Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 viewsNCP Medsurg
NCP Medsurg
Uploaded by
Justine Alexandra1) The patient has impaired decision making related to managing their diabetes which puts them at risk for unstable blood glucose levels.
2) Short term goals are to monitor the patient's blood glucose and help them identify ways to keep it in the normal range through medication adherence, diet, and lifestyle changes.
3) The nurse assesses the patient's knowledge, habits, and support system to develop an individualized plan to educate them on properly managing their diabetes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- ModyDocument6 pagesModyandriopaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationJana Patricia JalovaNo ratings yet
- 2017 Sample QuestionsDocument6 pages2017 Sample QuestionsMina MakramNo ratings yet
- TRUE METRIX GO Owners Booklet RF4TVH03r54 PDFDocument66 pagesTRUE METRIX GO Owners Booklet RF4TVH03r54 PDFtensg100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Independent: MedicationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Independent: MedicationWinsel Therese CAMARI�ASNo ratings yet
- University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing Espa: Ña BLVD., Manila, Philippines 1015Document3 pagesUniversity of Santo Tomas College of Nursing Espa: Ña BLVD., Manila, Philippines 1015Celiz HilarioNo ratings yet
- Health Problem Family Nusing Problem Goals of Care Objectives of CareDocument8 pagesHealth Problem Family Nusing Problem Goals of Care Objectives of CareMyrshaida IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Health Problem Family Nusing Problem Goals of Care Objectives of CareDocument2 pagesHealth Problem Family Nusing Problem Goals of Care Objectives of CareShai IbrahimNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument4 pagesJaundicepamelaideaNo ratings yet
- PCOS (Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome) Management Teaching PlanDocument5 pagesPCOS (Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome) Management Teaching PlanAudrey C. JunsayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (1) Day 1Document20 pagesNursing Care Plan (1) Day 1FATIMA PANDAOGNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationChrizley Shawn DeroniaNo ratings yet
- NCP Drug StudyDocument14 pagesNCP Drug StudyRica ParcasioNo ratings yet
- HTP 4Document4 pagesHTP 4Julius Mathew EnopiaNo ratings yet
- NCP - ConstipationDocument2 pagesNCP - Constipationgringo1388No ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementatio N Evaluation: Subjective: Short Term: Short TermDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementatio N Evaluation: Subjective: Short Term: Short TermMaverick LimNo ratings yet
- Format - Comprehensive Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesFormat - Comprehensive Nursing Care PlanVillanueva Gerald Jr LNo ratings yet
- Imbalance NutritionDocument4 pagesImbalance NutritionLeah Mae TomasNo ratings yet
- NCP MiniparDocument9 pagesNCP MiniparKyla Avila TorrevillasNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument3 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityStar AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Name: Grace AGE: 28 Gender: Female Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GeneralDocument2 pagesName: Grace AGE: 28 Gender: Female Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GeneralRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Sundus Maher Care PlanDocument6 pagesSundus Maher Care Planسُندس الحاجيNo ratings yet
- NCP Disturbed Sleep Pattern and Hypothermia (Care of Older Adult Issues)Document4 pagesNCP Disturbed Sleep Pattern and Hypothermia (Care of Older Adult Issues)Jenny AjocNo ratings yet
- NCP (Diarrhea)Document2 pagesNCP (Diarrhea)Rodj Bilang Jr.83% (30)
- NCP FoodDocument1 pageNCP FoodAdrian ArdamilNo ratings yet
- GI CASE ANALYSIS Group 3Document11 pagesGI CASE ANALYSIS Group 3Ma. Sofia Andrei AlcabazaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - NCP-PIHDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan - NCP-PIHAally ChandraNo ratings yet
- Askep Istirahat TidurDocument6 pagesAskep Istirahat TidurGracellia MullyNo ratings yet
- Quidet Jonnavie P. NCPDocument1 pageQuidet Jonnavie P. NCPjonnavie quidetNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning and NCP SDocument8 pagesDischarge Planning and NCP SRainier RamosNo ratings yet
