Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DSA00496247
DSA00496247
Uploaded by
EvaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Awg-9 Apg-71 Ba0595Document7 pagesAwg-9 Apg-71 Ba0595spacenavy90No ratings yet
- Advac Guerero Chapter 15Document18 pagesAdvac Guerero Chapter 15Drew BanlutaNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management in TATA POWERDocument104 pagesTotal Quality Management in TATA POWERAnil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Airbus EtopsDocument99 pagesAirbus Etopskonser100% (2)
- D D D D D D D D: DescriptionDocument20 pagesD D D D D D D D: Descriptionwaleed hsaneenNo ratings yet
- D D D D D D D D D D: SN75179B Differential Driver and Receiver PairDocument9 pagesD D D D D D D D D D: SN75179B Differential Driver and Receiver PairSamuel White RospigliozziNo ratings yet
- SN 75179Document10 pagesSN 75179normarina de barriosNo ratings yet
- SN 65 LVDM 176Document25 pagesSN 65 LVDM 176jeremyNo ratings yet
- D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D: SN75ALS170, SN75ALS170A Triple Differential Bus TransceiverDocument22 pagesD D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D: SN75ALS170, SN75ALS170A Triple Differential Bus TransceiverDedii KurniawanNo ratings yet
- SN75176BDocument12 pagesSN75176Bjnfgames1No ratings yet
- Datasheet 18Document29 pagesDatasheet 18Maicon SouzaNo ratings yet
- D D D D D D D D D D D D D: SN75ALS1177, SN75ALS1178 Dual Differential Drivers and ReceiversDocument16 pagesD D D D D D D D D D D D D: SN75ALS1177, SN75ALS1178 Dual Differential Drivers and ReceiversMichael_Stefan_5630No ratings yet
- AD7376Document20 pagesAD7376Benny Alconn100% (1)
- 3 V/5 V, Rail-to-Rail Quad, 8-Bit DAC AD7304/AD7305: Features Functional Block DiagramsDocument20 pages3 V/5 V, Rail-to-Rail Quad, 8-Bit DAC AD7304/AD7305: Features Functional Block DiagramsAvs ElectronNo ratings yet
- Tpic6595 PDFDocument9 pagesTpic6595 PDFljNo ratings yet
- SN75172 LCB 2 Ci TransceiverDocument16 pagesSN75172 LCB 2 Ci TransceiverHUGO SOARESNo ratings yet
- SN 65 Als 176Document16 pagesSN 65 Als 176atomo atomoNo ratings yet
- 10-Bit 60 MSPSDocument12 pages10-Bit 60 MSPSlucas_guerrero2No ratings yet
- D D D D D D D D D D D D: TLV5618A 2.7-V TO 5.5-V LOW-POWER DUAL 12-BIT Digital-To-Analog Converter With Power DownDocument23 pagesD D D D D D D D D D D D: TLV5618A 2.7-V TO 5.5-V LOW-POWER DUAL 12-BIT Digital-To-Analog Converter With Power DownJulio Rafael GamboaNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument15 pagesDatasheetMindSet MarcosNo ratings yet
- Strong Fet™ Irfb7545Pbf: Application V 60V R Typ. 4.9M Max 5.9M I 95ADocument10 pagesStrong Fet™ Irfb7545Pbf: Application V 60V R Typ. 4.9M Max 5.9M I 95Aejdigger ejNo ratings yet
- الكتروني الاقطابDocument13 pagesالكتروني الاقطابصنم الديمقراطيهNo ratings yet
- Low-Power Rs-485 Transceiver: Features DescriptionDocument18 pagesLow-Power Rs-485 Transceiver: Features DescriptionRUANG KOSONGNo ratings yet
- 6LB176 PDFDocument22 pages6LB176 PDFWill ?No ratings yet
- Strong Fet™ Irfb7446Pbf: Application V 40V R Typ. 2.6M Max 3.3M I 123A I 120ADocument10 pagesStrong Fet™ Irfb7446Pbf: Application V 40V R Typ. 2.6M Max 3.3M I 123A I 120ANobreak ServiceNo ratings yet
- D D D D D D D D D D D: Description/ordering InformationDocument14 pagesD D D D D D D D D D D: Description/ordering InformationКонстантин МережкоNo ratings yet
- Ad 7528Document8 pagesAd 7528somtchekusNo ratings yet
- 1TWD026202N0101Document65 pages1TWD026202N0101nknfiveNo ratings yet
- 12-Bit 200 KSPS Complete Sampling ADC AD678 : Input ImpedanceDocument14 pages12-Bit 200 KSPS Complete Sampling ADC AD678 : Input ImpedanceMohammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Features Description: Micropower Inverting DC/DC ConverterDocument6 pagesFeatures Description: Micropower Inverting DC/DC ConverterJosé FariaNo ratings yet
- TLC5620Document14 pagesTLC5620Dirson Volmir WilligNo ratings yet
- Ad 9228Document53 pagesAd 9228Deddy WilopoNo ratings yet
- Richtek Tech R7731AGE C250411Document14 pagesRichtek Tech R7731AGE C250411Игорь ПочепаNo ratings yet
- Irf2110 AplicationDocument30 pagesIrf2110 Aplicationanand100% (1)
- D D D D D D D D D D D: SN65175, SN75175 Quadruple Differential Line ReceiversDocument22 pagesD D D D D D D D D D D: SN65175, SN75175 Quadruple Differential Line ReceiversSekoNo ratings yet
- D D D D D D D D: Peripheral Drivers For High-Voltage High-Current Driver ApplicationsDocument16 pagesD D D D D D D D: Peripheral Drivers For High-Voltage High-Current Driver ApplicationsTiago PremerlNo ratings yet
- Ad5547 5557Document20 pagesAd5547 5557이길현No ratings yet
- D D D D D D D D: SN75437A Quadruple Peripheral DriverDocument7 pagesD D D D D D D D: SN75437A Quadruple Peripheral DriverCarlos Luis ColmenaresNo ratings yet
- RM9003A DatasheetDocument8 pagesRM9003A Datasheetminami.jiro.87No ratings yet
- Auirfr 5505 TRDocument13 pagesAuirfr 5505 TRneluNo ratings yet
- Strong Fet™ Irfb7546Pbf: Application V 60V R Typ. 6.0M Max 7.3M I 75ADocument10 pagesStrong Fet™ Irfb7546Pbf: Application V 60V R Typ. 6.0M Max 7.3M I 75AYaraNo ratings yet
