Professional Documents
Culture Documents
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
55 viewsA. Group I: Major Minerals: Food Sources Function Deficiency/Toxicity
A. Group I: Major Minerals: Food Sources Function Deficiency/Toxicity
Uploaded by
Mechelle ColumbeThis document provides information on group trace minerals and minerals, including their food sources, functions, and deficiency/toxicity symptoms. Major minerals discussed are calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium, phosphorus, sulfur, and chloride. Trace minerals include iron, iodine, manganese, copper, cobalt, and zinc. Each mineral entry lists key foods containing it and its roles in the body, with examples of deficiency or toxicity conditions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Print NCLEX Study - Mark Klimek Blue BookDocument17 pagesPrint NCLEX Study - Mark Klimek Blue Booklento1990100% (1)
- Magic MouthwashDocument5 pagesMagic MouthwashAdiAri Rosiu100% (3)
- New Hire Med. Assessment Study GuideDocument24 pagesNew Hire Med. Assessment Study GuideNada PersonalNo ratings yet
- Vitamins Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesVitamins Cheat SheetElijah GarciaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Notes Science Form 2Document9 pagesNutrition Notes Science Form 2Yi YingNo ratings yet
- Vitamins SpreadsheetDocument6 pagesVitamins SpreadsheetB-Rock Daniels100% (1)
- Vitamins: Vitamin What It Does Where Is It Found Daily ValueDocument5 pagesVitamins: Vitamin What It Does Where Is It Found Daily ValueCarole ShuNo ratings yet
- Commonly Used IV Cardiac Medications For Adults Pocket Reference Card PDFDocument12 pagesCommonly Used IV Cardiac Medications For Adults Pocket Reference Card PDFYannis Zoldenberg100% (1)
- Chapter 3 NutritionDocument16 pagesChapter 3 NutritionDARRSHANA A/P MURUGAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Form 2 NutritionDocument15 pagesForm 2 NutritionZern MegaNo ratings yet
- MineralsDocument22 pagesMineralsLatha SukumarNo ratings yet
- MineralsDocument22 pagesMineralsLatha SukumarNo ratings yet
- Minerals: Water and Body FluidsDocument4 pagesMinerals: Water and Body FluidsbrooklynNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MineralsDocument22 pagesIntroduction To MineralsJaveria MerajNo ratings yet
- Micronutrients: MineralsDocument3 pagesMicronutrients: MineralsRANDY ERNEST GESTOSANINo ratings yet
- Minerals Notes-CHAP 4Document4 pagesMinerals Notes-CHAP 4DIey ChokiEyNo ratings yet
- Minerals: Minerals Function Deficiency Toxicity Food SourcesDocument7 pagesMinerals: Minerals Function Deficiency Toxicity Food SourcesRikkimae NaagNo ratings yet
- 17.0 - Food and NutritionDocument16 pages17.0 - Food and NutritionBuddhini JNo ratings yet
- Pink Orange Cute Playful Illustrative Food Presentation - 20231023 - 203505 - 0000Document20 pagesPink Orange Cute Playful Illustrative Food Presentation - 20231023 - 203505 - 0000Bondoc John JustinNo ratings yet
- DietDocument60 pagesDietVanditha ChakaravarthyNo ratings yet
- Minerals TableDocument4 pagesMinerals Tableapi-512416839No ratings yet
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument26 pagesVitamins and MineralsAisha Doll100% (1)
- Diet & NutritionDocument117 pagesDiet & NutritionSubbalekshmiNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument6 pagesNutritionrkjoseph1410No ratings yet
- NUTRIDocument16 pagesNUTRIthisswannNo ratings yet
- Mine Rals: Nutrition and Diet Therapy Lecture Notes On Minerals and WaterDocument7 pagesMine Rals: Nutrition and Diet Therapy Lecture Notes On Minerals and Watermildred alidonNo ratings yet
- The Body Needs Many MineralsDocument3 pagesThe Body Needs Many MineralsTendekai GwatidzoNo ratings yet
- Notes Form 2 Chapter 3 NutritionDocument19 pagesNotes Form 2 Chapter 3 NutritionKaviish AnandanNo ratings yet
- Low Potassium Diet GuidelinesDocument2 pagesLow Potassium Diet GuidelinesmaitridiagnosticsNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: Group Member 1.ivy Chan 2.judy Low 3.claudia 4.albertina 5.christineDocument19 pagesNutrition: Group Member 1.ivy Chan 2.judy Low 3.claudia 4.albertina 5.christineDayah D DebabNo ratings yet
