Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bun and Creatinine 2
Bun and Creatinine 2
Uploaded by
CRISTINA MARIE PATACSIL0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views3 pagesThis document summarizes key information about blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine tests. It discusses how BUN and creatinine levels are elevated in renal disorders due to impaired excretion by the kidneys. It provides reference ranges for BUN (8-23 mg/dL) and creatinine (males: 0.9-1.5 mg/dL, females: 0.7-1.37 mg/dL) and describes factors that cause increased or decreased levels of each marker. The principles, reagents, procedures, and specimen considerations for performing the BUN and creatinine tests using chemical and enzymatic methods are also outlined.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes key information about blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine tests. It discusses how BUN and creatinine levels are elevated in renal disorders due to impaired excretion by the kidneys. It provides reference ranges for BUN (8-23 mg/dL) and creatinine (males: 0.9-1.5 mg/dL, females: 0.7-1.37 mg/dL) and describes factors that cause increased or decreased levels of each marker. The principles, reagents, procedures, and specimen considerations for performing the BUN and creatinine tests using chemical and enzymatic methods are also outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views3 pagesBun and Creatinine 2
Bun and Creatinine 2
Uploaded by
CRISTINA MARIE PATACSILThis document summarizes key information about blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine tests. It discusses how BUN and creatinine levels are elevated in renal disorders due to impaired excretion by the kidneys. It provides reference ranges for BUN (8-23 mg/dL) and creatinine (males: 0.9-1.5 mg/dL, females: 0.7-1.37 mg/dL) and describes factors that cause increased or decreased levels of each marker. The principles, reagents, procedures, and specimen considerations for performing the BUN and creatinine tests using chemical and enzymatic methods are also outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
CLINICAL CHEMISTRY LAB 1 FINALS ● UREMIA: Azotemia + Acidosis + Electrolyte
BLOOD UREA NITROGEN, CREATININE imbalance (hyperkalemia)
*elevated potassium levels
CLINICALLY SIGNIFICANT NPNs
● Urea 45%
● Uric Acid 20%
● Creatinine 20%
● Ammonia 0.2%
● Amino acid 20%
● Creatinine 1-2%
*urea is elevated first in renal disorders
BLOOD UREA NITROGEN (BUN)
UREA
● Major end-product of protein and amino acid
metabolism (from ammonia and amino acid)
*catabolism: breaking down of protein into simple
substances
● 45% most abundant of NPN; 80% total
nitrogen excreted
● Ammonia to Urea: Takes place in the liver
Roles of the Kidney: ● Sensitive but not specific method for renal
● Excretion disorder
● Homeostasis *we have to correlate it to creatinine
● Osmoregulation (maintaining overall fluid ● Filtered and reabsorbed at proximal tubules
balance) *we do not directly measure urea, we measure the
● Regulation of salts in the body nitrogen content of urea
● Regulation of pH
● Production of a hormone (EPO) SPECIMEN CONSIDERATIONS
*if there is a kidney disease/disorder, BUN and ● Non-fasting
creatinine is elevated ● Serum, Plasma, Whole blood, Urine
*kidney filters waste materials: food, medications, *whole blood is the least option
other toxic substances ● Fluoride and citrate will inhibit urease
*kidney produces Erythropoietin which is used for *do not use gray and blue top tubes
RBC production ● Avoid bacterial contamination in urine
*kidney regulates blood pressure *prolonged standing of urine will lead to bacterial
contamination
NON-PROTEIN NITROGEN ● Should be refrigerated when not analyzed
● Non-Protein Nitrogen: The major substance immediately
excreted by the kidneys
*waste materials PRINCIPLE OF THE TEST
● AZOTEMIA: Elevated NPNs in the blood 1. Chemical Method
(urea) ● Direct method
*urea is the most abundant NPN ● Diacetyl monoxime (DAM)
● Urea + DAM= Yellow diazine
derivative
*chemical method is not used in the lab anymore after reading (A1), read and record
2. Enzymatic Method absorbance (A2).
● Urease enzyme ● Calculate change in absorbance (△A= A2 -
*more specific and accurate A1) per minute.
