Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prob Set 1
Prob Set 1
Uploaded by
ChristianOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prob Set 1
Prob Set 1
Uploaded by
ChristianCopyright:
Available Formats
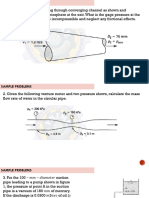
1. When 0.
03 m3/s flows through a 300-mm find the total energy head at point A with
pipe that later reduces to a 150-mm pipe, respect to a datum at the pump.
calculate the average velocities in the two
pipes.
2. If the velocity in a 300-mm pipe is 0.50 m/s,
what is the velocity in a 75-mm-diameter jet
issuing from a nozzle attached to the pipe?
3. What size pipe can carry 2.36 m3/s at an
average velocity of 3.0 m/s?
4. A 12" pipe carrying 3.93 cfs connects to a 6"
pipe. Find the velocity head in the 6" pipe.
5. A 150-mm pipe carries 0.0813 m3/s of water.
The pipe branches into two pipes, one 50 mm
in diameter and the other 100 mm in
diameter. If the velocity in the 50-mm pipe is
12.2 m/s, what is the velocity in the 100-mm
pipe?
6. A 300-mm pipe carries oil of sp gr 0.812 at a
rate of 0.111 m3/s, and the pressure at a point
A is 18.4 kPa gage. If point A is 1.89 m above
the datum plane, calculate the energy at A.
7. Water flows through a horizontal 150-mm
pipe under a pressure of 414 kPa. Assuming 14. Water flows through the turbine in the figure
no losses, what is the flow if the pressure at a at the rate of 0.214 m3/s and the pressures at
75-mm diameter reduction is 138 kPa? A and B, respectively, are 147.5 kPa and —
8. If oil of specific gravity 0.752 flows in 34.5 kPa. Determine the power delivered to
Problem 7., find flow Q. the turbine by the water.
9. If carbon tetrachloride (sp gr 1.594) flows in
Problem 7., find flow Q.
10. Water flows through a 200-mm-diameter
pipe at a velocity of 2.00 m/s. Determine the
volume flow rate, weight flow rate, and mass
flow rate.
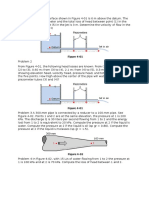
11. Gas flows through a conduit as shown in the
figure 1. For the data indicated on the figure,
determine the mass flow rate of the gas and
its mass density at section 2.
15. For the 50-mm-diameter siphon drawing oil
(sp gr = 0.82) from the oil reservoir as shown
in the figure, the head loss from point 1 to
point 2 is 1.50 m and from point 2 to point 3
is 2.40 m. Find the discharge of oil from the
siphon and the oil pressure at point 2.
12. A gas flows through a square conduit. At one
point along the conduit, the conduit sides are
0.100 m, the velocity is 7.55 m/s, and the
gas's mass density is (for its particular
pressure and temperature) 1.09 kg/m3. At a
second point, the conduit sides are 0.250 m
and the velocity is 2.02 m/s. Find the mass
flow rate of the gas and the gas's mass density
at the second point.
13. For the 100-mm-diameter suction pipe
leading to a pump shown in the figure , the
pressure at point A in the suction pipe is a
vacuum of 180 mm of mercury. If the
discharge is 0.0300 m3/s of oil (sp gr = 0.85),
16. A stream of water 75 mm in diameter
discharges into the atmosphere at a velocity
24.4 m/s. Find the power in the jet using the
datum plane through the center of the jet.
17. A 100-mm-diameter jet of water is
discharged (horizontally) from a nozzle into
the air. The flow rate of the water jet is 0.22
m3/s. Determine the power in the jet.
Assume the jet of water is at the datum.
18. Water flows upward in a vertical 300-mm
pipe at the rate of 0.222 m3/s. At point A in
the pipe the pressure is 210 kPa. At B, 4.57
m above A, the diameter is 600 mm, and the
lost head A to B equals 1.83 m. Determine
the pressure at B.
19. A 12" pipe contains a short section in which
the diameter is gradually reduced to 6" and
then enlarged again to 12". The 6" section is
2 ft below section A in the 12" section, where
the pressure is 75 psi. If a differential gage
containing mercury is attached to the 12" and
6" sections, what is the deflection of the gage
when the flow of water is 4.25 cfs
downward? Assume no lost head.
20. The pipe shown in the figure has a uniform
diameter of 150 mm. Assume the head loss
between points 1 and 2 is 1.2m and between
points 2 and 3 is 2.0 m. Determine the
discharge of water in the pipe and the
pressure head at point 2.