- Human Development and Human BehaviorDocument11 pagesHuman Development and Human BehaviormirtchNo ratings yet
- 2.1 The Classes of FoodDocument16 pages2.1 The Classes of FoodFatin NazirahNo ratings yet
- Vessel, Vein, & Nerve Health BlueprintDocument15 pagesVessel, Vein, & Nerve Health BlueprintMaureenDurandNo ratings yet
- Nutrition PART 3 - 0Document15 pagesNutrition PART 3 - 0rtyguhjiNo ratings yet
- Vitamins: Vitamin What? Where? Deficiency ToxicityDocument6 pagesVitamins: Vitamin What? Where? Deficiency ToxicitybrooklynNo ratings yet
- Mineral Sources Funtions Symptoms of Defiency CalciumDocument2 pagesMineral Sources Funtions Symptoms of Defiency CalciumPraveen HariNo ratings yet
- 6 Essential NutrientsDocument5 pages6 Essential NutrientsRussel Kate SulangNo ratings yet
- Fat Soluble VitaminsDocument4 pagesFat Soluble VitaminsSummiyah ShahbazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Nutrition: 2.1 Classes of FoodDocument11 pagesChapter 2: Nutrition: 2.1 Classes of Foodpclim2010No ratings yet
- Kwashiorkor: The Function of Fat IncludeDocument3 pagesKwashiorkor: The Function of Fat IncludeJASHINEE A/P BASKARAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Anemias Caused by Decreased Erythrocyte ProductionDocument5 pagesAnemias Caused by Decreased Erythrocyte ProductionJette Charmae OlboNo ratings yet
- WS ON MINERALS AND VITAMINS IB Biology SLDocument10 pagesWS ON MINERALS AND VITAMINS IB Biology SLFRNo ratings yet
- NCM116j Reviewer Endocrine UPDATEDDocument14 pagesNCM116j Reviewer Endocrine UPDATEDAliza Abn bklNo ratings yet
- Minerals MBC 301Document22 pagesMinerals MBC 301scottscarlet967No ratings yet
- Macrominerals: Major Minerals Mineral Function SourcesDocument2 pagesMacrominerals: Major Minerals Mineral Function Sourcesgelsa dragonNo ratings yet
- Biokeme: Minerals: Asia Pacific College of Advanced StudiesDocument5 pagesBiokeme: Minerals: Asia Pacific College of Advanced StudiesTrisha Anne MariNo ratings yet
- Human NutritionDocument23 pagesHuman NutritionverifyqbytezNo ratings yet
- 6.2 - Concept of Balanced DietDocument27 pages6.2 - Concept of Balanced DietNigel Subhash BakkerNo ratings yet
- Cielo, Divina Gracia V. BSM-1 Vitamins Function RDA Sources Effects of Deficiency Symptoms of Excess ADocument10 pagesCielo, Divina Gracia V. BSM-1 Vitamins Function RDA Sources Effects of Deficiency Symptoms of Excess ADivina Gracia Vibal CieloNo ratings yet
- Nutrient ChartDocument7 pagesNutrient ChartDanilo Clerigo Sr.No ratings yet
- Reviewer - 2017 KalusuGalingan Quiz Show PDFDocument73 pagesReviewer - 2017 KalusuGalingan Quiz Show PDFFred Fernando100% (1)
- Fundamentals of NutritionDocument6 pagesFundamentals of NutritionbananakyuNo ratings yet
- 01 - B7 Human Nutrition - PPT 2022-23Document45 pages01 - B7 Human Nutrition - PPT 2022-23Shelly ChanNo ratings yet
- Nutri (Minerals)Document83 pagesNutri (Minerals)Juliana LegarteNo ratings yet
- Summary of Major Minerals and Trace ElementsDocument2 pagesSummary of Major Minerals and Trace ElementsrishellemaepilonesNo ratings yet
- Vitamins: Vitamin What It Does Where Is It Found Daily Value BiotinDocument6 pagesVitamins: Vitamin What It Does Where Is It Found Daily Value BiotinissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- F2 Chapter 3 NutritionDocument17 pagesF2 Chapter 3 NutritionYAP SHAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: 3.1 Classes of FoodDocument7 pagesNutrition: 3.1 Classes of FoodYARSHANA A/P SIVAM MoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document36 pagesChapter 7HC GamerNo ratings yet
- PE FinalDocument26 pagesPE FinalCheryz Angel LabillesNo ratings yet
- InteractiveNFL Vitamins&MineralsChart October2021Document8 pagesInteractiveNFL Vitamins&MineralsChart October2021z03324408886No ratings yet
- F2 CHP 3 Nutrition (Chinese)Document18 pagesF2 CHP 3 Nutrition (Chinese)ChuahSiewHoon100% (2)
- AppendixC - Nutrient Chart PDFDocument7 pagesAppendixC - Nutrient Chart PDFMaria Christina LagartejaNo ratings yet
- High Protein Diet: Healthy High Protein Meal to add Weight, Build Strenght Including Low-carb and Muscle GrowthFrom EverandHigh Protein Diet: Healthy High Protein Meal to add Weight, Build Strenght Including Low-carb and Muscle GrowthNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument2 pagesConcept MapAngeline de GalaNo ratings yet
