Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3.feb 321 - Assignment Sheet 3
3.feb 321 - Assignment Sheet 3
Uploaded by
Timothy SimirenCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- HW - 4 Gas Turbine-Brayton Cycle Homework and Conceptual QuestionsDocument6 pagesHW - 4 Gas Turbine-Brayton Cycle Homework and Conceptual QuestionsjbeckerNo ratings yet
- Problem As Term oDocument28 pagesProblem As Term oneyma_02No ratings yet
- Sheet 1 (Thermo) - ProblemsDocument9 pagesSheet 1 (Thermo) - ProblemsKarim MetwallyNo ratings yet
- Principles of Thermodynamics NotesDocument12 pagesPrinciples of Thermodynamics NotesSaniya SohailNo ratings yet
- Ar Cycle 2Document4 pagesAr Cycle 2ELEONOR TABLINGONNo ratings yet
- GP CycleDocument11 pagesGP Cyclerajasekar KNo ratings yet
- AdsorptionDocument3 pagesAdsorptionali105No ratings yet
- Assignment IIDocument3 pagesAssignment IIannukiitNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 10 ProblemsDocument2 pagesTutorial 10 ProblemsRudhraa.RNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2: Dr. Gamal NadaDocument3 pagesThermodynamics 2: Dr. Gamal NadaEmptySilenceNo ratings yet
- 4 - Gas Power CycleDocument4 pages4 - Gas Power CycleMohamed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesGas Turbine ThermodynamicsTony EduokNo ratings yet
- Homework #10 PDFDocument3 pagesHomework #10 PDFAnonymous nHya4Z4No ratings yet
- Midterm ActivityDocument3 pagesMidterm ActivityKendrick RomeroNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument16 pagesThermoİBRAHİM HAZAR AYTULUNNo ratings yet
- Review UASDocument6 pagesReview UASkarenNo ratings yet
- AET Question Bank For AUC R2013 - SDocument5 pagesAET Question Bank For AUC R2013 - SGurunath AeroNo ratings yet
- QUESTION BANK ThermodynamicsDocument6 pagesQUESTION BANK Thermodynamicsvikas_1989No ratings yet
- Sistemas de PotenciaDocument6 pagesSistemas de PotenciaEduardo VCNo ratings yet
- Aet Model QN PaperDocument5 pagesAet Model QN PaperJagadishRajNo ratings yet
- Sheet 6 - ME 211TDocument2 pagesSheet 6 - ME 211TOmar AlkadyNo ratings yet
- Me2 Activity 3Document2 pagesMe2 Activity 3wangbibengNo ratings yet
- TutorialDocument12 pagesTutorialJohnson MangumaNo ratings yet
- Soal Latihan Termodinamika IIDocument5 pagesSoal Latihan Termodinamika IIPur NomoNo ratings yet
- Thermo HW 1-4Document1 pageThermo HW 1-4togilifeNo ratings yet
- Thermo of MechDocument2 pagesThermo of MecheyobNo ratings yet
- Gas Power Plant #1Document1 pageGas Power Plant #1Daniel KalderNo ratings yet
- EURME 303 (Applied Termo Dynamics 1)Document2 pagesEURME 303 (Applied Termo Dynamics 1)Sri KayNo ratings yet
- Me 1201 - Engineering Thermodynamics (3rd Sem. Mech.)Document22 pagesMe 1201 - Engineering Thermodynamics (3rd Sem. Mech.)محمد تانزيم ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 02 2014Document11 pagesTutorial Sheet 02 2014checkmeout803No ratings yet
- Tarea 10 TermodinamicaDocument5 pagesTarea 10 TermodinamicaMario GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Me 322aDocument1 pageMidterm Exam Me 322aStephanie ParkNo ratings yet
- Co1 Practice QuestionsDocument1 pageCo1 Practice QuestionsramsastryNo ratings yet
- Tarea de CiclosDocument6 pagesTarea de CiclosSebastiánGarcía100% (1)
- Latihan Soal-Soal Sistem Tenaga GasDocument6 pagesLatihan Soal-Soal Sistem Tenaga GasDhira GunawanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Topic 2 2020 RevisedDocument3 pagesTutorial Topic 2 2020 RevisedTara PillayNo ratings yet
