Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4 Mining - Lecture
4 Mining - Lecture
Uploaded by
REIN MATTHEW P. MALONZO0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views2 pagesMining involves extracting mineral resources from the earth through various stages: exploration to identify viable mineral deposits, development and design of the mining plan, construction of facilities, production which is the actual mining and processing, and closure/reclamation to return the land to its original state. Mining can occur via surface methods like open pit, dredging, strip, and placer mining that extract near-surface ore, or underground mining that extracts deeper ore deposits below the surface. The main stages are exploration, development, construction, production, and closure.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMining involves extracting mineral resources from the earth through various stages: exploration to identify viable mineral deposits, development and design of the mining plan, construction of facilities, production which is the actual mining and processing, and closure/reclamation to return the land to its original state. Mining can occur via surface methods like open pit, dredging, strip, and placer mining that extract near-surface ore, or underground mining that extracts deeper ore deposits below the surface. The main stages are exploration, development, construction, production, and closure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views2 pages4 Mining - Lecture
4 Mining - Lecture
Uploaded by
REIN MATTHEW P. MALONZOMining involves extracting mineral resources from the earth through various stages: exploration to identify viable mineral deposits, development and design of the mining plan, construction of facilities, production which is the actual mining and processing, and closure/reclamation to return the land to its original state. Mining can occur via surface methods like open pit, dredging, strip, and placer mining that extract near-surface ore, or underground mining that extracts deeper ore deposits below the surface. The main stages are exploration, development, construction, production, and closure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
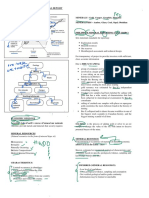
EARTH SCIENCE – MINING
Mineral Resources iii. Analyzing Chemical
properties of soil and water
• Used for different applications iv. Airborne and ground physical
• Example for cellphones (Silicon, survery
arsenopyrite, etc.) v. Identify Electric Currents
Can be in: b. Drilling
i. Evaluate type and grade of
Quarries – Sand, Gravel, Rocks minerals
Mining – Silver, Iron, Gold c. Modelling
2. Development and Design
Metallic Mineral Resources – Contains metal a. Determine whether the site can be
operated in an environmentally safe,
Non-Metallic Resources – Doesn’t contain metal economically sound and socially
(talc, fluorite, sulfur, sand, gravel responsible manner
b. Involves scoping, feasibility studies,
procurement of necessary facilities
Terms:
3. Construction
Mineral Resources–
a. Builds roads, processing facilities,
• Could be rocks or mineral environmental management system
4. Production
Mineral Occurrence (Locality) a. Stage where actual mining and
• Concentration of a mineral that is of processing of minerals are done
scientific or technical interest b. Gangue – Unwanted impurities like
sand and rocky minerals
Mineral Deposit 5. Closure and Reclamation
• Mineral occurrence of sufficient size / grade a. Process of closing the mine and
and concentration to enable extraction returning the land to its original state
b. Ensuring public health
Ore Deposit c. Establish new landform and
vegetation
• Tested and known to be economically
d. Stabilize land against erosion
profitable to mine
Types Of Mining
1. Surface Mining – Extract ore near the
Mining
earth’s surface
• Process of extracting mineral resources from a. Open Pit Mining – means big hole
earth. or pit in the group created by
blasting with explosives or drilling.