- Constipation HTP GeriaDocument6 pagesConstipation HTP GeriaJez RarangNo ratings yet
- Rinskasan Dokumen PerawatDocument6 pagesRinskasan Dokumen PerawatAndi FildaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationKobe ManuelNo ratings yet
- Abdellah S TheoryDocument6 pagesAbdellah S TheoryBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Nursing InterventionDocument3 pagesNursing InterventionMiskan FebrianiNo ratings yet
- Sample TCP - GraceGuitguitenDocument4 pagesSample TCP - GraceGuitguitenLauren JalandoniNo ratings yet
- BSN2 2FNCP2Document2 pagesBSN2 2FNCP2Kobe ManuelNo ratings yet
- Altered Nutrition NCPDocument2 pagesAltered Nutrition NCPLeiAnnManaleseNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part-1Document9 pagesUnit 1 Part-1MOHAN SANAPATHINo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan No. 1: Obesity Related ToDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan No. 1: Obesity Related ToAngelo Louise CastilloNo ratings yet
- Stroke Care Plan PDFDocument1 pageStroke Care Plan PDFJot grewalNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Budget of Work FinalDocument8 pagesGrade 8 Budget of Work FinalNar ZieNo ratings yet
- Actual Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesActual Nursing Care PlanJinky Nacar DomingoNo ratings yet
- Table FourDocument7 pagesTable FourLawrence AckahNo ratings yet
- Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Related To Altered Image, Inadequate Nutrient Intake, and Chronic Vomiting.Document2 pagesImbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Related To Altered Image, Inadequate Nutrient Intake, and Chronic Vomiting.Senyorita KHaye100% (1)
- Activity On Care PlanningDocument14 pagesActivity On Care PlanningClaire Maurice JuaneroNo ratings yet
- OB - NCP (Episiotomy)Document3 pagesOB - NCP (Episiotomy)eosNo ratings yet
- Chapoco Week 10Document4 pagesChapoco Week 10sofia yapNo ratings yet
- Forro Intestinal Obstruction-2Document4 pagesForro Intestinal Obstruction-2Shiehan Mae ForroNo ratings yet
- Constipation Care PlanDocument1 pageConstipation Care Planglenda roblesNo ratings yet
- Subjective Cues: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalDocument3 pagesSubjective Cues: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalPia Mae BuayaNo ratings yet
- GRPD SomaticNCP-1Document2 pagesGRPD SomaticNCP-1Macmac GalabacNo ratings yet
- Self Care Deficit NCPDocument3 pagesSelf Care Deficit NCPJUSTIN ALZATENo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PosterDocument1 pageEndocrine System PosterMarre Ramirez LópezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan TophiDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan TophiAndrea Isabel U. O'DellNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Process (NCP) Risk-Prone Health Behavior PrepartumDocument2 pagesNursing Care Process (NCP) Risk-Prone Health Behavior PrepartumFrederene JavelonaNo ratings yet
- Knowledge DdeficitDocument2 pagesKnowledge DdeficitnovagaryNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: University of The EastDocument8 pagesCollege of Nursing: University of The EastroblesNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis NCP FINALDocument6 pagesCholelithiasis NCP FINALShreshthi VermaNo ratings yet
- Health Optimizing Physical Education 11 - Module 1: Most Essential Learning CompetencyDocument2 pagesHealth Optimizing Physical Education 11 - Module 1: Most Essential Learning CompetencyGuenn RamosNo ratings yet
- 2 Family Care Plan Health DeficitDocument2 pages2 Family Care Plan Health DeficitMikee Fernandez TangubNo ratings yet
- Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalDocument3 pagesSubjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalNicholas TagleNo ratings yet
- Coa Revised Paper.Document16 pagesCoa Revised Paper.Justine AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Module DisorderDocument9 pagesModule DisorderJustine AlexandraNo ratings yet
- 4 Quiz Group 13: Answer: DDocument5 pages4 Quiz Group 13: Answer: DJustine AlexandraNo ratings yet
- 3 Quiz Group 5:: Ans: CDocument5 pages3 Quiz Group 5:: Ans: CJustine AlexandraNo ratings yet