*coupled enzymatic method
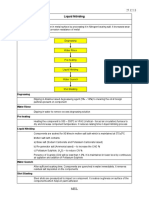
PROCEDURES (for Chem Machine)
● Prepare BUN working reagent according to
instructions.
● Pipette 1000 uL working reagent into tubes
labeled “standard”, “control”, “patient”
● Add 10 uL of sample and mix.
*Enzymes: Urease and GLDH (Glutamic ● After 2 minutes, feed onto the machine.
Dehydrogenase) ● Analyze and record your results.
*Urease converts Urea to Ammonium carbonate
*GLDH catalyzes the conversion of NADH to NAD+ REFERENCE RANGE: 8-23 mg/dL
*Final product is NAD+ and measured in the
spectrophotometer at 340 nm INCREASED BUN
● Chronic renal disease
REAGENT PREPARATION ● Stress
● Reconstitute BUN Working Reagent (12 mL ● Burns
distilled water) ● High protein diet
*usually powdered form ● Dehydration
*reconstitution: dissolve in distilled water using
serologic/automatic pipettes DECREASED BUN
● Urea Nitrogen Standard is ready to use. ● Poor nutrition
● Hepatic disease
MATERIALS ● Impaired absorption
● Spectrophotometer ● Pregnancy
● Distilled water *protein anabolism
● Semi-automated machine
● Constant temperature block or bath 37°C, or CREATININE
temperature-controlled cuvette ● Final product of creatine phosphate in
● Accurate pipetting devices muscles. (muscle metabolism)
*same pipettes used with glucose and cholesterol ● Produced from 3 AA- Methionine, Arginine,
test Lysine
● Test tubes and rack ● Partially secreted by PCT
● Timer ● Specific but not sensitive to renal disorders.
● Not affected by protein diet
PROCEDURES (for Spectro) ● Index of overall renal function
● Prepare BUN working reagent according to ● Solely a waste product
instructions. *creatinine is more specific than BUN
● Pipette 1000 uL working reagent into tubes
labeled “standard”, “control”, “patient” SPECIMEN CONSIDERATIONS
*standard, blank, patient ● Non-fasting
● Add 10 uL of sample and mix. ● Hemolyzed samples should be avoided
● After exactly 30 seconds, read and record ● Cephalosphorin (antibiotic) - false
absorbance (A1). 7. At exactly 60 seconds increase/elevation
● Female: 0.7 - 1.37 mg/dL
PRINCIPLE
1. Chemical Method (Jaffe Method) INCREASED CREATININE
● A yellow-orange tautomer of creatinine ● Impaired renal function
picrate is formed when creatinine is ● Chronic nephritis
mixed with alkaline picrate ● Congestive heart failure
*weak pumping of blood can lead to decreased blood
flow and therefore decreased removal of waste
*measure the colored complex on a
DECREASED CREATININE
spectrophotometer at 510 nm
● Decreased muscle mass
*the rate of formation of color change is directly
● Advance severe liver disease
proportional to the creatinine concentration
● Pregnancy
● Inadequate protein diet
WORKING REAGENT
● 1000 uL sodium Picrate
● Combine equal volumes of creatinine picric
acid reagent (500 uL, reaget A) and
creatinine sodium hydroxide (500 uL,
reagent B), mix well.
● Combined (working) reagent is stable for up
to one (1) month.
PROCEDURES (for Spectro)
● Prepare creatinine working reagent according
to instructions.
● Pipette 1000 uL working reagent into tubes
labeled “standard”, “control”, “patient”.
● Add 50 uL of sample and mix.
● After exactly 30 seconds, read and record
absorbance (A1). 7. At exactly 60 seconds
after reading (A1), read and record
absorbance (A2).
● Calculate change in absorbance (△A = A2 -
A1) per minute.
PROCEDURES (for Machine)
● Prepare creatinine working reagent according
to instructions.
● Pipette 1000 uL working reagent into tubes
labeled “standard”, “control”, “patient”.
● Add 50 uL of sample and mix.
● Incubate for 2 minutes.
● Feed onto your machine.
