Professional Documents
Culture Documents
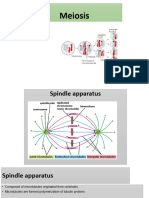
Ws. 5 Meiosis
Ws. 5 Meiosis
Uploaded by
Gwenn DalautaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Bitcoin To $1M, Ethereum To $180,000 by 2030 ARKDocument1 pageBitcoin To $1M, Ethereum To $180,000 by 2030 ARKOwen HalpertNo ratings yet
- Symbolism in Exhibitional Architecture - Philosophy of Space (By: Adonis El Hussein)Document104 pagesSymbolism in Exhibitional Architecture - Philosophy of Space (By: Adonis El Hussein)Адонис Ель ХуссеинNo ratings yet
- AbsorptionDocument39 pagesAbsorptionAlexânder De Paula Rodrigues100% (2)
- Police Log July 4, 2016Document12 pagesPolice Log July 4, 2016MansfieldMAPoliceNo ratings yet
- Stats Tools PackageDocument44 pagesStats Tools PackageMuhammad Asif Khan100% (1)
- Cyto Unit 5Document3 pagesCyto Unit 5Vince CarrilloNo ratings yet
- MEIOSISDocument8 pagesMEIOSISAmelie BalibagonNo ratings yet
- 1 Sexual Reproduction Req MeiosisDocument7 pages1 Sexual Reproduction Req MeiosisSerena BautistaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle BrainstormingDocument3 pagesCell Cycle BrainstormingKimberley MendozaNo ratings yet
- MEIOSISDocument2 pagesMEIOSISKate Lynne CamonayanNo ratings yet
- Meiosis IDocument11 pagesMeiosis IHarshu JunghareNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle NotesDocument57 pagesCell Cycle NotesHEMNATHVICKY SRINIVASANNo ratings yet
- Cellular Reproduction: Science 8 4 Quarter Lesson 2Document45 pagesCellular Reproduction: Science 8 4 Quarter Lesson 2Cynthia RectoNo ratings yet
- LeptoteneDocument3 pagesLeptoteneJan GuerreroNo ratings yet
- 7 MeiosisDocument8 pages7 Meiosisdevanshianand555No ratings yet
- Stages of Mitosis and Meiosis Given 2N 6Document29 pagesStages of Mitosis and Meiosis Given 2N 6rnzyrlcasinilloNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Class 9Document4 pagesCell Division Class 9pillapandurangapatruduNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 Lab Sheet LUKEDocument6 pagesActivity 3 Lab Sheet LUKElukegaid07951No ratings yet
- Handout MeiosisDocument4 pagesHandout MeiosisMoira Regina Lugo QuiogueNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument22 pagesMeiosisKOMAL NAVARIYANo ratings yet
- Gen Bio G1 Report G4 QuizDocument5 pagesGen Bio G1 Report G4 QuizHans Kirby Pacatang DumdumNo ratings yet
- 2.5 - MeiosisDocument31 pages2.5 - MeiosisdamsaviNo ratings yet
- 10 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument10 pages10 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionAarushi GoyalNo ratings yet
- Why Meiosis Is Called Reductional DivisionDocument3 pagesWhy Meiosis Is Called Reductional DivisionDipesh SAPKOTANo ratings yet
- Spotter No 5Document6 pagesSpotter No 5subikshansubikshan28No ratings yet
- Telophase I: Haploid Chromosomes Sister ChromatidsDocument1 pageTelophase I: Haploid Chromosomes Sister ChromatidschocoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21 of General Biology 2021-2022Document21 pagesLecture 21 of General Biology 2021-2022Mohammad zreadNo ratings yet
- 2111240, Baishli Sur, B7Document5 pages2111240, Baishli Sur, B7Baishali SurNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument6 pagesCell CycleSTEINER 97No ratings yet
- (L3) - Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument48 pages(L3) - Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionNayan PawarNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument6 pagesCell Cycle and Cell DivisionJeyanthiNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell Cycle and Cell DivisionParth GoyalNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio ReviewerDocument5 pagesGen Bio ReviewerAbegail CanedaNo ratings yet
