Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Linked List in Data Structures
Introduction To Linked List in Data Structures
Uploaded by
Noopur SinghOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Linked List in Data Structures
Introduction To Linked List in Data Structures
Uploaded by
Noopur SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to Linked List in Data
Structures
Linked lists are the new data structure we'll explore today. The study of linked lists will
certainly be detailed, but first, I would like to inform you about one of the fundamental
differences between linked lists and arrays.
Arrays demand a contiguous memory location. Lengthening an array is not possible. We would
have to copy the whole array to some bigger memory location to lengthen its size. Similarity
inserting or deleting an element causes the elements to shift right and left, respectively.
But linked lists are stored in a non-contiguous memory location. To add a new element, we just
have to create a node somewhere in the memory and get it pointed by the previous element. And
deleting an element is just as easy as that. We just have to skip pointing to that particular node.
Lengthening a linked list is not a big deal.
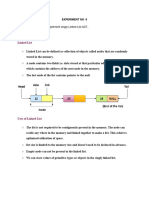
Structure of a Linked List:
Every element in a linked list is called a node and consists of two parts, the data part, and the
pointer part. The data part stores the value, while the pointer part stores the pointer pointing to
the address of the next node.
Both of these structures (arrays and linked lists) are linear data structures.
Linked Lists VS Arrays:
Figure 1: Arrays vs. Linked lists
Why Linked Lists?
Memory and the capacity of an array remain fixed, while in linked lists, we can keep adding and
removing elements without any capacity constraint.
Drawbacks of Linked Lists:
Extra memory space for pointers is required (for every node, extra space for a pointer
is needed)
Random access is not allowed as elements are not stored in contiguous memory
locations.
Implementations
Linked lists are implemented in C language using a structure. You can refer to the snippet
below.
Understanding the snippet below:
1. We construct a structure named Node.
2. Define two of its members, an integer data, which holds the node's data, and a
structure pointer, next, which points to the address of the next structure node.
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next; // Self referencing structure
};
Copy
Code Snippet 1: Implementation of a linked list
These were just the basics of the linked lists. We haven’t delved into details yet. There’s a lot to
cover in this data structure. Just sit back and enjoy.
You might also like
- Data Structures & Algorithms Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandData Structures & Algorithms Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- ADSADocument14 pagesADSAkanteti.srisandhyaNo ratings yet
- Linked List1Document8 pagesLinked List1focaba4283No ratings yet
- Introduction, Single Linked List, Circular Linked List, Doubly Linked List, Multiply Linked List, ApplicationsDocument58 pagesIntroduction, Single Linked List, Circular Linked List, Doubly Linked List, Multiply Linked List, ApplicationsG.ChinmayiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Link List - Rules and List ImplementationDocument21 pagesLecture 4 - Link List - Rules and List ImplementationROBLEDO John RonnelNo ratings yet
- 3 Linked ListsDocument64 pages3 Linked ListsSateesh Bonthala0% (1)
- Lab # 04 (Data Structure and Algorithm)Document5 pagesLab # 04 (Data Structure and Algorithm)lucasNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 - Linked ListDocument30 pagesUnit-2 - Linked Listssaurabhsingh890No ratings yet
- DS ChitraDocument35 pagesDS Chitraketan soniNo ratings yet
- 74 - BD - Data Structures and Algorithms - Narasimha KarumanchiDocument23 pages74 - BD - Data Structures and Algorithms - Narasimha KarumanchiTritonCPCNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 ListsDocument23 pagesLecture 5 Listsjames waithakaNo ratings yet
- Link ListDocument20 pagesLink ListRaja AnsNo ratings yet
- Data Structure Chapter2Document52 pagesData Structure Chapter2Ed GowharNo ratings yet
- 202003251324427324himanshu Linked ListDocument60 pages202003251324427324himanshu Linked Listaparna gurramNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document69 pagesChapter 3Abenezer AbrhamNo ratings yet
- Mahedi 1.1 1.2Document7 pagesMahedi 1.1 1.2Mahedi HassanNo ratings yet
- Linked List - Set 1 (Introduction) : Class Linkedlist (Node Head // Head of The ListDocument8 pagesLinked List - Set 1 (Introduction) : Class Linkedlist (Node Head // Head of The Listshoaib ansariNo ratings yet
