Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Methodology Statement For Power Meter p1
Methodology Statement For Power Meter p1
Uploaded by
Charlie Dela RosaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Methodology Statement For Power Meter p1
Methodology Statement For Power Meter p1
Uploaded by
Charlie Dela RosaCopyright:
Available Formats
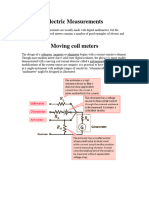
Methodology Statement For Panel Meter / Energy Meters
DESCRIPTION
Most power meters measure voltage and current separately and display the power
value in Watts.
Most voltmeters use either electromechanical or analog-to-digital conversion
techniques to determine voltage amplitude. Current is measured in amperes (A),
which can be measured two ways:
1. Many meters use an inductive coil clamped over the power line. This
current clamp may be separate or part of the meter. The current in the line
induces a proportional voltage (typically 1 mV for 1A of current) into the
current clamp. The voltage is then measured by the meter.
2. For lower currents, the power line current can be passed through a resistive
shunt in the meter, and the voltage drop is measured across the shunt.
Some current/power clamps measure the true power directly, providing a
proportional voltage to the meter.
DEFINITION
The voltmeter is the voltage measuring devices. It is connected in parallel with
the electrical
circuit whose potential is to be measured. The connection polarity of the
voltmeter is same as that of the ammeter i.e. the positive terminal is connected
to the positive polarity of the supply and the negative potential is connected to
the negative polarity.
The resistance across the voltmeter is very large as compared to the
ammeter. This resistance does not allow the current to flow through the
voltmeter and thus the exact value of the voltage across the measuring point is
measured. The value of resistance in ideal voltmeter is approximately equal to
infinity.
The ammeter is the measuring instruments which are used to measure the current in the circuit. It
measures the small amount of current in milliamperes or micro-amperes. The ammeter is placed in
series with the measuring circuit so that the whole current of the circuit passes through it.
You might also like
- Chapter 4 Electrical Instruments and MeasurementsDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Electrical Instruments and Measurementszxufra lumanglasNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Power MeterDocument5 pagesTopic 5 Power MeterAcidDukeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Power MetersDocument5 pagesChapter 5: Power Metersche syakirNo ratings yet
- VoltmeterDocument2 pagesVoltmetervijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Electrical QuantitiesDocument15 pagesMeasurement of Electrical QuantitiesVeronica CazacNo ratings yet
- AC & DC MetersDocument2 pagesAC & DC Metersk85yfbwhynNo ratings yet
- Ammeter, Voltmeter, DC Motor, Electric Generator, UPSDocument13 pagesAmmeter, Voltmeter, DC Motor, Electric Generator, UPSatiqurrehman0074No ratings yet
- Ammeter VoltmeterDocument17 pagesAmmeter Voltmeterfarihakanwal2021No ratings yet
- غۆڤاندDocument7 pagesغۆڤاندavdfdfdfNo ratings yet
- Objectives: Lab 1-Introduction To Basic Electrical Measuring InstrumentsDocument7 pagesObjectives: Lab 1-Introduction To Basic Electrical Measuring Instrumentsßirũk Bmt100% (1)
- Direct Current MetersDocument10 pagesDirect Current MetersShem Japheth EscalonaNo ratings yet
- How To Connect An Ammeter (Amperemeter)Document2 pagesHow To Connect An Ammeter (Amperemeter)Jendral Deby IrawanNo ratings yet
- Clamp MeterDocument3 pagesClamp Meterarsenic_94No ratings yet
- Measurement of CurrentDocument3 pagesMeasurement of CurrentAnkur MathurNo ratings yet
- ElectricalDocument6 pagesElectrical3re0oooNo ratings yet
- Electronic VoltmeterDocument7 pagesElectronic VoltmeterBoss barkatNo ratings yet
- 5 Unit - 3Document13 pages5 Unit - 3Guna PriyaNo ratings yet
- Current Voltage MeasurementDocument35 pagesCurrent Voltage MeasurementAaqib AliNo ratings yet
- VoltmeterDocument6 pagesVoltmeterAndi DelimaNo ratings yet
- Analog Meters: Instrumentation and ControlsDocument21 pagesAnalog Meters: Instrumentation and ControlsceindenaeNo ratings yet
- VoltmeterDocument5 pagesVoltmeterhumaid15No ratings yet