- General Biology Prefinal ReviewerDocument11 pagesGeneral Biology Prefinal ReviewerterenzcajuraoNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle: Activity 3Document5 pagesThe Cell Cycle: Activity 3Cobe Christian LascunaNo ratings yet
- Cyto Unit 4Document2 pagesCyto Unit 4Vince CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Meiosis CopyDocument35 pagesMeiosis CopyAnnecalacal SabocoNo ratings yet
- POSTGRADUATE TEACHING DEPARTMENT OF ZOOLOGY PPT NewDocument18 pagesPOSTGRADUATE TEACHING DEPARTMENT OF ZOOLOGY PPT NewChetan MasramNo ratings yet
- Exp No 7 Meiosis in Onion Bud CellDocument3 pagesExp No 7 Meiosis in Onion Bud CellShadab AhmadNo ratings yet
- Mitosis A ND Meiosis 2Document43 pagesMitosis A ND Meiosis 2Maclharenn TiquiNo ratings yet
- Copia de Meiosis Gummy Worm LabDocument8 pagesCopia de Meiosis Gummy Worm Labgopan629No ratings yet
- Cor 007 Day 16Document23 pagesCor 007 Day 16Rain VicenteNo ratings yet
- Cell Division PrintDocument10 pagesCell Division PrintNabaratna BiswalNo ratings yet
- 3 ScanDocument5 pages3 ScanAsadNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument44 pagesCell Cycle and Cell DivisionKILLER FFNo ratings yet
- Meiosis 1Document31 pagesMeiosis 1Mhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Prophase IDocument1 pageProphase IOmar Khalif Amad PendatunNo ratings yet
- 660a7b133fc74400185b8875 - ## - Cell Cycle and Cell Division Short NotesDocument1 page660a7b133fc74400185b8875 - ## - Cell Cycle and Cell Division Short Notespradhananita848No ratings yet
- MitosismeiosisDocument44 pagesMitosismeiosisalanamaharaj20No ratings yet
- KERYOKINESISDocument6 pagesKERYOKINESISMahibahNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Mitosis and MeiosisDocument2 pagesDifferences Between Mitosis and MeiosisJeannifer ManjaresNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio ReviewerDocument3 pagesGen Bio ReviewerJustin JaranillaNo ratings yet
- Genbio Reviwer FinalsDocument5 pagesGenbio Reviwer FinalsChesley CarolinoNo ratings yet
- Text Boxes Have Links To Different SlideDocument21 pagesText Boxes Have Links To Different SlideJuana Montoya VenegasNo ratings yet
- Spotting Experiment 4Document4 pagesSpotting Experiment 4ayazajju661No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Chromosomal Basis of HeredityDocument35 pagesLesson 2 Chromosomal Basis of HereditycglorbecNo ratings yet
- Meiosis StudentDocument33 pagesMeiosis StudentChernaemiller123No ratings yet
- Aneuploidy Cleavage Furrow and Cell Plate Karyotype: Distinguish BetweenDocument2 pagesAneuploidy Cleavage Furrow and Cell Plate Karyotype: Distinguish Betweeneclipse1130No ratings yet
- 3.3 ReviewerDocument2 pages3.3 Reviewerstem.patinosamcharrieNo ratings yet
- Meosis DescriptionDocument3 pagesMeosis DescriptionMarch Jillian Chloe Tan ViñarNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesCell DivisionGale SatsatinNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument2 pagesMeiosisMerann NepaNo ratings yet
- CELL DIVISION-MeiosisDocument37 pagesCELL DIVISION-MeiosisAVINASH VARMANo ratings yet
- Prism Cryogenic Oxygen Generators: Reliable On-Site SupplyDocument4 pagesPrism Cryogenic Oxygen Generators: Reliable On-Site SupplyEdwin RosasNo ratings yet
- Feb 3 Questions Nuclear WasteDocument4 pagesFeb 3 Questions Nuclear WastedcudfhiudfiuNo ratings yet
- Sony KV 13TR27 Chasis.P 3BDocument29 pagesSony KV 13TR27 Chasis.P 3BTereza Yamileth Coto ENo ratings yet
- Zathapyin Bridge Final Report (Rev-2)Document4 pagesZathapyin Bridge Final Report (Rev-2)Wanna PhyoNo ratings yet
- Abe 424 Farm Structures and Environmental ControlDocument42 pagesAbe 424 Farm Structures and Environmental ControlAmabi SilasNo ratings yet