- Assign - Engg. ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesAssign - Engg. ThermodynamicsSagarZopeNo ratings yet
- ME 201 AssignmentDocument3 pagesME 201 Assignmentmz_haqNo ratings yet
- B7: Applied Thermodynamics: Hilary Term 2018 Richard StoneDocument4 pagesB7: Applied Thermodynamics: Hilary Term 2018 Richard StoneMoemen MetwallyNo ratings yet
- Taier TDDocument2 pagesTaier TDMrDareraNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics - هيرارح اكيمانيدDocument16 pagesThermodynamics - هيرارح اكيمانيدHafiz Mahar28No ratings yet
- 062 - ME8391 ME6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Question BankDocument12 pages062 - ME8391 ME6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Question BankAjay KaviNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios TermodinamicaDocument7 pagesEjercicios TermodinamicaJavier Lopez VegaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Topic 5Document2 pagesTutorial Topic 5李世聪No ratings yet
- Bda 30403 2Document6 pagesBda 30403 2zinilNo ratings yet
- Balance de Energia y Entropia en Volumen de Control SolucionarioDocument1 pageBalance de Energia y Entropia en Volumen de Control SolucionarioMonica TorresNo ratings yet
- MMAN2700ThermoProblemSheet6 - 1st Law Steady FlowDocument3 pagesMMAN2700ThermoProblemSheet6 - 1st Law Steady Flowgrandw9524No ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument94 pagesProblemscatudalbryanNo ratings yet
- แบบฝึกหัด PDFDocument15 pagesแบบฝึกหัด PDFFah PinsudaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 ProblemsDocument6 pagesChapter 9 ProblemsKartikKhatriNo ratings yet
- Problems Carnot and RankineDocument12 pagesProblems Carnot and RankineHassan SheikhNo ratings yet
- 5 ListatermodinamicamoranDocument7 pages5 ListatermodinamicamoranIsabela CostaNo ratings yet
- Homework #7Document3 pagesHomework #7Sebastián SantarrosaNo ratings yet
- Exer 00Document9 pagesExer 00Yash RajNo ratings yet
- 0 S PP Chap6Document57 pages0 S PP Chap6Adib Nawawi100% (1)
- ThermoDocument3 pagesThermopranavNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- 1.problem Sheet1Document1 page1.problem Sheet1Timothy SimirenNo ratings yet
- 3 Soil FormationDocument16 pages3 Soil FormationTimothy SimirenNo ratings yet
- 2.lecture Two - Self Assessment QuestionsDocument2 pages2.lecture Two - Self Assessment QuestionsTimothy SimirenNo ratings yet
- Africa's Food Security Policy Option - FlyerDocument1 pageAfrica's Food Security Policy Option - FlyerTimothy SimirenNo ratings yet
- 7 Soil Description and ClassificationDocument27 pages7 Soil Description and ClassificationTimothy SimirenNo ratings yet
3.feb 321 - Assignment Sheet 3
3.feb 321 - Assignment Sheet 3
Uploaded by
Timothy SimirenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3.feb 321 - Assignment Sheet 3
3.feb 321 - Assignment Sheet 3
Uploaded by
Timothy SimirenCopyright:
Available Formats
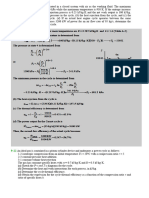
FEB 321: ASSIGNMENT SHEET 3 FOR PRACTICE
1. Show the Carnot cycle on a T-S diagram and indicate the areas that represent the heat
supplied QH, heat rejected QL, and the network output Wnet, out on this diagram.
2. Air is compressed from an initial state of 100 kPa and 17°C to a final state of 600 kPa and
57°C. Determine the entropy change of air during this compression process by using (a)
property values from the air table and (b) average specific heats.
3. Air is compressed in a car engine from 22°C and 95 kPa in a reversible and adiabatic
manner. If the compression ratio V1/V2 of this engine is 8, determine the final temperature
of the air.