You might also like
- College of Engineering, Computer Studies and Architecture: Problem Sets in Hydraulics (HYDL01E)Document8 pagesCollege of Engineering, Computer Studies and Architecture: Problem Sets in Hydraulics (HYDL01E)Ria LauronNo ratings yet
- Chap 16Document5 pagesChap 16shaito100% (2)
- Tutorial Sheet 7Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 7AmyRapaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Chapter 2 Problem SetDocument6 pagesHydraulics Chapter 2 Problem SetjosephussucoNo ratings yet
- Soal Tugas BernoulliDocument7 pagesSoal Tugas BernoulliAnnisaNurulFadilahNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems and Problem Set in Fluid FlowDocument7 pagesSample Problems and Problem Set in Fluid Flowreynaldgurion09No ratings yet
- Problems 244 294Document14 pagesProblems 244 294Happy Feets50% (6)
- Case Study - Fluid Mechanics - Bernouli Equation-1Document1 pageCase Study - Fluid Mechanics - Bernouli Equation-1KAYSAR HAMIDNo ratings yet
- ECW 231 Tutorial and Answers Continuity and Energy Eqn and Their Applications - Sept19Document8 pagesECW 231 Tutorial and Answers Continuity and Energy Eqn and Their Applications - Sept19hairinnisaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Bernoulli Equation Part 2Document2 pagesTutorial Bernoulli Equation Part 2Muhamad Hazim ZaabaNo ratings yet
- Assignement 3 FMDocument3 pagesAssignement 3 FMREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- BernaulliDocument6 pagesBernaulliCamille SemillaNo ratings yet
- Aalim Muhammed Salegh College of Engineering Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument6 pagesAalim Muhammed Salegh College of Engineering Department of Mechanical EngineeringMaran ElangovanNo ratings yet
- MTO - PROBLEM - SHEETS - 2and 3Document5 pagesMTO - PROBLEM - SHEETS - 2and 3MOHIT GUPTANo ratings yet
- FM QB At-2Document3 pagesFM QB At-2Tarini DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Me331-Quiz No. 3 - Problems OnlyDocument1 pageMe331-Quiz No. 3 - Problems OnlyEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Review Chem Eng3 Flow of Fluids PDFDocument4 pagesReview Chem Eng3 Flow of Fluids PDFOwenPonceUmacobNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii FLUID DYNAMICS: Surface and Body Forces, Concepts of Fluid System andDocument23 pagesUnit-Iii FLUID DYNAMICS: Surface and Body Forces, Concepts of Fluid System andyrajesh1050% (2)
- ES 65 Drill 2Document2 pagesES 65 Drill 2edmark icalina100% (1)
- Assignment Set 3 of CE (ES) 401 2023Document7 pagesAssignment Set 3 of CE (ES) 401 2023Kausik BeraNo ratings yet
- B Tech Mechanical QuestionsDocument11 pagesB Tech Mechanical QuestionsAnkita VermaNo ratings yet
- Sheet (1) Fluid Mechanics 2Document6 pagesSheet (1) Fluid Mechanics 2drawanyNo ratings yet
- Mto Problem Sheets 1 2 3Document5 pagesMto Problem Sheets 1 2 3Prakash DoliyaNo ratings yet
- Power Plant and Industrial Plant Design Pre-Board/RefresherDocument13 pagesPower Plant and Industrial Plant Design Pre-Board/RefresherMark Gil Jalbuena AltezaNo ratings yet
- A Laminar Flow Is Taking Place in A Pipe of Diameter 200 MMDocument9 pagesA Laminar Flow Is Taking Place in A Pipe of Diameter 200 MMANBU RAJ ANo ratings yet
- 9A01304 Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pages9A01304 Fluid MechanicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Compile AssignmentDocument13 pagesCompile AssignmentSilva deNo ratings yet
- CE001DDocument1 pageCE001DRahul AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Fluids Nov / Dec 2013 Important Questions Unit - IDocument5 pagesMechanics of Fluids Nov / Dec 2013 Important Questions Unit - IjvinothupendraNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics - Series 1 (Fundamentals of Fluid Flow) - Sample Problems PDFDocument2 pagesHydraulics - Series 1 (Fundamentals of Fluid Flow) - Sample Problems PDFNica Remollo100% (3)
- Fluid Mechanics - Problems - Solutions July 4 - EducspaceDocument19 pagesFluid Mechanics - Problems - Solutions July 4 - EducspaceAdrian SelgasNo ratings yet
