takes the main
- ICC membership groups thousands of
responsibility for transport and risk of the
companies of every size in over 120
purchased goods. However, in other cases
countries worldwide,
the seller wants to have better control of the
mainly through its national committees. delivery process and to be able to select
transport and/or insurance, and
- They represent a broad cross-section of
consequently chooses delivery terms where
business activity, including manufacturing,
these aspects are better protected.
trade, services
PRODUCT RISKS
and the professions.
Product risks are risks that the seller
- its core services/activities include:
automatically has to accept as an integral
● practical services to business part of their commitment. First, it is a matter
of the product itself, or the agreed delivery;
● working against commercial crime
For example, specified performance
● being an advocate for international warranties or agreed maintenance or service
business obligations.
● spreading business expertise There are many examples of how new and
unexpected working conditions in the
● promoting growth and prosperity
buyer’s country have led to reduced
● setting rules and standards performance of the delivered goods. It could
be negligence concerning operating
● promoting the multilateral trading system
procedures or restrictions, careless
Through membership of the ICC, companies treatment or lack of current maintenance,
shape rules and policies that stimulate but also damage due to the climate or for
international trade environmental reasons.
and investment. These companies in turn MANUFACTURING RISKS
count on the prestige and expertise of the
The concept of product risk could also
ICC to get business views
include some elements of the manufacturing
across to governments and process itself
intergovernmental organizations, whose
(although in principle that subject falls
decisions affect corporate finances and
beyond the scope of this topic). This risk
appears all too frequently when the product defined by standard policy wordings issued
is tailor-made or has unique specifications. by the Institute of London Underwriters (or
In these cases there is often no other readily the American Institute of Marine
Underwriters). These are called Institute
available buyer if the transaction cannot be
Cargo Clauses.
completed, in which case the seller has to
carry the cost of any necessary While there are numerous clauses that will
readjustment, if that is even an option. apply to different cargos, the widest cover is
provided under Institute Cargo Clauses A
Risks of this nature occur as early as the
(Institute Cargo Clauses [Air] for transport by
product planning phase but may often be
air), or with more restrictive cover under
difficult to cover from that time owing to the
Institute Cargo Clauses B and Institute Cargo
special nature of these products. But they
Clauses C. (The new A-clauses have replaced
also involve specific risks for the buyer, who
the previous Institute Cargo Clauses All
often has to enter into payment obligations
Risks.) Cargo insurance is therefore normally
at an early stage but without the security of
provided through one of these Institute
the product itself until it has been delivered
Cargo Clauses A, B or C, plus separate war
and installed.
clauses and strike clauses.
To safeguard the interests of both parties,
From the seller’s perspective, there are
the terms of payment are often divided into
basically three different ways to insure the
part-payments related to the production and
cargo, either with an OPEN INSURANCE
delivery phases, in combination with
POLICY covering most or all shipments
separate guarantees, to cover the risks as
within the seller’s basic trade as agreed in
they occur in different phases of the advance with the insurer, or with a SPECIFIC
transaction. INSURANCE POLICY, covering specific
shipments on an ad hoc basis or those which
TRANSPORT RISKS AND CARGO INSURANCE
are outside the set criteria of the open
From a general risk perspective, it is not only policy. The open policy is by far the most
the product but also the physical movement common in international trade, normally
of the goods from the seller to the buyer that reviewed on an annual basis, and with a 30-
has to be evaluated, based on aspects such to 60-day cancellation clause should
as the nature of the product, size of delivery, conditions deteriorate substantially. The
the buyer and their country, and the actual third basic form of cargo insurance is seller’s
transportation route. Most goods in interest CONTINGENCY INSURANCE,
international trade, apart from smaller and normally only offered as a complement to
non-expensive deliveries, are covered by the open policy or as an integral part of a
cargo insurance, providing cover against specific policy, and on an undisclosed basis
physical loss or damage while in transit, by as far as the buyer is concerned. This
land, sea or air, or by a combination of these insurance covers the risk that the goods may
modes of transport. arrive at their destination in a damaged
condition, resulting in the buyer’s refusal
The cover under a cargo insurance (which is
a sub-branch of marine insurance) is almost to accept them (even if the risk was on their
always part according to the terms of delivery), or
they may simply be unable or unwilling to is relatively easy to obtain a fair picture of
pay for commercial or political reasons, potential buyers, either to study their
including failure to produce a valid import published accounts or to ask for an
independent business credit report, which is
license.
