Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 viewsRole of Microorganisms in Food Preservation
Role of Microorganisms in Food Preservation
Uploaded by
tonima rahmanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
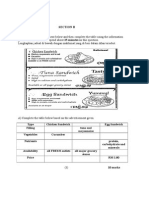
- Trinity Gese Grade 4 Practice Test 2Document3 pagesTrinity Gese Grade 4 Practice Test 2Diego Coen CadenasNo ratings yet
- The Meal Prep Manual - Desserts PDFDocument69 pagesThe Meal Prep Manual - Desserts PDFdijshshNo ratings yet
- Soalan ENGLISH BI Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 4 Paper 2Document7 pagesSoalan ENGLISH BI Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 4 Paper 2prakash76100% (1)
- The Comparison Study Between The Junk Food and Obesity.Document17 pagesThe Comparison Study Between The Junk Food and Obesity.Kaleeswari VNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 INTERNATIONAL CUISINE TOPICDocument22 pagesLesson 1 INTERNATIONAL CUISINE TOPICBai Norsandreah A. AlangNo ratings yet
- Big English 1 Unit5-9Document5 pagesBig English 1 Unit5-9leiliabbasi91No ratings yet
- Farm AnimalsDocument4 pagesFarm AnimalsAnil Bhat100% (1)
- Food Vocab3 PDFDocument4 pagesFood Vocab3 PDFChiara Irene Thea CappellinaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Introduction To Professional CookeryDocument11 pagesCH 1 Introduction To Professional CookeryDJ Gaurav Endless OfficialNo ratings yet
- Study On The Pork Market Worldwide: December 2017Document7 pagesStudy On The Pork Market Worldwide: December 2017Sau LeovikNo ratings yet
- AddRes - KIR A1 Workbook AK - CompleteDocument13 pagesAddRes - KIR A1 Workbook AK - CompleteBeatriz CrosaNo ratings yet
- Chocolate PairingsDocument1 pageChocolate PairingsMaestro Treinta AqpNo ratings yet
- PL HOREKA 6 MEI 2023 LENGKAP - CDocument10 pagesPL HOREKA 6 MEI 2023 LENGKAP - CRamadhana ArbiNo ratings yet
- F&B Service English 1Document8 pagesF&B Service English 1aliko555No ratings yet
- Sotto Dinner Menu 6.7.17Document1 pageSotto Dinner Menu 6.7.17Tierney PlumbNo ratings yet
- Feather Meal For Fish FeedDocument5 pagesFeather Meal For Fish FeedInternational Aquafeed magazine100% (1)
- Chilis Philippines Menu Jul 2023Document20 pagesChilis Philippines Menu Jul 2023MJNo ratings yet
- By: Josh Velasquez NF 25 Wednesday 7p Mt. Sac Spring 2013 Professor: C.E Betty CrockerDocument10 pagesBy: Josh Velasquez NF 25 Wednesday 7p Mt. Sac Spring 2013 Professor: C.E Betty CrockerJ_jvelasquezNo ratings yet
- Country Creek Drive Estero, FL 33928Document16 pagesCountry Creek Drive Estero, FL 33928receptionhallsNo ratings yet
- Costing Form For RestaurantDocument94 pagesCosting Form For RestaurantJulius Retiro de la CruzNo ratings yet
- A Project Report ON A Study of Promotion Strategy and Customer Perception of MC Donalds in IndiaDocument18 pagesA Project Report ON A Study of Promotion Strategy and Customer Perception of MC Donalds in IndiaShailav SahNo ratings yet
- Listen Supermarket 2Document2 pagesListen Supermarket 2soniacardosoneves11No ratings yet
- Mamusa Case AnalysisDocument8 pagesMamusa Case AnalysisIann AcutinaNo ratings yet
- Madison County Inspection ReportsDocument5 pagesMadison County Inspection ReportsMike BrownNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Meat Quality and Carcass Characteristics of Broiler Chickens As Affected by Feed Withdrawal With Electrolytes Added To WaterDocument8 pagesEvaluation of Meat Quality and Carcass Characteristics of Broiler Chickens As Affected by Feed Withdrawal With Electrolytes Added To WaterInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Healthier Broccoli Cheddar Soup by Chef Nikki Dinki - The Dr. Oz ShowDocument3 pagesHealthier Broccoli Cheddar Soup by Chef Nikki Dinki - The Dr. Oz Showcecytetics1eNo ratings yet
- Prepare Vegetable DishesDocument55 pagesPrepare Vegetable DishesRedginald Calderon100% (1)
- Exercise PAS Inggris Kls 9Document20 pagesExercise PAS Inggris Kls 9Ghozy Arrafi Maulana K.RNo ratings yet
- Nebraska State Fair $2 Tuesday SpecialsDocument1 pageNebraska State Fair $2 Tuesday SpecialsNTV NewsNo ratings yet
