Professional Documents
Culture Documents
02 DNA Replication Reading
02 DNA Replication Reading
Uploaded by
lightning TigerOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
02 DNA Replication Reading
02 DNA Replication Reading
Uploaded by
lightning TigerCopyright:
Available Formats
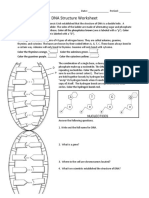
DNA Replication Reading Name: _____________
Underline new terms as you read. Talking to the text is optional.
On the back of this sheet, summarize each of the 4 steps with 2 sentences and 1 diagram.
(8 sentences and 4 diagrams total!)
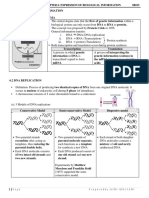
When the double helix structure of DNA was first Step 3: Once a DNA polymerase has begun adding
discovered, scientists were very excited about the nucleotides to a growing double helix, the protein
complementary relationship between the sequences remains attached until all of the DNA has been
of nucleotides. They predicted that the copied and it is signaled to detach. This process
complementary structure was used as the basis to produces 2 DNA molecules, each composed of a
make exact copies of the DNA each time a cell new and an original strand. The nucleotide
divided. Watson and Crick, the dudes who sequences in both of these DNA molecules are
discovered the structure of DNA, proposed that one identical to each other and to the original DNA
DNA strand serves as a template, or pattern, on molecule.
which the other strand is built. Within five years of
Step 4 - Checking for errors: In the course of
the discovery of DNA structure, scientists had firm
DNA replication, errors sometimes occur and the
evidence that the complementary strands of the
wrong nucleotide is added to the new strand. An
double helix do indeed serve as templates for
important feature of DNA replication is that DNA
building DNA.
polymerases have a “proof-reading” role; they can
The process of making a copy of DNA is called add nucleotides to a growing strand only if the
DNA replication. Recall that DNA replication previous nucleotide is correctly paired to its
occurs during the synthesis (S) phase of the cell complementary base. In the event of a mismatched
cycle, before a cell divides. nucleotide, DNA polymerase is capable of
backtracking, removing the incorrect nucleotide and
Step 1: Before DNA replication can begin, the
replacing it with the correct one. This proofreading
double helix unwinds. This is accomplished by
prevents most errors in DNA replication. Indeed,
proteins called DNA helicases, which open the
only 1 error per 1 billion nucleotides typically
double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds that
occurs.
link the complementary nitrogen bases between the
2 strands. Once the 2 strands are separated,
additional proteins attach to each strand, holding
them apart and preventing them from twisting
back into their double helical shape. The 2 areas
on either end of the DNA where the double helix
separates are called replication forks because of
their Y shape.
Step 2: At the replication fork, proteins known
as DNA polymerases move along each of the
DNA strands, adding nucleotides to the exposed
nitrogen bases, according to the base-pairing
rules. As the DNA polymerases move along, 2
new double helixes are formed.
Modified from: Johnson and Raven. Biology. Princeton University Press: Holt, Rinehart, and Winston. 2001. Pp 196-197.
You might also like
- Lesson Plan - DNA Replication (REVISED)Document6 pagesLesson Plan - DNA Replication (REVISED)Keziah ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Junior HighDocument7 pagesLesson Plan Junior HighMark Leo Saldua Gelizon100% (1)
- Neither Physics Nor Chemistry A History of Quantum Chemistry (Transformations Studies in The History of Science and Technology) (PRG)Document367 pagesNeither Physics Nor Chemistry A History of Quantum Chemistry (Transformations Studies in The History of Science and Technology) (PRG)yyyyy100% (1)
- Lesson 5 CYTO DNA ReplicationDocument4 pagesLesson 5 CYTO DNA ReplicationTherese TimbalNo ratings yet
- Molecular Mechanism of DNA Replication (Article) - Khan AcademyDocument1 pageMolecular Mechanism of DNA Replication (Article) - Khan AcademyShreyansh PareekNo ratings yet
- L3+4 - DNA Replication and Genetic Code StudentDocument31 pagesL3+4 - DNA Replication and Genetic Code StudentHaris KhokharNo ratings yet