a more reliable way of dealing with customer
Cargo insurance can be obtained directly risks. This will often also give much broader
from an insurance company or, very often information about the buyer and their
today, directly through the transporting business, and not simply some
company or the forwarding agent handling
selected economic figures from which the
the goods. In some countries it is also quite
seller often cannot draw any decisive
common to use independent cargo
conclusions.
insurance brokers, who may be more able to
select the most cost-efficient insurance CREDIT INFORMATION
package, based on specific conditions or the
Export trade may be an important factor in
trade structure in each individual case.
the potential growth of business; however,
However, the seller should always ensure the risks involved in carrying out
that the selected insurer is part of an international business can also be high. In
established international network for little more than a decade, the world of
dealing with claims and settlement commerce has changed dramatically. In this
procedures. This is often also a requisite of commercial environment, the global
the buyer, and if not explicitly agreed in the suppliers of CREDIT INFORMATION have
sales contract, such conditions may appear become a vital source of knowledge and
later on, for example in the insurance expertise, based on the great wealth of
specifications in a letter of credit (LC). information that they maintain about
consumers and how they behave, about
COMMERCIAL RISKS (PURCHASER RISKS)
businesses and how they perform, and about
Commercial risk, also called purchaser risk, different markets and how they are
is often defined as the risk of the buyer going changing.
into bankruptcy or being in any other way
The more the seller understands their
incapable of fulfilling their contractual
customers, the more they are able to
obligations. One might first think of the
respond to their individual needs and
buyer’s payment obligations but, as seen
circumstances. Credit information in itself
above, it also covers all other obligations of
may also help the seller to reach new
the buyer, according to the contract,
customers and to build, nurture and
necessary for the seller to fulfill their
maximize lasting customer relationships. It
obligations.
thus forms a vital part of establishing the
How does the seller, therefore, evaluate the
structure of a potential export transaction
buyer’s ability to fulfill their obligations? In
and, in particular, the terms of payment to
most industrialized countries within the
be used. In some cases the information can
Organization for Economic Co-operation and
be provided instantly, inexpensively and in a
Development (OECD) area, it
standardized manner over the internet,
but in other cases a more researched profile the handling, or aiding the handling, of
is required. assets, knowing that they are the result of
crime, terrorism or illegal drug activities.
Continued Lecture Part 6 (from MODULE 3)
A reputable business adds respectability to
ADVERSE BUSINESS RISKS
any organization being used for laundering
Adverse business risks include all business operations, and money launderers will try to
practices of a negative nature, which are not use any business, directly through
only common but also almost endemic in ownership or indirectly by deceit.
some parts of the world. This could have Developing nations are particularly
serious consequences for the individual vulnerable to money launderers because
transaction, but also for the general business they usually have poorly regulated financial
and financial standing of the seller, as well as
systems. These provide the greatest
their moral reputation.
opportunities to criminals.
We are, of course, referring to all sorts of
In general terms, a suspicious transaction is
corrupt practices that flourish in many
one that is outside the normal range of
countries, particularly in connection with
transactions from the seller’s point of view,
larger contracts or projects: Bribery, Money
in particular in relation to new customers or
laundering and a variety of Facilitation
where an old customer changes
payments:
transaction structure in an unusual way. It
“Bribery in general can broadly be defined as
can include:
the receiving or offering of an undue reward
by or to any holder of public office or a ● unusual payment settlements
private employee designed to influence
● unusual transfer instructions
them in the exercise of their duty, and thus
to incline them to act contrary to the known ● secretiveness
rules of honesty and integrity.” ● rapid movements in and out of accounts
This quotation is taken from a UK ● numerous transfers
government body, and even if it is not a legal
definition, it gives an accurate description of ● complicated accounts structures
the problem. THE NEED FOR STRONG POLICY
If bribery is generally a technique to press The World Bank (WB) and the Organization
the seller for undue rewards, money for Economic Co-operation and
laundering often has the opposite purpose, Development (OECD) have put a great deal
which is to invite the seller to do a deal that of resources into combating corruption
may on the face of it seem very worldwide, and in most countries corruption
advantageous, but where the true intention is now illegal even when committed abroad.
is to disguise or conceal the actual origin of The companies also have full responsibility
the money involved. for the wrongdoings of their employees
abroad when acting for the company.