- Camarines Norte State College: College of Engineering SummDocument1 pageCamarines Norte State College: College of Engineering Summshuckss taloNo ratings yet
- Flow of Fluids QuizDocument2 pagesFlow of Fluids QuizJhon Oliver De JoseNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Task 1Document3 pagesModule 3 Task 1Light HouseNo ratings yet
- Assignment Set 2 of CE (ES) 401 2023Document7 pagesAssignment Set 2 of CE (ES) 401 2023Kausik BeraNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - Problems - July 4Document7 pagesFluid Mechanics - Problems - July 4John Paul JacalanNo ratings yet
- Fluid LabDocument2 pagesFluid LabShahidulHoqueSohelNo ratings yet
- MT Assignment - IDocument2 pagesMT Assignment - IDeneshVijayNo ratings yet
- Wala LangDocument3 pagesWala LangEthyl Jean Monday GallarteNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - ProblemsDocument4 pagesFluid Mechanics - ProblemsClement Chima50% (2)
- Fluid Mechanics and Machinery Question BankDocument8 pagesFluid Mechanics and Machinery Question BankGnana Subramanian ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Final Requirement Fluid MechDocument2 pagesFinal Requirement Fluid MechGeva GarradoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics 1Document8 pagesFluid Mechanics 1Rj Jocson100% (1)
- Assignment 2 20232024-1Document8 pagesAssignment 2 20232024-1mhaikalirsyad03No ratings yet
- CENG 197 Problem Set 1 PDFDocument18 pagesCENG 197 Problem Set 1 PDFChristian Acter0% (1)
- Sheet 5Document3 pagesSheet 5Hussien El-masryNo ratings yet
- Unit Operations IIDocument2 pagesUnit Operations IIChristian Mercado PagsinohinNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument5 pagesUnit IJackson ..No ratings yet
- Sheet 3Document4 pagesSheet 3Mohamed TallyNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Part 2 Ready To Print CE PaperDocument15 pagesProblem Set Part 2 Ready To Print CE PaperJeffward Jaguio0% (1)
- HydraulicsDocument5 pagesHydraulicsMark Daryl Lopez Billedo100% (1)
- Tutorial 1 Viscous Flow in PipesDocument5 pagesTutorial 1 Viscous Flow in PipesAcap AliasNo ratings yet
- Question Bank MechDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank MechSandeep MoreNo ratings yet
- FluidDocument1 pageFluidMahmoud Abo ElhamdNo ratings yet
- Ha 5Document2 pagesHa 5PRIYANSHU VATSNo ratings yet
- Al On Internal Flows KjiouDocument2 pagesAl On Internal Flows KjiouAravind SomasundaramNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 MEC 207Document7 pagesAssignment 4 MEC 207Praveen SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ce315 Ce31s4 p2.4 de GuzmanDocument3 pagesCe315 Ce31s4 p2.4 de GuzmanChristianNo ratings yet
- Ce315 Ce31s4 Plate 7Document8 pagesCe315 Ce31s4 Plate 7ChristianNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 - EvaporationDocument5 pagesAssignment 4 - EvaporationChristianNo ratings yet
- Plate #1Document2 pagesPlate #1ChristianNo ratings yet
- Titration Ws AnswersDocument1 pageTitration Ws AnswersChristianNo ratings yet
- PS2Document1 pagePS2ChristianNo ratings yet
- CapacitanceDocument23 pagesCapacitanceChristianNo ratings yet
- Tower Crane TBGDocument48 pagesTower Crane TBGChristianNo ratings yet
- SOILMECHANICS Laboratory Manual 11 ExperimentsDocument58 pagesSOILMECHANICS Laboratory Manual 11 ExperimentsChristianNo ratings yet
- Paper 12 10970 6015Document11 pagesPaper 12 10970 6015ChristianNo ratings yet
- StoichiometryDocument51 pagesStoichiometryChristianNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - TorsionDocument28 pagesModule 3 - TorsionChristianNo ratings yet
- Module 1.1 StressDocument33 pagesModule 1.1 StressChristianNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document27 pagesGroup 1ChristianNo ratings yet
- Strain RBF-2Document32 pagesStrain RBF-2ChristianNo ratings yet
- Turbojet Engine With T-S DiagramDocument10 pagesTurbojet Engine With T-S Diagramprakash tyagiNo ratings yet