- ObjectivesDocument36 pagesObjectivesMARIAN SABENECIONo ratings yet
- Lesson 2B - DNA ReplicationDocument2 pagesLesson 2B - DNA ReplicationHazel FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- DNA REPLICATION OnlineDocument25 pagesDNA REPLICATION OnlineKyle RefugioNo ratings yet
- Replication, Transcription, Translation, Mutation HWDocument20 pagesReplication, Transcription, Translation, Mutation HWtahamidNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and RepairDocument7 pagesDNA Replication and RepairJhun Lerry TayanNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument7 pagesDNA Replicationlubuto TuntepeNo ratings yet
- Sci10 q3w4L1Document26 pagesSci10 q3w4L1Cedric BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Day 3Document8 pagesDay 3Kinberly AnnNo ratings yet
- Quiz Microbial Genetics TortoraDocument17 pagesQuiz Microbial Genetics TortorapascabioNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Notes - 34 DNA ReplicationDocument2 pagesIB Biology Notes - 34 DNA ReplicationJohn Philip D. NapalNo ratings yet
- ReplicationDocument3 pagesReplicationHarshu JunghareNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument45 pagesDNA ReplicationTchr Ezra ChangNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Day 1 Dna Replication 1Document45 pagesProtein Synthesis Day 1 Dna Replication 1markNo ratings yet
- Unit 5.1 DNA ReplicationDocument7 pagesUnit 5.1 DNA ReplicationDaniel SinyangweNo ratings yet
- 14.4__DNA_Replication_in_ProkaryotesDocument4 pages14.4__DNA_Replication_in_Prokaryoteskartisharma9352813220No ratings yet
- 2.7 7.1DNAReplicationDocument33 pages2.7 7.1DNAReplicationKhin (Darin) Hnin PhyuNo ratings yet
- D1.1 (Dna Structure & Replication)Document11 pagesD1.1 (Dna Structure & Replication)D-WizardNo ratings yet
- vt59.2708 21321403689 - 889739862127141 - 7332965126770472921 - N.pptxdna The Human Body Recipe InfographicsDocument1 pagevt59.2708 21321403689 - 889739862127141 - 7332965126770472921 - N.pptxdna The Human Body Recipe InfographicsCassandra Bernice ReyesNo ratings yet
- 3.dna ReplicationDocument7 pages3.dna ReplicationCharm BatiancilaNo ratings yet
- DNADocument22 pagesDNAgregoryyy09No ratings yet
- Lecture 7 BBT312 DNA Replication Part IDocument24 pagesLecture 7 BBT312 DNA Replication Part IBol BirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6.2 - DNA ReplicationDocument100 pagesChapter 6.2 - DNA Replicationnie20060301No ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument6 pagesIlovepdf Mergedmngnmg8No ratings yet
- CertificateDocument15 pagesCertificateAbhishek AryaNo ratings yet
- Grp.2 DNA REPLICATION EMERALDDocument48 pagesGrp.2 DNA REPLICATION EMERALDLinda Ann BacunadorNo ratings yet
- Theme 4 Module 2 Script W2021Document13 pagesTheme 4 Module 2 Script W2021ayaan31aliNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of BiologyDocument6 pagesCentral Dogma of BiologyJhun Lerry TayanNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument5 pagesDNA Replication and Protein SynthesisFrezelVillaBasiloniaNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument6 pagesDNA ReplicationGeorge TarraNo ratings yet
- Sci 9 Dna Replication WsDocument2 pagesSci 9 Dna Replication WsfabyunaaaNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication NotesDocument3 pagesDna Replication NotesYash VardhanNo ratings yet
- 12 3 PWPT PDFDocument22 pages12 3 PWPT PDFapi-262378640No ratings yet
- Grade-10-LAS-Week-4A-3rd - QuarterDocument5 pagesGrade-10-LAS-Week-4A-3rd - QuarterYaRNo ratings yet
- PCR: An Outstanding MethodDocument17 pagesPCR: An Outstanding MethodPriyaranjan KumarNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Unit IV and VDocument60 pagesMolecular Biology Unit IV and VchitraNo ratings yet
- General Biology - DNA ReplicationDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology - DNA ReplicationChristine Marylou PalomoNo ratings yet
- Lesson-3 Protein-Synthesis WorksheetDocument10 pagesLesson-3 Protein-Synthesis WorksheetEnriquez, Hannah Roniella R.No ratings yet
- REPLICATIONDocument9 pagesREPLICATIONdineshNo ratings yet
- Essay On Dna in Which You Compare Dna Replication With Protein SynthesisDocument6 pagesEssay On Dna in Which You Compare Dna Replication With Protein Synthesisdwf6nx2z100% (1)