It covers criminal activities, corruption and
breaches of financial sanctions. It includes
As a consequence of the inclusion of anti- However, in practice, it may be difficult to
corruption laws, which are in place in most separate commercial risk and political risk
countries today, it is also incorporated in the because political decisions, or other similar
procedures of their government acts by local authorities, also affect the local
departments, For example in the rules of the company and its capabilities of honoring the
respective export credit agency (which will contract. For example, some countries may
be described at length later in this lecture). change taxes, import duties or currency
Any violation of the anti-corruption regulations, often with immediate effect,
statement that the seller has to give when which could undermine the basis for
applying for such insurance could have contracts already signed.
serious implications for its validity.
Other common measures include import
Every company involved in overseas trade restrictions or other regulations intended to
or investments should have a clear anti- promote local industry and to save foreign
corruption policy that is implemented and currency. Even with just the risks of such
clearly understood by all its employees, and actions, they all have the same negative
supervised by the management in an implications for the transaction and the
appropriate way. Such a policy is also buyer’s possibility of fulfilling their part of
supported by local laws, which give both the the contract.
company and its employees a much stronger
OTHER FORMS OF POLITICAL RISK OR
moral and legal defense against every
SIMILAR RISK
attempt to extort bribes from them or to
induce them into any other form of corrupt Apart from the real political risks already
practice. discussed, there are other measures taken
by authorities in the buyer’s home country
POLITICAL RISKS
that can affect the buyer and their ability or
Political risk or country risk is often defined willingness to fulfill the transaction; For
as: example, demands for product standards,
new or changed energy or environmental
“the risk of a separate commercial
requirements – measures that could have a
transaction not being realized in a
genuine purpose or be put in place partly to
contractual
act as trade barriers to promote sectors or
way due to measures emanating from the important industries within the country.
government or authority of the buyer’s Irrespective of the purpose, such actions,
often called ‘Non-tariff Barriers’, could have
own or any other foreign country.”
a negative impact on already agreed
No matter how reliable the buyer may be in business transactions, since such measures
fulfilling their obligations and paying in local are often introduced with immediate effect.
currency,their obligations to the seller
Countries involved in the transit of goods
(according to the contract) are nevertheless
have to be considered as well as countries
dependent on the current situation in their
related to
own country – or along the route of
transport to that country. subcontractors or suppliers of crucial
components. In these cases, perhaps it is not
the political risk as defined, but other general conception of preferred trade
measures that are more important; for currencies, even though the highest
example, the risk of labour market conflicts preference is normally for the currency of
in the form of strikes or lockouts that could the home country. The Japan Yen, the Swiss
interrupt delivery of components needed for Franc together with the US Dollar and the
the timely execution of the agreed sales British Pound would probably be regarded as
contract. strong currencies in the long run anyway,
while others would be seen as neutral, weak,
CURRENCY RISKS
unstable or volatile.
If payment is going to be made in a currency
However, a division into strong or weak
other than that in which the seller incurs
currencies may have its justification in a
their costs, a new currency risk will arise. In
longer perspective where the home
most cases, the seller’s main costs will be in
countries have (or have not) maintained
their own local currency, which
economic and political stability over the
automatically creates such a risk if invoicing
years, together with a strong economy, low
in another currency. The size of that risk will
inflation and stable confidence in the future
depend on the currency and the outstanding
maintenance of this policy. But the
period until payment.
development of increased trade imbalances
Since the introduction of the euro, invoicing and country indebtedness together with
in that currency has become increasingly subsequent competitive currency
common in European trade and also with devaluations aiming to strengthen a
sellers outside the euro zone. Even with the country’s own exports have made currency
problems currently affecting this particular
exchange rates much more volatile in recent
currency, the development is likely to
years.
accelerate with additional countries joining
the euro zone.