- Odisha Agriculture Statistics 2018-19Document185 pagesOdisha Agriculture Statistics 2018-19ABHINAV VIVEKNo ratings yet
Role of Microorganisms in Food Preservation
Role of Microorganisms in Food Preservation
Uploaded by
tonima rahman0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageRole of Microorganisms in Food Preservation
Role of Microorganisms in Food Preservation
Uploaded by
tonima rahmanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Editorial
Volume 8:2, 2022 Journal of Food & Industrial Microbiology
ISSN: 2572-4134 Open Access
Role of Microorganisms in Food Preservation
Joseph Houhoula*
Department of Food Science and Technology, Faculty of Food Sciences, University of West Attica, Greece
Editorial mechanical qualities. One option to address these challenges is to combine
biodegradable polymers with other valuable components. Packaging is one
of the most important factors of food safety. Food safety can be improved
For many years, the food industry has used a variety of chemicals to prevent the
by using nanotechnology to increase the efficiency and quality of packaging
growth of bacteria that cause food to spoil. Their use, in combination with high-
materials. Nanoparticle packages can intelligently respond to environmental
temperature processing, helps to extend the useful life of foods by inhibiting
circumstances or alert consumers about dangerous compounds or air pollution.
pathogenic and spoilage microorganisms' activity; yet, they may have a negative
Plastics are frequently employed in the FP sector. Their ability to restrict
impact on some foods' organoleptic and sensory features. Bio-preservatives
the passage of oxygen, water, and carbon dioxide is, however, limited. The
have been developed to lessen the use of these preservation and processing
permeability of food containers can be improved by using plastics containing
processes. Bio-preservatives are naturally occurring substances derived
nanoparticles. Packages incorporating clay nanoparticles, for example, have
from plants, animals, and microbes that extend the shelf life of food. These
superior mechanical, thermal, and barrier qualities, preventing oxygen, carbon
substances suppress pathogenic organisms in food to a bare minimum or even
dioxide, and moisture from passing through. They also help to increase the
eradicate them entirely, while also improving food functioning and quality. Many
shelf life of food, retain its colour and flavour, and prevent microbe growth [4,5].
of these substances are antimicrobials that also serve as antioxidants, tear
down cell membranes, and impair biosynthetic bacteria' pathways. However, Because meat demand has increased, livestock industrial farming has
as a result of the negative effects of synthetic food additives on consumers' been formed to improve animal productivity. As a result, intensive livestock
health and the environment, consumers' interest in natural preservative husbandry and animal growth enhancement were required to boost productivity.
chemicals is increasing. Consumer awareness of the serious health dangers Antibiotics in animal feed were used to meet the requirements. Despite the
connected with eating meals made with synthetic additives has risen, as fact that antibiotics effectively prevent the spread of infectious diseases, the
has demand for safe food products made with natural components. These misuse of in-feed antibiotics has resulted in a slew of issues, including antibiotic
bioactive compounds produced from plants, animals, and beneficial microbes resistance, antibiotic residues in livestock products, ecosystem pollution from
have been hailed as promising alternatives to synthetic food additives. Many of livestock manure, and weak disease resistance in livestock. As a result, the
these chemicals are antimicrobials as well as antioxidants, and they tear down development of natural antibacterial compounds is required to address the
cell membranes and disrupt biosynthetic bacteria' pathways. However, as a issues produced by in-feed antibiotic overuse.