REFERENCE RANGE
● Male: 0.9 -1.50 mg/dL
You might also like
- Manual Vilter 440 and 450xlDocument41 pagesManual Vilter 440 and 450xlJose Antonio Yupa MedinaNo ratings yet
- Fs - Evilla, E. (Vertam Farms Opc) 2020Document44 pagesFs - Evilla, E. (Vertam Farms Opc) 2020Ma Teresa B. Cerezo100% (2)
- CC Lab 6 TransesDocument6 pagesCC Lab 6 TransesCiara PamonagNo ratings yet
- CC Lab 6 TransesDocument6 pagesCC Lab 6 TransesCiara PamonagNo ratings yet
- L11 Non Protein NitrogenDocument9 pagesL11 Non Protein NitrogenArmyl Raul CanadaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry Lecture NPNDocument5 pagesClinical Chemistry Lecture NPNmizunoNo ratings yet
- NPN ReviewDocument46 pagesNPN Reviewmika de guzmanNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Clin Chem 4 1Document6 pagesComprehensive Clin Chem 4 1Binky SophiaNo ratings yet
- 10 NPNs ShortDocument6 pages10 NPNs ShortBenson PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry - NPNDocument14 pagesClinical Chemistry - NPNShania DawnNo ratings yet
- cc1 LecDocument18 pagescc1 LecRayvince LopezNo ratings yet
- (Urease - GLDH) : Intended Use MethodDocument2 pages(Urease - GLDH) : Intended Use MethodMohamed AlarefeNo ratings yet
- (CC1) LEC-W12-Nonprotein Nitrogen CompoundsDocument10 pages(CC1) LEC-W12-Nonprotein Nitrogen CompoundsAira UsiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry 1 - Notes NPNDocument4 pagesClinical Chemistry 1 - Notes NPNlcrujidoNo ratings yet
- Renal Function and The Significance of Non-Protein Nitrogen CompoundsDocument12 pagesRenal Function and The Significance of Non-Protein Nitrogen CompoundsSrujana BudheNo ratings yet
- Fluitest Urea: Catalog NoDocument4 pagesFluitest Urea: Catalog NoDarko MaksimovicNo ratings yet
- Non Protein Nitrogens 1Document22 pagesNon Protein Nitrogens 1Sheine EspinoNo ratings yet
- 16.estimation of Blood UreaDocument23 pages16.estimation of Blood UreaKing of Science ytNo ratings yet
- Non-Protein Nitrogen Compounds1 (FINALS)Document60 pagesNon-Protein Nitrogen Compounds1 (FINALS)Marydith Ortillo100% (1)
- Blood Urea Nitrogen Determination PDFDocument20 pagesBlood Urea Nitrogen Determination PDFAlan Daniel España100% (1)
- Finals Topic 2 Clin Chem NpnsDocument6 pagesFinals Topic 2 Clin Chem NpnsErl Jerome CabayaoNo ratings yet
- Non-Protein Nitrogenous Compounds (NPN)Document52 pagesNon-Protein Nitrogenous Compounds (NPN)Dylan S.100% (1)
- Infinity Urea Liquid Reagent ENDocument2 pagesInfinity Urea Liquid Reagent ENKouame FrancisNo ratings yet
- BUN CC LabDocument2 pagesBUN CC LabMaw BerryNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Non Protein NitrogenDocument6 pages7.1 Non Protein NitrogenGio Joaquin SantosNo ratings yet
- Non-Protein Nitrogenous Compounds (NPN'S) : Reman A. Alingasa, RMTDocument47 pagesNon-Protein Nitrogenous Compounds (NPN'S) : Reman A. Alingasa, RMTLoulou Apollo100% (1)
- Standard LFT and It's Clinical SignificanceDocument28 pagesStandard LFT and It's Clinical SignificanceanimathzNo ratings yet
- BUN Beckman InsertDocument2 pagesBUN Beckman InsertArnoldo FelixNo ratings yet
- NPNDocument37 pagesNPNMustafa KhandgawiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry 1 Notes NPNDocument4 pagesClinical Chemistry 1 Notes NPNDavid HosamNo ratings yet
- Fluitest Urea: BiolyzerDocument4 pagesFluitest Urea: BiolyzerLhiyvind PaoNo ratings yet