Traditionally, however, the USD has been
the preferred third-party currency. This
applies both to international trade in
general, but particularly to raw materials
and certain commodities, and for many
other services such as freight and insurance.
It is also commonly used in countries where
the United States maintains or historically
has had a strong economic or political
influence.
ASSESSMENT OF CURRENCIES
Traditionally, currencies have been divided
into ‘strong’ and ‘weak’, and this view has
affected the
Since fluctuations in currency values result in
foreign exchange risk, the financial manager
Continued Lecture Part 7 (from MODULE 3)
must understand the factors causing these
FOREIGN EXCHANGE RATES changes in currency values. Although, the
value of a currency is determined by the
Firms that do business internationally must
AGGREGATE SUPPLY/DEMAND FOR THAT
be concerned with EXCHANGE RATES which
CURRENCY, this alone does not help financial
are the relationships among the values of
managers understand or predict the changes
currencies. For example, a Philippine
in exchange rates.
firm/business selling products in Europe will
be very interested in the relationship of the The major reasons for exchange rate
Euro to Philippine Peso as well as the US movements which include
Dollar. INFLATION,INTEREST RATES, BALANCE OF
PAYMENTS (BOP), GOVERNMENT’S POLICIES
The constant change in exchange rates
or INTERVENTION and OTHER FACTORS so
causes problems for financial managers as
forth are discussed briefly in the following
the change in relative purchasing power
sections below.
between countries affects imports and
exports, interest rates and other economic 1. Inflation
variables. The relative strength of a
Inflation tends to deflate the value of a
particular currency to other countries many
currency b’coz holding the currency results
times over a business cycle.
in reduced purchasing power.
FACTORS INFLUENCING EXCHANGE RATES
2. Interest rates
As with any other market, the exchange rate
If interest returns in a particular country are
between two currencies is determined by
higher relative to other countries, individuals
the supply of and the demand of those
currencies. The present international and companies will be enticed to invest in
monetary system consists of a mixture of that country. As a result. There will be an
“FREELY” floating exchange rates and fixed increased demand for the country’s
rates. currency.
The currencies of the major trading 3. Balance of payments (BOP)
partners of the USA are traded in FREE
BOP is used to refer to a system of accounts
MARKETS . This activity, however, is subject
that catalogs the flow of goods bet’n the
to intervention by many countries central
residents of two countries.
banks. Factors that tend to increase the
supply or decrease the demand schedule for 4. Government intervention
a given currency will bring down the value
Through intervention (i.e.- Buying/Selling
that currency in a foreign exchange markets.
the currency in the foreign exchange
Similarly, the factors that tend decrease the
markets), the central bank (BSP) of a country
supply, or increase the demand for a
may support or depress the value of its
currency will raise the value of that currency.
currency.
5. Other factors Apart from ordinary overdrafts during
production and delivery, the need for
Other factors that may affect exchange rates
finance is also determined by the length of
are political and economic stability,
credit that the seller may have to offer as
extended stock market rallies and significant
part of the deal. If so, the financial risk is
declines in the demand for major exports.
increased in line with the prolonged
FINANCIAL RISKS commercial and/or political risk.
In practice, every international trade FINANCIAL RISK AND CASH MANAGEMENT
transaction contains an element of financial
Other forms of financial risk are more
risk. Purchasing, production and shipment all
obvious but have to be underlined in this
place a financial burden on the transaction
context; for example, if the seller misjudges
that forces the seller to determine how
the risks involved in the transaction and
alternative terms of payment would affect
becomes exposed through terms of payment
liquidity during its different phases until
that do not cover the real risk situation, or
payment – and how this should be financed.
mistakenly enters into the deal without
And, if the deal is not settled as intended, an
proper risk protection. It goes without saying
additional financial risk occurs.
that such miscalculations can have serious
When using subcontractors, who do not financial consequences, from delays in
share the risks of the transaction and are payment to loss of capital.