- Flexion Type Teardrop FractureDocument20 pagesFlexion Type Teardrop FractureMufti Akhmad Shadiq AfnsNo ratings yet
- Overview of Guillain-Barré Syndrome: I. Literature ReviewDocument10 pagesOverview of Guillain-Barré Syndrome: I. Literature ReviewS Dian RNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) - UpToDateDocument57 pagesPediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) - UpToDateSofíaNo ratings yet
- Seizure Final DocDocument8 pagesSeizure Final DocVictoria KuwonaNo ratings yet
- Cancer CaDocument6 pagesCancer CaRocco WalksNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Course Code: PHR510 Section: 1 Submitted To: Ms. Tahmina YasminDocument25 pagesPresented By: Course Code: PHR510 Section: 1 Submitted To: Ms. Tahmina YasminXd DipNo ratings yet
- Complete DNS fILE SOLVEDDocument82 pagesComplete DNS fILE SOLVEDFareed KhanNo ratings yet
- NAVLE Competencies FINALDocument19 pagesNAVLE Competencies FINALShubham HarishNo ratings yet
- Enlg Argumenative Essay 1Document15 pagesEnlg Argumenative Essay 1aishazariya02No ratings yet
- Blood TransfusionDocument6 pagesBlood TransfusionSophia Mae RoseteNo ratings yet
- Steroid Injections: Read This If You Are Planning On Having A Steroid InjectionDocument3 pagesSteroid Injections: Read This If You Are Planning On Having A Steroid InjectionyudhaNo ratings yet
- Second Grading Exam in MAPEH-10Document4 pagesSecond Grading Exam in MAPEH-10Reymundo PenialaNo ratings yet
- Sanjeevini Combination Sheet For SSC 9 Blood Pressure LowDocument1 pageSanjeevini Combination Sheet For SSC 9 Blood Pressure LowEduardoNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument31 pagesPreviewpdfsamNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 4 - Balamad, Maria Karla M.Document3 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 4 - Balamad, Maria Karla M.Maria Karla BalamadNo ratings yet
- Fungus and Mycology For DermatophytesDocument2 pagesFungus and Mycology For DermatophytesCharan RebelNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields and Human HealthDocument5 pagesElectromagnetic Fields and Human HealthAmanjot100% (1)
- Textbook Ebook Diagnostic Ultrasound For Sonographers Aya Kamaya All Chapter PDFDocument43 pagesTextbook Ebook Diagnostic Ultrasound For Sonographers Aya Kamaya All Chapter PDFolivia.anderson705100% (9)
- Lower Limb Trauma: Cast Application For Common FracturesDocument58 pagesLower Limb Trauma: Cast Application For Common FracturesdrusmanjamilhcmdNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Intradialytic Stretching Exercise On Pain Due To Muscle Cramps Among Patients Undergoing HaemodialysisDocument7 pagesEffectiveness of Intradialytic Stretching Exercise On Pain Due To Muscle Cramps Among Patients Undergoing HaemodialysisAhmad IsmailNo ratings yet
- Thesis Topics On Snake BiteDocument4 pagesThesis Topics On Snake Biteshannonsandbillings100% (2)
- Micropara LabDocument8 pagesMicropara LabFatima KateNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2-Research Process 1 and 2Document7 pagesLesson 2-Research Process 1 and 2Jigs YumangNo ratings yet
- Body Temperature PDFDocument56 pagesBody Temperature PDFBanupriya-No ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Foot Reflexology On Pain Among Hemodialysis PatientsDocument5 pagesEffectiveness of Foot Reflexology On Pain Among Hemodialysis PatientsIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
A. Group I: Major Minerals: Food Sources Function Deficiency/Toxicity
A. Group I: Major Minerals: Food Sources Function Deficiency/Toxicity
Uploaded by
Mechelle Columbe100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
55 views4 pagesThis document provides information on group trace minerals and minerals, including their food sources, functions, and deficiency/toxicity symptoms. Major minerals discussed are calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium, phosphorus, sulfur, and chloride. Trace minerals include iron, iodine, manganese, copper, cobalt, and zinc. Each mineral entry lists key foods containing it and its roles in the body, with examples of deficiency or toxicity conditions.