- NCP1 Impaired Skin... NCP3 Knowledge DeficietDocument6 pagesNCP1 Impaired Skin... NCP3 Knowledge DeficietJustine AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Health and Natural Sciences Central Council Group 4 - MNK Business Questions and AnswersDocument2 pagesHealth and Natural Sciences Central Council Group 4 - MNK Business Questions and AnswersJustine AlexandraNo ratings yet
- UPDATED Drug StudyDocument6 pagesUPDATED Drug StudyJustine AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory and DiagnosticsDocument10 pagesLaboratory and DiagnosticsJustine AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Philippine Colonialism (Limasawa, Magellan)Document4 pagesPhilippine Colonialism (Limasawa, Magellan)Justine AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Philippine Colonialism (Limasawa, Magellan)Document4 pagesPhilippine Colonialism (Limasawa, Magellan)Justine AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Fasting Blood Glucose (FBG) Sugar and Glycosylated Hemoglobin (HbA1C)Document28 pagesFasting Blood Glucose (FBG) Sugar and Glycosylated Hemoglobin (HbA1C)ask1400No ratings yet
- Abilify Dosing GuideDocument2 pagesAbilify Dosing GuidemtassyNo ratings yet
- Urine Glucose TestDocument6 pagesUrine Glucose TestSelim HanNo ratings yet
- Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic StateDocument8 pagesHyperosmolar Hyperglycemic StateEsra AljafferNo ratings yet
- DM 20 ItemsDocument4 pagesDM 20 ItemsDayanara TagaloguinNo ratings yet
- SAP HANA in Healthcare Real-Time Big Data AnalysisDocument25 pagesSAP HANA in Healthcare Real-Time Big Data AnalysisKESHAVA HBNo ratings yet
- Type 2 DM PathoDocument5 pagesType 2 DM PathoPearl JuntillaNo ratings yet
- ManejodiabetesDocument44 pagesManejodiabetesVinicius SepúlvedaNo ratings yet
- Week 10: Drugs Administered For The Treatment of Diabetes MellitusDocument7 pagesWeek 10: Drugs Administered For The Treatment of Diabetes Mellitusashley larsonNo ratings yet
- Practice in Clinical BiochemistryDocument112 pagesPractice in Clinical BiochemistryMohamed Magdi100% (1)
- Pathogenesisof Cardiovasculardiseasein Diabetes: Andrea V. Haas,, Marie E. McdonnellDocument13 pagesPathogenesisof Cardiovasculardiseasein Diabetes: Andrea V. Haas,, Marie E. McdonnellPaulina DiazNo ratings yet
- Steroid Tapering and Supportive Treatment Guidance V1.0 PDFDocument1 pageSteroid Tapering and Supportive Treatment Guidance V1.0 PDFNthutagaol TrusNo ratings yet
- MEHU130 - U2 - T43 - Nefropatia DiabeticaDocument110 pagesMEHU130 - U2 - T43 - Nefropatia DiabeticaStefani AtlleNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology of Diabetes MellitusDocument49 pagesEpidemiology of Diabetes MellitusSantosh K YatnattiNo ratings yet
- Metformin GlucophageDocument1 pageMetformin GlucophageENo ratings yet
- PHARMACARDS GonzagaDocument38 pagesPHARMACARDS GonzagaJay Marie GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Glucose Tolerance Test: Prakash MishraDocument31 pagesGlucose Tolerance Test: Prakash MishraRoyal LibraryNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus in ChildrenDocument29 pagesDiabetes Mellitus in ChildrenwoldemariamNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument5 pagesDiabetes MellitusKeij AranetaNo ratings yet
- Humulin 3070 Ca Pmi CartDocument5 pagesHumulin 3070 Ca Pmi CartJoshua DeonarineNo ratings yet
- The Newborn at Risk Because of Maternal IllnessDocument6 pagesThe Newborn at Risk Because of Maternal IllnessJoanna Bee Rose MagyawiNo ratings yet
- Norditropin Travel Letter0611-000348 1v 2Document18 pagesNorditropin Travel Letter0611-000348 1v 2Hary Kernet MerkapaNo ratings yet
- GDMDocument13 pagesGDMSharmistha DebnathNo ratings yet
- DM Questions ReviewDocument5 pagesDM Questions ReviewJayson Britania MayugaNo ratings yet
- Perioperative NursingDocument32 pagesPerioperative NursingMaria Garcia Pimentel Vanguardia II100% (2)
- Initial Management of Blood Glucose in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - UpToDateDocument24 pagesInitial Management of Blood Glucose in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - UpToDateJessica ArciniegasNo ratings yet
- User Instruction Manual: Blood Glucose Monitoring SystemDocument140 pagesUser Instruction Manual: Blood Glucose Monitoring Systemcinthia olivaNo ratings yet
NCP Medsurg
NCP Medsurg
Uploaded by
Justine Alexandra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views6 pages1) The patient has impaired decision making related to managing their diabetes which puts them at risk for unstable blood glucose levels.