- Emi PPT2Document103 pagesEmi PPT2akashdeep kaurNo ratings yet
- Intrumentation Unit LL (2.7)Document3 pagesIntrumentation Unit LL (2.7)gurungpg143No ratings yet
- Multimeter VIMPDocument61 pagesMultimeter VIMPSysu KumarNo ratings yet
- Ammeter ShortDocument2 pagesAmmeter ShortkappubhattNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document7 pagesExperiment 2anasser0772No ratings yet
- Experiment No 1Document8 pagesExperiment No 1mahamchudry2No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document5 pagesChapter 2khuzaimNo ratings yet
- مصطفى محمدDocument8 pagesمصطفى محمدBoss barkatNo ratings yet
- CNT 103 How To Use A Digital MultimeterDocument41 pagesCNT 103 How To Use A Digital Multimeternaraval tablingon100% (1)
- Training Report On Study of 33/11KV MV Substations at APDCL (Assam Power Distribution Corporation LTD.)Document16 pagesTraining Report On Study of 33/11KV MV Substations at APDCL (Assam Power Distribution Corporation LTD.)KAZI SAHARIAR RAHI100% (2)
- What Is An OhmmeterDocument4 pagesWhat Is An OhmmeterballDISCOVERIES PHballDISCOVERIESNo ratings yet
- Sensors and Instrumentation ProjectDocument9 pagesSensors and Instrumentation ProjectSai Sandeep RayanuthalaNo ratings yet
- 3 UnitDocument36 pages3 Unitbitseee RandDNo ratings yet
- Expirement 1 - Fundamental Electrical MeasurementsDocument8 pagesExpirement 1 - Fundamental Electrical MeasurementsJhajha AlboniaNo ratings yet
- Experiment-1 (Basic Electrical Engineering)Document4 pagesExperiment-1 (Basic Electrical Engineering)Rambir SinghNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Familiarization With Electrical Measuring InstrumentsDocument10 pagesExperiment 1 Familiarization With Electrical Measuring InstrumentsCorps LaroprocNo ratings yet
- Presentasi MultimeterDocument41 pagesPresentasi MultimetermdNo ratings yet
- Galvanometer's Conversion To Ammeter and VoltmeterDocument1 pageGalvanometer's Conversion To Ammeter and Voltmeteranshvishwakarma2005No ratings yet
- LU1.2.Use Basic Electric MetersDocument23 pagesLU1.2.Use Basic Electric Metersnguemaabraham1No ratings yet
- AmmeterDocument115 pagesAmmetermhnmndrkNo ratings yet
- Clamp MeterDocument3 pagesClamp MeterAnkush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Question: Discuss in Detail About The Current and Voltage Measurement Instruments. AlsoDocument7 pagesQuestion: Discuss in Detail About The Current and Voltage Measurement Instruments. AlsoSanjana chowdaryNo ratings yet
- EE 442 Laboratory Experiment 2 Introduction To The Measurement of Voltage, Current, Resistance and Voltmeter LoadingDocument12 pagesEE 442 Laboratory Experiment 2 Introduction To The Measurement of Voltage, Current, Resistance and Voltmeter LoadingAdrien MunyanezaNo ratings yet
- Direct Current Measurements: of byDocument17 pagesDirect Current Measurements: of byLaurence MalanumNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measuring Instruments: (Voltmeter, Ammeter, and Ohmmeter)Document4 pagesElectrical Measuring Instruments: (Voltmeter, Ammeter, and Ohmmeter)angelo macatangayNo ratings yet
- Electronic Voltmeter: Advantage Over Conventional Multi MeterDocument7 pagesElectronic Voltmeter: Advantage Over Conventional Multi MeterVishal Pandey M LE 06No ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Transducers and Measuring Instruments: Current and Voltage MeasurementDocument30 pagesChapter-3 Transducers and Measuring Instruments: Current and Voltage MeasurementYab TadNo ratings yet
- Measuring Equipments in ElectricityDocument15 pagesMeasuring Equipments in ElectricityPulxar TVINo ratings yet
- Circuit+Lab+Report+No 6Document19 pagesCircuit+Lab+Report+No 6Kenneth DomingoNo ratings yet
- Ee006-Midterms 3.1. Introduction To Electrical Metering and Measurements What Is A Meter?Document13 pagesEe006-Midterms 3.1. Introduction To Electrical Metering and Measurements What Is A Meter?Caila PanerioNo ratings yet
- Electrical & Electronic InstrumentationDocument26 pagesElectrical & Electronic InstrumentationKamal PhyNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Measurement DiscussionDocument5 pagesActivity 2 Measurement DiscussionJoel Kelly MabaoNo ratings yet
- History Ammeters VoltmetersDocument10 pagesHistory Ammeters VoltmetersRichard MortimerNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Experiment No 1Document14 pagesGroup 1 Experiment No 1Carl OlayaNo ratings yet