Original Description:
Original Title
Document (4)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information on group trace minerals and minerals, including their food sources, functions, and deficiency/toxicity symptoms. Major minerals discussed are calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium, phosphorus, sulfur, and chloride. Trace minerals include iron, iodine, manganese, copper, cobalt, and zinc. Each mineral entry lists key foods containing it and its roles in the body, with examples of deficiency or toxicity conditions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
55 views4 pagesA. Group I: Major Minerals: Food Sources Function Deficiency/Toxicity
A. Group I: Major Minerals: Food Sources Function Deficiency/Toxicity
Uploaded by
Mechelle ColumbeThis document provides information on group trace minerals and minerals, including their food sources, functions, and deficiency/toxicity symptoms. Major minerals discussed are calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium, phosphorus, sulfur, and chloride. Trace minerals include iron, iodine, manganese, copper, cobalt, and zinc. Each mineral entry lists key foods containing it and its roles in the body, with examples of deficiency or toxicity conditions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Exercise on Group Trace Minerals and Minerals
Name: Columbe, Mechelle M.
Score:
Year: and Section: BSN – 2D
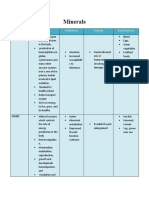
A. GROUP I: MAJOR MINERALS
FOOD SOURCES FUNCTION DEFICIENCY/TOXICITY
CALCIUM Milk, cheese • Development of bones and teeth Deficiency
Sardines • Transmission of nerve impulses ➢ Osteoporosis
Salmon • Blood clotting ➢ Osteomalacia
Some dark green • Normal heart action ➢ Rickets
leafy vegetables • Normal muscle activity ➢ Tetany
➢ Retarded growth
➢ Poor tooth and bone
formation
MAGNESIUM Green, leafy • Synthesis of ATP Deficiency
vegetables • Transmission of nerve impulses ➢ Normally unknown
Whole grains • Activation of metabolic enzymes ➢ Mental, emotional, and
Avocados • Constituent of bones, muscles, and muscles disorders
Nuts red blood cells
Milk •Necessary for healthy muscles and nerves
Legumes
Bananas
SODIUM Table salt • Maintenance of fluid balance Deficiency
Eggs • Transmission of nerve impulses ➢ Nausea
Seafood • Osmosis ➢ Exhaustion
Milk • Acid-base balance ➢ Muscle cramps
• Regulation of muscle and nerve irritability Toxicity
➢ Increase in blood pressure
➢ Edema
POTASSIUM Oranges, bananas • Contraction of muscles Deficiency
Beef, eggs • Maintenance of fluid balance ➢ Hypokalemia
Poultry • Transmission of nerve impulses ➢ Muscle weakness
Milk, cheese • Osmosis ➢ Confusion
• Regular heart rhythm ➢ Abnormal heartbeat
• Cell metabolism Toxicity
➢ Hyperkalemia
➢ Potential life-threatening
irregular heartbeats
PHOSPHORUS Milk, cheese • Development of bones and teeth Deficiency
Lean meat • Maintenance of normal acid-base ➢ Poor tooth and bone
Poultry balance of the blood formation
Fish • Constituent of all body cells ➢ Weakness
Whole-grain • Necessary for effectiveness of some ➢ Anorexia
cereals Legumes vitamins ➢ General malaise
Nuts • Metabolism of carbohydrates, fats,
and proteins
SULFUR Eggs • Maintenance of protein structure Unknown
Poultry • For building hair, nails, and all body tissues
Fish • Constituent of all body cells
CHLORIDE Table salt • Gastric acidity Deficiency
Eggs • Regulation of osmotic pressure ➢ Imbalance in gastric acidity
Seafood • Osmosis ➢ Imbalance in blood pH
Milk • Fluid-base balance ➢ Nausea
• Formation of hydrochloric acid ➢ Exhaustion
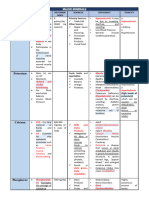
B. GROUP II: TRACE MINERALS
FOOD SOURCES FUNCTION DEFICIENCY/TOXICITY
IRON Liver (Pork) • Constitute of hemoglobin and ➢ Anemia
Enriched Rice myoglobin ➢ Hemosidorosis
Rice Bran iron has important role to play as a carrier ➢ Hemochromatosis
Saluyot of oxygen needed for cellular respiration
Sitao Leaves • Necessary for hemoglobin
Spaghetti formation • An active component of tissue
Dried Beans enzyme involved in the conversion of
Ampalaya Leaves beta carotene to vitamin A, synthesis of
Kamote Leaves purines, antibody production, collagen
Gabi Leaves, synthesis & the other functions associated
Seaweeds with the respiratory chain.