2) Short term goals are to monitor the patient's blood glucose and help them identify ways to keep it in the normal range through medication adherence, diet, and lifestyle changes.
3) The nurse assesses the patient's knowledge, habits, and support system to develop an individualized plan to educate them on properly managing their diabetes.
Original Description:
Original Title
NCP Medsurg (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The patient has impaired decision making related to managing their diabetes which puts them at risk for unstable blood glucose levels.
2) Short term goals are to monitor the patient's blood glucose and help them identify ways to keep it in the normal range through medication adherence, diet, and lifestyle changes.
3) The nurse assesses the patient's knowledge, habits, and support system to develop an individualized plan to educate them on properly managing their diabetes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views6 pagesNCP Medsurg
NCP Medsurg
Uploaded by
Justine Alexandra1) The patient has impaired decision making related to managing their diabetes which puts them at risk for unstable blood glucose levels.
2) Short term goals are to monitor the patient's blood glucose and help them identify ways to keep it in the normal range through medication adherence, diet, and lifestyle changes.
3) The nurse assesses the patient's knowledge, habits, and support system to develop an individualized plan to educate them on properly managing their diabetes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
Binlingan
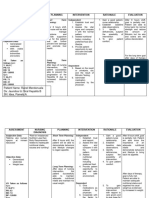
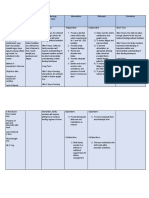
Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Explanation
Subjective: Ineffective Pattern of Short term: 1.) Assess the patient’s 1.) The patient’s point of view Short term:
“Nakalive po kasi Health regulating and 1.) After 2 hours perception of his or her reveals if he or she is open 1.) After 2 hours
ako kanina at manageme integrating into the patient will health status to change. The patient has the patient
hindi ko kop o nt r/t daily living a verbalize the to recognize that increased verbalized the
napansin yung impaired therapeutic reason why he health issues are caused by reason why he
oras. Hindi ko po decision regimen needs to follow 2.) Assess the patient’s their inability to manage needs to follow
na take yung making his therapeutic family dynamic their health. his therapeutic
gamut ko akala ko regimen; 3.) Assess the patient’s regimen;
po kasi okay lang for the a) The body can’t knowledge about his or 2.) Family and friends can a) The body can’t
na hindi kasi hindi treatment of make insulin her behavior influence behavior and make insulin
naman po ako illness and its anymore 4.) Help the patient social activities that might anymore
kumain” as sequelae b) The body needs identify daily habits contribute to the patient’s b) The body needs
verbalized by the the right amount of that prevent him or her lifestyle. the right amount of
patient insulin to keep the from implementing 3.) To change, the patient has insulin to keep the
that it is blood sugar levels in healthy habits to know about the blood sugar levels in
Objective: unsatisfactory a healthy range. 5.) Help the patient with inadequacy of skills to a healthy range.
-Impaired decision for meeting c) Without insulin, managing medication maintain a healthy lifestyle. c) Without insulin,
making specific health the body will break schedules The nurse needs to know if the body will break
goals down its own fat 6.) Reeducate about the patient wants to down its own fat
and muscle, indication and schedule change but does not have and muscle,
resulting in weight times of medications as the means or is unwilling to resulting in weight
(e.g. impaired loss and lead to well reasons why he change. loss and lead to
decision further needs to be comply 4.) Unhealthy lifestyle habits further
making) complications with the treatment can be slowly replaced by complications
regimen. healthy activities that
2.) After 3 hours the improve the patient’s 2.) After 3 hours the
patient will identify health patient identified
ways for him to 5.) The patient might be ways for him to
follow his willing to do it but finds it follow his
therapeutic to be complicated to therapeutic
regimen; accomplish. Use regimen;
a) Place the medication organizer, a) Place the
medication were it alarm clock in the phone medication were it
is visible calendars to help keep is visible
things organized. b) Set an alarm clock
6.) It might make it easier to in the phone to
remind when it’s
time to take his
medication.