- Kinoton FP30D Operating ManualDocument87 pagesKinoton FP30D Operating ManualTomekLecocqNo ratings yet
- Battery-Box Hvs / HVM: PremiumDocument2 pagesBattery-Box Hvs / HVM: PremiumIulian GrigoreNo ratings yet
- Blessed Thistle and Blue VervainDocument4 pagesBlessed Thistle and Blue VervainSoror OnyxNo ratings yet
- Precos Souza CruzDocument12 pagesPrecos Souza CruzPablo ToazzaNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument13 pagesProjectAkshat UniyalNo ratings yet
- ME8099-Robotics QB SRM - by WWW - EasyEngineering.net QB 1Document11 pagesME8099-Robotics QB SRM - by WWW - EasyEngineering.net QB 1VenkadeshNo ratings yet
- Excel Meracik Nutrisi Bandung 11 Feb 2018Document30 pagesExcel Meracik Nutrisi Bandung 11 Feb 2018Ariev WahyuNo ratings yet
- NTP 2020 Kakatiya - Mega - Textile - ParkDocument2 pagesNTP 2020 Kakatiya - Mega - Textile - ParkNv MannaNo ratings yet
- Air System - Atlas Copco FX 1 Instruction Book (Page 13) - ManualsLibDocument1 pageAir System - Atlas Copco FX 1 Instruction Book (Page 13) - ManualsLibYoseph EdyNo ratings yet
- Table of Fundamental Constants in Theoretical PhysicsDocument1 pageTable of Fundamental Constants in Theoretical PhysicsTunarisNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure, Bohr Model and IsotopesDocument17 pagesAtomic Structure, Bohr Model and IsotopeskushanNo ratings yet
- Ce503 RBTDocument2 pagesCe503 RBTTarang ShethNo ratings yet
- Microbes As Bio Fertilizer: Name:-Deep Gaikwad STD:-XII (Science) Subject:-BiologyDocument12 pagesMicrobes As Bio Fertilizer: Name:-Deep Gaikwad STD:-XII (Science) Subject:-Biologyultra gamingNo ratings yet
- Nickel Alloy Inconel 718 Properties and Applications by United Performance MetalsDocument4 pagesNickel Alloy Inconel 718 Properties and Applications by United Performance MetalsShubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- 14th Jan 330pm NuptialsDocument30 pages14th Jan 330pm Nuptialsvivsubs18No ratings yet
- User's ManualDocument42 pagesUser's ManualSupriya ManojNo ratings yet
- Extra NumericalsDocument2 pagesExtra NumericalsDeep KambleNo ratings yet
- The Baldur's Gate Series 2 - Shadows of AmnDocument99 pagesThe Baldur's Gate Series 2 - Shadows of AmnJustin Moore100% (1)
- High Voltage Testing Measurement Equipment CatalogDocument46 pagesHigh Voltage Testing Measurement Equipment CatalogHari HidayatNo ratings yet
- Gen - Physics 12 Q4 WK8Document18 pagesGen - Physics 12 Q4 WK8Mark Julius Felix PagudNo ratings yet
Ws. 5 Meiosis
Ws. 5 Meiosis
Uploaded by
Gwenn DalautaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ws. 5 Meiosis
Ws. 5 Meiosis
Uploaded by
Gwenn DalautaCopyright:
Available Formats
CAPITOL UNIVERSITY
Cagayan de Oro City
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL
SUBJECT: General Biology 1
TOPIC: Cell Division: Meiosis LESSON CODE: W1L1
MODALITY: Blended WORKSHEET NO:5
WORKSHEET
NAME: GWENN C. DALAUTA
SECTION: EINSTEIN
INSTRUCTIONS: Complete the table below by providing the description and highlighting the events in each of the
phases of meiosis I and II, and illustrating these events (you can use coloring pens/materials in doing this).
Phases of Meiosis I and II Description Drawing/ Illustration
● Prophase 1 is a process
that is involved 5 stages
Prophase I namely, leptotene,
zygotene, pachytene,
diplotene, and diakinesis,
and the first stage of the
meiotic division. When
homologous
chromosomes pair and
form synapses, crossing-
over can occur and the
chromosomes can
recombine to create non-
identical haploid
chromatids.
Five stages:
● Leptotene stage - The
chromosome emerges as
chromatin condenses.
● Zygote stage - Synapsis
begins with a
synaptonemal complex
forming between
homologous
chromosomes
● Pachytene stage –
Synapsis is coplete.