Malunggay
Leaves, Peanuts
Green & Red
Monggo
Mustard Leaves,
Sesame Seeds
Petsay, Soybeans
Pork Kidney,
Spleen, Lung, Beef
Liver
Egg
Alimango, Aligue,
Clams, Hipon,
Tulingan
IODINE Iodized salt • Synthesis of thyroxine, a hormone in the ➢ Goiter
Seafood thyroid gland ➢ Cretinism
Some plant foods ➢ Myxedema
grown in soil
bordering the
sea(seaweeds)
MANGANESE Nuts • Activator of a number of metabolic ➢ Its deficiency has not been
Whole cereal reactions documented
grains • Acts as catalyst of a number of ➢ Toxicity from excessive
Dried legumes enzymes necessary in glucose & fat ingestion of manganese is
Tea metabolism unknown
Green leafy • Increases storage of thiamine ➢ However, people who have
vegetables Dried inhaled high concentrations
fruits
of manganese dust have
Fresh fruits Non-
developed neurological
leafy vegetables
problems
COPPER Organs of meats • Essential in the formation of hemoglobin ➢ Depigmentation of the skin
Shellfish (oyster) and hair
Nuts • Promotes absorption of iron from ➢ CNS abnormalities
Cocoa the GIT & the transportation of such from ➢ hypotonia
Leafy vegetables the tissues to the plasma. ➢ hypothermia
Eggs • Valuable catalyst in oxidation- ➢ Skeletal mineralization in
Muscle of meat reduction mechanism s of living cells as infants & children
Fish well as a constituent of several of the
Poultry oxidative enzymes for amino acids.
Cherries • Also helps to maintain the integrity
Mushroom of the myelin sheath to surrounding nerve
Whole grain fibers.
Cereals • It is part of tyrosinase which is
Beans involved in the formation of melanin
Peas pigment of hair and skin.
Fresh fruits • It helps in bone formation.
Refined cereals
COBALT Liver • Constituent of B12 Deficiency
Kidney • Essential factor which is necessary for ➢ pernicious anemia
Oyster, clams RBC formation.
Lean meat • Essential for normal function of all Excess
Poultry cells. ➢ polycythemia
Salt water fish
Milk
ZINC Meat • It is involved in a wide range of cellular ➢ Decreased appetite and
Fish functions being an taste acuity alopecia
Eggs integral part of several metallo enzymes and ➢ delayed growth, dwarfism,
Dairy products also acts as regulator of activities of certain ➢ hypogonadism (subnormal
Wheat germ Nuts enzymes in the body. ➢ development of male sex
Legumes. • It is present in RNA. ➢ organs),
• It is related to the hormone insulin, poor wound healing,
glucagons, ACTH- adrenocorticotropic ➢ anemia acnelike
hormone, growth hormone, gonadotrophin ➢ rash,
& testosterone. ➢ impaired immune response
• It plays a role in the acceleration of ➢
wound healing and for a normal sense of
taste.
MOLYBDENIUM Milk • Constituent of enzymes and is thought ➢ No deficiencies have been
Liver to play a role in metabolism noted in people who
Legumes • Present inbound as an integral part of consume a normal diet.
Cereals the various enzyme molecules. ➢ Headache, irritability, night
blindness, lethargy, coma,
abnormal metabolism of
containing sulphur
containing amino acids.
➢ Excessive intake can inhibit
copper absorption.
FLOURIDE Fluoridated Water • It forms a more stable compound in ➢ The deficiency of fluoride
Fish the dentine and enamel of the teeth thus can result in increased tooth
Tea contain reducing dental caries and minimizing bone decay.
fluoride loss. ➢ Excessive amounts of
• It is effective in the treatment of fluoride in drinking water
osteoporosis. have been known to cause
permanent discoloration or
mottling of children’s teeth.