- Chapter 07Document9 pagesChapter 07znx5fdtkkjNo ratings yet
- 4 DnaDocument6 pages4 Dnadr_47839666No ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument32 pagesDNA ReplicationSudipta MandolNo ratings yet
- Compressed Notes Chapter 6: Expression of Biological Information Sb015Document10 pagesCompressed Notes Chapter 6: Expression of Biological Information Sb015SYAZWAN BIN MUSTAFA MoeNo ratings yet
- Central DogmaDocument4 pagesCentral DogmaalxndrasenalesNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication: By: Group 3Document26 pagesDna Replication: By: Group 3Jesse Kate GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Molecular GeneticsDocument15 pagesMolecular GeneticsBiruk SamuelNo ratings yet
- Yacomine - Essential Biology 3.4 & 7.2 DNA Replication (HL Only) - 3211Document5 pagesYacomine - Essential Biology 3.4 & 7.2 DNA Replication (HL Only) - 3211joeyacomine100% (1)
- DoubleHelix Pulse Chase Primer TeacherDocument11 pagesDoubleHelix Pulse Chase Primer TeacherAneesh IyerNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: THINK: Why Does DNA Need To Replicate?Document33 pagesDNA Replication: THINK: Why Does DNA Need To Replicate?AkshiNo ratings yet
- L2 & 3 The NucleusDocument54 pagesL2 & 3 The NucleusAmarachi MaduabuchiNo ratings yet
- The DNA Detective: Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Genetic CodeFrom EverandThe DNA Detective: Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Genetic CodeNo ratings yet
- Summary of Jennifer A. Doudna and Samuel H. Sternberg's A Crack in CreationFrom EverandSummary of Jennifer A. Doudna and Samuel H. Sternberg's A Crack in CreationNo ratings yet
- It's In Your DNA! What Is DNA? - Biology Book 6th Grade | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandIt's In Your DNA! What Is DNA? - Biology Book 6th Grade | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Mahadevan Arivazhakan - SP2 - Reg. Preterite Verbs HandoutDocument2 pagesKami Export - Mahadevan Arivazhakan - SP2 - Reg. Preterite Verbs Handoutlightning TigerNo ratings yet
- PRACTICE Abs Value GraphsDocument2 pagesPRACTICE Abs Value Graphslightning TigerNo ratings yet
- Spanish Literature Powerpoint Movements LiteraturaDocument57 pagesSpanish Literature Powerpoint Movements Literaturalightning TigerNo ratings yet
- Mend ProbsDocument12 pagesMend Probslightning TigerNo ratings yet
- A2T+Chapter+5+Overview+2021 2022Document2 pagesA2T+Chapter+5+Overview+2021 2022lightning TigerNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Functions WorksheetDocument4 pagesEvaluating Functions Worksheetlightning TigerNo ratings yet
- HHS Math A2 Course Information Sheet 2021Document1 pageHHS Math A2 Course Information Sheet 2021lightning TigerNo ratings yet
- Gizmo Period 1Document1 pageGizmo Period 1lightning TigerNo ratings yet
- Gizmo Period 1Document1 pageGizmo Period 1lightning TigerNo ratings yet
- A2T Chapter 2 Exit TicketsDocument2 pagesA2T Chapter 2 Exit Ticketslightning TigerNo ratings yet
- Gizmo Period 1Document1 pageGizmo Period 1lightning TigerNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Exponential Graphing HomeworkDocument2 pages6.1 Exponential Graphing Homeworklightning TigerNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Trigonometry 4th Edition by YoungDocument35 pagesSolution Manual For Trigonometry 4th Edition by Younglightning TigerNo ratings yet
- 13 DNA Mutation SimulationDocument2 pages13 DNA Mutation Simulationlightning TigerNo ratings yet
- 4.8 Homework PracticeDocument2 pages4.8 Homework Practicelightning TigerNo ratings yet
- 12 DNA ColoringDocument2 pages12 DNA Coloringlightning TigerNo ratings yet
- 4.8 Homework PracticeDocument2 pages4.8 Homework Practicelightning TigerNo ratings yet
- 07 Royal Disease WorksheetDocument1 page07 Royal Disease Worksheetlightning TigerNo ratings yet
- 6.3 Inverse Review Homework 2021Document2 pages6.3 Inverse Review Homework 2021lightning TigerNo ratings yet
- 4.8 Homework PracticeDocument2 pages4.8 Homework Practicelightning TigerNo ratings yet
- 4.9 Homework PracticeDocument2 pages4.9 Homework Practicelightning TigerNo ratings yet
- gr10 MathDocument19 pagesgr10 Mathlightning TigerNo ratings yet