result of the negative effects of synthetic food additives on consumers' health
and the environment, consumers' interest in natural preservative chemicals is
expanding. Consumer awareness of the serious health concerns connected Conflicts of Interest
with foods made with synthetic additives has risen, as has demand for safe
food products made with natural components. Bioactive compounds produced The authors declare no conflict of interest.
from plants, animals, and beneficial microorganisms have been suggested as
possible alternatives to synthetic food additives [1-3]. References
Microorganisms can be found in a wide range of food products and can have
an impact on food quality and quantity. Food products provide an ideal habitat 1. Franco, Antonio, Rosanna Salvia, Carmen Scieuzo, and Eric Schmitt, et al.
for microbes to thrive. Food deterioration or breakdown can be caused by “Lipids from insects in cosmetics and for personal care products.” Insects
microorganism development. Furthermore, when bacteria are present in food, 13 (2021): 41.
they might induce food poisoning. Microorganisms are also employed in the
2. Park, Soon-Ik, Jong-Wan Kim, and Sung Moon Yoe. “Purification and
manufacturing of some foods. Microorganisms are utilised in the manufacturing
characterization of a novel antibacterial peptide from black soldier fly
of foods such as yoghurt, pickles, and cheese.
(Hermetia illucens) larvae.” Dev Comp Immunol 52 (2015): 98-106.
Plastics are a cause of concern in today's culture. Recycling plastics is
3. Khan, Sohail Hassan. “Recent advances in role of insects as alternative
the most difficult component of its use. Plastics are neither recyclable nor
protein source in poultry nutrition.” J Appl Anim Res 46 (2018): 1144-1157.
biodegradable, posing a severe environmental danger. Due to their high
potential, biodegradable materials are currently being studied for use in FP. 4. Dörper, A., T. Veldkamp, and M. Dicke. “Use of black soldier fly and house
These materials can be used to replace biodegradable plastics and lessen fly in feed to promote sustainable poultry production.” J Insects Food Feed
the environmental damage they create. Biodegradable materials, on the 7 (2020): 761-780.
other hand, are less resistant to water and gas penetration and have poor
5. Baltzer, Sylvia A., and Melissa H. Brown. “Antimicrobial peptides–promising
alternatives to conventional antibiotics.” J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 20
(2011): 228-235.
*Address for Correspondence: Joseph Houhoula, Department of Food Science
and Technology, Faculty of Food Sciences, University of West Attica, Greece;
E-mail: houhoula.joseph58@yahoomail.com
Copyright: © 2022 Houhoula J. This is an open-access article distributed
under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits
unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the
original author and source are credited.
Received: 10-Mar-2022, Manuscript No. jfim-22-62920; Editor assigned:
12-Mar-2022, Pre QC No. P-62920; Reviewed: 18-Mar-2022, QC No.