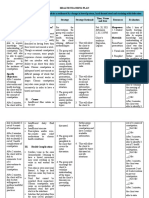
Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Explanation
Subjective: Risk for Beta cells Short term: Independent: 1.) This is to monitor Short term:
‘Hindi ko po na unstable produce little or 1.) After 2 hours the 1.) Assess feet for peripheral perfusion and 1.) After 2
take yung blood no insulin patient’s blood temperature, pulses, neuropathy. hours the patient’s
insulin ko” Glucose glucose will be in color, and sensation. blood glucose is in
level the normal range 2.) Non-adherence to dietary the normal range 70
Objective: glucose builds up 70 -105 mg/dL 2.) Assess eating guidelines for a specific -105 mg/dL
Blood in the patterns. clinical condition can result
glucose bloodstream 2.) After 4 hours the in fluctuations in blood 2.) After 4
level: instead of going patient will glucose. hours the patient
Polyuria: 60 into the cells identify ways to 3.) Assist the patient 3.) This information provides identified ways to
mL/2 hrs keep his blood in identifying the basis for individualized keep his blood
Nausea glucose level in eating patterns dietary instruction related glucose level in the
Fruity This buildup of the normal range; that need to be to the clinical condition normal range;
breath glucose in the a) Monitor blood that contributes to a) Monitor
Oral cavity blood is called sugar levels to see modified. fluctuation in blood glucose blood sugar levels to
is dry hyperglycemia what makes them levels. see what makes
go up or down. 4.) Hypertension is commonly them go up or
Too much insulin b) Eat at regular associated with diabetes. down.
hypoglycemia. times, and don't 4.) Monitor blood Control of BP prevents b) Eat at
skip meals. pressure and coronary artery disease, regular times, and
c) Consume foods report BP of more stroke, retinopathy, and don't skip meals.
and beverages than 160 mm Hg nephropathy. c) Choose
with lower in (systolic). 5.) Capillary blood glucose foods and beverages
calories, saturated monitoring provides the with lower in
fat, trans fat, patient with immediate calories, saturated
sugar, and salt. 5.) Teach the patient information about blood fat, trans fat, sugar,
d) Regular exercise on measuring glucose and salt.
as tolerated capillary blood 6.) Maintaining adequate d) Regular
glucose blood glucose supply is exercise as tolerated
critical during exercise
6.) Encourage the because it constitutes an
patient to exercise appreciable fraction of the
Long Term fuel for the working muscle
1.) After 1 month the 7.) Encourage the and, as is the case at rest, Long Term
patient would patient to have a supplies virtually all the 1.) After 1
improve his health balanced fuel for the central nervous month the patient
and has limited to carbohydrate- system. improved his health
no signs of controlled diet. 7.) Eating a balanced and has limited to
hyperglycemia or Dependent carbohydrate-controlled no signs of
hypoglycemia. Doctors’ orders: diet especially for insulin hyperglycemia or
1.) Insulin IV bolus dependent patient you may hypoglycemia.
STAT- 9.75 units need more or less
(0.15 units/kg) carbohydrate at a meal or
snack to ensure a healthy
blood glucose range.
Doctors order
1.) Insulin is required to lower
blood glucose levels in type
1 diabetes.
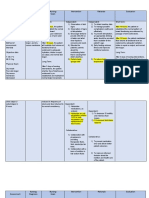
Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Explanation
Subjective: Activity Little to no Short term: Independent: Independent: Short term:
“Nanghihina po intolerance insulin 1.) After 5 hours the 1.) Assess the patients 1.) To plan the appropriate 1.) After 5 hours th
ako” r/t inability to production patient will perceived activities that fits to the patient verbalized
verbalize and capability for patient’s capabilities
Objective: take up and showed
show willingness increased activity 2.) To avoid the occurance
Generalized glucose willingness to
to participate in 2.) Assist the patient of bone sores and help
fatigue secondary to to assume in a in the comfort of the participate in the
the plan of
Pulse type 1 dm Cells can’t absorb plan of activities to
activities to comfortable patient.
oximeter: positions for rest 3.) To reduce stress and
the glucose in increase activity increase activity
93%
the blood tolerance. and sleep. excess stimulation, tolerance.
RR: 23 cpm 3.) Provide a promoting rest.
