Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 6 (GenBio)
Module 6 (GenBio)
Uploaded by
Christian Angel GomezCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- O Level Biology Notes MapurangaDocument95 pagesO Level Biology Notes Mapurangapeterchiyanja100% (2)
- Cell Membrane Information WorksheetDocument4 pagesCell Membrane Information WorksheetD100% (1)
- Cell Membrane Flow of MaterialsDocument13 pagesCell Membrane Flow of Materialsnorhain4.aNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesCell MembraneQaran PrintingNo ratings yet
- Cell MebraneDocument10 pagesCell MebraneChandra SihombingNo ratings yet
- THE CELL MEMBRANE (Coloured)Document6 pagesTHE CELL MEMBRANE (Coloured)tsteadmanNo ratings yet
- 2.4 - Membranes: 2.4.1 - Draw and Label A Diagram To Show The Structure of MembranesDocument6 pages2.4 - Membranes: 2.4.1 - Draw and Label A Diagram To Show The Structure of MembranesDuong TongNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document14 pagesPresentation 2Maya TareqNo ratings yet
- 9gkneylgi4kueakdv8q9gkney50iscvv SolutionDocument2 pages9gkneylgi4kueakdv8q9gkney50iscvv SolutionArya MohajerNo ratings yet
- 2a-Membranes and Transport 2Document67 pages2a-Membranes and Transport 2kfy8vr7wtwNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY NOTES iAL Biology Unit 1Document7 pagesBIOLOGY NOTES iAL Biology Unit 1Student Alejandro Zhou WeiNo ratings yet
- Letran de Davao, IncDocument3 pagesLetran de Davao, IncPatricia DianeNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane TransportDocument3 pagesCell Membrane TransportHarry TeasdaleNo ratings yet
- The Cell MembraneDocument9 pagesThe Cell MembraneShuchi HossainNo ratings yet
- Biology Module 2: Section 2.5Document20 pagesBiology Module 2: Section 2.5Nasteexo CaliNo ratings yet
- Ch. 5 Pre-ReadingDocument7 pagesCh. 5 Pre-ReadingDJ ISAACS50% (2)
- Cellular Transport Mechanism: General Biology 1Document12 pagesCellular Transport Mechanism: General Biology 1Kenn KennNo ratings yet
- Explanation and Acceptable Reason YeahDocument3 pagesExplanation and Acceptable Reason YeahMj DeguzmanNo ratings yet
- Dela Ysla Russell Iverson T. Biology1Document4 pagesDela Ysla Russell Iverson T. Biology1Elaiza Nicole AccatanNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument30 pagesEarth and Life ScienceChristian VitalesNo ratings yet
- Understanding Biology 1St Edition Mason Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument31 pagesUnderstanding Biology 1St Edition Mason Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFerik.looney743100% (11)
- Transport MechanismsDocument30 pagesTransport MechanismsApril VeraNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Grade 12Document8 pagesCell Membrane Grade 12Olayinka SalmonNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mosaic Model NotesDocument4 pagesFluid Mosaic Model NotesanzalnaamanNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument17 pagesCell MembraneEloisa MadrilenoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Notes Cellular Basis of LifeDocument11 pagesLecture 3 Notes Cellular Basis of Lifeochienganthony001No ratings yet
- q1 Genbio1 Slkweek6 EditDocument13 pagesq1 Genbio1 Slkweek6 EditInele Ellia AgReNo ratings yet
- Advanced Biology Q3Document3 pagesAdvanced Biology Q3MARITHE ROJIANNE MERCADONo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 OutlineDocument5 pagesChapter 5 OutlineShirley PinedaNo ratings yet
- Plasma Membrane Student PPTDocument14 pagesPlasma Membrane Student PPTlube aguasNo ratings yet
- Significance of Liquid in Biological Membranes and Transport MechanismDocument10 pagesSignificance of Liquid in Biological Membranes and Transport Mechanismroshan khanNo ratings yet
- 008 - The Cell Surface MembraneDocument2 pages008 - The Cell Surface MembraneSanah KhanNo ratings yet
- LESSON - 11 - Gen Biology 1Document4 pagesLESSON - 11 - Gen Biology 1Jhay Luiz Cajigal ArquinesNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes: Topic-2ADocument9 pagesBiology Notes: Topic-2Alaiba amirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Cell Membranes and Transport: SummaryDocument4 pagesChapter 4: Cell Membranes and Transport: SummaryMerimaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure - Cell Membrane and TransportDocument6 pagesCell Structure - Cell Membrane and TransportKulsoom UsmanNo ratings yet