Q-62920; Revised: 23-Mar-2022, Manuscript No. R-62920; Published: How to cite this article: Houhoula, Joseph. “Role of Microorganisms in Food
28-Mar-2022, DOI: 10.37421/2572-4134.2022.8.241. Preservation.” J Food Ind Microbiol 8 (2022): 241
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Trinity Gese Grade 4 Practice Test 2Document3 pagesTrinity Gese Grade 4 Practice Test 2Diego Coen CadenasNo ratings yet
- The Meal Prep Manual - Desserts PDFDocument69 pagesThe Meal Prep Manual - Desserts PDFdijshshNo ratings yet
- Soalan ENGLISH BI Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 4 Paper 2Document7 pagesSoalan ENGLISH BI Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 4 Paper 2prakash76100% (1)
- The Comparison Study Between The Junk Food and Obesity.Document17 pagesThe Comparison Study Between The Junk Food and Obesity.Kaleeswari VNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 INTERNATIONAL CUISINE TOPICDocument22 pagesLesson 1 INTERNATIONAL CUISINE TOPICBai Norsandreah A. AlangNo ratings yet
- Big English 1 Unit5-9Document5 pagesBig English 1 Unit5-9leiliabbasi91No ratings yet
- Farm AnimalsDocument4 pagesFarm AnimalsAnil Bhat100% (1)
- Food Vocab3 PDFDocument4 pagesFood Vocab3 PDFChiara Irene Thea CappellinaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Introduction To Professional CookeryDocument11 pagesCH 1 Introduction To Professional CookeryDJ Gaurav Endless OfficialNo ratings yet
- Study On The Pork Market Worldwide: December 2017Document7 pagesStudy On The Pork Market Worldwide: December 2017Sau LeovikNo ratings yet
- AddRes - KIR A1 Workbook AK - CompleteDocument13 pagesAddRes - KIR A1 Workbook AK - CompleteBeatriz CrosaNo ratings yet
- Chocolate PairingsDocument1 pageChocolate PairingsMaestro Treinta AqpNo ratings yet
- PL HOREKA 6 MEI 2023 LENGKAP - CDocument10 pagesPL HOREKA 6 MEI 2023 LENGKAP - CRamadhana ArbiNo ratings yet
- F&B Service English 1Document8 pagesF&B Service English 1aliko555No ratings yet
- Sotto Dinner Menu 6.7.17Document1 pageSotto Dinner Menu 6.7.17Tierney PlumbNo ratings yet
- Feather Meal For Fish FeedDocument5 pagesFeather Meal For Fish FeedInternational Aquafeed magazine100% (1)
- Chilis Philippines Menu Jul 2023Document20 pagesChilis Philippines Menu Jul 2023MJNo ratings yet
- By: Josh Velasquez NF 25 Wednesday 7p Mt. Sac Spring 2013 Professor: C.E Betty CrockerDocument10 pagesBy: Josh Velasquez NF 25 Wednesday 7p Mt. Sac Spring 2013 Professor: C.E Betty CrockerJ_jvelasquezNo ratings yet
- Country Creek Drive Estero, FL 33928Document16 pagesCountry Creek Drive Estero, FL 33928receptionhallsNo ratings yet
- Costing Form For RestaurantDocument94 pagesCosting Form For RestaurantJulius Retiro de la CruzNo ratings yet
- A Project Report ON A Study of Promotion Strategy and Customer Perception of MC Donalds in IndiaDocument18 pagesA Project Report ON A Study of Promotion Strategy and Customer Perception of MC Donalds in IndiaShailav SahNo ratings yet
- Listen Supermarket 2Document2 pagesListen Supermarket 2soniacardosoneves11No ratings yet
- Mamusa Case AnalysisDocument8 pagesMamusa Case AnalysisIann AcutinaNo ratings yet
- Madison County Inspection ReportsDocument5 pagesMadison County Inspection ReportsMike BrownNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Meat Quality and Carcass Characteristics of Broiler Chickens As Affected by Feed Withdrawal With Electrolytes Added To WaterDocument8 pagesEvaluation of Meat Quality and Carcass Characteristics of Broiler Chickens As Affected by Feed Withdrawal With Electrolytes Added To WaterInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Healthier Broccoli Cheddar Soup by Chef Nikki Dinki - The Dr. Oz ShowDocument3 pagesHealthier Broccoli Cheddar Soup by Chef Nikki Dinki - The Dr. Oz Showcecytetics1eNo ratings yet
- Prepare Vegetable DishesDocument55 pagesPrepare Vegetable DishesRedginald Calderon100% (1)
- Exercise PAS Inggris Kls 9Document20 pagesExercise PAS Inggris Kls 9Ghozy Arrafi Maulana K.RNo ratings yet
- Nebraska State Fair $2 Tuesday SpecialsDocument1 pageNebraska State Fair $2 Tuesday SpecialsNTV NewsNo ratings yet
- Odisha Agriculture Statistics 2018-19Document185 pagesOdisha Agriculture Statistics 2018-19ABHINAV VIVEKNo ratings yet