Stages of Mining:
1. Exploration - Searching of areas that b. Dredging – Mining from the bottom
contain mineral resources viable for mining of a body of water
a. Prospecting
i. Evaluation of land’s geology. c. Strip Mining – Involves removal of
ii. Identifies Geohazards a thin strip of overburden above
desired deposit
EARTH SCIENCE – MINING
d. Placer Mining – Mining of stream
bed deposits of mineral. uses water
to separate valuable ore from the
surrounding sediment
2. Underground Mining – Utilized to extract
ore minerals from the orebody deep under
the earth’s surface
You might also like
- Movie Recommendation SystemDocument41 pagesMovie Recommendation SystemSowmya Srinivasan100% (3)
- Mine Design ProjectDocument11 pagesMine Design ProjectShaiter NaseffNo ratings yet
- (Handouts) Geological and Geophysical Exploration in CEDocument9 pages(Handouts) Geological and Geophysical Exploration in CEJaash De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- REVIEW-Soil ScienceDocument20 pagesREVIEW-Soil ScienceChristian Delas Herras100% (4)
- Maruti Suzuki Final ProjectDocument63 pagesMaruti Suzuki Final ProjectMilind Singanjude75% (4)
- Nature of PlanningDocument2 pagesNature of Planningjaanaan92% (24)
- Mineral ResourcesDocument3 pagesMineral ResourcesLeonie LanzadoNo ratings yet
- Ore MineralsDocument6 pagesOre MineralsSofia DomingoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MiningDocument55 pagesIntroduction To Miningهادي الموسويNo ratings yet
- Week 9 - Mine Rock ExcavationDocument12 pagesWeek 9 - Mine Rock ExcavationNilakshiManawaduNo ratings yet
- Mining Geology, Midexam NoteDocument11 pagesMining Geology, Midexam NoteAbu NaeemNo ratings yet
- Mining EngineeringDocument5 pagesMining Engineeringsharan31No ratings yet
- How Do Minerals End Up in The Things We UseDocument2 pagesHow Do Minerals End Up in The Things We UseFrancesca YanzonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Mining PDFDocument6 pagesChapter 6 Mining PDFhamza zalahNo ratings yet
- Death Valley NP Historic Resource Study of Mining Vols 1 and 2Document982 pagesDeath Valley NP Historic Resource Study of Mining Vols 1 and 2Russell HartillNo ratings yet
- Ore MineralsDocument4 pagesOre MineralsBeyhNo ratings yet
- During The Programme - Mining To RehabDocument5 pagesDuring The Programme - Mining To Rehabbridget.duncanNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro To Mineral ExplorationDocument17 pages1 Intro To Mineral ExplorationGabrielNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Week 3 FinalDocument19 pagesEarth Science Week 3 FinalMykhaela Louize GumbanNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet How Ores Are Found, Mined and Processed For Human UseDocument7 pagesLearning Activity Sheet How Ores Are Found, Mined and Processed For Human UseLeanne Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Earth Science: Quarter 1 - Module 6: Ore Minerals: How They Are Found, Mined, and ProcessedDocument14 pagesEarth Science: Quarter 1 - Module 6: Ore Minerals: How They Are Found, Mined, and ProcessedAnneLayda100% (2)
- 01 Introduction To MiningDocument19 pages01 Introduction To MiningGeleta SafeNo ratings yet
- Deep Ocean MissionDocument4 pagesDeep Ocean Mission19-ECE-119 Ritik SinhaNo ratings yet
- Draft A Manual On Standard Operating Procedures in Mineral ExplorationDocument39 pagesDraft A Manual On Standard Operating Procedures in Mineral Explorationzeeshan269No ratings yet
- Grade 11 ExaminationDocument3 pagesGrade 11 ExaminationCleofe Jean AntonioNo ratings yet
- Quiz Minerals EesDocument1 pageQuiz Minerals EesGLENN MENDOZANo ratings yet
- Earth Science Reviewer 2019 PerioDocument7 pagesEarth Science Reviewer 2019 PerioLhemar Julia BayocaNo ratings yet
- Site Planning - The Art of Arranging Structures On TheDocument4 pagesSite Planning - The Art of Arranging Structures On TheMaiian Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- How Minerals Are Found, Mined and ProcessedDocument21 pagesHow Minerals Are Found, Mined and ProcessedSana pasia100% (1)
- Handout MINERAL RESOURCESDocument3 pagesHandout MINERAL RESOURCESStephanie VicenteNo ratings yet
