Professional Documents
Culture Documents
05 Activity 1 - ARG
05 Activity 1 - ARG
Uploaded by
Marc AgradeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
05 Activity 1 - ARG
05 Activity 1 - ARG
Uploaded by
Marc AgradeCopyright:
Available Formats
Marc Adrian G.
Agrade A305
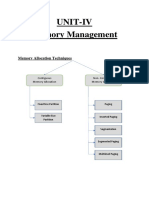
Platform Technology
1. Which partitioning setup could possibly reduce internal fragmentation and how?
- In the case of fixed partitioning, the partitions are wasted and would stay unused if the process
size is less than the partition size. When memory is wasted in this manner, it is referred to as
internal fragmentation. Internal fragmentation happens when a process demands more space
than the size of its given memory block or utilizes less space than the size of its allotted memory
block space.
2. Based on the two partitioning setup above, would you recommend the implementation
of the fixed partitioning technique in developing automated machines? Why or why not?
- My personal advice is that it be a fixed partition since one of the benefits of permanent
partitions is that data loss may be avoided during power outages or when software fails.
Equalsized partitions have facilitated faster data recovery in crucial scenarios, which would be
critical for any organization.
3. In your perspective, what are the possible downside of utilizing an equally sized
memory partitions? Rationalize your answer.
- A disadvantage of fixed partitions is the significant restriction that comes with the fixed or
allotted area in the specific partition. It is possible to have a big number of partitions while
providing one or two very large partitions. Huge partitions allow for the complete loading of large
applications. To lock a process's memory, it must be less than the partition's maximum size.
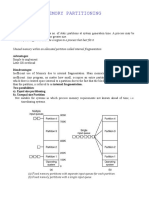
4. What do you think is the possible reason why Process 2 was pulled/swapped out € of
the memory?
- A process may be shifted from main memory for one of two reasons: it may be idle or it may
have been interrupted. In the above example, process 2 is most likely switched since it is idle.
5. When Process 1 finishes the execution (g) and Process 2 is swapped back in the
memory (h), what possible condition or phenomenon can occur within the memory?
Rationalize your answer.
- The processes are not completely eliminated until they are successfully implemented. In the
scheduling method, the CPU has been assigned to generate a certain process. This process is
what keeps the CPU busy and will eventually be terminated to relive the CPU.
6. If you are to develop a file management system, would you suggest the
implementation of the dynamic partitioning technique in memory management? Why or
why not?
- Yes, I would say. It would be ideal for me to utilize the dynamic partitioning strategy since it
attempts to solve the difficulties presented by fixed partitioning. Overall, because dynamic
partitioning partitions are produced based on the demands of the process, it is apparent that
there will be no internal fragmentation because there will be no unnecessary residual space in
the partition.
You might also like
- How Do I Convert My Root Disk To RAID1 After Installation of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7Document7 pagesHow Do I Convert My Root Disk To RAID1 After Installation of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7Aravind RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Installing Backtrack 5 R3 in Virtual Machine Step by Step (How To) - Computers and YouDocument22 pagesInstalling Backtrack 5 R3 in Virtual Machine Step by Step (How To) - Computers and YouRanjan Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- 05 Activity 1 OSDocument2 pages05 Activity 1 OSSharedNo ratings yet
- Platform TechnologyDocument2 pagesPlatform TechnologyRCOANo ratings yet
- CPE 301 Operating Systems November 26, 2022Document3 pagesCPE 301 Operating Systems November 26, 2022stapaNo ratings yet
- 05 ActDocument3 pages05 ActAbe SakalNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document3 pagesPart 1Muse Amor OrillaNo ratings yet
- 05 Activity 1 SantosDocument1 page05 Activity 1 SantosMatthew SantosNo ratings yet
- TALINAO 05 Acitivty 1Document4 pagesTALINAO 05 Acitivty 1Orange ShellyNo ratings yet
- 05 - Activity - 1Document5 pages05 - Activity - 1DATU AL-ANSARI UKONo ratings yet
- Unit-III (Memory Management)Document20 pagesUnit-III (Memory Management)Sunny ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Memory Management@Unit 3Document14 pagesMemory Management@Unit 3MANJU SharmaNo ratings yet
- Memory ManagementDocument20 pagesMemory Managementnehavj664No ratings yet
- Foundations of It Assignment.Document1 pageFoundations of It Assignment.okemwavictor72No ratings yet
- Analysis of Allocation Algorithms in Memory ManagementDocument3 pagesAnalysis of Allocation Algorithms in Memory ManagementEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 Memory ManagementDocument31 pagesUNIT 4 Memory ManagementMohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Q.1 Explain Memory Management Requirements?: - The Available Memory Is Generally Shared Among ADocument10 pagesQ.1 Explain Memory Management Requirements?: - The Available Memory Is Generally Shared Among ARamesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Memory ManagementDocument11 pagesChapter Three: Memory ManagementmehariNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 ManagementDocument12 pagesUnit 7 ManagementCindy CortezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Memory ManagementDocument60 pagesChapter 6 - Memory Managementsibhat mequanintNo ratings yet
- OS Unit 4Document76 pagesOS Unit 4HARSHA VINAY KOTNI HU21CSEN0100574No ratings yet
- Fixed (Or Static) Partitioning in Operating SystemDocument6 pagesFixed (Or Static) Partitioning in Operating SystemnirobNo ratings yet
- Memory Management in Operating SystemDocument5 pagesMemory Management in Operating Systemgyan prakashNo ratings yet
- OS Unit-3Document13 pagesOS Unit-3Madhu SudhanNo ratings yet
- TCS Aspire - Chapter 4Document6 pagesTCS Aspire - Chapter 4himanshu_garg93No ratings yet
- Huzaifa Task 7Document7 pagesHuzaifa Task 7fiazhussainlakNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document34 pagesUnit 4Naveen KumarNo ratings yet
- 05 Activity 1 MamingDocument2 pages05 Activity 1 MamingJameson MamingNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Contiguous Memory AllocationDocument3 pages4.3 Contiguous Memory Allocationmadhurivithanala07No ratings yet
- OS Unit 6Document13 pagesOS Unit 6BHAKTI AYAREKARNo ratings yet
- Mms 1Document33 pagesMms 1Aashi NegiNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 MemoryManagementDocument63 pagesUnit 5 MemoryManagementkalyan goudNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Memory ManagementDocument7 pagesModule 7 Memory ManagementnatsuNo ratings yet
- OS (405) - Activity-4Document8 pagesOS (405) - Activity-4Faiz PathanNo ratings yet
- Memory ManagementDocument10 pagesMemory ManagementSaroj MisraNo ratings yet
- Opearating SystemDocument5 pagesOpearating SystemMunish ManglaNo ratings yet
- Memory PartitioningDocument3 pagesMemory PartitioningpNo ratings yet
- TOPIC THREE Computer PersonelDocument4 pagesTOPIC THREE Computer PersonelOigara Onwong'aNo ratings yet
- Contigious Memory AllocationDocument24 pagesContigious Memory Allocationshahalameenu2003No ratings yet
- Memory Management of Operating SystemDocument37 pagesMemory Management of Operating Systemluqman192No ratings yet
- OS Chapter ThreeDocument9 pagesOS Chapter Threejan luNo ratings yet
- Os Unit-3Document34 pagesOs Unit-3Palagani BhagyasriNo ratings yet
- 3.memory Management - 20240103Document157 pages3.memory Management - 20240103prototypes6341No ratings yet
- Os - Memory Management in Operating SystemDocument10 pagesOs - Memory Management in Operating Systemluckysighania93No ratings yet
- Lec 12Document22 pagesLec 122.8M viewsNo ratings yet
- MMGMNT PDFDocument55 pagesMMGMNT PDFalihamzaNo ratings yet
- Memory ManagementDocument17 pagesMemory ManagementAmicable YcotNo ratings yet
- Partitioning Algorithms Operating SystemsDocument4 pagesPartitioning Algorithms Operating SystemsDIPTANU SAHANo ratings yet
- Topic Notes: Memory Management: Computer Science 322 Operating SystemsDocument25 pagesTopic Notes: Memory Management: Computer Science 322 Operating SystemsNeetika KatariaNo ratings yet
- AsdfghDocument42 pagesAsdfghbalu 1203No ratings yet
- UNIT 3 CHAPTER 5 (Memory Management)Document10 pagesUNIT 3 CHAPTER 5 (Memory Management)Faizal KhanNo ratings yet
- Ru CS Os 05Document42 pagesRu CS Os 05lutfullahNo ratings yet
- 05-Activity-1-Platform-Technology - Umpad - Christian Rhey - A. - BSCPE - G302Document2 pages05-Activity-1-Platform-Technology - Umpad - Christian Rhey - A. - BSCPE - G302Christian UmpadNo ratings yet
- FragmentationDocument3 pagesFragmentationHARISHNo ratings yet
- OS Research ReportDocument7 pagesOS Research ReportNimra ShahNo ratings yet
- Unit5 OsDocument20 pagesUnit5 Osईश्वर महालेNo ratings yet
- 05 Handout 1 (PlatTech)Document2 pages05 Handout 1 (PlatTech)See HorseNo ratings yet
- 3.memory Management 20240103Document41 pages3.memory Management 20240103prototypes6341No ratings yet
- Operating System MCA BPUT Unit-5Document31 pagesOperating System MCA BPUT Unit-5danger boyNo ratings yet
- Os Unit 4 ModifyDocument28 pagesOs Unit 4 ModifyKylee PerezNo ratings yet
- SAS Programming Guidelines Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandSAS Programming Guidelines Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- 01 Laboratory Exercise 1 - ARGDocument3 pages01 Laboratory Exercise 1 - ARGMarc AgradeNo ratings yet
- 01 Quiz 1A - ARGDocument1 page01 Quiz 1A - ARGMarc AgradeNo ratings yet
- 10 Activity 1 - ARGDocument2 pages10 Activity 1 - ARGMarc AgradeNo ratings yet
- Analysis TableDocument1 pageAnalysis TableMarc AgradeNo ratings yet
- 08 Laboratory Exercise 1 - ARGDocument2 pages08 Laboratory Exercise 1 - ARGMarc AgradeNo ratings yet
- Historical Facts of Chinatown, Binondo, ManilaDocument10 pagesHistorical Facts of Chinatown, Binondo, ManilaMarc AgradeNo ratings yet
- 09 Activity 1 - ARGDocument1 page09 Activity 1 - ARGMarc AgradeNo ratings yet
- 06 Activity 1Document1 page06 Activity 1Marc AgradeNo ratings yet
- Rizal's Life and Works - MIDTERM EXAMDocument1 pageRizal's Life and Works - MIDTERM EXAMMarc AgradeNo ratings yet
- 06 Quiz 1 - ARGDocument1 page06 Quiz 1 - ARGMarc AgradeNo ratings yet
- 06 Task-Performance ARGDocument1 page06 Task-Performance ARGMarc AgradeNo ratings yet
- 02TP1Document3 pages02TP1Marc AgradeNo ratings yet
- 041QUIZDocument2 pages041QUIZMarc AgradeNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: Silver Oak College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument27 pagesLaboratory Manual: Silver Oak College of Engineering and TechnologyBilal ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Exp1 RA2112703010019Document30 pagesExp1 RA2112703010019FaceNo ratings yet
- Disk DrivesDocument214 pagesDisk Drivesdubravko_akmacicNo ratings yet
- Information About Basesoftware Winnt4.0 V06.03.06 For Pcu50Document2 pagesInformation About Basesoftware Winnt4.0 V06.03.06 For Pcu50willianogroNo ratings yet
- Win2016 S2A 110 Global 00Document60 pagesWin2016 S2A 110 Global 00Saurabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Analysing The MBR With Hex WorkshopDocument25 pagesAnalysing The MBR With Hex WorkshopAli KazmiNo ratings yet
- Solaris Cheat Sheet: SmitDocument6 pagesSolaris Cheat Sheet: SmitKevinNilsson100% (2)
- Partitioned Tables and Indexes: Introduction To PartitioningDocument18 pagesPartitioned Tables and Indexes: Introduction To PartitioningSraVanKuMarThadakamallaNo ratings yet
- DB2 Installatn On ServerDocument3 pagesDB2 Installatn On ServerAjmal RahmanNo ratings yet
- Booting - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument16 pagesBooting - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSandeep RoyNo ratings yet
- RESTORE DATABASE - IBM DB2 9.7 For Linux, UNIX, and WindowsDocument13 pagesRESTORE DATABASE - IBM DB2 9.7 For Linux, UNIX, and Windowsolippo19No ratings yet
- Ibm Utl Sguide 8.41 AnyosDocument14 pagesIbm Utl Sguide 8.41 AnyosAnderson CamposNo ratings yet
- Oracle Database 19c RAC Installation On OL7 Part 1Document120 pagesOracle Database 19c RAC Installation On OL7 Part 1rporllesNo ratings yet
- Disk Management in LinuxDocument3 pagesDisk Management in LinuxSarah FatimaNo ratings yet
- Pa80 User PDFDocument10 pagesPa80 User PDFNenad StankovNo ratings yet
- Iis FundamentalsDocument18 pagesIis FundamentalsRiyas JacksparowNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing: Quarter 2 Installing and Configuring Computer Systems Module 2: Prepare InstallerDocument43 pagesComputer Systems Servicing: Quarter 2 Installing and Configuring Computer Systems Module 2: Prepare InstallerErwin Bucasas100% (4)
- ICT CSS Q2 Mod2 Prepare Installer v4Document36 pagesICT CSS Q2 Mod2 Prepare Installer v4rez hablo100% (1)
- InstallationInstructionsDocument84 pagesInstallationInstructionsDipti BhanjaNo ratings yet
- manualVMWare PDFDocument152 pagesmanualVMWare PDFmxmigueNo ratings yet
- 3102 WorkbookDocument153 pages3102 Workbookmansoor.ahmed100No ratings yet
- Use Reset To Restore Your Windows 10 PC: Topics in This Guide IncludeDocument5 pagesUse Reset To Restore Your Windows 10 PC: Topics in This Guide Includealfonso_rios_34No ratings yet
- HP FutureSmart ResetsDocument1 pageHP FutureSmart ResetsaleNo ratings yet
- How To Create A Recovery Partition On Windows 10Document6 pagesHow To Create A Recovery Partition On Windows 10Vincent StanleyNo ratings yet
- CHP 6 Physical Database Design and PerformanceDocument44 pagesCHP 6 Physical Database Design and PerformanceFikile NgwevuNo ratings yet
- Rmprepusb: Important: Always Run These Utilities With Administrator PrivilegesDocument13 pagesRmprepusb: Important: Always Run These Utilities With Administrator PrivilegesEslam A. AliNo ratings yet
- Install Windows 7 or Windows 8 From USB Drive - Pen DriveDocument93 pagesInstall Windows 7 or Windows 8 From USB Drive - Pen DriveDarshan FarswanNo ratings yet
- Linux Labs: Timothy RamtekeDocument74 pagesLinux Labs: Timothy Ramtekemario1349100% (1)