- 4.8 Homework Practice: Analyzing Graphs of Polynomial FunctionsDocument2 pages4.8 Homework Practice: Analyzing Graphs of Polynomial Functionslightning TigerNo ratings yet
- 4.7 Homework PracticeDocument2 pages4.7 Homework Practicelightning TigerNo ratings yet
- What Is An Argumentative EssayDocument6 pagesWhat Is An Argumentative Essaylightning TigerNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Mahadevan Arivazhakan - SP2 - Reg. Preterite Verbs HandoutDocument2 pagesKami Export - Mahadevan Arivazhakan - SP2 - Reg. Preterite Verbs Handoutlightning TigerNo ratings yet
- N - MagCore EXTRACTOR ALL - CatalogDocument12 pagesN - MagCore EXTRACTOR ALL - CatalogtalaaaaNo ratings yet
- TDS-367 Glucam P20 Fragrance PDFDocument7 pagesTDS-367 Glucam P20 Fragrance PDFAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Msds Benzoate de MetiloDocument5 pagesMsds Benzoate de MetiloCristobal ValdebenitoNo ratings yet
- Inventory StatusDocument19 pagesInventory StatusMuhaiminul IslamNo ratings yet
- Static Calculation CWDocument64 pagesStatic Calculation CWlayaljamal2100% (1)
- FDA Regulation of Color Additives in DrugsDocument47 pagesFDA Regulation of Color Additives in Drugssai sumanth bNo ratings yet
- Pithecellobium Dulce Medicinal Plant Traditional Knowledge Nutritional and Therapeutic Potential Sulekha Et Al 2021Document10 pagesPithecellobium Dulce Medicinal Plant Traditional Knowledge Nutritional and Therapeutic Potential Sulekha Et Al 2021María José TorallaNo ratings yet
- Axens Gas - Processes - Brochure - EnglishDocument9 pagesAxens Gas - Processes - Brochure - Englishmusta05No ratings yet
- Crowell. Newtonian Physics (230s) PDFDocument230 pagesCrowell. Newtonian Physics (230s) PDFJovan SrejicNo ratings yet
- Photosynthasis Summative Project - FinalDocument4 pagesPhotosynthasis Summative Project - Finalapi-201420572No ratings yet
- Optimisation Analyses of Fluid-Thermal S PDFDocument54 pagesOptimisation Analyses of Fluid-Thermal S PDFShazia Farman Ali QaziNo ratings yet
- School Level Science Fair Experiments: Standard 4Document25 pagesSchool Level Science Fair Experiments: Standard 4SHAVITHA A/P MADAVAN KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Technical Data of Vacuum Formed Ceramic Fiber PDFDocument2 pagesTechnical Data of Vacuum Formed Ceramic Fiber PDFba ajinNo ratings yet
- Rotational Viscometers and TypesDocument6 pagesRotational Viscometers and Typesanur33No ratings yet
- Anodic Protection Lecture23 PDFDocument5 pagesAnodic Protection Lecture23 PDFKantilal MalwaniaNo ratings yet
- HR ProjectDocument39 pagesHR ProjectSreelal P M LalNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: CalorimetryDocument2 pagesExperiment 1: CalorimetryMaryNicoleDatlanginNo ratings yet
- Mannnnnnnnnufacturing Process of Nylon 6 and Nylon 6,6Document3 pagesMannnnnnnnnufacturing Process of Nylon 6 and Nylon 6,6Ranjana RajanNo ratings yet
- Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology 2005 PDFDocument773 pagesAnnual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology 2005 PDFditabokNo ratings yet
- A Citizen's Guide To BioremediationDocument2 pagesA Citizen's Guide To BioremediationRenatoNo ratings yet
- Baerlocher PVC Profiles 2007 SofiaDocument27 pagesBaerlocher PVC Profiles 2007 SofiaSaša AleksićNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of EPA and DHA in Fish Oil Nutritional Capsules by GC-MSDocument6 pagesComparative Analysis of EPA and DHA in Fish Oil Nutritional Capsules by GC-MSzeinab talaatNo ratings yet
- MSDS Blasocut: Blaser Swisslube IncDocument4 pagesMSDS Blasocut: Blaser Swisslube InczaqNo ratings yet
- Use of Vacuum Line - 17Document20 pagesUse of Vacuum Line - 17Sachin BokanNo ratings yet
- International Marine Paint Specifications - 1. Definitions and AbbreviationsDocument5 pagesInternational Marine Paint Specifications - 1. Definitions and AbbreviationsChrisDanger250% (2)
- Physical ScienceDocument5 pagesPhysical Sciencecatherine aleluyaNo ratings yet
- Offshore Engineering Glossary TermsDocument8 pagesOffshore Engineering Glossary TermsDhakshina K100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument34 pagesChapter 4 Aromatic HydrocarbonsAbdirashid Adam IsakNo ratings yet
- High Temperature Plastic Deformation of CuZn30 BraDocument6 pagesHigh Temperature Plastic Deformation of CuZn30 Bramahan nikNo ratings yet