paid according to separate agreements, the
The FINANCIAL RISKS are generally
risk increases accordingly and even more so
intimately connected to the structure of the
should the seller have to offer a supplier
TERMS OF PAYMENT. The safer they can be
credit for a shorter or longer period. When it
made, the more the financial risk will
comes to larger and more complex
automatically be reduced, the timing of the
transactions, this financial risk aspect is even
payments will be more accurate and the
more obvious. One of the major problems
liquidity aspect of the transaction better
for the seller could be to obtain bankable
assessed – in fact, the very essence of CASH
collateral for the increased need for finance
MANAGEMENT.
and guarantees. Even after production and
delivery, the seller could still be financially The safer the terms of payment the parties
exposed in case of unforeseen events and have agreed upon, the more costly they will
delays until final payment. normally be. And, if they contain bank
security, such as a Letter of Credit (LC) or a
The real risk also tends to increase with
Bank Guarantee, that may also reduce
longer and consequently more costly
available credit limits within the buyer’s own
transport distances. Bureaucratic delays in
bank.
many countries, as well as delays in the
banking system, will have the same result –
the final payment to the seller will not be
made as anticipated according to the
contract.
You might also like
- ISO 22301: 2019 - An introduction to a business continuity management system (BCMS)From EverandISO 22301: 2019 - An introduction to a business continuity management system (BCMS)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Insurance and TypesDocument4 pagesInsurance and TypesRaghavendra BarikNo ratings yet
- Cargo Insurance: International Trade GuidesDocument6 pagesCargo Insurance: International Trade GuidesstarysairaaNo ratings yet
- Cargo Insurance: International Trade GuidesDocument6 pagesCargo Insurance: International Trade GuidesnimitpunyaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Hazard Risk.Document9 pagesChapter 5 - Hazard Risk.Adil Javed CHNo ratings yet
- Transport Insurance For International TradeDocument6 pagesTransport Insurance For International TradeyenleNo ratings yet
- Lloyds - Covid-19 - White Paper - FINAL2 - Chapter2Document4 pagesLloyds - Covid-19 - White Paper - FINAL2 - Chapter2Menekşe UçaroğluNo ratings yet
- UT Griffiths Insurance SubmittedDocument19 pagesUT Griffiths Insurance SubmittedpostscriptNo ratings yet
- Parametric Insurance For DisastersDocument6 pagesParametric Insurance For DisastersMohammed Touhami GOUASMINo ratings yet
- Assessment 6 - BACALSODocument3 pagesAssessment 6 - BACALSOArnel YtacNo ratings yet
- Part 3 - InsuranceDocument11 pagesPart 3 - InsuranceJohnSmithNo ratings yet
- Construction InsuranceDocument9 pagesConstruction InsuranceBritton WhitakerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document5 pagesChapter 7Eko WaluyoNo ratings yet
- Construction Insurance ProvisionsDocument3 pagesConstruction Insurance ProvisionsHoussam ZeinNo ratings yet
- Activities On Trade FinanceDocument5 pagesActivities On Trade FinanceSrishanNo ratings yet
- Trade Finance Not SummarizedDocument70 pagesTrade Finance Not Summarized20192329No ratings yet
- Cargo Insurance Unit 6Document43 pagesCargo Insurance Unit 6Shikha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cargo InsuranceDocument7 pagesCargo InsuranceshirdawaNo ratings yet
- IMU Marine Insurance and Vetting InspectionsDocument31 pagesIMU Marine Insurance and Vetting Inspectionszaheerbc100% (2)
- Ba311 Week9Document4 pagesBa311 Week9Patrick SolomonNo ratings yet
- Marine Insurance Dissertation TopicDocument6 pagesMarine Insurance Dissertation TopicNeedSomeoneToWriteMyPaperForMeBillings100% (1)