- Plasma Membrane The Big PictureDocument4 pagesPlasma Membrane The Big PictureNicolas Gomez CombellasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Student Copy ZoologyDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Student Copy Zoologyapi-523871804No ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Q1 Week 7Document14 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Q1 Week 7JewelNo ratings yet
- Mahan 2Document7 pagesMahan 2KANT JAMES D. MAHANNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument2 pagesCell MembranegrxcieeNo ratings yet
- Anaphy LecDocument6 pagesAnaphy LecfilesNo ratings yet
- Module 7, Anatomy and Physiogy (ABEGAIL C. RELUNIA)Document4 pagesModule 7, Anatomy and Physiogy (ABEGAIL C. RELUNIA)Abegail ReluniaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mosaic ModelDocument4 pagesFluid Mosaic Modelapi-2924390320% (1)
- MODULE 12 - GB1 (Cell Transport)Document8 pagesMODULE 12 - GB1 (Cell Transport)NATHANIEL CORTEZNo ratings yet
- Cell MembranesDocument5 pagesCell MembranesTiaraHadiAshariNo ratings yet
- Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument11 pagesMembrane Structure and FunctionShiloh FrederickNo ratings yet
- AkdogDocument10 pagesAkdognorhain4.aNo ratings yet
- SF - MD.0145.T.22 Ally Omary MwambelaDocument10 pagesSF - MD.0145.T.22 Ally Omary MwambelaAlly OmaryNo ratings yet
- Egg Membrane Project For 12Document18 pagesEgg Membrane Project For 12Hemanth Kumar100% (1)
- Animal Physiology Theory Lec1Document24 pagesAnimal Physiology Theory Lec1ao868598No ratings yet
- Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane)Document6 pagesCell Membrane (Plasma Membrane)Rica NorcioNo ratings yet
- BIOWEEK5RANESDocument29 pagesBIOWEEK5RANESvrbatitangNo ratings yet
- ASSIGMENT of Environmental Toxicology 12Document8 pagesASSIGMENT of Environmental Toxicology 12naeem attaNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane: Function and Structure Grade 11 BiologyDocument51 pagesCell Membrane: Function and Structure Grade 11 BiologyChester WengerNo ratings yet
- Biological Membranes: by Hajar SaihiDocument10 pagesBiological Membranes: by Hajar SaihiMariam El KhatibNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mosaic Model ActivityDocument4 pagesFluid Mosaic Model ActivityLarvin Andrei E. BechaydaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Fluid Mosaic ModelDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Fluid Mosaic ModelShnanca CarterNo ratings yet
- Full Download Zoology 9th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Zoology 9th Edition Miller Solutions Manualcaveneywilliams100% (19)
- Being An Influencer Is No JokeDocument1 pageBeing An Influencer Is No JokeChristian Angel GomezNo ratings yet
- ARTICLE (Gomez, Christian Angel A.)Document2 pagesARTICLE (Gomez, Christian Angel A.)Christian Angel GomezNo ratings yet
- FOY CAMERA (Gomez and Aluad)Document2 pagesFOY CAMERA (Gomez and Aluad)Christian Angel GomezNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper (Gomez Christian Angel A.)Document1 pageReaction Paper (Gomez Christian Angel A.)Christian Angel GomezNo ratings yet
Module 6 (GenBio)
Module 6 (GenBio)
Uploaded by
Christian Angel GomezOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 6 (GenBio)
Module 6 (GenBio)
Uploaded by
Christian Angel GomezCopyright:
Available Formats
Christian Angel A.
Gomez
STEM 12-TESLA
Let us answer the following questions. Explain your answer. Write your answer in your
activity notebook.
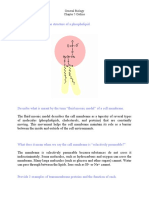
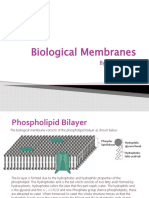
1. Explain the orientation of the phospholipid molecules in the presence of water.
The orientation of the phospholipid molecules in the presence of water explains why water
is considered a universal solvent. The molecules are arranged so that the polar head group is
hydrophilic, or water-loving, and the long, hydrophobic, or water-hating, tails are arranged in
the middle of the membrane. This gives the membrane a hydrophobic core and a hydrophilic
surface. The hydrophobic tails are non-polar and cannot interact with water molecules.
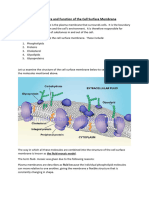
2. Enumerate the structures found in a plasma membrane and give the function of
each.