- Irfb4310Zpbf Irfs4310Zpbf Irfsl4310Zpbf: V 100V R Typ. 4.8M: Max. 6.0M: I 127A C I 120ADocument11 pagesIrfb4310Zpbf Irfs4310Zpbf Irfsl4310Zpbf: V 100V R Typ. 4.8M: Max. 6.0M: I 127A C I 120ALuis FigueroaNo ratings yet
- 9n90b 9n90cDocument7 pages9n90b 9n90cSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- s7200 System Manual PinoutDocument1 pages7200 System Manual Pinoutluis palaciosNo ratings yet
- Adm 2486Document20 pagesAdm 2486tinkeringengineerNo ratings yet
- N-And P-Channel 30-V (D-S) MOSFET: General Description FeaturesDocument1 pageN-And P-Channel 30-V (D-S) MOSFET: General Description FeaturesRicardo VillarroelNo ratings yet
- 3A, 18V, 340Khz Synchronous Step-Down Converter: General Description FeaturesDocument14 pages3A, 18V, 340Khz Synchronous Step-Down Converter: General Description FeaturesAgung KaryaNo ratings yet
- APM9948J: Features Pin DescriptionDocument9 pagesAPM9948J: Features Pin DescriptionGsay TockerNo ratings yet
- Variable Resolution, Monolithic Resolver-to-Digital Converters AD2S81A/AD2S82ADocument16 pagesVariable Resolution, Monolithic Resolver-to-Digital Converters AD2S81A/AD2S82AAilton SorlagNo ratings yet
- Ic DatasheetDocument19 pagesIc DatasheetAmin UdinNo ratings yet
- Scds 137Document22 pagesScds 137Katvia LiannaNo ratings yet
- Sir474Dp: Vishay SiliconixDocument13 pagesSir474Dp: Vishay Siliconixservicom3001No ratings yet
- Ucc2808 2Document10 pagesUcc2808 2servitec informaticaNo ratings yet
- LMB162GDCDocument1 pageLMB162GDCameer4009 ahmedNo ratings yet
- 0001 RevBDocument3 pages0001 RevBManuel A. Silva PainénNo ratings yet
- CD 54 HC 4511Document22 pagesCD 54 HC 4511rizalNo ratings yet
- Features Applications: D D D D D D D D D D D D D D DDocument15 pagesFeatures Applications: D D D D D D D D D D D D D D DĐịnh Xuân HàNo ratings yet
- 90N10Document5 pages90N10Oymy YaseenNo ratings yet
- Ad1674 - 12-Bit 100 KspsadcDocument13 pagesAd1674 - 12-Bit 100 Kspsadc40818248No ratings yet
- SN 74 Abt 16500 BDocument11 pagesSN 74 Abt 16500 Bmaxa95xf4No ratings yet
- Ad 768Document20 pagesAd 768Tim Lai Ky UcNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversFrom EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversNo ratings yet
- Service Standard 05 Prevention and Control of InfectionDocument25 pagesService Standard 05 Prevention and Control of InfectionSuhaimeNo ratings yet
- Advanced Tax Laws and PracticeDocument8 pagesAdvanced Tax Laws and Practicesheena2saNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper Human BehaviorDocument1 pageReaction Paper Human BehaviorEsteve DagdagNo ratings yet
- Technical Proposal CAREDocument9 pagesTechnical Proposal CAREfeyera100% (1)
- Solar Dryer IFRJDocument18 pagesSolar Dryer IFRJdzaki ramadhanNo ratings yet
- Geophysic and Res ManagementDocument33 pagesGeophysic and Res Managementdina mutia sariNo ratings yet
- Product Data: 220 VA Power Amplifier - Type 2707Document6 pagesProduct Data: 220 VA Power Amplifier - Type 2707jhon vargasNo ratings yet
- Goat Production HandbookDocument100 pagesGoat Production HandbookAdrianNo ratings yet
- Vesda Laser Focus 250Document2 pagesVesda Laser Focus 250WERMERMNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Problem SolutionsDocument36 pagesTutorial 2 Problem SolutionsshazNo ratings yet
- Business StudiesDocument13 pagesBusiness StudiesSargam ShahNo ratings yet
- Mec 422 Lecture 4Document37 pagesMec 422 Lecture 4Zhen LinNo ratings yet
- Keyboard Shortcuts For Windows and MacDocument13 pagesKeyboard Shortcuts For Windows and MacJahirul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Using A ComputerDocument30 pagesUsing A ComputerJEEHANDSOME RANDOMNo ratings yet
- Final Year Project ReportDocument27 pagesFinal Year Project ReportVaibhav BokareNo ratings yet
- Green Economy & TradeDocument4 pagesGreen Economy & TradeAbdiel HernándezNo ratings yet
- Papers SelectionDocument3 pagesPapers Selectionanony starkNo ratings yet
- Uso Cursores Anidados PDFDocument7 pagesUso Cursores Anidados PDFIvan AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- E-Gold Secrets: Free)Document19 pagesE-Gold Secrets: Free)Mohamed WahidNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Contingency - Squeeze (Shoe, Top Liner) : Desired DesiredDocument2 pages1.1 Contingency - Squeeze (Shoe, Top Liner) : Desired DesiredilkerkozturkNo ratings yet
- KBT65DP15 15RT0Document1 pageKBT65DP15 15RT0Andre LanaNo ratings yet
- Duolingo 50 Words Essay Questions and AnswerDocument7 pagesDuolingo 50 Words Essay Questions and AnswerMaria AgnesNo ratings yet
- District Wise List of Working Units of Eou'SDocument21 pagesDistrict Wise List of Working Units of Eou'SOm PrakashNo ratings yet
- Mindset MattersDocument19 pagesMindset Mattersracer100% (2)
- Vinyl Acetate Monomer VAM BrochureDocument2 pagesVinyl Acetate Monomer VAM BrochureMuslim Nasir100% (1)
- Competitive Tactics: TacticDocument18 pagesCompetitive Tactics: TacticRaniella SarmientoNo ratings yet
DSA00496247
DSA00496247
Uploaded by
EvaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DSA00496247
DSA00496247
Uploaded by
EvaCopyright:
Available Formats
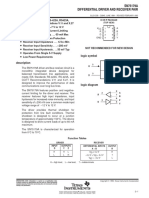
SN65LBC176A, SN75LBC176A
DIFFERENTIAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SLLS376B– MAY 2000 – REVISED SEPTEMBER 2000