- Total Marks: 25 Duration: One Hour: Xii-Msths Case Study Questions - Test Term-IDocument8 pagesTotal Marks: 25 Duration: One Hour: Xii-Msths Case Study Questions - Test Term-ISABARI SRINIVAS ANo ratings yet
- Essential Orthopaedics 2Nd Edition Mark D Miller Full ChapterDocument67 pagesEssential Orthopaedics 2Nd Edition Mark D Miller Full Chaptermargaret.jones429100% (8)
- Samsung UA55KU7000 55 Inch 139cm Smart Ultra HD LED LCD TV User ManualDocument18 pagesSamsung UA55KU7000 55 Inch 139cm Smart Ultra HD LED LCD TV User ManualGuruprasad NagarajasastryNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument23 pagesFluid and ElectrolytesNanaNo ratings yet
- Wachemo UniversityDocument48 pagesWachemo UniversityMarshet yohannes100% (1)
- Powerful Words To Use in PresentationsDocument9 pagesPowerful Words To Use in PresentationsGlobal CommNo ratings yet
- San Miguel National High School Scuala ST., San Juan, San Miguel, Bulacan Summative Test - Oral Communication in Context S.Y. 2021-2022Document3 pagesSan Miguel National High School Scuala ST., San Juan, San Miguel, Bulacan Summative Test - Oral Communication in Context S.Y. 2021-2022Erica AlbaoNo ratings yet
- Surface Preparation Standards JotunDocument2 pagesSurface Preparation Standards JotunbacabacabacaNo ratings yet
- 49 - HD - 2000 New Logo LowDocument12 pages49 - HD - 2000 New Logo LowAgata OwczarekNo ratings yet
- NXF Perforated Cable Tray en 2017Document65 pagesNXF Perforated Cable Tray en 2017LANKAPALLISURINo ratings yet
- Proposed Syllabus: University of North BengalDocument53 pagesProposed Syllabus: University of North BengalDebolina BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Rt7010 Lighting of Railway Premises PDFDocument17 pagesRt7010 Lighting of Railway Premises PDFCezary P.No ratings yet
- 5th-Sunday-of-Lent (2) .2Document1 page5th-Sunday-of-Lent (2) .2Emmanuel ToretaNo ratings yet
- Three Lever ClassesDocument5 pagesThree Lever ClassesSourabh SharafNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis Template For Technology Planning Needs AssessmentDocument12 pagesSWOT Analysis Template For Technology Planning Needs Assessmentapi-290597914No ratings yet
- Gut DecontaminationDocument17 pagesGut DecontaminationRaju NiraulaNo ratings yet
- Itext in Action 2Nd Edition: Chapter 4: Organizing Content in TablesDocument3 pagesItext in Action 2Nd Edition: Chapter 4: Organizing Content in Tablesalinux75No ratings yet
- Clinical JudgementDocument5 pagesClinical Judgementapi-663643642No ratings yet
- Baseband Radio Node Customized Delta Telefonica VCT 2018Document79 pagesBaseband Radio Node Customized Delta Telefonica VCT 2018sammyd2009100% (2)
- Crew Health Self-Declaration and Daily Temperature Record - Global - Onsigner Version OCT2020Document2 pagesCrew Health Self-Declaration and Daily Temperature Record - Global - Onsigner Version OCT2020Knowrain ParasNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Class 12Document22 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Class 12Siddharth SinghNo ratings yet
- Apply For Car Loan in Canada From Canadian Auto CenterDocument1 pageApply For Car Loan in Canada From Canadian Auto CenterCanadian Auto CenterNo ratings yet
- Fernerkundungsbasierte, Automatisierte, Multisensorale Brandflächendetektion Im Kruger National Park, SüdafrikaDocument151 pagesFernerkundungsbasierte, Automatisierte, Multisensorale Brandflächendetektion Im Kruger National Park, SüdafrikawurstomanNo ratings yet
- M.C.Qs On Indus Valley CivilizationDocument3 pagesM.C.Qs On Indus Valley CivilizationRekha MishraNo ratings yet
- StartupDocument2 pagesStartupAdhy KhairunyNo ratings yet
- Volume 7 No 8 2018Document142 pagesVolume 7 No 8 2018Salhi AmaraNo ratings yet
- Ephesians 4 - InterlinearDocument5 pagesEphesians 4 - InterlinearSidney AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Research Process - StepsDocument31 pagesResearch Process - StepsPulkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Planning and Control: MPC 6 EditionDocument44 pagesManufacturing Planning and Control: MPC 6 EditionSagar GuptaNo ratings yet