- Stages of Mine LifeDocument16 pagesStages of Mine LifeGerald PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Mining MethodsDocument9 pagesIntroduction to Mining Methodsjldbismanos01320No ratings yet
- Mining 1Document49 pagesMining 1Kunwar AdarshNo ratings yet
- Cor 5 - Week 6Document8 pagesCor 5 - Week 6Nazer M. LacaboNo ratings yet
- ES Module 3 Mineral Exploration PDFDocument2 pagesES Module 3 Mineral Exploration PDFyhajj jamesNo ratings yet
- STS Detailed OutlineDocument11 pagesSTS Detailed OutlineCHARLES KEVIN MINANo ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals and Their Exploitation: Environmental ManagementDocument20 pagesRocks and Minerals and Their Exploitation: Environmental ManagementMohamed HeshamNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument6 pagesREVIEWERlamberto revecheNo ratings yet
- Board Exam-EM1Document21 pagesBoard Exam-EM1ronnel laurenteNo ratings yet
- 25 Questions in Resource GeoDocument3 pages25 Questions in Resource GeohenrichtupasNo ratings yet
- 02 - Prospecting and Exploration 025-105Document41 pages02 - Prospecting and Exploration 025-105ramanaNo ratings yet
- Hazards of Excavations Training OutlineDocument5 pagesHazards of Excavations Training OutlineJohnNo ratings yet
- Surface Mining Notes Terminology/definitionsDocument10 pagesSurface Mining Notes Terminology/definitionsEng.Jackson MwendwaNo ratings yet
- First 5 ChaptersDocument21 pagesFirst 5 ChaptersalfaazmcsNo ratings yet
- Mne125 Introduction To Mineral DepositDocument13 pagesMne125 Introduction To Mineral DepositShane NakhuiNo ratings yet
- Minerals - 1Document3 pagesMinerals - 1Brajesh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Classification: Under The Act The Principal Mining, Minerals Are Divided Into 3 GroupsDocument9 pagesClassification: Under The Act The Principal Mining, Minerals Are Divided Into 3 GroupsMuhammad HidayatNo ratings yet
- Reviewer (Geo) DocxDocument5 pagesReviewer (Geo) DocxJean Gabrelle DoradoNo ratings yet
- Learning MODULE (Week 5) in Earth Science 12: Luna Goco Colleges, IncDocument5 pagesLearning MODULE (Week 5) in Earth Science 12: Luna Goco Colleges, IncKarenn Estrañero LuzonNo ratings yet
- Pe Em4251Document4 pagesPe Em4251garthraymundogamingNo ratings yet
- (Notes) Mineral ResourcesDocument2 pages(Notes) Mineral ResourcesDenver Cho-oyNo ratings yet
- MLET2023 - MSTeams-Earth Science DrillsDocument3 pagesMLET2023 - MSTeams-Earth Science DrillsRavian Mhe BitonNo ratings yet
- ChacateDocument6 pagesChacateDércio ChacateNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Ore MineralsDocument3 pagesLesson 6 - Ore MineralsRowela Mariel MorongNo ratings yet
- Draft DETAILED OUTLINEDocument7 pagesDraft DETAILED OUTLINECharles Kevin MinaNo ratings yet
- Metal Mining IDocument59 pagesMetal Mining IANSHUL YADAVNo ratings yet
- Earth Sci - MiningDocument24 pagesEarth Sci - Miningacejohn1023No ratings yet
- Lecture 4.1 - Prospecting and Exploration PDFDocument91 pagesLecture 4.1 - Prospecting and Exploration PDFvanjovi lofrancoNo ratings yet
- Soil Exam1.pdf Soil Exam2.pdf Soil Exam3 PDFDocument63 pagesSoil Exam1.pdf Soil Exam2.pdf Soil Exam3 PDFArchie MilanoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document2 pagesQuiz 2Mark CalixtoNo ratings yet
- Earth Sci FinalsDocument6 pagesEarth Sci Finalskc.jarobillaNo ratings yet
- Esci Revs 6-10Document7 pagesEsci Revs 6-10Angela AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Exercise LogDocument1 pageExercise LogREIN MATTHEW P. MALONZONo ratings yet
- Philippine Stock ExchangeDocument1 pagePhilippine Stock ExchangeREIN MATTHEW P. MALONZONo ratings yet
- Mas MaayosDocument2 pagesMas MaayosREIN MATTHEW P. MALONZONo ratings yet
- PERDEV Lesson 4Document21 pagesPERDEV Lesson 4REIN MATTHEW P. MALONZONo ratings yet
- Stress ManagementDocument11 pagesStress ManagementREIN MATTHEW P. MALONZONo ratings yet
- Week 9 Soil ResourcesDocument31 pagesWeek 9 Soil ResourcesREIN MATTHEW P. MALONZONo ratings yet
- 45 Second ChallengeDocument6 pages45 Second ChallengeREIN MATTHEW P. MALONZONo ratings yet
- 7 Soil ResourcesDocument6 pages7 Soil ResourcesREIN MATTHEW P. MALONZONo ratings yet