4. Steam enters an adiabatic turbine steadily at 3 MPa and 400°C and leaves at 50 kPa and
100°C. If the power output of the turbine is 2 MW, determine (a) the isentropic efficiency
of the turbine and (b) the mass flow rate of the steam flowing through the turbine.
Hint: Steam flows steadily in a turbine between inlet and exit states. For a specified power
output, the isentropic efficiency and the mass flow rate are to be determined.
Assumptions: 1 Steady operating conditions exist. 2 The changes in kinetic
and potential energies are negligible.
5. Air is compressed by an adiabatic compressor from 100 kPa and 12°C to a pressure of 800
kPa at a steady rate of 0.2 kg/s. If the isentropic efficiency of the compressor is 80 percent,
determine (a) the exit temperature of air and (b) the required power input to the compressor.
Hint: Air is compressed to a specified pressure at a specified rate. For a given isentropic
efficiency, the exit temperature and the power input are to be determined.
Assumptions 1 Steady operating conditions exist. 2 Air is an ideal gas. 3 The changes in
kinetic and potential energies are negligible.
You might also like
- HW - 4 Gas Turbine-Brayton Cycle Homework and Conceptual QuestionsDocument6 pagesHW - 4 Gas Turbine-Brayton Cycle Homework and Conceptual QuestionsjbeckerNo ratings yet
- Problem As Term oDocument28 pagesProblem As Term oneyma_02No ratings yet
- Sheet 1 (Thermo) - ProblemsDocument9 pagesSheet 1 (Thermo) - ProblemsKarim MetwallyNo ratings yet
- Principles of Thermodynamics NotesDocument12 pagesPrinciples of Thermodynamics NotesSaniya SohailNo ratings yet
- Ar Cycle 2Document4 pagesAr Cycle 2ELEONOR TABLINGONNo ratings yet
- GP CycleDocument11 pagesGP Cyclerajasekar KNo ratings yet
- AdsorptionDocument3 pagesAdsorptionali105No ratings yet
- Assignment IIDocument3 pagesAssignment IIannukiitNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 10 ProblemsDocument2 pagesTutorial 10 ProblemsRudhraa.RNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2: Dr. Gamal NadaDocument3 pagesThermodynamics 2: Dr. Gamal NadaEmptySilenceNo ratings yet
- 4 - Gas Power CycleDocument4 pages4 - Gas Power CycleMohamed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesGas Turbine ThermodynamicsTony EduokNo ratings yet
- Homework #10 PDFDocument3 pagesHomework #10 PDFAnonymous nHya4Z4No ratings yet
- Midterm ActivityDocument3 pagesMidterm ActivityKendrick RomeroNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument16 pagesThermoİBRAHİM HAZAR AYTULUNNo ratings yet
- Review UASDocument6 pagesReview UASkarenNo ratings yet
- AET Question Bank For AUC R2013 - SDocument5 pagesAET Question Bank For AUC R2013 - SGurunath AeroNo ratings yet
- QUESTION BANK ThermodynamicsDocument6 pagesQUESTION BANK Thermodynamicsvikas_1989No ratings yet
- Sistemas de PotenciaDocument6 pagesSistemas de PotenciaEduardo VCNo ratings yet
- Aet Model QN PaperDocument5 pagesAet Model QN PaperJagadishRajNo ratings yet
- Sheet 6 - ME 211TDocument2 pagesSheet 6 - ME 211TOmar AlkadyNo ratings yet
- Me2 Activity 3Document2 pagesMe2 Activity 3wangbibengNo ratings yet
- TutorialDocument12 pagesTutorialJohnson MangumaNo ratings yet
- Soal Latihan Termodinamika IIDocument5 pagesSoal Latihan Termodinamika IIPur NomoNo ratings yet
- Thermo HW 1-4Document1 pageThermo HW 1-4togilifeNo ratings yet
- Thermo of MechDocument2 pagesThermo of MecheyobNo ratings yet
- Gas Power Plant #1Document1 pageGas Power Plant #1Daniel KalderNo ratings yet
- EURME 303 (Applied Termo Dynamics 1)Document2 pagesEURME 303 (Applied Termo Dynamics 1)Sri KayNo ratings yet