Crossing over take place of
genetic material appearing
between non-sister
chromatids
● Diplotene stage – The
synapsis or synaptonemal
complex starts to dissolve
and A process known as
terminalization begins to
separate the homologous
chromosomes.
● Diakinesis stage – The
chiasmata go through
terminlization as the
homologous
chromosomes continue to
separate. The homologous
have been shortened and
condensed.
● The chromosomes start to
condense again, and the
Prophase II nuclear membrane and
nucleolus break down or
simply disappear. The
formation of spindle fibers
begins.
● Metaphase I is the second
stage in meiosis I. Along
Metaphase I the cell's center or either
side of the equatorial
plate, homologous pairs of
chromosomes align.
● In Metaphase II the
chromosomes line up at
Metaphase II the equatorial plate. The
kinetochores are then
attached to the
centromere of each sister
chromatid, preparing to
move themselves at
opposite poles.
● Anaphase I is the third
stage in meiosis, where
Anaphase I the homologous
chromosomes separate in
this stage. The sister
chromatids are still there
on each chromosome, and
some of the chromatids
have exchanged DNA in
them from the crossing
over.
● In Anaphase II, the sister
chromatids begin to
Anaphase II separate, with each sister
chromatid moving to the
opposite pole.
● Telophase I is the fourth
or final stage of meiosis,
Telophase 1 The homologous
chromosomes travel to
the cell's opposing poles
with only half as many
chromosomes as normal,
but they still have pairs of
connected chromatids.
The nuclear membrane
begins to emerge once
more. At the same time
that telophase 1 appears
Cytokinesis occurs to
complete the creation of
two haploid daughter
cells.
● In Telophase II, Where the
chromosomes uncoil, and
Telophase II four haploid cells are
formed. Finally,
cytokinesis splits the cells,
producing four haploid
cells and two diploid
daughter cells from the
product of mitosis.
END
You might also like
- Bitcoin To $1M, Ethereum To $180,000 by 2030 ARKDocument1 pageBitcoin To $1M, Ethereum To $180,000 by 2030 ARKOwen HalpertNo ratings yet
- Symbolism in Exhibitional Architecture - Philosophy of Space (By: Adonis El Hussein)Document104 pagesSymbolism in Exhibitional Architecture - Philosophy of Space (By: Adonis El Hussein)Адонис Ель ХуссеинNo ratings yet
- AbsorptionDocument39 pagesAbsorptionAlexânder De Paula Rodrigues100% (2)
- Police Log July 4, 2016Document12 pagesPolice Log July 4, 2016MansfieldMAPoliceNo ratings yet
- Stats Tools PackageDocument44 pagesStats Tools PackageMuhammad Asif Khan100% (1)
- Cyto Unit 5Document3 pagesCyto Unit 5Vince CarrilloNo ratings yet
- MEIOSISDocument8 pagesMEIOSISAmelie BalibagonNo ratings yet
- 1 Sexual Reproduction Req MeiosisDocument7 pages1 Sexual Reproduction Req MeiosisSerena BautistaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle BrainstormingDocument3 pagesCell Cycle BrainstormingKimberley MendozaNo ratings yet
- MEIOSISDocument2 pagesMEIOSISKate Lynne CamonayanNo ratings yet
- Meiosis IDocument11 pagesMeiosis IHarshu JunghareNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle NotesDocument57 pagesCell Cycle NotesHEMNATHVICKY SRINIVASANNo ratings yet
- Cellular Reproduction: Science 8 4 Quarter Lesson 2Document45 pagesCellular Reproduction: Science 8 4 Quarter Lesson 2Cynthia RectoNo ratings yet
- LeptoteneDocument3 pagesLeptoteneJan GuerreroNo ratings yet
- 7 MeiosisDocument8 pages7 Meiosisdevanshianand555No ratings yet
- Stages of Mitosis and Meiosis Given 2N 6Document29 pagesStages of Mitosis and Meiosis Given 2N 6rnzyrlcasinilloNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Class 9Document4 pagesCell Division Class 9pillapandurangapatruduNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 Lab Sheet LUKEDocument6 pagesActivity 3 Lab Sheet LUKElukegaid07951No ratings yet
- Handout MeiosisDocument4 pagesHandout MeiosisMoira Regina Lugo QuiogueNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument22 pagesMeiosisKOMAL NAVARIYANo ratings yet
- Gen Bio G1 Report G4 QuizDocument5 pagesGen Bio G1 Report G4 QuizHans Kirby Pacatang DumdumNo ratings yet
- 2.5 - MeiosisDocument31 pages2.5 - MeiosisdamsaviNo ratings yet
- 10 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument10 pages10 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionAarushi GoyalNo ratings yet
- Why Meiosis Is Called Reductional DivisionDocument3 pagesWhy Meiosis Is Called Reductional DivisionDipesh SAPKOTANo ratings yet
- Spotter No 5Document6 pagesSpotter No 5subikshansubikshan28No ratings yet
- Telophase I: Haploid Chromosomes Sister ChromatidsDocument1 pageTelophase I: Haploid Chromosomes Sister ChromatidschocoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21 of General Biology 2021-2022Document21 pagesLecture 21 of General Biology 2021-2022Mohammad zreadNo ratings yet
- 2111240, Baishli Sur, B7Document5 pages2111240, Baishli Sur, B7Baishali SurNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument6 pagesCell CycleSTEINER 97No ratings yet
- (L3) - Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument48 pages(L3) - Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionNayan PawarNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument6 pagesCell Cycle and Cell DivisionJeyanthiNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell Cycle and Cell DivisionParth GoyalNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio ReviewerDocument5 pagesGen Bio ReviewerAbegail CanedaNo ratings yet
- General Biology Prefinal ReviewerDocument11 pagesGeneral Biology Prefinal ReviewerterenzcajuraoNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle: Activity 3Document5 pagesThe Cell Cycle: Activity 3Cobe Christian LascunaNo ratings yet
- Cyto Unit 4Document2 pagesCyto Unit 4Vince CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Meiosis CopyDocument35 pagesMeiosis CopyAnnecalacal SabocoNo ratings yet
- POSTGRADUATE TEACHING DEPARTMENT OF ZOOLOGY PPT NewDocument18 pagesPOSTGRADUATE TEACHING DEPARTMENT OF ZOOLOGY PPT NewChetan MasramNo ratings yet
- Exp No 7 Meiosis in Onion Bud CellDocument3 pagesExp No 7 Meiosis in Onion Bud CellShadab AhmadNo ratings yet
- Mitosis A ND Meiosis 2Document43 pagesMitosis A ND Meiosis 2Maclharenn TiquiNo ratings yet
- Copia de Meiosis Gummy Worm LabDocument8 pagesCopia de Meiosis Gummy Worm Labgopan629No ratings yet
- Cor 007 Day 16Document23 pagesCor 007 Day 16Rain VicenteNo ratings yet
- Cell Division PrintDocument10 pagesCell Division PrintNabaratna BiswalNo ratings yet
- 3 ScanDocument5 pages3 ScanAsadNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument44 pagesCell Cycle and Cell DivisionKILLER FFNo ratings yet
- Meiosis 1Document31 pagesMeiosis 1Mhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Prophase IDocument1 pageProphase IOmar Khalif Amad PendatunNo ratings yet
- 660a7b133fc74400185b8875 - ## - Cell Cycle and Cell Division Short NotesDocument1 page660a7b133fc74400185b8875 - ## - Cell Cycle and Cell Division Short Notespradhananita848No ratings yet
- MitosismeiosisDocument44 pagesMitosismeiosisalanamaharaj20No ratings yet
- KERYOKINESISDocument6 pagesKERYOKINESISMahibahNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Mitosis and MeiosisDocument2 pagesDifferences Between Mitosis and MeiosisJeannifer ManjaresNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio ReviewerDocument3 pagesGen Bio ReviewerJustin JaranillaNo ratings yet
- Genbio Reviwer FinalsDocument5 pagesGenbio Reviwer FinalsChesley CarolinoNo ratings yet
- Text Boxes Have Links To Different SlideDocument21 pagesText Boxes Have Links To Different SlideJuana Montoya VenegasNo ratings yet
- Spotting Experiment 4Document4 pagesSpotting Experiment 4ayazajju661No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Chromosomal Basis of HeredityDocument35 pagesLesson 2 Chromosomal Basis of HereditycglorbecNo ratings yet
- Meiosis StudentDocument33 pagesMeiosis StudentChernaemiller123No ratings yet
- Aneuploidy Cleavage Furrow and Cell Plate Karyotype: Distinguish BetweenDocument2 pagesAneuploidy Cleavage Furrow and Cell Plate Karyotype: Distinguish Betweeneclipse1130No ratings yet
- 3.3 ReviewerDocument2 pages3.3 Reviewerstem.patinosamcharrieNo ratings yet
- Meosis DescriptionDocument3 pagesMeosis DescriptionMarch Jillian Chloe Tan ViñarNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesCell DivisionGale SatsatinNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument2 pagesMeiosisMerann NepaNo ratings yet
- CELL DIVISION-MeiosisDocument37 pagesCELL DIVISION-MeiosisAVINASH VARMANo ratings yet
- Prism Cryogenic Oxygen Generators: Reliable On-Site SupplyDocument4 pagesPrism Cryogenic Oxygen Generators: Reliable On-Site SupplyEdwin RosasNo ratings yet
- Feb 3 Questions Nuclear WasteDocument4 pagesFeb 3 Questions Nuclear WastedcudfhiudfiuNo ratings yet
- Sony KV 13TR27 Chasis.P 3BDocument29 pagesSony KV 13TR27 Chasis.P 3BTereza Yamileth Coto ENo ratings yet
- Zathapyin Bridge Final Report (Rev-2)Document4 pagesZathapyin Bridge Final Report (Rev-2)Wanna PhyoNo ratings yet
- Abe 424 Farm Structures and Environmental ControlDocument42 pagesAbe 424 Farm Structures and Environmental ControlAmabi SilasNo ratings yet
- Kinoton FP30D Operating ManualDocument87 pagesKinoton FP30D Operating ManualTomekLecocqNo ratings yet
- Battery-Box Hvs / HVM: PremiumDocument2 pagesBattery-Box Hvs / HVM: PremiumIulian GrigoreNo ratings yet
- Blessed Thistle and Blue VervainDocument4 pagesBlessed Thistle and Blue VervainSoror OnyxNo ratings yet
- Precos Souza CruzDocument12 pagesPrecos Souza CruzPablo ToazzaNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument13 pagesProjectAkshat UniyalNo ratings yet
- ME8099-Robotics QB SRM - by WWW - EasyEngineering.net QB 1Document11 pagesME8099-Robotics QB SRM - by WWW - EasyEngineering.net QB 1VenkadeshNo ratings yet
- Excel Meracik Nutrisi Bandung 11 Feb 2018Document30 pagesExcel Meracik Nutrisi Bandung 11 Feb 2018Ariev WahyuNo ratings yet
- NTP 2020 Kakatiya - Mega - Textile - ParkDocument2 pagesNTP 2020 Kakatiya - Mega - Textile - ParkNv MannaNo ratings yet
- Air System - Atlas Copco FX 1 Instruction Book (Page 13) - ManualsLibDocument1 pageAir System - Atlas Copco FX 1 Instruction Book (Page 13) - ManualsLibYoseph EdyNo ratings yet
- Table of Fundamental Constants in Theoretical PhysicsDocument1 pageTable of Fundamental Constants in Theoretical PhysicsTunarisNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure, Bohr Model and IsotopesDocument17 pagesAtomic Structure, Bohr Model and IsotopeskushanNo ratings yet
- Ce503 RBTDocument2 pagesCe503 RBTTarang ShethNo ratings yet
- Microbes As Bio Fertilizer: Name:-Deep Gaikwad STD:-XII (Science) Subject:-BiologyDocument12 pagesMicrobes As Bio Fertilizer: Name:-Deep Gaikwad STD:-XII (Science) Subject:-Biologyultra gamingNo ratings yet
- Nickel Alloy Inconel 718 Properties and Applications by United Performance MetalsDocument4 pagesNickel Alloy Inconel 718 Properties and Applications by United Performance MetalsShubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- 14th Jan 330pm NuptialsDocument30 pages14th Jan 330pm Nuptialsvivsubs18No ratings yet
- User's ManualDocument42 pagesUser's ManualSupriya ManojNo ratings yet
- Extra NumericalsDocument2 pagesExtra NumericalsDeep KambleNo ratings yet
- The Baldur's Gate Series 2 - Shadows of AmnDocument99 pagesThe Baldur's Gate Series 2 - Shadows of AmnJustin Moore100% (1)
- High Voltage Testing Measurement Equipment CatalogDocument46 pagesHigh Voltage Testing Measurement Equipment CatalogHari HidayatNo ratings yet
- Gen - Physics 12 Q4 WK8Document18 pagesGen - Physics 12 Q4 WK8Mark Julius Felix PagudNo ratings yet