D High-Speed Low-Power LinBiCMOS SN65LBC176AQD (Marked as L176AQ)
Circuitry Designed for Signaling Rates† Up SN65LBC176AD (Marked as BL176A)
SN65LBC176AP (Marked as 65LBC176A)
to 30 Mbps
SN75LBC176AD (Marked as LB176A)
D Bus-Pin ESD Protection Exceeds 12 kV SN75LBC176AP (Marked as 75LBC176A)
HBM (TOP VIEW)
D Compatible With ANSI Standard
R 1 8 VCC
TIA/EIA-485-A and ISO 8482:1987(E)
RE B
D
2 7
Low Skew DE 3 6 A
D Designed for Multipoint Transmission on D 4 5 GND
Long Bus Lines in Noisy Environments
D Very Low Disabled Supply-Current
Requirements . . . 700 µA Maximum
D Common Mode Voltage Range of –7 V
logic diagram (positive logic)
to 12 V 3
D Thermal-Shutdown Protection
DE
D Driver Positive and Negative Current D
4
Limiting 2
D
RE
Open-Circuit Fail-Safe Receiver Design 6
1 A
D Receiver Input Sensitivity . . . ± 200 mV Max R 7
B
Bus
D Receiver Input Hysteresis . . . 50 mV Typ
D Glitch-Free Power-Up and Power-Down Function Tables
Protection DRIVER
D Available in Q-Temp Automotive INPUT ENABLE OUTPUTS
High Reliability Automotive Applications D DE A B
Configuration Control / Print Support H H H L
Qualification to Automotive Standards L H L H
X L Z Z
description Open H H L
The SN65LBC176A, SN65LBC176AQ, and RECEIVER
SN75LBC176A differential bus transceivers are
DIFFERENTIAL INPUTS ENABLE OUTPUT
monolithic, integrated circuits designed for VA – VB RE R
bidirectional data communication on multipoint VID ≥ 0.2 V L H
bus-transmission lines. They are designed for – 0.2 V < VID < 0.2 V L ?
balanced transmission lines and are compatible VID ≤ – 0.2 V L L
with ANSI standard TIA/EIA-485-A and ISO 8482. X H Z
Open L H
The A version offers improved switching perfor-
mance over its predecessors without sacrificing H = high level, L = low level, ? = indeterminate,
X = irrelevant, Z = high impedance (off)
significantly more power.
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
† Signaling rate by TIA/EIA-485-A definition restrict transition times to 30% of the bit length, and much higher signaling rates may be achieved
without this requirement as displayed in the TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS of this device.
LinBiCMOS and LinASIC are trademarks of Texas Instruments.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date. Copyright 2000, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 1
SN65LBC176A, SN75LBC176A
DIFFERENTIAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SLLS376B– MAY 2000 – REVISED SEPTEMBER 2000
description (continued)
The SN65LBC176A, SN65LBC176AQ, and SN75LBC176A combine a 3-state, differential line driver and a
differential input line receiver, both of which operate from a single 5-V power supply. The driver and receiver
have active-high and active-low enables, respectively, which can externally connect together to function as a
direction control. The driver differential outputs and the receiver differential inputs connect internally to form a
differential input /output (I/O) bus port that is designed to offer minimum loading to the bus whenever the driver
is disabled or VCC = 0. This port features wide positive and negative common-mode voltage ranges, making
the device suitable for party-line applications. Very low device supply current can be achieved by disabling the
driver and the receiver.
AVAILABLE OPTIONS
PACKAGE
TA SMALL OUTLINE PLASTIC
(D) DUAL-IN-LINE
0°C to 70°C SN75LBC176AD SN75LBC176AP
– 40°C to 85°C SN65LBC176AD SN65LBC176AP
– 40°C to 125°C SN65LBC176AQD —
schematics of inputs and outputs
A Input
VCC
D, DE, and RE Inputs
VCC 16 V 100 kΩ
4 kΩ
100 kΩ
18 kΩ
1 kΩ Input
Input
16 V 4 kΩ
8V
B Input
R Output VCC
VCC
16 V
40 Ω 4 kΩ
Output 18 kΩ
Input
100 kΩ
8V
16 V 4 kΩ
2 POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
SN65LBC176A, SN75LBC176A
DIFFERENTIAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SLLS376B– MAY 2000 – REVISED SEPTEMBER 2000
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)†
Supply voltage, VCC (see Note 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to 6 V
Voltage range at any bus terminal (A or B) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . – 10 V to 15 V
Input voltage, VI (D, DE, R, or RE) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to VCC + 0.5 V
Electrostatic discharge: Bus terminals and GND, Class 3, A: (see Note 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 kV
Bus terminals and GND, Class 3, B: (see Note 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 400 V
All terminals, Class 3, A: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 kV
All terminals, Class 3, B: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 400 V
Continuous total power dissipation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Dissipation Rating Table
Storage temperature range, Tstg . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . – 65°C to 150°C
Lead temperature 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 260°C
† Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
NOTES: 1. All voltage values, except differential I/O bus voltage, are with respect to network ground terminal.
2. The maximum operating junction temperature is internally limited. Use the dissipation rating table to operate below this temperature.
DISSIPATION RATING TABLE
TA ≤ 25°C DERATING FACTOR‡ TA = 70°C TA = 85°C TA = 125°C
PACKAGE
POWER RATING ABOVE TA = 25°C POWER RATING POWER RATING POWER RATING
D 725 mW 5.8 mW/°C 464 mW 377 mW 145 mW
P 1000 mW 8.0 mW/°C 640 mW 520 mW —
‡ This is the inverse of the junction-to-ambient thermal resistance when board-mounted and with no air flow.
recommended operating conditions
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
Supply voltage, VCC 4.75 5 5.25 V
12
Voltage at any bus terminal (separately or common mode),
mode) VI or VIC V
–7
High-level input voltage, VIH (output recessive) D, DE, and RE 2 VCC V
Low-level input voltage, VIL (output dominant) D, DE, and RE 0 0.8 V
Differential input voltage, VID (see Note 3) –12§ 12 V
Driver – 60
High level output current,
High-level current IOH mA
Receiver –8
Driver 60
Low level output current
Low-level current, IOL mA
Receiver 8
SN65LBC176AQ – 40 125
Operating free-air temperature, TA SN65LBC176A – 40 85 °C
SN75LBC176A 0 70
§ The algebraic convention, in which the least positive (most negative) limit is designated as minimum, is used in this data sheet.
NOTE 3: Differential input /output bus voltage is measured at the noninverting terminal A with respect to the inverting terminal B.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 3
SN65LBC176A, SN75LBC176A
DIFFERENTIAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SLLS376B– MAY 2000 – REVISED SEPTEMBER 2000
driver electrical characteristics over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP† MAX UNIT
VIK Input clamp voltage II = – 18 mA –1.5 –0.8 V
SN65LBC176AQ 1.5 4 6
IO = 0 SN65LBC176A,
SN75LBC176A 4 V
SN65LBC176AQ 0.9 1.5 6
| VOD | Differential out
output
ut voltage RL = 54 Ω, See Figure 1 SN65LBC176A 1 1.5 3 V
SN75LBC176A 1.1 1.5 3
V
SN65LBC176AQ 0.9 1.5 6
Vtest = – 7 V to 12 V, See Figure 2 SN65LBC176A 1 1.5 3 V
SN75LBC176A 1.1 1.5 3 V
Change in magnitude of
∆| VOD | See Figures 1 and 2 –0.2 0.2 V
differential output voltage
SN65LBC176AQ 1.8 2.4 3
Steady-state
Steady state common-mode
common mode
VOC(SS) output voltage SN65LBC176A,
1.8 2.4 2.8
SN75LBC176A
See Figure 1 V
Change
g in steady-state
y SN65LBC176AQ –0.2 0.2
∆ VOC(SS) common-mode output SN65LBC176A,
voltage† –0.1 0.1
SN75LBC176A
High-impedance output
IOZ See receiver input currents
current
High-level enable input
IIH current VI = 2 V –100 µA
IIL Low-level enable input current VI = 0.8 V –100 µA
IOS Short-circuit output current – 7 V ≤ VO ≤ 12 V –250 ±70 250 mA
Receiver disabled and driver enabled 5 9
VI = 0 or VCC,
ICC Supply current Receiver disabled and driver disabled 0.4 0.7 mA
No load
Receiver enabled and driver enabled 8.5 15
† All typical values are at VCC = 5 V, TA = 25°C.
driver switching characteristics over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise
noted)
SN65LBC176A
TEST SN65LBC176AQ SN75LBC176A
PARAMETER UNIT
CONDITIONS
MIN TYP† MAX MIN TYP† MAX
tPLH Propagation delay time, low-to-high-level output 2 12 2 6 12 ns
tPHL Propagation delay time, high-to-low-level output RL = 54 Ω, 2 12 2 6 12 ns
tsk(p) Pulse skew ( | tPLH – tPHL | ) CL = 50 pF, 2 0.3 1 ns
tr Differential output signal rise time See Figure 3 1.2 8 4 7.5 11 ns
tf Differential output signal fall time 1.2 8 4 7.5 11 ns
Propagation delay time, high-impedance-to-high- RL = 110 Ω,
tPZH level output See Figure 4 22 12 22 ns
Propagation delay time, high-impedance-to-low- RL = 110 Ω,
tPZL level output See Figure 5 25 12 22 ns
Propagation delay time, high-level-to-high- RL = 110 Ω,
tPHZ impedance output See Figure 4 22 12 22 ns
Propagation delay time, low-level-to-high- RL = 110 Ω,
tPLZ impedance output See Figure 5 22 12 22 ns
† All typical values are at VCC = 5 V, TA = 25°C.
4 POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
SN65LBC176A, SN75LBC176A
DIFFERENTIAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SLLS376B– MAY 2000 – REVISED SEPTEMBER 2000
receiver electrical characteristics over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise
noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP† MAX UNIT
Positive-going input threshold
VIT + voltage IO = –8 mA 0.2 V
Negative-going input threshold
VIT – voltage – 0.2 V
IO = 8 mA
Vhys Hysteresis voltage (VIT + – VIT –) 50 mV
VIK Enable-input clamp voltage II = – 18 mA – 1.5 – 0.8 V
VOH High-level output voltage VID = 200 mV, IOH = – 8 mA, See Figure 6 4 4.9 V
VOL Low-level output voltage VID = 200 mV, IOL = 8 mA, See Figure 6 0.1 0.8 V
SN65LBC176AQ –10 10
IOZ High-impedance-state output current VO = 0 to VCC SN65LBC176A, µA
–1 1
SN75LBC176A
VIH = 12 V, VCC = 5 V 0.4 1
VIH = 12 V, VCC = 0 0.5 1
II Bus input current Other input at 0 V mA
VIH = – 7 V, VCC = 5 V –0.8 – 0.4
VIH = – 7 V, VCC = 0 –0.8 – 0.3
IIH High-level enable-input current VIH = 2 V – 100 µA
IIL Low-level enable-input current VIL = 0.8 V – 100 µA
Receiver enabled and driver disabled 4 7
VI = 0 or VCC,
ICC Supply current Receiver disabled and driver disabled 0.4 0.7 mA
No load
Receiver enabled and driver enabled 8.5 15
† All typical values are at VCC = 5 V, TA = 25°C.
receiver switching characteristics over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise
noted)
SN65LBC176A
SN65LBC176AQ SN75LBC176A
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS UNIT
MIN TYP† MAX MIN TYP† MAX
tPLH Propagation delay time, output↑ 7 30 7 13 20 ns
VID = – 1.5
1 5 V to
t 1.5
1 5 V,
V
tPHL Propagation delay time, output↓ 7 30 7 13 20 ns
See Figure 7
tsk(p) Pulse skew ( | tPHL – tPLH | ) 6 0.5 1.5 ns
tr Rise time, output 5 2.1 3.3 ns
See Figure 7
tf Fall time, output 5 2.1 3.3 ns
tPZH Output enable time to high level 50 30 45 ns
tPZL Output enable time to low level CL = 10 pF, 50 30 45 ns
tPHZ Output disable time from high level See Figure 8 60 20 40 ns
tPLZ Output disable time from low level 40 20 40 ns
† All typical values are at VCC = 5 V, TA = 25°C.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 5
SN65LBC176A, SN75LBC176A
DIFFERENTIAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SLLS376B– MAY 2000 – REVISED SEPTEMBER 2000
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
Vtest
R1
375 Ω
Y
27 Ω
D
RL = 60 Ω VOD
0 or 3 V VOD 0 V or 3 V
27 Ω VOC
Z
R2
Figure 1. Driver VOD and VOC – 7 V < Vtest < 12 V 375 Ω
Vtest
Figure 2. Driver VOD3
3V
Input 1.5 V 1.5 V
CL = 50 pF
(see Note B) 0V
RL = 54 Ω tPLH tPHL
Generator
50 Ω VO
(see Note A)
≈ 1.5 V
90%
Output 50%
10%
≈ – 1.5 V
tr tf
TEST CIRCUIT VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
NOTES: A. The input pulse is supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: PRR ≤ 1 MHz, 50% duty cycle, tr ≤ 6 ns, tf ≤ 6 ns,
ZO = 50 Ω.
B. CL includes probe and jig capacitance.
Figure 3. Driver Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
Output 3V
S1 Input 1.5 V 1.5 V
3V 0V
tPZH 0.5 V
CL = 50 pF RL = 110 Ω
VOH
Generator (see Note B)
50 Ω Output 2.3 V
(see Note A)
tPHZ Voff ≈ 0 V
TEST CIRCUIT VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
NOTES: A. The input pulse is supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: PRR ≤ 1 MHz, 50% duty cycle, tr ≤ 6 ns, tf ≤ 6 ns,
ZO = 50 Ω.
B. CL includes probe and jig capacitance.
Figure 4. Driver Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
6 POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
SN65LBC176A, SN75LBC176A
DIFFERENTIAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SLLS376B– MAY 2000 – REVISED SEPTEMBER 2000
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
5V 3V
RL = 110 Ω Input 1.5 V 1.5 V
S1 0V
0V Output tPZL
tPLZ
CL = 50 pF
Generator (see Note B) 5V
50 Ω 2.3 V 0.5 V
(see Note A) Output
VOL
TEST CIRCUIT VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
NOTES: A. The input pulse is supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: PRR ≤ 1 MHz, 50% duty cycle, tr ≤ 6 ns, tf ≤ 6 ns,
ZO = 50 Ω.
B. CL includes probe and jig capacitance.
Figure 5. Driver Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
IO
VID
VO
Figure 6. Receiver VOH and VOL
3V
Input 1.5 V 1.5 V
Generator Output 0V
50 Ω
(see Note A)
1.5 V tPLH tPHL
CL = 10 pF VOH
(see Note B) 90%
Output 1.3 V 1.3 V
0V
10%
VOL
tR tF
TEST CIRCUIT VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
NOTES: A. The input pulse is supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: PRR ≤ 1 MHz, 50% duty cycle, tr ≤ 6 ns, tf ≤ 6 ns,
ZO = 50 Ω.
B. CL includes probe and jig capacitance.
Figure 7. Receiver Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 7
SN65LBC176A, SN75LBC176A
DIFFERENTIAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SLLS376B– MAY 2000 – REVISED SEPTEMBER 2000
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
S1
1.5 V
2 kΩ S2
–1.5 V 5V
CL = 10 pF 5 kΩ
(see Note B)
Generator
(see Note A) 50 Ω
S3
TEST CIRCUIT
3V 3V
S1 to 1.5 V S1 to –1.5 V
Input 1.5 V S2 Open Input 1.5 V S2 Closed
S3 Closed S3 Open
0V 0V
tPZH
tPZL
VOH ≈ 4.5 V
Output 1.5 V
Output 1.5 V
0V
VOL
3V 3V
S1 to 1.5 V S1 to –1.5 V
Input 1.5 V S2 Closed Input 1.5 V S2 Closed
S3 Closed S3 Closed
0V 0V
tPHZ
tPLZ
≈ 1.3 V
VOH
Output 0.5 V Output 0.5 V
≈ 1.3 V VOL
VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
NOTES: A. The input pulse is supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: PRR ≤ 1 MHz, 50% duty cycle, tr ≤ 6 ns, tf ≤ 6 ns,
ZO = 50 Ω.
B. CL includes probe and jig capacitance.
Figure 8. Receiver Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
8 POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
SN65LBC176A, SN75LBC176A
DIFFERENTIAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SLLS376B– MAY 2000 – REVISED SEPTEMBER 2000
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Receiver Output
Driver Input
120 Ω 120 Ω
Driver Input Receiver Output
Figure 9. Typical Waveform of Non-Return-To-Zero (NRZ), Pseudorandom Binary Sequence (PRBS) Data
at 100 Mbps Through 15m, of CAT 5 Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable
TIA/EIA-485-A defines a maximum signaling rate as that in which the transition time of the voltage transition
of a logic-state change remains less than or equal to 30% of the bit length. Transition times of greater length
perform quite well even though they do not meet the standard by definition.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 9
SN65LBC176A, SN75LBC176A
DIFFERENTIAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SLLS376B– MAY 2000 – REVISED SEPTEMBER 2000
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
AVERAGE SUPPLY CURRENT LOGIC INPUT CURRENT
vs vs
FREQUENCY INPUT VOLTAGE
40 –30
Driver
35
–25
I CC – Average Supply Current – mA
30
I I – Input Current – µ A
–20
25
20 –15
15
–10
10
Receiver
–5
5
0 0
0.05 0.5 1 2 5 10 20 30 0 1 2 3 4 5
f – Frequency – MHz VI – Input Voltage – V
Figure 10 Figure 11
INPUT CURRENT LOW-LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE
vs vs
INPUT VOLTAGE LOW-LEVEL OUTPUT CURRENT
800 2.00
600 1.75
VOL – Low-Level Output voltage – V
I I – Input Current – µ A
1.50 VCC = 5
400
1.25
200
1.00
0
0.75
–200
0.50
Bus Input Current
–400 0.25
–600 0
–8 –6 –4 –2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
VI – Input Voltage – V IOL – Low-Level Output Current – mA
Figure 12 Figure 13
10 POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
SN65LBC176A, SN75LBC176A
DIFFERENTIAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SLLS376B– MAY 2000 – REVISED SEPTEMBER 2000
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
DRIVER HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE DRIVER DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT VOLTAGE
vs vs
HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT CURRENT AVERAGE CASE TEMPERATURE
5 2
VOD – Average Differential Output Voltage – V
4.5
VOH – High-Level Output Voltage – V
4 VCC = 5.25 V
1.5
3.5
2.5 VCC = 5 V 1
2
VCC = 4.75 V
1.5
0.5
1
0.5
0 0
0 –10 –20 –30 –40 –50 –60 –70 –80 –40 0 25 70 85
IOH – High-Level Output Current – (mA) Average Case Temperature – ° C
Figure 14 Figure 15
RECEIVER PROPAGATION TIME DRIVER PROPAGATION DELAY TIME
vs vs
CASE TEMPERATURE CASE TEMPERATURE
13.8 7.4
13.7 7.2
13.6 7
Propagation Delay Time – ns
TPHL Receiver (ns)
13.5 6.8
13.4 6.6
13.3 6.4
13.2 6.2
13.1 6
13 5.8
12.9 5.6
–40 0 25 70 80 –40 0 25 70 85
Case Temperature ° C Case Temperature – ° C
Figure 16 Figure 17
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 11
SN65LBC176A, SN75LBC176A
DIFFERENTIAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SLLS376B– MAY 2000 – REVISED SEPTEMBER 2000
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
DRIVER OUTPUT CURRENT
vs
SUPPLY VOLTAGE
90
65
40
I O – Output Current – mA
15
IOH
–10
–35
–60
–85
–110
–135 IOL
–160
–185
–210
0 3 4 5 6
VCC – Supply Voltage – V
Figure 18
12 POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
SN65LBC176A, SN75LBC176A
DIFFERENTIAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SLLS376B– MAY 2000 – REVISED SEPTEMBER 2000
MECHANICAL INFORMATION
D (R-PDSO-G**) PLASTIC SMALL-OUTLINE PACKAGE
14 PINS SHOWN
0.050 (1,27)
0.020 (0,51)
0.010 (0,25) M
0.014 (0,35)
14 8
0.008 (0,20) NOM
0.244 (6,20)
0.228 (5,80)
0.157 (4,00)
0.150 (3,81)
Gage Plane
0.010 (0,25)
1 7
0°– 8°
0.044 (1,12)
A 0.016 (0,40)
Seating Plane
0.010 (0,25) 0.004 (0,10)
0.069 (1,75) MAX
0.004 (0,10)
PINS **
8 14 16
DIM
0.197 0.344 0.394
A MAX
(5,00) (8,75) (10,00)
0.189 0.337 0.386
A MIN
(4,80) (8,55) (9,80)
4040047 / D 10/96
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters).
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Body dimensions do not include mold flash or protrusion, not to exceed 0.006 (0,15).
D. Falls within JEDEC MS-012
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 13
SN65LBC176A, SN75LBC176A
DIFFERENTIAL BUS TRANSCEIVERS
SLLS376B– MAY 2000 – REVISED SEPTEMBER 2000
MECHANICAL INFORMATION
P (R-PDIP-T8) PLASTIC DUAL-IN-LINE
0.400 (10,60)
0.355 (9,02)
8 5
0.260 (6,60)
0.240 (6,10)
1 4
0.070 (1,78) MAX
0.325 (8,26)
0.020 (0,51) MIN
0.300 (7,62)
0.015 (0,38)
Gage Plane
0.200 (5,08) MAX
Seating Plane
0.125 (3,18) MIN 0.010 (0,25) NOM
0.100 (2,54) 0.430 (10,92)
MAX
0.021 (0,53)
0.010 (0,25) M
0.015 (0,38)
4040082/D 05/98
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters).
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Falls within JEDEC MS-001
For the latest package information, go to http://www.ti.com/sc/docs/package/pkg_info.htm
14 POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue
any product or service without notice, and advise customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information
to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold
subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment, including those
pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation of liability.
TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are utilized to the extent
TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Specific testing of all parameters of each device is not necessarily
performed, except those mandated by government requirements.
Customers are responsible for their applications using TI components.
In order to minimize risks associated with the customer’s applications, adequate design and operating
safeguards must be provided by the customer to minimize inherent or procedural hazards.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. TI does not warrant or represent
that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other
intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any combination, machine, or process in which such
semiconductor products or services might be or are used. TI’s publication of information regarding any third
party’s products or services does not constitute TI’s approval, warranty or endorsement thereof.
Copyright 2000, Texas Instruments Incorporated
You might also like
- Awg-9 Apg-71 Ba0595Document7 pagesAwg-9 Apg-71 Ba0595spacenavy90No ratings yet
- Advac Guerero Chapter 15Document18 pagesAdvac Guerero Chapter 15Drew BanlutaNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management in TATA POWERDocument104 pagesTotal Quality Management in TATA POWERAnil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Airbus EtopsDocument99 pagesAirbus Etopskonser100% (2)
- D D D D D D D D: DescriptionDocument20 pagesD D D D D D D D: Descriptionwaleed hsaneenNo ratings yet
- D D D D D D D D D D: SN75179B Differential Driver and Receiver PairDocument9 pagesD D D D D D D D D D: SN75179B Differential Driver and Receiver PairSamuel White RospigliozziNo ratings yet
- SN 75179Document10 pagesSN 75179normarina de barriosNo ratings yet
- SN 65 LVDM 176Document25 pagesSN 65 LVDM 176jeremyNo ratings yet
- D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D: SN75ALS170, SN75ALS170A Triple Differential Bus TransceiverDocument22 pagesD D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D: SN75ALS170, SN75ALS170A Triple Differential Bus TransceiverDedii KurniawanNo ratings yet
- SN75176BDocument12 pagesSN75176Bjnfgames1No ratings yet
- Datasheet 18Document29 pagesDatasheet 18Maicon SouzaNo ratings yet
- D D D D D D D D D D D D D: SN75ALS1177, SN75ALS1178 Dual Differential Drivers and ReceiversDocument16 pagesD D D D D D D D D D D D D: SN75ALS1177, SN75ALS1178 Dual Differential Drivers and ReceiversMichael_Stefan_5630No ratings yet
- AD7376Document20 pagesAD7376Benny Alconn100% (1)
- 3 V/5 V, Rail-to-Rail Quad, 8-Bit DAC AD7304/AD7305: Features Functional Block DiagramsDocument20 pages3 V/5 V, Rail-to-Rail Quad, 8-Bit DAC AD7304/AD7305: Features Functional Block DiagramsAvs ElectronNo ratings yet
- Tpic6595 PDFDocument9 pagesTpic6595 PDFljNo ratings yet
- SN75172 LCB 2 Ci TransceiverDocument16 pagesSN75172 LCB 2 Ci TransceiverHUGO SOARESNo ratings yet
- SN 65 Als 176Document16 pagesSN 65 Als 176atomo atomoNo ratings yet
- 10-Bit 60 MSPSDocument12 pages10-Bit 60 MSPSlucas_guerrero2No ratings yet
- D D D D D D D D D D D D: TLV5618A 2.7-V TO 5.5-V LOW-POWER DUAL 12-BIT Digital-To-Analog Converter With Power DownDocument23 pagesD D D D D D D D D D D D: TLV5618A 2.7-V TO 5.5-V LOW-POWER DUAL 12-BIT Digital-To-Analog Converter With Power DownJulio Rafael GamboaNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument15 pagesDatasheetMindSet MarcosNo ratings yet
- Strong Fet™ Irfb7545Pbf: Application V 60V R Typ. 4.9M Max 5.9M I 95ADocument10 pagesStrong Fet™ Irfb7545Pbf: Application V 60V R Typ. 4.9M Max 5.9M I 95Aejdigger ejNo ratings yet
- الكتروني الاقطابDocument13 pagesالكتروني الاقطابصنم الديمقراطيهNo ratings yet
- Low-Power Rs-485 Transceiver: Features DescriptionDocument18 pagesLow-Power Rs-485 Transceiver: Features DescriptionRUANG KOSONGNo ratings yet
- 6LB176 PDFDocument22 pages6LB176 PDFWill ?No ratings yet
- Strong Fet™ Irfb7446Pbf: Application V 40V R Typ. 2.6M Max 3.3M I 123A I 120ADocument10 pagesStrong Fet™ Irfb7446Pbf: Application V 40V R Typ. 2.6M Max 3.3M I 123A I 120ANobreak ServiceNo ratings yet
- D D D D D D D D D D D: Description/ordering InformationDocument14 pagesD D D D D D D D D D D: Description/ordering InformationКонстантин МережкоNo ratings yet
- Ad 7528Document8 pagesAd 7528somtchekusNo ratings yet
- 1TWD026202N0101Document65 pages1TWD026202N0101nknfiveNo ratings yet
- 12-Bit 200 KSPS Complete Sampling ADC AD678 : Input ImpedanceDocument14 pages12-Bit 200 KSPS Complete Sampling ADC AD678 : Input ImpedanceMohammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Features Description: Micropower Inverting DC/DC ConverterDocument6 pagesFeatures Description: Micropower Inverting DC/DC ConverterJosé FariaNo ratings yet
- TLC5620Document14 pagesTLC5620Dirson Volmir WilligNo ratings yet
- Ad 9228Document53 pagesAd 9228Deddy WilopoNo ratings yet
- Richtek Tech R7731AGE C250411Document14 pagesRichtek Tech R7731AGE C250411Игорь ПочепаNo ratings yet
- Irf2110 AplicationDocument30 pagesIrf2110 Aplicationanand100% (1)
- D D D D D D D D D D D: SN65175, SN75175 Quadruple Differential Line ReceiversDocument22 pagesD D D D D D D D D D D: SN65175, SN75175 Quadruple Differential Line ReceiversSekoNo ratings yet
- D D D D D D D D: Peripheral Drivers For High-Voltage High-Current Driver ApplicationsDocument16 pagesD D D D D D D D: Peripheral Drivers For High-Voltage High-Current Driver ApplicationsTiago PremerlNo ratings yet
- Ad5547 5557Document20 pagesAd5547 5557이길현No ratings yet
- D D D D D D D D: SN75437A Quadruple Peripheral DriverDocument7 pagesD D D D D D D D: SN75437A Quadruple Peripheral DriverCarlos Luis ColmenaresNo ratings yet
- RM9003A DatasheetDocument8 pagesRM9003A Datasheetminami.jiro.87No ratings yet
- Auirfr 5505 TRDocument13 pagesAuirfr 5505 TRneluNo ratings yet
- Strong Fet™ Irfb7546Pbf: Application V 60V R Typ. 6.0M Max 7.3M I 75ADocument10 pagesStrong Fet™ Irfb7546Pbf: Application V 60V R Typ. 6.0M Max 7.3M I 75AYaraNo ratings yet
- Irfb4310Zpbf Irfs4310Zpbf Irfsl4310Zpbf: V 100V R Typ. 4.8M: Max. 6.0M: I 127A C I 120ADocument11 pagesIrfb4310Zpbf Irfs4310Zpbf Irfsl4310Zpbf: V 100V R Typ. 4.8M: Max. 6.0M: I 127A C I 120ALuis FigueroaNo ratings yet
- 9n90b 9n90cDocument7 pages9n90b 9n90cSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- s7200 System Manual PinoutDocument1 pages7200 System Manual Pinoutluis palaciosNo ratings yet
- Adm 2486Document20 pagesAdm 2486tinkeringengineerNo ratings yet
- N-And P-Channel 30-V (D-S) MOSFET: General Description FeaturesDocument1 pageN-And P-Channel 30-V (D-S) MOSFET: General Description FeaturesRicardo VillarroelNo ratings yet
- 3A, 18V, 340Khz Synchronous Step-Down Converter: General Description FeaturesDocument14 pages3A, 18V, 340Khz Synchronous Step-Down Converter: General Description FeaturesAgung KaryaNo ratings yet
- APM9948J: Features Pin DescriptionDocument9 pagesAPM9948J: Features Pin DescriptionGsay TockerNo ratings yet
- Variable Resolution, Monolithic Resolver-to-Digital Converters AD2S81A/AD2S82ADocument16 pagesVariable Resolution, Monolithic Resolver-to-Digital Converters AD2S81A/AD2S82AAilton SorlagNo ratings yet
- Ic DatasheetDocument19 pagesIc DatasheetAmin UdinNo ratings yet
- Scds 137Document22 pagesScds 137Katvia LiannaNo ratings yet
- Sir474Dp: Vishay SiliconixDocument13 pagesSir474Dp: Vishay Siliconixservicom3001No ratings yet
- Ucc2808 2Document10 pagesUcc2808 2servitec informaticaNo ratings yet
- LMB162GDCDocument1 pageLMB162GDCameer4009 ahmedNo ratings yet
- 0001 RevBDocument3 pages0001 RevBManuel A. Silva PainénNo ratings yet
- CD 54 HC 4511Document22 pagesCD 54 HC 4511rizalNo ratings yet
- Features Applications: D D D D D D D D D D D D D D DDocument15 pagesFeatures Applications: D D D D D D D D D D D D D D DĐịnh Xuân HàNo ratings yet
- 90N10Document5 pages90N10Oymy YaseenNo ratings yet
- Ad1674 - 12-Bit 100 KspsadcDocument13 pagesAd1674 - 12-Bit 100 Kspsadc40818248No ratings yet
- SN 74 Abt 16500 BDocument11 pagesSN 74 Abt 16500 Bmaxa95xf4No ratings yet
- Ad 768Document20 pagesAd 768Tim Lai Ky UcNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversFrom EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversNo ratings yet
- Service Standard 05 Prevention and Control of InfectionDocument25 pagesService Standard 05 Prevention and Control of InfectionSuhaimeNo ratings yet
- Advanced Tax Laws and PracticeDocument8 pagesAdvanced Tax Laws and Practicesheena2saNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper Human BehaviorDocument1 pageReaction Paper Human BehaviorEsteve DagdagNo ratings yet
- Technical Proposal CAREDocument9 pagesTechnical Proposal CAREfeyera100% (1)
- Solar Dryer IFRJDocument18 pagesSolar Dryer IFRJdzaki ramadhanNo ratings yet
- Geophysic and Res ManagementDocument33 pagesGeophysic and Res Managementdina mutia sariNo ratings yet
- Product Data: 220 VA Power Amplifier - Type 2707Document6 pagesProduct Data: 220 VA Power Amplifier - Type 2707jhon vargasNo ratings yet
- Goat Production HandbookDocument100 pagesGoat Production HandbookAdrianNo ratings yet
- Vesda Laser Focus 250Document2 pagesVesda Laser Focus 250WERMERMNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Problem SolutionsDocument36 pagesTutorial 2 Problem SolutionsshazNo ratings yet
- Business StudiesDocument13 pagesBusiness StudiesSargam ShahNo ratings yet
- Mec 422 Lecture 4Document37 pagesMec 422 Lecture 4Zhen LinNo ratings yet
- Keyboard Shortcuts For Windows and MacDocument13 pagesKeyboard Shortcuts For Windows and MacJahirul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Using A ComputerDocument30 pagesUsing A ComputerJEEHANDSOME RANDOMNo ratings yet
- Final Year Project ReportDocument27 pagesFinal Year Project ReportVaibhav BokareNo ratings yet
- Green Economy & TradeDocument4 pagesGreen Economy & TradeAbdiel HernándezNo ratings yet
- Papers SelectionDocument3 pagesPapers Selectionanony starkNo ratings yet
- Uso Cursores Anidados PDFDocument7 pagesUso Cursores Anidados PDFIvan AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- E-Gold Secrets: Free)Document19 pagesE-Gold Secrets: Free)Mohamed WahidNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Contingency - Squeeze (Shoe, Top Liner) : Desired DesiredDocument2 pages1.1 Contingency - Squeeze (Shoe, Top Liner) : Desired DesiredilkerkozturkNo ratings yet
- KBT65DP15 15RT0Document1 pageKBT65DP15 15RT0Andre LanaNo ratings yet
- Duolingo 50 Words Essay Questions and AnswerDocument7 pagesDuolingo 50 Words Essay Questions and AnswerMaria AgnesNo ratings yet
- District Wise List of Working Units of Eou'SDocument21 pagesDistrict Wise List of Working Units of Eou'SOm PrakashNo ratings yet
- Mindset MattersDocument19 pagesMindset Mattersracer100% (2)
- Vinyl Acetate Monomer VAM BrochureDocument2 pagesVinyl Acetate Monomer VAM BrochureMuslim Nasir100% (1)
- Competitive Tactics: TacticDocument18 pagesCompetitive Tactics: TacticRaniella SarmientoNo ratings yet