Phospholipid - This basic cellular structure acts as a barrier to protect the cell against
various environmental insults and more importantly, enables multiple cellular
processes to occur in subcellular compartments.
Cholesterol - Cholesterol is a fat-like, waxy substance that helps your body make cell
membranes, many hormones, and vitamin D.
Aquaporins - are integral membrane proteins that serve as channels in the transfer of
water, and in some cases, small solutes across the membrane.
3. How do diffusion and facilitated diffusion differ?
Diffusion is a process that allows molecules or ions to move into or out of a tissue or
organ. Diffusion is important for delivering nutrients and removing toxins from the body.
Diffusion often occurs through membranes. The diffusion of solutes through transport
proteins in the plasma membrane is referred to as facilitated diffusion. Facilitated diffusion is
a type of passive transport. Even though transport proteins are involved in facilitated
diffusion, it is still passive transport because the solute moves down the concentration
gradient.
4. How do endocytosis and exocytosis allow movement of materials in and out of the
cell?
Plasma membranes are thin, lipid bilayers that are embedded in the cell membrane. These
membranes allow for the selective uptake and release of materials into and out of cells.
Endocytosis and exocytosis are two important mechanisms by which these membranes allow
for the movement of materials.
You might also like
- O Level Biology Notes MapurangaDocument95 pagesO Level Biology Notes Mapurangapeterchiyanja100% (2)
- Cell Membrane Information WorksheetDocument4 pagesCell Membrane Information WorksheetD100% (1)
- Cell Membrane Flow of MaterialsDocument13 pagesCell Membrane Flow of Materialsnorhain4.aNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesCell MembraneQaran PrintingNo ratings yet
- Cell MebraneDocument10 pagesCell MebraneChandra SihombingNo ratings yet
- THE CELL MEMBRANE (Coloured)Document6 pagesTHE CELL MEMBRANE (Coloured)tsteadmanNo ratings yet
- 2.4 - Membranes: 2.4.1 - Draw and Label A Diagram To Show The Structure of MembranesDocument6 pages2.4 - Membranes: 2.4.1 - Draw and Label A Diagram To Show The Structure of MembranesDuong TongNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document14 pagesPresentation 2Maya TareqNo ratings yet
- 9gkneylgi4kueakdv8q9gkney50iscvv SolutionDocument2 pages9gkneylgi4kueakdv8q9gkney50iscvv SolutionArya MohajerNo ratings yet
- 2a-Membranes and Transport 2Document67 pages2a-Membranes and Transport 2kfy8vr7wtwNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY NOTES iAL Biology Unit 1Document7 pagesBIOLOGY NOTES iAL Biology Unit 1Student Alejandro Zhou WeiNo ratings yet
- Letran de Davao, IncDocument3 pagesLetran de Davao, IncPatricia DianeNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane TransportDocument3 pagesCell Membrane TransportHarry TeasdaleNo ratings yet
- The Cell MembraneDocument9 pagesThe Cell MembraneShuchi HossainNo ratings yet
- Biology Module 2: Section 2.5Document20 pagesBiology Module 2: Section 2.5Nasteexo CaliNo ratings yet
- Ch. 5 Pre-ReadingDocument7 pagesCh. 5 Pre-ReadingDJ ISAACS50% (2)
- Cellular Transport Mechanism: General Biology 1Document12 pagesCellular Transport Mechanism: General Biology 1Kenn KennNo ratings yet
- Explanation and Acceptable Reason YeahDocument3 pagesExplanation and Acceptable Reason YeahMj DeguzmanNo ratings yet
- Dela Ysla Russell Iverson T. Biology1Document4 pagesDela Ysla Russell Iverson T. Biology1Elaiza Nicole AccatanNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument30 pagesEarth and Life ScienceChristian VitalesNo ratings yet
- Understanding Biology 1St Edition Mason Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument31 pagesUnderstanding Biology 1St Edition Mason Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFerik.looney743100% (11)
- Transport MechanismsDocument30 pagesTransport MechanismsApril VeraNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Grade 12Document8 pagesCell Membrane Grade 12Olayinka SalmonNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mosaic Model NotesDocument4 pagesFluid Mosaic Model NotesanzalnaamanNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument17 pagesCell MembraneEloisa MadrilenoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Notes Cellular Basis of LifeDocument11 pagesLecture 3 Notes Cellular Basis of Lifeochienganthony001No ratings yet