- Me 1201 - Engineering Thermodynamics (3rd Sem. Mech.)Document22 pagesMe 1201 - Engineering Thermodynamics (3rd Sem. Mech.)محمد تانزيم ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 02 2014Document11 pagesTutorial Sheet 02 2014checkmeout803No ratings yet
- Tarea 10 TermodinamicaDocument5 pagesTarea 10 TermodinamicaMario GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Me 322aDocument1 pageMidterm Exam Me 322aStephanie ParkNo ratings yet
- Co1 Practice QuestionsDocument1 pageCo1 Practice QuestionsramsastryNo ratings yet
- Tarea de CiclosDocument6 pagesTarea de CiclosSebastiánGarcía100% (1)
- Latihan Soal-Soal Sistem Tenaga GasDocument6 pagesLatihan Soal-Soal Sistem Tenaga GasDhira GunawanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Topic 2 2020 RevisedDocument3 pagesTutorial Topic 2 2020 RevisedTara PillayNo ratings yet
- Assign - Engg. ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesAssign - Engg. ThermodynamicsSagarZopeNo ratings yet
- ME 201 AssignmentDocument3 pagesME 201 Assignmentmz_haqNo ratings yet
- B7: Applied Thermodynamics: Hilary Term 2018 Richard StoneDocument4 pagesB7: Applied Thermodynamics: Hilary Term 2018 Richard StoneMoemen MetwallyNo ratings yet
- Taier TDDocument2 pagesTaier TDMrDareraNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics - هيرارح اكيمانيدDocument16 pagesThermodynamics - هيرارح اكيمانيدHafiz Mahar28No ratings yet
- 062 - ME8391 ME6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Question BankDocument12 pages062 - ME8391 ME6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Question BankAjay KaviNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios TermodinamicaDocument7 pagesEjercicios TermodinamicaJavier Lopez VegaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Topic 5Document2 pagesTutorial Topic 5李世聪No ratings yet
- Bda 30403 2Document6 pagesBda 30403 2zinilNo ratings yet
- Balance de Energia y Entropia en Volumen de Control SolucionarioDocument1 pageBalance de Energia y Entropia en Volumen de Control SolucionarioMonica TorresNo ratings yet
- MMAN2700ThermoProblemSheet6 - 1st Law Steady FlowDocument3 pagesMMAN2700ThermoProblemSheet6 - 1st Law Steady Flowgrandw9524No ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument94 pagesProblemscatudalbryanNo ratings yet
- แบบฝึกหัด PDFDocument15 pagesแบบฝึกหัด PDFFah PinsudaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 ProblemsDocument6 pagesChapter 9 ProblemsKartikKhatriNo ratings yet
- Problems Carnot and RankineDocument12 pagesProblems Carnot and RankineHassan SheikhNo ratings yet
- 5 ListatermodinamicamoranDocument7 pages5 ListatermodinamicamoranIsabela CostaNo ratings yet
- Homework #7Document3 pagesHomework #7Sebastián SantarrosaNo ratings yet
- Exer 00Document9 pagesExer 00Yash RajNo ratings yet
- 0 S PP Chap6Document57 pages0 S PP Chap6Adib Nawawi100% (1)
- ThermoDocument3 pagesThermopranavNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- 1.problem Sheet1Document1 page1.problem Sheet1Timothy SimirenNo ratings yet
- 3 Soil FormationDocument16 pages3 Soil FormationTimothy SimirenNo ratings yet
- 2.lecture Two - Self Assessment QuestionsDocument2 pages2.lecture Two - Self Assessment QuestionsTimothy SimirenNo ratings yet
- Africa's Food Security Policy Option - FlyerDocument1 pageAfrica's Food Security Policy Option - FlyerTimothy SimirenNo ratings yet
- 7 Soil Description and ClassificationDocument27 pages7 Soil Description and ClassificationTimothy SimirenNo ratings yet