- 3 Rocks - Lecture (Need Edit)Document2 pages3 Rocks - Lecture (Need Edit)REIN MATTHEW P. MALONZONo ratings yet
- 2 Minerals - LectureDocument2 pages2 Minerals - LectureREIN MATTHEW P. MALONZONo ratings yet
- 5 Energy SourcesDocument1 page5 Energy SourcesREIN MATTHEW P. MALONZONo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - 7 (1st Sem) Earth SciDocument15 pagesLesson 1 - 7 (1st Sem) Earth SciREIN MATTHEW P. MALONZONo ratings yet
- 1 Earth - LectureDocument2 pages1 Earth - LectureREIN MATTHEW P. MALONZONo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - 7 (1st Sem) Earth SciDocument15 pagesLesson 1 - 7 (1st Sem) Earth SciREIN MATTHEW P. MALONZONo ratings yet
- Types of CommunicationDocument2 pagesTypes of CommunicationREIN MATTHEW P. MALONZONo ratings yet
- Assure RMS PDFDocument2 pagesAssure RMS PDFDesi EryonNo ratings yet
- Chennai BPODocument908 pagesChennai BPOsonaiya software solutions100% (1)
- ToyotaDocument4 pagesToyotasunny837No ratings yet
- PayfixationoptionsDocument5 pagesPayfixationoptionsGK TiwariNo ratings yet
- Jumping Through HoopsDocument4 pagesJumping Through HoopsCharles RusnellNo ratings yet
- AWS Well Architected FrameworkDocument30 pagesAWS Well Architected FrameworkkichnaNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Emergency Lights Load: WattsDocument1 pageCalculation of Emergency Lights Load: WattsSandeep DeodharNo ratings yet
- Altagamma Bain Worldwide Market Monitor - Update 2019 PDFDocument15 pagesAltagamma Bain Worldwide Market Monitor - Update 2019 PDFHaider RazaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 Internet ShoppingDocument1 pageQuiz 1 Internet ShoppingEloy RicouzNo ratings yet
- Pennsylvania Department of Health Letter To Tower HealthDocument2 pagesPennsylvania Department of Health Letter To Tower HealthWHYY NewsNo ratings yet
- Government Led Joint Assessment in Conflict Affected Districts of Xarardheere & Ceel DheerDocument9 pagesGovernment Led Joint Assessment in Conflict Affected Districts of Xarardheere & Ceel DheerBarre Moulid ShuqulNo ratings yet
- CDUXLSIMDocument336 pagesCDUXLSIMlocoboeingNo ratings yet
- Nas-1000 Ais SartDocument2 pagesNas-1000 Ais SartAntonio VellaraNo ratings yet
- Franchise Application Form: (I) APPLICANT INFORMATION (For Individuals, Please Fill in Applicable Fields)Document2 pagesFranchise Application Form: (I) APPLICANT INFORMATION (For Individuals, Please Fill in Applicable Fields)Nha Nguyen HoangNo ratings yet
- Answer Script - ISDocument21 pagesAnswer Script - ISanishjoseph007No ratings yet
- Pemanfaatan Media Sosial Dan Ecommerce Sebagai Media Pemasaran Dalam Mendukung Peluang Usaha Mandiri Pada Masa Pandemi Covid 19Document12 pagesPemanfaatan Media Sosial Dan Ecommerce Sebagai Media Pemasaran Dalam Mendukung Peluang Usaha Mandiri Pada Masa Pandemi Covid 19Min HwagiNo ratings yet
- How To Conduct An OR Study?Document2 pagesHow To Conduct An OR Study?Brylle James BigorniaNo ratings yet
- Digitales: ArchivDocument9 pagesDigitales: ArchivbanbanNo ratings yet
- Geh 6760Document98 pagesGeh 6760Hung NgoNo ratings yet
- Exam Preparation Chartered Member Solutions 20080403Document36 pagesExam Preparation Chartered Member Solutions 20080403Jordy NgNo ratings yet
- 3 Simpson Wickelgren (2007) Naked Exclusion Efficient Breach and Downstream Competition1Document10 pages3 Simpson Wickelgren (2007) Naked Exclusion Efficient Breach and Downstream Competition1211257No ratings yet
- Red Hat Jboss Enterprise Application Platform 7.1: Getting Started GuideDocument61 pagesRed Hat Jboss Enterprise Application Platform 7.1: Getting Started Guidesomanath padhyNo ratings yet
- Hotel Administration and Management Network - AbstractDocument3 pagesHotel Administration and Management Network - AbstractMehadi Hasan RoxyNo ratings yet
- Edu 3 AssDocument19 pagesEdu 3 Assparvathy bNo ratings yet
- Myanmar Companies Law 2017Document188 pagesMyanmar Companies Law 2017Let's Save Myanmar100% (1)
- ASBA V State Petition For Transfer FINALDocument13 pagesASBA V State Petition For Transfer FINALKTARNo ratings yet
- Barangay CertificateDocument4 pagesBarangay CertificateMark Vincent SolisNo ratings yet