- UNIT-I DS NotesDocument62 pagesUNIT-I DS NotesBandi SirishaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 CompleteDocument28 pagesChapter 2 CompleteVasantha KumariNo ratings yet
- DS Ex 6Document7 pagesDS Ex 6animationmake14No ratings yet
- 10 - Linked ListDocument57 pages10 - Linked ListMohit KambojNo ratings yet
- Sahil Kumar DSA Ca2Document8 pagesSahil Kumar DSA Ca2Sahil KumarNo ratings yet
- Data Structures and AlgorithmDocument7 pagesData Structures and AlgorithmOmkar JhaNo ratings yet
- DS Unit 1Document96 pagesDS Unit 1BADMANNo ratings yet
- LinkedlistDocument64 pagesLinkedlistAbhinav JainNo ratings yet
- DS Sem 2 Case Study PDFDocument10 pagesDS Sem 2 Case Study PDFchaituNo ratings yet
- Chap-1 Linked ListsDocument28 pagesChap-1 Linked ListsCHENGAMMA CHITTETINo ratings yet
- Linked ListDocument17 pagesLinked Listgouse5815No ratings yet
- Data Structure Lecture 5Document29 pagesData Structure Lecture 5eng.abdishakuur2022No ratings yet
- Linked List, Stack, QueueDocument13 pagesLinked List, Stack, QueueTaqi IsmailNo ratings yet
- Algo Chap 3-5Document153 pagesAlgo Chap 3-5zerihun nanaNo ratings yet
- Singly Linked ListDocument13 pagesSingly Linked ListHamza HashmiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Linked ListsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Linked ListsUbaid AltafNo ratings yet
- Term Paper On Linked ListDocument8 pagesTerm Paper On Linked Listc5r3aep1100% (1)
- 1) Linked ListDocument18 pages1) Linked ListLol TelrNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Linked List: Next Item"Document64 pagesUnit 2 Linked List: Next Item"Abhay GoswamiNo ratings yet
- 1c TheoryDocument5 pages1c Theorykoroxa6604No ratings yet
- Polynomial As Data Structure and Linked ListDocument4 pagesPolynomial As Data Structure and Linked Listrubinahafeez011No ratings yet
- Array PDFDocument10 pagesArray PDFMuzammal AnsariNo ratings yet
- Linked ListDocument3 pagesLinked ListAditya YadavNo ratings yet
- List Adt: 1. What Is A Data Structure?Document7 pagesList Adt: 1. What Is A Data Structure?nandanNo ratings yet
- DS Unit IDocument54 pagesDS Unit IRoyal Durgaprasad UNIVERSAL tech creativeNo ratings yet
- Most Imp LinkedLIst Interview QuesDocument47 pagesMost Imp LinkedLIst Interview QuesPrakhar MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- 13.1 C Programming - Linked ListsDocument3 pages13.1 C Programming - Linked Listsneo_411No ratings yet
- Linked ListDocument11 pagesLinked ListGosh KreativityNo ratings yet
- Dsa Lab 06Document5 pagesDsa Lab 06Hanzla ZafarNo ratings yet
- Linked ListDocument13 pagesLinked ListChirag JainNo ratings yet
- Source: Diginotes - In: Prepared by Citech Ms. Pankaja K and Ms. Geetha PDocument31 pagesSource: Diginotes - In: Prepared by Citech Ms. Pankaja K and Ms. Geetha PAdarsh KMNo ratings yet
- Linked List Slide-2Document20 pagesLinked List Slide-2abrarNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii: Linked Lists: Free (PTR)Document32 pagesUnit-Iii: Linked Lists: Free (PTR)satishNo ratings yet
- 7.1 What Is Data Structure?Document23 pages7.1 What Is Data Structure?Kenil TogadiyaNo ratings yet
- DSL Pract (Oral) QuestionDocument14 pagesDSL Pract (Oral) QuestionSanchit KharadeNo ratings yet
- 191CSC303T - DS - Unit 1Document5 pages191CSC303T - DS - Unit 120-4082-Mohammad irfan SheikhNo ratings yet
- DsMahiwaya PDFDocument21 pagesDsMahiwaya PDFMahiwaymaNo ratings yet
- DSA Unit 2 - Question BankDocument11 pagesDSA Unit 2 - Question Bankvengai marbhanNo ratings yet
- Singly Linked List - Chapter 3 - Linked Lists - Data Structures and Algorithms - Narasimha KarumanchiDocument15 pagesSingly Linked List - Chapter 3 - Linked Lists - Data Structures and Algorithms - Narasimha Karumanchit82078044No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Linked Lists - Data Structures and Algorithms - Narasimha KarumanchiDocument89 pagesChapter 3 - Linked Lists - Data Structures and Algorithms - Narasimha Karumanchit82078044No ratings yet
- Imp - Data-Structures QuestionsDocument16 pagesImp - Data-Structures QuestionsBLACK xDEMONNo ratings yet
- DSA Lab 8Document13 pagesDSA Lab 8uaengineering ManzoorNo ratings yet
- ADVANCED DATA STRUCTURES FOR ALGORITHMS: Mastering Complex Data Structures for Algorithmic Problem-Solving (2024)From EverandADVANCED DATA STRUCTURES FOR ALGORITHMS: Mastering Complex Data Structures for Algorithmic Problem-Solving (2024)No ratings yet
- Project OutlineDocument1 pageProject OutlineNoopur SinghNo ratings yet
- What Is Machine Learning?Document2 pagesWhat Is Machine Learning?Noopur SinghNo ratings yet
- Functions of Operating System:: Process ManagementDocument2 pagesFunctions of Operating System:: Process ManagementNoopur SinghNo ratings yet
- Process ConceptDocument2 pagesProcess ConceptNoopur SinghNo ratings yet
- Inserting A New Element in An ArrayDocument1 pageInserting A New Element in An ArrayNoopur SinghNo ratings yet