- q1 Genbio1 Slkweek6 EditDocument13 pagesq1 Genbio1 Slkweek6 EditInele Ellia AgReNo ratings yet
- Advanced Biology Q3Document3 pagesAdvanced Biology Q3MARITHE ROJIANNE MERCADONo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 OutlineDocument5 pagesChapter 5 OutlineShirley PinedaNo ratings yet
- Plasma Membrane Student PPTDocument14 pagesPlasma Membrane Student PPTlube aguasNo ratings yet
- Significance of Liquid in Biological Membranes and Transport MechanismDocument10 pagesSignificance of Liquid in Biological Membranes and Transport Mechanismroshan khanNo ratings yet
- 008 - The Cell Surface MembraneDocument2 pages008 - The Cell Surface MembraneSanah KhanNo ratings yet
- LESSON - 11 - Gen Biology 1Document4 pagesLESSON - 11 - Gen Biology 1Jhay Luiz Cajigal ArquinesNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes: Topic-2ADocument9 pagesBiology Notes: Topic-2Alaiba amirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Cell Membranes and Transport: SummaryDocument4 pagesChapter 4: Cell Membranes and Transport: SummaryMerimaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure - Cell Membrane and TransportDocument6 pagesCell Structure - Cell Membrane and TransportKulsoom UsmanNo ratings yet
- Plasma Membrane The Big PictureDocument4 pagesPlasma Membrane The Big PictureNicolas Gomez CombellasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Student Copy ZoologyDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Student Copy Zoologyapi-523871804No ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Q1 Week 7Document14 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Q1 Week 7JewelNo ratings yet
- Mahan 2Document7 pagesMahan 2KANT JAMES D. MAHANNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument2 pagesCell MembranegrxcieeNo ratings yet
- Anaphy LecDocument6 pagesAnaphy LecfilesNo ratings yet
- Module 7, Anatomy and Physiogy (ABEGAIL C. RELUNIA)Document4 pagesModule 7, Anatomy and Physiogy (ABEGAIL C. RELUNIA)Abegail ReluniaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mosaic ModelDocument4 pagesFluid Mosaic Modelapi-2924390320% (1)
- MODULE 12 - GB1 (Cell Transport)Document8 pagesMODULE 12 - GB1 (Cell Transport)NATHANIEL CORTEZNo ratings yet
- Cell MembranesDocument5 pagesCell MembranesTiaraHadiAshariNo ratings yet
- Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument11 pagesMembrane Structure and FunctionShiloh FrederickNo ratings yet
- AkdogDocument10 pagesAkdognorhain4.aNo ratings yet
- SF - MD.0145.T.22 Ally Omary MwambelaDocument10 pagesSF - MD.0145.T.22 Ally Omary MwambelaAlly OmaryNo ratings yet
- Egg Membrane Project For 12Document18 pagesEgg Membrane Project For 12Hemanth Kumar100% (1)
- Animal Physiology Theory Lec1Document24 pagesAnimal Physiology Theory Lec1ao868598No ratings yet
- Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane)Document6 pagesCell Membrane (Plasma Membrane)Rica NorcioNo ratings yet
- BIOWEEK5RANESDocument29 pagesBIOWEEK5RANESvrbatitangNo ratings yet
- ASSIGMENT of Environmental Toxicology 12Document8 pagesASSIGMENT of Environmental Toxicology 12naeem attaNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane: Function and Structure Grade 11 BiologyDocument51 pagesCell Membrane: Function and Structure Grade 11 BiologyChester WengerNo ratings yet
- Biological Membranes: by Hajar SaihiDocument10 pagesBiological Membranes: by Hajar SaihiMariam El KhatibNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mosaic Model ActivityDocument4 pagesFluid Mosaic Model ActivityLarvin Andrei E. BechaydaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Fluid Mosaic ModelDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Fluid Mosaic ModelShnanca CarterNo ratings yet
- Full Download Zoology 9th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Zoology 9th Edition Miller Solutions Manualcaveneywilliams100% (19)
- Being An Influencer Is No JokeDocument1 pageBeing An Influencer Is No JokeChristian Angel GomezNo ratings yet
- ARTICLE (Gomez, Christian Angel A.)Document2 pagesARTICLE (Gomez, Christian Angel A.)Christian Angel GomezNo ratings yet
- FOY CAMERA (Gomez and Aluad)Document2 pagesFOY CAMERA (Gomez and Aluad)Christian Angel GomezNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper (Gomez Christian Angel A.)Document1 pageReaction Paper (Gomez Christian Angel A.)Christian Angel GomezNo ratings yet