- Effecting Marine InsuranceDocument4 pagesEffecting Marine InsuranceRavindi HandaragamaNo ratings yet
- KuvukulesivetabusDocument2 pagesKuvukulesivetabusPrasad PNo ratings yet
- Insurance Documents Used in Trade G4Document19 pagesInsurance Documents Used in Trade G4LAURA CAMILA HERNANDEZ UPEGUINo ratings yet
- Re InsuranceDocument51 pagesRe Insuranceameydalvi91No ratings yet
- Coronavirus COVID19 - Client GuidanceDocument15 pagesCoronavirus COVID19 - Client GuidanceManoj Ek50% (2)
- Credit InsuranceDocument51 pagesCredit InsuranceMayur Federer Kunder100% (8)
- Glossary of Common Insurance Terms: WarrantyDocument6 pagesGlossary of Common Insurance Terms: Warrantyijed moussaNo ratings yet
- Construction Insurance TypesDocument10 pagesConstruction Insurance TypesHoussam ZeinNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 R M&A TransactionsDocument3 pagesCOVID-19 R M&A TransactionsrdiazeplaNo ratings yet
- 6c IAA RB Ch6 ReinsuranceDocument22 pages6c IAA RB Ch6 ReinsuranceBison-Fûté LebesguesNo ratings yet
- Reinsurance Basic GuideDocument80 pagesReinsurance Basic GuideAyaaz Fazulbhoy100% (3)
- Chapter 6Document9 pagesChapter 6ibrahim JimaleNo ratings yet
- Credit Insurance. DOI: © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument3 pagesCredit Insurance. DOI: © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All Rights ReservedJames HetNo ratings yet
- General TakafulDocument28 pagesGeneral Takafulkhadijah zulkifliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 24Document30 pagesLecture 24Jawad HaiderNo ratings yet
- Icc A 2009Document3 pagesIcc A 2009Sana KhairiNo ratings yet
- Defect LiabilitiesDocument8 pagesDefect LiabilitiesAshoke RoyNo ratings yet
- Ten Tips For Mitigating Risk in Construction Projects: Fine Print OnlineDocument2 pagesTen Tips For Mitigating Risk in Construction Projects: Fine Print OnlineLiya StaariNo ratings yet
- M&A Vocabulary - Explained by The Experts - Indemnity vs. Warranty Under Common Law - Rödl & PartnerDocument2 pagesM&A Vocabulary - Explained by The Experts - Indemnity vs. Warranty Under Common Law - Rödl & PartnerDAO9No ratings yet
- Project 1Document7 pagesProject 1Rajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Untitled 1cutsom SaaDocument14 pagesUntitled 1cutsom SaaSIMBARASHE MABHEKANo ratings yet
- SCLT 6316 Assignment 3Document5 pagesSCLT 6316 Assignment 3mikeNo ratings yet
- TACN2Document8 pagesTACN2K58 TRAN ANH VANNo ratings yet
- Gozen SeleneDocument50 pagesGozen SeleneRijad ÇerkiniNo ratings yet
- Reserving InsuranceDocument19 pagesReserving InsuranceDarwin DcNo ratings yet
- International Trade Lecture 9 2022Document6 pagesInternational Trade Lecture 9 2022latyshovllad2011No ratings yet
- N 137Document53 pagesN 137Aep SaepudinNo ratings yet
- Reinsurance Basic GuideDocument80 pagesReinsurance Basic GuideNur AliaNo ratings yet
- Reinsurance: January 1998Document28 pagesReinsurance: January 1998Sudhakar GuntukaNo ratings yet
- IC 85 ReinsuranceDocument84 pagesIC 85 ReinsuranceAnand sharma0% (1)
- General Insurance UwDocument90 pagesGeneral Insurance UwsushantducatiNo ratings yet
- What Is Cargo InsuranceDocument2 pagesWhat Is Cargo InsuranceSumith PawarNo ratings yet
- Procurement Management - Kumar AnimeshDocument8 pagesProcurement Management - Kumar Animeshkumaranimesh2606No ratings yet
- Non Life Insurance PoliciesDocument8 pagesNon Life Insurance PoliciesAmanuel AbebawNo ratings yet
- Credit Default Swaps (CDS) and Financial Guarantee (FG) InsuranceDocument33 pagesCredit Default Swaps (CDS) and Financial Guarantee (FG) InsuranceGeorge Lekatis100% (1)
- Textbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 7, Exit Transactions: The Process of Selling an Urgent Care CenterFrom EverandTextbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 7, Exit Transactions: The Process of Selling an Urgent Care CenterNo ratings yet