- PotentiometerDocument7 pagesPotentiometerCarmella Mae QuidiligNo ratings yet
- How To Use A Digital Multimeter The Quick Guide To Learn How To Use A Digital Multimeter To Measure Voltage, Current and More Correctly, Diagnose and Fix Anything ElectronicDocument44 pagesHow To Use A Digital Multimeter The Quick Guide To Learn How To Use A Digital Multimeter To Measure Voltage, Current and More Correctly, Diagnose and Fix Anything ElectronicamseraucNo ratings yet
- MAIN TOPIC Electrical Quantities in InstrumentationDocument68 pagesMAIN TOPIC Electrical Quantities in InstrumentationLoreto CorderoNo ratings yet
- Summary of Standard Uncertainty ComponentsDocument1 pageSummary of Standard Uncertainty ComponentsCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Verification of ComparatorDocument1 pageVerification of ComparatorCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Gravity 'G' On Calibration of BalanceDocument1 pageEffect of Gravity 'G' On Calibration of BalanceCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Maximum Capacity of The Balance or The Range To Be CalibratedDocument1 pageMaximum Capacity of The Balance or The Range To Be CalibratedCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Preconditions, PreparationsDocument1 pagePreconditions, PreparationsCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Repeatability TestDocument1 pageRepeatability TestCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- AdjustmentDocument2 pagesAdjustmentCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Standards Such As The AMS 2750 FDocument1 pageStandards Such As The AMS 2750 FCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Furnace Decription and SpecificationDocument1 pageFurnace Decription and SpecificationCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Details of Calculations For S. No 5: Standard Deviation S (X) 0.009 °CDocument1 pageDetails of Calculations For S. No 5: Standard Deviation S (X) 0.009 °CCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Roles and ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesRoles and ResponsibilitiesCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Testing Preparation and ExecutionDocument2 pagesTesting Preparation and ExecutionCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Forklift Inspection ChecksheetDocument1 pageForklift Inspection ChecksheetCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic TestDocument4 pagesPneumatic TestCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Safety RequirementsDocument1 pageSafety RequirementsCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic TestDocument2 pagesHydrostatic TestCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Audit Findings For SDEDocument2 pagesAudit Findings For SDECharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Equip For ServiceDocument2 pagesEquip For ServiceCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Required Personal Protective EquipmentDocument5 pagesRequired Personal Protective EquipmentCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Reference Standard ListaDocument4 pagesReference Standard ListaCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Requested Reference Standards (03-Oct-22)Document2 pagesRequested Reference Standards (03-Oct-22)Charlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Engine and LubricantsDocument1 pageEngine and LubricantsCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Furnace 30 To 1200 CDocument3 pagesFurnace 30 To 1200 CCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Control MeasuresDocument4 pagesControl MeasuresCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet For ThermocoupleDocument4 pagesData Sheet For ThermocoupleCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Vacum GaugeDocument1 pageVacum GaugeCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Lyrics - Always (Marco Sison)Document1 pageLyrics - Always (Marco Sison)Charlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- LIFTING EQUIPMENT REFERENCE STANDARDS LOG SHEET - Rev0Document2 pagesLIFTING EQUIPMENT REFERENCE STANDARDS LOG SHEET - Rev0Charlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Resistance Generate 330 M OhmsDocument3 pagesResistance Generate 330 M OhmsCharlie Dela RosaNo ratings yet