CHROMIUM Meat • Associated with glucose and lipid ➢ Chromium deficiency
Mushrooms metabolism appears to be related to
Nuts • Decrease with age except in the lungs, disturbances in glucose
Organ meats where chromium accumulates metabolism
Wheat germ
SELENIUM Seafood • Component of an enzyme that acts as ➢ Symptoms of selenium
Kidney an antioxidant deficiency are unclear, but
Liver • Protects cells against oxidation and selenium supplements
Muscle meats spares vitamin E appear to be effective in
treating Keshan disease.
➢ High doses (1 mg or more
daily) are toxic and can cause
vomiting, loss of hair and nails,
and skin lesions.
VANADIUM Mushrooms • Involved in the appetite crystal formation of ➢ Growth retardation
Shellfish tooth enamel, hence may contribute to ➢ Bone deformities
Black pepper resistant to dental decay. ➢ Infertility
Parsley
Dill weed
Beer
Wine
Grain and grain
products
Artificially
sweetened drinks.
You might also like
- Print NCLEX Study - Mark Klimek Blue BookDocument17 pagesPrint NCLEX Study - Mark Klimek Blue Booklento1990100% (1)
- Magic MouthwashDocument5 pagesMagic MouthwashAdiAri Rosiu100% (3)
- New Hire Med. Assessment Study GuideDocument24 pagesNew Hire Med. Assessment Study GuideNada PersonalNo ratings yet
- Vitamins Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesVitamins Cheat SheetElijah GarciaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Notes Science Form 2Document9 pagesNutrition Notes Science Form 2Yi YingNo ratings yet
- Vitamins SpreadsheetDocument6 pagesVitamins SpreadsheetB-Rock Daniels100% (1)
- Vitamins: Vitamin What It Does Where Is It Found Daily ValueDocument5 pagesVitamins: Vitamin What It Does Where Is It Found Daily ValueCarole ShuNo ratings yet
- Commonly Used IV Cardiac Medications For Adults Pocket Reference Card PDFDocument12 pagesCommonly Used IV Cardiac Medications For Adults Pocket Reference Card PDFYannis Zoldenberg100% (1)
- Chapter 3 NutritionDocument16 pagesChapter 3 NutritionDARRSHANA A/P MURUGAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Form 2 NutritionDocument15 pagesForm 2 NutritionZern MegaNo ratings yet
- MineralsDocument22 pagesMineralsLatha SukumarNo ratings yet
- MineralsDocument22 pagesMineralsLatha SukumarNo ratings yet
- Minerals: Water and Body FluidsDocument4 pagesMinerals: Water and Body FluidsbrooklynNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MineralsDocument22 pagesIntroduction To MineralsJaveria MerajNo ratings yet
- Micronutrients: MineralsDocument3 pagesMicronutrients: MineralsRANDY ERNEST GESTOSANINo ratings yet
- Minerals Notes-CHAP 4Document4 pagesMinerals Notes-CHAP 4DIey ChokiEyNo ratings yet
- Minerals: Minerals Function Deficiency Toxicity Food SourcesDocument7 pagesMinerals: Minerals Function Deficiency Toxicity Food SourcesRikkimae NaagNo ratings yet
- 17.0 - Food and NutritionDocument16 pages17.0 - Food and NutritionBuddhini JNo ratings yet
- Pink Orange Cute Playful Illustrative Food Presentation - 20231023 - 203505 - 0000Document20 pagesPink Orange Cute Playful Illustrative Food Presentation - 20231023 - 203505 - 0000Bondoc John JustinNo ratings yet
- DietDocument60 pagesDietVanditha ChakaravarthyNo ratings yet
- Minerals TableDocument4 pagesMinerals Tableapi-512416839No ratings yet
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument26 pagesVitamins and MineralsAisha Doll100% (1)
- Diet & NutritionDocument117 pagesDiet & NutritionSubbalekshmiNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument6 pagesNutritionrkjoseph1410No ratings yet
- NUTRIDocument16 pagesNUTRIthisswannNo ratings yet
- Mine Rals: Nutrition and Diet Therapy Lecture Notes On Minerals and WaterDocument7 pagesMine Rals: Nutrition and Diet Therapy Lecture Notes On Minerals and Watermildred alidonNo ratings yet
- The Body Needs Many MineralsDocument3 pagesThe Body Needs Many MineralsTendekai GwatidzoNo ratings yet
- Notes Form 2 Chapter 3 NutritionDocument19 pagesNotes Form 2 Chapter 3 NutritionKaviish AnandanNo ratings yet