- CW - Midterm NotesDocument10 pagesCW - Midterm NotesMharibelle AmbaNo ratings yet
- Final Chapter 6Document14 pagesFinal Chapter 6Gizachew NadewNo ratings yet
- 2 - INTRO TO Financial FSDocument19 pages2 - INTRO TO Financial FSmuhammad akbar bahmiNo ratings yet
- Wise 271276736 2810 - 42Document3 pagesWise 271276736 2810 - 42Soslew DoeksNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment Without Rahul PartDocument22 pagesGroup Assignment Without Rahul PartagungNo ratings yet
- Cae05 Intermediate Accounting 2: Activity Chapter 3 Explain The Following Terms in Essay. Loan Origination Costs and FeesDocument2 pagesCae05 Intermediate Accounting 2: Activity Chapter 3 Explain The Following Terms in Essay. Loan Origination Costs and FeesRandelle James FiestaNo ratings yet
- Homework Exercise 1Document3 pagesHomework Exercise 1EgyptianNo ratings yet
- June 2017Document599 pagesJune 2017Asif sheikhNo ratings yet
- Free Cash FlowsDocument2 pagesFree Cash FlowsMuhammad Awais SabirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-Currency Derivatives: SolutionDocument10 pagesChapter 5-Currency Derivatives: SolutionMinh Trương TuệNo ratings yet
- Ejemplo de Bill of Lading PDFDocument1 pageEjemplo de Bill of Lading PDFAndre Alonso DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Percakapan Dengan ReservasiDocument7 pagesPercakapan Dengan ReservasiDe PremaNo ratings yet
- Ch13 Capital Structure and LeverageDocument49 pagesCh13 Capital Structure and LeverageSukmawatiiNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft OfficeDocument2 pagesNew Microsoft Officerajat_gandhiNo ratings yet
- Fairstone Terms and Conditions PDFDocument10 pagesFairstone Terms and Conditions PDFGarrett GilesNo ratings yet
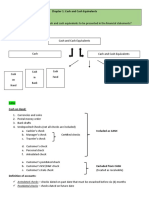
- Chapter 1: Cash and Cash Equivalents Expected Question(s) :: Cash On Hand Cash Fund Cash in BankDocument8 pagesChapter 1: Cash and Cash Equivalents Expected Question(s) :: Cash On Hand Cash Fund Cash in BankJulie Mae Caling MalitNo ratings yet
- CA Inter Costing May 2024Document471 pagesCA Inter Costing May 2024guptaharshit2204No ratings yet
- Sapthagiri - Inv-131Document3 pagesSapthagiri - Inv-131KK SinghNo ratings yet
- Lampiran A / Senarai Kod Dan Jenis Aktiviti Perniagaan Kod / KeteranganDocument2 pagesLampiran A / Senarai Kod Dan Jenis Aktiviti Perniagaan Kod / KeterangandanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer GED 104 - The Contemporary WorldDocument11 pagesReviewer GED 104 - The Contemporary WorldEurs RocamoraNo ratings yet
- Practical FAQs On Supply and Taxability 04.02.2022Document223 pagesPractical FAQs On Supply and Taxability 04.02.2022Aashish GargNo ratings yet
- Quota Impacts and DisadvantagesDocument2 pagesQuota Impacts and DisadvantagesDarshika Singh - KumarNo ratings yet
- SS2202036 - House BLDocument1 pageSS2202036 - House BLSon KimNo ratings yet
- Southeast University: AssignmentDocument11 pagesSoutheast University: AssignmentNifaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics - Chapter 12Document19 pagesMacroeconomics - Chapter 12tomshave28No ratings yet
- Ch-3 IMDocument9 pagesCh-3 IMJohnny KinfeNo ratings yet
- MCQ Topic Vise-MinDocument405 pagesMCQ Topic Vise-MinHitesh -No ratings yet
- Invoice No 305 313Document9 pagesInvoice No 305 313Aakash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management For EM StudentsDocument24 pagesInventory Management For EM StudentsShahriar KabirNo ratings yet
- Eriksen e Silva (2009) - The Vulnerability Context of A Savanna Area in Mozambique PDFDocument20 pagesEriksen e Silva (2009) - The Vulnerability Context of A Savanna Area in Mozambique PDFJossias Hélder HumbaneNo ratings yet