PR: 102bpm 2.)After 3 days of
2.) After 3 days of comfortable and 4.) Patient education
BP: 35.5 C effective nursing
effective nursing quiet and promotes patient-
environment. centered care. interventions, the
interventions, the
Cells will starve patient report an 4.) Educate to the 5.) To prevent a sudden patient reported a
and will not increase in activity patient the workload increase in activity
function properly tolerance and will importance of rest tolerance and will
be able to do and energy be able to do ADL’
ADL’s and conservation. and participate in
participate in self- 5.) Increase the
self-care activities
Insufficient care activities activity gradually
physologic Long Term
energy to Long Term 1.)After 1 week th
1.) After 1 week the patient will be able
complete
patient will be to increase activity
required desired able to increase tolerance evidence
daily activities activity tolerance by absence of
evidenced by weakness
absence of
weakness
You might also like
- ModyDocument6 pagesModyandriopaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationJana Patricia JalovaNo ratings yet
- 2017 Sample QuestionsDocument6 pages2017 Sample QuestionsMina MakramNo ratings yet
- TRUE METRIX GO Owners Booklet RF4TVH03r54 PDFDocument66 pagesTRUE METRIX GO Owners Booklet RF4TVH03r54 PDFtensg100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Independent: MedicationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Independent: MedicationWinsel Therese CAMARI�ASNo ratings yet
- University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing Espa: Ña BLVD., Manila, Philippines 1015Document3 pagesUniversity of Santo Tomas College of Nursing Espa: Ña BLVD., Manila, Philippines 1015Celiz HilarioNo ratings yet
- Health Problem Family Nusing Problem Goals of Care Objectives of CareDocument8 pagesHealth Problem Family Nusing Problem Goals of Care Objectives of CareMyrshaida IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Health Problem Family Nusing Problem Goals of Care Objectives of CareDocument2 pagesHealth Problem Family Nusing Problem Goals of Care Objectives of CareShai IbrahimNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument4 pagesJaundicepamelaideaNo ratings yet
- PCOS (Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome) Management Teaching PlanDocument5 pagesPCOS (Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome) Management Teaching PlanAudrey C. JunsayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (1) Day 1Document20 pagesNursing Care Plan (1) Day 1FATIMA PANDAOGNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationChrizley Shawn DeroniaNo ratings yet
- NCP Drug StudyDocument14 pagesNCP Drug StudyRica ParcasioNo ratings yet
- HTP 4Document4 pagesHTP 4Julius Mathew EnopiaNo ratings yet
- NCP - ConstipationDocument2 pagesNCP - Constipationgringo1388No ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementatio N Evaluation: Subjective: Short Term: Short TermDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementatio N Evaluation: Subjective: Short Term: Short TermMaverick LimNo ratings yet
- Format - Comprehensive Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesFormat - Comprehensive Nursing Care PlanVillanueva Gerald Jr LNo ratings yet
- Imbalance NutritionDocument4 pagesImbalance NutritionLeah Mae TomasNo ratings yet
- NCP MiniparDocument9 pagesNCP MiniparKyla Avila TorrevillasNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument3 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityStar AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Name: Grace AGE: 28 Gender: Female Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GeneralDocument2 pagesName: Grace AGE: 28 Gender: Female Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GeneralRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Sundus Maher Care PlanDocument6 pagesSundus Maher Care Planسُندس الحاجيNo ratings yet
- NCP Disturbed Sleep Pattern and Hypothermia (Care of Older Adult Issues)Document4 pagesNCP Disturbed Sleep Pattern and Hypothermia (Care of Older Adult Issues)Jenny AjocNo ratings yet
- NCP (Diarrhea)Document2 pagesNCP (Diarrhea)Rodj Bilang Jr.83% (30)
- NCP FoodDocument1 pageNCP FoodAdrian ArdamilNo ratings yet
- GI CASE ANALYSIS Group 3Document11 pagesGI CASE ANALYSIS Group 3Ma. Sofia Andrei AlcabazaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - NCP-PIHDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan - NCP-PIHAally ChandraNo ratings yet
- Askep Istirahat TidurDocument6 pagesAskep Istirahat TidurGracellia MullyNo ratings yet
- Quidet Jonnavie P. NCPDocument1 pageQuidet Jonnavie P. NCPjonnavie quidetNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning and NCP SDocument8 pagesDischarge Planning and NCP SRainier RamosNo ratings yet
- Constipation HTP GeriaDocument6 pagesConstipation HTP GeriaJez RarangNo ratings yet
- Rinskasan Dokumen PerawatDocument6 pagesRinskasan Dokumen PerawatAndi FildaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationKobe ManuelNo ratings yet
- Abdellah S TheoryDocument6 pagesAbdellah S TheoryBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Nursing InterventionDocument3 pagesNursing InterventionMiskan FebrianiNo ratings yet
- Sample TCP - GraceGuitguitenDocument4 pagesSample TCP - GraceGuitguitenLauren JalandoniNo ratings yet
- BSN2 2FNCP2Document2 pagesBSN2 2FNCP2Kobe ManuelNo ratings yet
- Altered Nutrition NCPDocument2 pagesAltered Nutrition NCPLeiAnnManaleseNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part-1Document9 pagesUnit 1 Part-1MOHAN SANAPATHINo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan No. 1: Obesity Related ToDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan No. 1: Obesity Related ToAngelo Louise CastilloNo ratings yet
- Stroke Care Plan PDFDocument1 pageStroke Care Plan PDFJot grewalNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Budget of Work FinalDocument8 pagesGrade 8 Budget of Work FinalNar ZieNo ratings yet
- Actual Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesActual Nursing Care PlanJinky Nacar DomingoNo ratings yet
- Table FourDocument7 pagesTable FourLawrence AckahNo ratings yet
- Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Related To Altered Image, Inadequate Nutrient Intake, and Chronic Vomiting.Document2 pagesImbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Related To Altered Image, Inadequate Nutrient Intake, and Chronic Vomiting.Senyorita KHaye100% (1)
- Activity On Care PlanningDocument14 pagesActivity On Care PlanningClaire Maurice JuaneroNo ratings yet
- OB - NCP (Episiotomy)Document3 pagesOB - NCP (Episiotomy)eosNo ratings yet
- Chapoco Week 10Document4 pagesChapoco Week 10sofia yapNo ratings yet
- Forro Intestinal Obstruction-2Document4 pagesForro Intestinal Obstruction-2Shiehan Mae ForroNo ratings yet
- Constipation Care PlanDocument1 pageConstipation Care Planglenda roblesNo ratings yet
- Subjective Cues: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalDocument3 pagesSubjective Cues: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalPia Mae BuayaNo ratings yet
- GRPD SomaticNCP-1Document2 pagesGRPD SomaticNCP-1Macmac GalabacNo ratings yet
- Self Care Deficit NCPDocument3 pagesSelf Care Deficit NCPJUSTIN ALZATENo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PosterDocument1 pageEndocrine System PosterMarre Ramirez LópezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan TophiDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan TophiAndrea Isabel U. O'DellNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Process (NCP) Risk-Prone Health Behavior PrepartumDocument2 pagesNursing Care Process (NCP) Risk-Prone Health Behavior PrepartumFrederene JavelonaNo ratings yet
- Knowledge DdeficitDocument2 pagesKnowledge DdeficitnovagaryNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: University of The EastDocument8 pagesCollege of Nursing: University of The EastroblesNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis NCP FINALDocument6 pagesCholelithiasis NCP FINALShreshthi VermaNo ratings yet
- Health Optimizing Physical Education 11 - Module 1: Most Essential Learning CompetencyDocument2 pagesHealth Optimizing Physical Education 11 - Module 1: Most Essential Learning CompetencyGuenn RamosNo ratings yet
- 2 Family Care Plan Health DeficitDocument2 pages2 Family Care Plan Health DeficitMikee Fernandez TangubNo ratings yet
- Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalDocument3 pagesSubjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalNicholas TagleNo ratings yet
- Coa Revised Paper.Document16 pagesCoa Revised Paper.Justine AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Module DisorderDocument9 pagesModule DisorderJustine AlexandraNo ratings yet
- 4 Quiz Group 13: Answer: DDocument5 pages4 Quiz Group 13: Answer: DJustine AlexandraNo ratings yet
- 3 Quiz Group 5:: Ans: CDocument5 pages3 Quiz Group 5:: Ans: CJustine AlexandraNo ratings yet
- NCP1 Impaired Skin... NCP3 Knowledge DeficietDocument6 pagesNCP1 Impaired Skin... NCP3 Knowledge DeficietJustine AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Health and Natural Sciences Central Council Group 4 - MNK Business Questions and AnswersDocument2 pagesHealth and Natural Sciences Central Council Group 4 - MNK Business Questions and AnswersJustine AlexandraNo ratings yet
- UPDATED Drug StudyDocument6 pagesUPDATED Drug StudyJustine AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory and DiagnosticsDocument10 pagesLaboratory and DiagnosticsJustine AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Philippine Colonialism (Limasawa, Magellan)Document4 pagesPhilippine Colonialism (Limasawa, Magellan)Justine AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Philippine Colonialism (Limasawa, Magellan)Document4 pagesPhilippine Colonialism (Limasawa, Magellan)Justine AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Fasting Blood Glucose (FBG) Sugar and Glycosylated Hemoglobin (HbA1C)Document28 pagesFasting Blood Glucose (FBG) Sugar and Glycosylated Hemoglobin (HbA1C)ask1400No ratings yet
- Abilify Dosing GuideDocument2 pagesAbilify Dosing GuidemtassyNo ratings yet
- Urine Glucose TestDocument6 pagesUrine Glucose TestSelim HanNo ratings yet
- Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic StateDocument8 pagesHyperosmolar Hyperglycemic StateEsra AljafferNo ratings yet
- DM 20 ItemsDocument4 pagesDM 20 ItemsDayanara TagaloguinNo ratings yet
- SAP HANA in Healthcare Real-Time Big Data AnalysisDocument25 pagesSAP HANA in Healthcare Real-Time Big Data AnalysisKESHAVA HBNo ratings yet
- Type 2 DM PathoDocument5 pagesType 2 DM PathoPearl JuntillaNo ratings yet
- ManejodiabetesDocument44 pagesManejodiabetesVinicius SepúlvedaNo ratings yet
- Week 10: Drugs Administered For The Treatment of Diabetes MellitusDocument7 pagesWeek 10: Drugs Administered For The Treatment of Diabetes Mellitusashley larsonNo ratings yet
- Practice in Clinical BiochemistryDocument112 pagesPractice in Clinical BiochemistryMohamed Magdi100% (1)
- Pathogenesisof Cardiovasculardiseasein Diabetes: Andrea V. Haas,, Marie E. McdonnellDocument13 pagesPathogenesisof Cardiovasculardiseasein Diabetes: Andrea V. Haas,, Marie E. McdonnellPaulina DiazNo ratings yet
- Steroid Tapering and Supportive Treatment Guidance V1.0 PDFDocument1 pageSteroid Tapering and Supportive Treatment Guidance V1.0 PDFNthutagaol TrusNo ratings yet
- MEHU130 - U2 - T43 - Nefropatia DiabeticaDocument110 pagesMEHU130 - U2 - T43 - Nefropatia DiabeticaStefani AtlleNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology of Diabetes MellitusDocument49 pagesEpidemiology of Diabetes MellitusSantosh K YatnattiNo ratings yet
- Metformin GlucophageDocument1 pageMetformin GlucophageENo ratings yet
- PHARMACARDS GonzagaDocument38 pagesPHARMACARDS GonzagaJay Marie GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Glucose Tolerance Test: Prakash MishraDocument31 pagesGlucose Tolerance Test: Prakash MishraRoyal LibraryNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus in ChildrenDocument29 pagesDiabetes Mellitus in ChildrenwoldemariamNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument5 pagesDiabetes MellitusKeij AranetaNo ratings yet
- Humulin 3070 Ca Pmi CartDocument5 pagesHumulin 3070 Ca Pmi CartJoshua DeonarineNo ratings yet
- The Newborn at Risk Because of Maternal IllnessDocument6 pagesThe Newborn at Risk Because of Maternal IllnessJoanna Bee Rose MagyawiNo ratings yet
- Norditropin Travel Letter0611-000348 1v 2Document18 pagesNorditropin Travel Letter0611-000348 1v 2Hary Kernet MerkapaNo ratings yet
- GDMDocument13 pagesGDMSharmistha DebnathNo ratings yet
- DM Questions ReviewDocument5 pagesDM Questions ReviewJayson Britania MayugaNo ratings yet
- Perioperative NursingDocument32 pagesPerioperative NursingMaria Garcia Pimentel Vanguardia II100% (2)
- Initial Management of Blood Glucose in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - UpToDateDocument24 pagesInitial Management of Blood Glucose in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - UpToDateJessica ArciniegasNo ratings yet
- User Instruction Manual: Blood Glucose Monitoring SystemDocument140 pagesUser Instruction Manual: Blood Glucose Monitoring Systemcinthia olivaNo ratings yet