- Low Potassium Diet GuidelinesDocument2 pagesLow Potassium Diet GuidelinesmaitridiagnosticsNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: Group Member 1.ivy Chan 2.judy Low 3.claudia 4.albertina 5.christineDocument19 pagesNutrition: Group Member 1.ivy Chan 2.judy Low 3.claudia 4.albertina 5.christineDayah D DebabNo ratings yet
- Human Development and Human BehaviorDocument11 pagesHuman Development and Human BehaviormirtchNo ratings yet
- 2.1 The Classes of FoodDocument16 pages2.1 The Classes of FoodFatin NazirahNo ratings yet
- Vessel, Vein, & Nerve Health BlueprintDocument15 pagesVessel, Vein, & Nerve Health BlueprintMaureenDurandNo ratings yet
- Nutrition PART 3 - 0Document15 pagesNutrition PART 3 - 0rtyguhjiNo ratings yet
- Vitamins: Vitamin What? Where? Deficiency ToxicityDocument6 pagesVitamins: Vitamin What? Where? Deficiency ToxicitybrooklynNo ratings yet
- Mineral Sources Funtions Symptoms of Defiency CalciumDocument2 pagesMineral Sources Funtions Symptoms of Defiency CalciumPraveen HariNo ratings yet
- 6 Essential NutrientsDocument5 pages6 Essential NutrientsRussel Kate SulangNo ratings yet
- Fat Soluble VitaminsDocument4 pagesFat Soluble VitaminsSummiyah ShahbazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Nutrition: 2.1 Classes of FoodDocument11 pagesChapter 2: Nutrition: 2.1 Classes of Foodpclim2010No ratings yet
- Kwashiorkor: The Function of Fat IncludeDocument3 pagesKwashiorkor: The Function of Fat IncludeJASHINEE A/P BASKARAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Anemias Caused by Decreased Erythrocyte ProductionDocument5 pagesAnemias Caused by Decreased Erythrocyte ProductionJette Charmae OlboNo ratings yet
- WS ON MINERALS AND VITAMINS IB Biology SLDocument10 pagesWS ON MINERALS AND VITAMINS IB Biology SLFRNo ratings yet
- NCM116j Reviewer Endocrine UPDATEDDocument14 pagesNCM116j Reviewer Endocrine UPDATEDAliza Abn bklNo ratings yet
- Minerals MBC 301Document22 pagesMinerals MBC 301scottscarlet967No ratings yet
- Macrominerals: Major Minerals Mineral Function SourcesDocument2 pagesMacrominerals: Major Minerals Mineral Function Sourcesgelsa dragonNo ratings yet
- Biokeme: Minerals: Asia Pacific College of Advanced StudiesDocument5 pagesBiokeme: Minerals: Asia Pacific College of Advanced StudiesTrisha Anne MariNo ratings yet
- Human NutritionDocument23 pagesHuman NutritionverifyqbytezNo ratings yet
- 6.2 - Concept of Balanced DietDocument27 pages6.2 - Concept of Balanced DietNigel Subhash BakkerNo ratings yet
- Cielo, Divina Gracia V. BSM-1 Vitamins Function RDA Sources Effects of Deficiency Symptoms of Excess ADocument10 pagesCielo, Divina Gracia V. BSM-1 Vitamins Function RDA Sources Effects of Deficiency Symptoms of Excess ADivina Gracia Vibal CieloNo ratings yet
- Nutrient ChartDocument7 pagesNutrient ChartDanilo Clerigo Sr.No ratings yet
- Reviewer - 2017 KalusuGalingan Quiz Show PDFDocument73 pagesReviewer - 2017 KalusuGalingan Quiz Show PDFFred Fernando100% (1)
- Fundamentals of NutritionDocument6 pagesFundamentals of NutritionbananakyuNo ratings yet
- 01 - B7 Human Nutrition - PPT 2022-23Document45 pages01 - B7 Human Nutrition - PPT 2022-23Shelly ChanNo ratings yet
- Nutri (Minerals)Document83 pagesNutri (Minerals)Juliana LegarteNo ratings yet
- Summary of Major Minerals and Trace ElementsDocument2 pagesSummary of Major Minerals and Trace ElementsrishellemaepilonesNo ratings yet
- Vitamins: Vitamin What It Does Where Is It Found Daily Value BiotinDocument6 pagesVitamins: Vitamin What It Does Where Is It Found Daily Value BiotinissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- F2 Chapter 3 NutritionDocument17 pagesF2 Chapter 3 NutritionYAP SHAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: 3.1 Classes of FoodDocument7 pagesNutrition: 3.1 Classes of FoodYARSHANA A/P SIVAM MoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document36 pagesChapter 7HC GamerNo ratings yet
- PE FinalDocument26 pagesPE FinalCheryz Angel LabillesNo ratings yet
- InteractiveNFL Vitamins&MineralsChart October2021Document8 pagesInteractiveNFL Vitamins&MineralsChart October2021z03324408886No ratings yet