- Amilase PDFDocument2 pagesAmilase PDFFariz KasyidiNo ratings yet
- Cc1 Reading SummarizedDocument10 pagesCc1 Reading SummarizedPrecious EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Measure UnDocument2 pagesMeasure Untuan vănNo ratings yet
- Non ProteinDocument7 pagesNon ProteinMelanie ParisNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry - NPNDocument7 pagesClinical Chemistry - NPNCamella Beatrice Lujan ValleNo ratings yet
- Amylase LipaseDocument5 pagesAmylase LipaseJames SandovalNo ratings yet
- BSBE - Package Insert of AMMDocument2 pagesBSBE - Package Insert of AMMBình Trần VănNo ratings yet
- Infinity™ Amylase Liquid Stable Reagent: Symbols in Product Labelling Product SummaryDocument2 pagesInfinity™ Amylase Liquid Stable Reagent: Symbols in Product Labelling Product SummaryDharmesh PatelNo ratings yet
- CC1 LAB Creatinine PDFDocument34 pagesCC1 LAB Creatinine PDFAlan Daniel EspañaNo ratings yet
- G92078R02Document6 pagesG92078R02Галина МиловановаNo ratings yet
- UrinaryDocument3 pagesUrinaryIYA LABAO100% (1)
- Report 5-8 in ProviDocument5 pagesReport 5-8 in ProviWilson AgustinNo ratings yet
- Exercises-13-15-Cc1-Lab Non-Protein NitrogensDocument5 pagesExercises-13-15-Cc1-Lab Non-Protein NitrogensAndrei VanderNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids MetabolismDocument24 pagesAmino Acids MetabolismYeri KimNo ratings yet
- Urea Nitrogen InsertoDocument2 pagesUrea Nitrogen Insertotlalzinth.nayarathNo ratings yet
- To Convert BUN MG/DL To Urea In, BUN Multiplied With 2.14 - To Convert BUN MG/DL To Urea In, BUN Multiplied With 0.36Document6 pagesTo Convert BUN MG/DL To Urea In, BUN Multiplied With 2.14 - To Convert BUN MG/DL To Urea In, BUN Multiplied With 0.36RALPH JAN T. RIONo ratings yet
- PI e UREA 16Document2 pagesPI e UREA 16Moch Abdul RokimNo ratings yet
- Indiko and Indiko Plus Brochure PDFDocument8 pagesIndiko and Indiko Plus Brochure PDFMANISH AJITWALIANo ratings yet
- Urea U.V.: High Linearity Kinetic MethodDocument2 pagesUrea U.V.: High Linearity Kinetic MethodSesi AgustinNo ratings yet
- Urea LSDocument2 pagesUrea LSdrabdullahmlsNo ratings yet
- Urea/Bun: A) CAPSO 3 (Cyclohexylamino) 2 Hydroxy 1 Propanesulfonic Acid B) BICIN N, N Bis (2 Hydroxyethyl) GlycineDocument5 pagesUrea/Bun: A) CAPSO 3 (Cyclohexylamino) 2 Hydroxy 1 Propanesulfonic Acid B) BICIN N, N Bis (2 Hydroxyethyl) GlycineGwyneth NovesterasNo ratings yet
- LabStripU11 GL Instructions For UseDocument4 pagesLabStripU11 GL Instructions For UseAurian TormesNo ratings yet
- LabStrips U11 Plus GLDocument4 pagesLabStrips U11 Plus GLAurian TormesNo ratings yet
- Indiko and Indiko Plus BrochureDocument8 pagesIndiko and Indiko Plus BrochuresharenNo ratings yet
- MEASURE CRE (Fixed)Document3 pagesMEASURE CRE (Fixed)Trần Văn BìnhNo ratings yet
- Acid Phosphatase (Acp)Document1 pageAcid Phosphatase (Acp)Risqon Anjahiranda AdiputraNo ratings yet
- Renal Function TestsDocument8 pagesRenal Function TestsQasmNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - BUN & CreatinineDocument60 pagesLecture 6 - BUN & CreatinineAbdoulhaleem MoNo ratings yet
- Mtap 2 CC1 FinalsDocument9 pagesMtap 2 CC1 FinalsI love dem Coffee (Migz)No ratings yet
- Aspartate Aminotransferase (Ast/Got)Document2 pagesAspartate Aminotransferase (Ast/Got)Ivana BajunovicNo ratings yet
- Investors Presentation 1Document26 pagesInvestors Presentation 1Positive ThinkerNo ratings yet
- Sop - L&od R&RDocument14 pagesSop - L&od R&RJeewan PawarNo ratings yet
- 4H1662 AnimalScienceAnywhere-Meat CutsDocument13 pages4H1662 AnimalScienceAnywhere-Meat CutsshylynnNo ratings yet
- AK Khan Telecom Limited: Orientation ScheduleDocument2 pagesAK Khan Telecom Limited: Orientation Schedulemozammel80No ratings yet
- VP or Business DevelopmentDocument2 pagesVP or Business Developmentapi-78878196No ratings yet
- Semantic Segmentation Data Labelling: Classes and InstructionsDocument9 pagesSemantic Segmentation Data Labelling: Classes and InstructionsMar FieldsNo ratings yet
- 22 Passage 2 - Western Immigration of Canada Q14-26Document6 pages22 Passage 2 - Western Immigration of Canada Q14-26Cương Nguyễn DuyNo ratings yet
- ANT332 Answer Key 6Document3 pagesANT332 Answer Key 6mariefmuntheNo ratings yet
- Liquid Nitriding - ProcessDocument1 pageLiquid Nitriding - ProcesssivamettNo ratings yet
- MAin The PEOPLE v. Michael R. TOMANELLIDocument4 pagesMAin The PEOPLE v. Michael R. TOMANELLIcb1998No ratings yet
- Personal Details: SRM Institute of Science and TechnologyDocument2 pagesPersonal Details: SRM Institute of Science and TechnologyZenelNo ratings yet
- Fruits and Veg SCMDocument11 pagesFruits and Veg SCMamoldhawanNo ratings yet
- PowerDB Uninstall Guide PDFDocument4 pagesPowerDB Uninstall Guide PDFMarco C. PumaNo ratings yet
- Web Bill: Noor Muhammad S/O Muhammad Pinjri Pur Haveli NTN: 00000000000Document1 pageWeb Bill: Noor Muhammad S/O Muhammad Pinjri Pur Haveli NTN: 00000000000Syed Waqar ShahNo ratings yet
- Kopi-O: Seating ProductsDocument8 pagesKopi-O: Seating Productsishanj1991No ratings yet
- Charts of Male, Female Vote Percentage & Number of Electors, PC For General Elections (1951 To 2004)Document1 pageCharts of Male, Female Vote Percentage & Number of Electors, PC For General Elections (1951 To 2004)dagotrasuraj888No ratings yet
- Đề cũ 4Document30 pagesĐề cũ 4Lê Hồng ThịnhNo ratings yet
- Airbus Family Figures BookletDocument17 pagesAirbus Family Figures BookletCoffardNo ratings yet
- Persuasive WritingDocument34 pagesPersuasive WritingRoda RodaNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Mathematical Statistics With Applications, Pg. 409, Ex. 39Document5 pagesSolutions To Mathematical Statistics With Applications, Pg. 409, Ex. 39Ivi DownhamNo ratings yet
- Local Property CasesDocument70 pagesLocal Property CasesjoyNo ratings yet
- Communication Aids and Strategies Using Tools of TechnologyDocument14 pagesCommunication Aids and Strategies Using Tools of TechnologyJussel CataloNo ratings yet
- MC Condenser Technical ManualDocument35 pagesMC Condenser Technical Manualjuan manuel guerrero florezNo ratings yet
- AC3102 Course OutlineDocument23 pagesAC3102 Course OutlineJasmine TayNo ratings yet
- Hands On 3.1 ActDocument7 pagesHands On 3.1 Actmarkkyle collantesNo ratings yet
- 28-Tax-Capitol Wireless Inc vs. Provincial Treas. of BatangasDocument2 pages28-Tax-Capitol Wireless Inc vs. Provincial Treas. of BatangasJoesil Dianne SempronNo ratings yet
- Mistral: DehumidifierDocument16 pagesMistral: DehumidifierAntreprenor XNo ratings yet
- Mochamad Juwildia Prayoga - Motivation Letter MAECIDocument2 pagesMochamad Juwildia Prayoga - Motivation Letter MAECIMochamad JuwildiaNo ratings yet