- F2 CHP 3 Nutrition (Chinese)Document18 pagesF2 CHP 3 Nutrition (Chinese)ChuahSiewHoon100% (2)
- AppendixC - Nutrient Chart PDFDocument7 pagesAppendixC - Nutrient Chart PDFMaria Christina LagartejaNo ratings yet
- High Protein Diet: Healthy High Protein Meal to add Weight, Build Strenght Including Low-carb and Muscle GrowthFrom EverandHigh Protein Diet: Healthy High Protein Meal to add Weight, Build Strenght Including Low-carb and Muscle GrowthNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument2 pagesConcept MapAngeline de GalaNo ratings yet
- Flexion Type Teardrop FractureDocument20 pagesFlexion Type Teardrop FractureMufti Akhmad Shadiq AfnsNo ratings yet
- Overview of Guillain-Barré Syndrome: I. Literature ReviewDocument10 pagesOverview of Guillain-Barré Syndrome: I. Literature ReviewS Dian RNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) - UpToDateDocument57 pagesPediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) - UpToDateSofíaNo ratings yet
- Seizure Final DocDocument8 pagesSeizure Final DocVictoria KuwonaNo ratings yet
- Cancer CaDocument6 pagesCancer CaRocco WalksNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Course Code: PHR510 Section: 1 Submitted To: Ms. Tahmina YasminDocument25 pagesPresented By: Course Code: PHR510 Section: 1 Submitted To: Ms. Tahmina YasminXd DipNo ratings yet
- Complete DNS fILE SOLVEDDocument82 pagesComplete DNS fILE SOLVEDFareed KhanNo ratings yet
- NAVLE Competencies FINALDocument19 pagesNAVLE Competencies FINALShubham HarishNo ratings yet
- Enlg Argumenative Essay 1Document15 pagesEnlg Argumenative Essay 1aishazariya02No ratings yet
- Blood TransfusionDocument6 pagesBlood TransfusionSophia Mae RoseteNo ratings yet
- Steroid Injections: Read This If You Are Planning On Having A Steroid InjectionDocument3 pagesSteroid Injections: Read This If You Are Planning On Having A Steroid InjectionyudhaNo ratings yet
- Second Grading Exam in MAPEH-10Document4 pagesSecond Grading Exam in MAPEH-10Reymundo PenialaNo ratings yet
- Sanjeevini Combination Sheet For SSC 9 Blood Pressure LowDocument1 pageSanjeevini Combination Sheet For SSC 9 Blood Pressure LowEduardoNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument31 pagesPreviewpdfsamNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 4 - Balamad, Maria Karla M.Document3 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 4 - Balamad, Maria Karla M.Maria Karla BalamadNo ratings yet
- Fungus and Mycology For DermatophytesDocument2 pagesFungus and Mycology For DermatophytesCharan RebelNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields and Human HealthDocument5 pagesElectromagnetic Fields and Human HealthAmanjot100% (1)
- Textbook Ebook Diagnostic Ultrasound For Sonographers Aya Kamaya All Chapter PDFDocument43 pagesTextbook Ebook Diagnostic Ultrasound For Sonographers Aya Kamaya All Chapter PDFolivia.anderson705100% (9)
- Lower Limb Trauma: Cast Application For Common FracturesDocument58 pagesLower Limb Trauma: Cast Application For Common FracturesdrusmanjamilhcmdNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Intradialytic Stretching Exercise On Pain Due To Muscle Cramps Among Patients Undergoing HaemodialysisDocument7 pagesEffectiveness of Intradialytic Stretching Exercise On Pain Due To Muscle Cramps Among Patients Undergoing HaemodialysisAhmad IsmailNo ratings yet
- Thesis Topics On Snake BiteDocument4 pagesThesis Topics On Snake Biteshannonsandbillings100% (2)
- Micropara LabDocument8 pagesMicropara LabFatima KateNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2-Research Process 1 and 2Document7 pagesLesson 2-Research Process 1 and 2Jigs YumangNo ratings yet
- Body Temperature PDFDocument56 pagesBody Temperature PDFBanupriya-No ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Foot Reflexology On Pain Among Hemodialysis PatientsDocument5 pagesEffectiveness of Foot Reflexology On Pain Among Hemodialysis PatientsIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet