Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 viewsEALSFinals
EALSFinals
Uploaded by
Hannah EstebarThis document summarizes different types of energy resources and waste management. It discusses renewable and nonrenewable energy resources like fossil fuels, nuclear energy, geothermal energy, hydroelectric energy, wind energy, and solar energy. It also covers different types of waste like solid waste, liquid waste, and gaseous waste. Some key laws around environmental protection and waste management in the Philippines are mentioned. The recycling process and different waste disposal methods are briefly outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Chrome Ore Beneficiation Challenges and Oppurtunities-A Review-Y. Rama Murthy, Sunil Kumar Tripathy, C. Raghu KumarDocument6 pagesChrome Ore Beneficiation Challenges and Oppurtunities-A Review-Y. Rama Murthy, Sunil Kumar Tripathy, C. Raghu KumarSudikondala PurushothamNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 What Is Renewable EnergyDocument4 pagesLesson 1 What Is Renewable Energyangelicamariz.tanNo ratings yet
- Makapasar Sa Sci CutieDocument18 pagesMakapasar Sa Sci CutieChristian MonterroyoNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Definitions - The Carbon Cycle and Energy Security - Edexcel Geography A-LevelDocument3 pagesGlossary of Definitions - The Carbon Cycle and Energy Security - Edexcel Geography A-LevelLeo GreenwoodNo ratings yet
- Renewable Nonrenewable Solar Electricity Wind Geothermal Biomass HydropowerDocument18 pagesRenewable Nonrenewable Solar Electricity Wind Geothermal Biomass HydropowermannuNo ratings yet
- GEOG Nature Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesGEOG Nature Lecture NotesVincent CheungNo ratings yet
- Energy Resources - Non-Renewable Energy ResourcesDocument60 pagesEnergy Resources - Non-Renewable Energy ResourcesMarco Antonio MatanguihanNo ratings yet
- Impacts - Considering The Effects On The: Oleum OilDocument4 pagesImpacts - Considering The Effects On The: Oleum OilKrisha DimailigNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument19 pagesElectricityAdie Alie PumpNo ratings yet
- Fossil Fuel: Non-Renewable Energy Renewable Energy Biomass Hydropower Wind PowerDocument33 pagesFossil Fuel: Non-Renewable Energy Renewable Energy Biomass Hydropower Wind PowerJoyce Ann SosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Energy Resources PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 3 - Energy Resources PDFNicoleNo ratings yet
- Oil & Gas ConsumptionDocument35 pagesOil & Gas ConsumptionSuleiman BaruniNo ratings yet
- Solar, Wind, Water (Hydro), Biomass, and Geothermal.: Energy ResourcesDocument16 pagesSolar, Wind, Water (Hydro), Biomass, and Geothermal.: Energy ResourcesjenduekieNo ratings yet
- Solar, Wind, Water (Hydro), Biomass, and Geothermal.: Energy ResourcesDocument16 pagesSolar, Wind, Water (Hydro), Biomass, and Geothermal.: Energy ResourcesjenduekieNo ratings yet
- Ts Day 5Document20 pagesTs Day 5api-350193855No ratings yet
- Renewable and Non-Renewable Energy and ResourcesDocument7 pagesRenewable and Non-Renewable Energy and ResourcesChristine Rizza Ablao NavarroNo ratings yet
- Sourses of EnergyDocument5 pagesSourses of EnergyArshid WaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Energy ResourcesDocument24 pagesLesson 6 Energy ResourcesDanilo Sare IIINo ratings yet
- Es Chapter 3Document19 pagesEs Chapter 3Itsme lieliesNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Nonrenewable EnergyDocument10 pagesRenewable and Nonrenewable EnergyElaine RoseNo ratings yet
- Goal:: Letter MatrixDocument1 pageGoal:: Letter MatrixPint EraNo ratings yet
- ESN Reporting FinalDocument109 pagesESN Reporting FinalJose Miguel RuizNo ratings yet
- Toyol EnergyDocument1 pageToyol EnergyzinilNo ratings yet
- Earth Science S-WPS OfficeDocument14 pagesEarth Science S-WPS OfficeBai Johaira BenitoNo ratings yet
- Energy Source How Does It Work? Pros Cons Solar PowerDocument13 pagesEnergy Source How Does It Work? Pros Cons Solar Powerapi-272945780No ratings yet
- Renewable ResourcesDocument5 pagesRenewable ResourcessumitrochakrabortiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 and 16 Enviro SciDocument4 pagesChapter 15 and 16 Enviro SciAnonymous oTtlhPNo ratings yet
- JC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: TOPIC: Energy Resources (Part 1)Document11 pagesJC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: TOPIC: Energy Resources (Part 1)Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Worksheet Week 3Document4 pagesScience 9 Worksheet Week 3Jaybie Tejada100% (1)
- Notes TeacherenergyunitDocument15 pagesNotes Teacherenergyunitapi-213591933No ratings yet
- 3 Energy ResourcesDocument21 pages3 Energy ResourcesJessica May DimeNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction To Energy ScienceDocument42 pagesModule 1: Introduction To Energy ScienceNishita Waghmare50% (2)
- Understanding Climate Change GlossaryDocument1 pageUnderstanding Climate Change GlossaryBomdzele Eric JuniorNo ratings yet
- Handout 2.10.f PDFDocument3 pagesHandout 2.10.f PDFToru -No ratings yet
- Harnessing Energy From Different SourcesDocument3 pagesHarnessing Energy From Different SourcesMARVIN HILARIONo ratings yet
- Harnessing Energy From Different SourcesDocument3 pagesHarnessing Energy From Different SourcesMARVIN HILARIONo ratings yet
- Module 3Document15 pagesModule 3SumanpalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Energy SourcesDocument28 pagesChapter 9 Energy SourcesJung HoonNo ratings yet
- Commercial ApplicationsDocument6 pagesCommercial ApplicationsAaryaman Rathi (Yr. 21-23)No ratings yet
- ESPERE Climate EncyclopaediaDocument52 pagesESPERE Climate EncyclopaediaLayla Ratna AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Coal EnergyDocument4 pagesCoal Energytisya95No ratings yet
- ELEC AssignmentDocument5 pagesELEC AssignmentMiko Ong TanNo ratings yet
- 20bscagh065 Siddharth ChakrabortyDocument21 pages20bscagh065 Siddharth ChakrabortySiddharth ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- PhysciDocument27 pagesPhyscisophia lizarondoNo ratings yet
- Wind and Other Renewable Energy SourcesDocument25 pagesWind and Other Renewable Energy SourcesVarun Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Alternative EnergyDocument59 pagesAlternative Energynecessio200No ratings yet
- Name: Class: Subject:: M.Saad Baig Vi-A ScienceDocument6 pagesName: Class: Subject:: M.Saad Baig Vi-A ScienceM Fahad BaigNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Disaster Management: Near-Surface Disposal:-CoalDocument2 pagesNuclear Disaster Management: Near-Surface Disposal:-CoalRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document6 pagesUnit 6Ernie CoachNo ratings yet
- Sources of Energy: Chapter - 14Document9 pagesSources of Energy: Chapter - 14milind dhamaniyaNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension Exercise Subjects: Geography & English Sources of Renewable Energy"Document4 pagesReading Comprehension Exercise Subjects: Geography & English Sources of Renewable Energy"etwinningNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 End of Year Exam CoverageDocument27 pagesGrade 6 End of Year Exam CoverageMouza Al ArimiNo ratings yet
- 1940 - F23 - L19 - Climate Change - 1Document32 pages1940 - F23 - L19 - Climate Change - 1ashwingupta88077No ratings yet
- Week 4 Lecture For StudentsDocument52 pagesWeek 4 Lecture For StudentsKevin De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- What Is Non-Renewable EnergyDocument5 pagesWhat Is Non-Renewable EnergyRida FatimaNo ratings yet
- Energy Sources JustificationDocument13 pagesEnergy Sources Justificationapi-272862164No ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument16 pagesEnergy ResourcesBhaskar TiwariNo ratings yet
- Envi Sci ReportDocument4 pagesEnvi Sci ReportMyra Dionela SorianoNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Sources - Wave, Geothermal and Biomass Energy Edition : Environment Books for Kids | Children's Environment BooksFrom EverandRenewable Energy Sources - Wave, Geothermal and Biomass Energy Edition : Environment Books for Kids | Children's Environment BooksNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Renewable Energy Sources : Environment Books for Kids | Children's Environment BooksFrom EverandAn Introduction to Renewable Energy Sources : Environment Books for Kids | Children's Environment BooksNo ratings yet
- Hydrolithological Investigation For Near-Surface ADocument10 pagesHydrolithological Investigation For Near-Surface AEdilson LourencoNo ratings yet
- L3&4 - Geology and Landscapes WorksheetDocument6 pagesL3&4 - Geology and Landscapes WorksheetCelia KilzieNo ratings yet
- Tugas WorkSheet Webinar ELKPDDocument7 pagesTugas WorkSheet Webinar ELKPDIrma ShintaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Rate of Penetration (ROP) Prediction in Drilling Using Physics-Based and Data-Driven ModelsDocument30 pagesAnalysis of Rate of Penetration (ROP) Prediction in Drilling Using Physics-Based and Data-Driven ModelsChinedu NwabuezeNo ratings yet
- 2017 Val Dufeu From Macro To Micro-Archaeology. An Introduction To Geo-Archaeology and SoilDocument15 pages2017 Val Dufeu From Macro To Micro-Archaeology. An Introduction To Geo-Archaeology and SoilSERGIO GIRALDO ARIASNo ratings yet
- Stratigraphy and Depositional Setting of The LateDocument18 pagesStratigraphy and Depositional Setting of The LateRodrigo Requelme BorjaNo ratings yet
- Origin of Oceans:: When The Super Continent Pangaea Broke IntoDocument28 pagesOrigin of Oceans:: When The Super Continent Pangaea Broke IntoRafia SaeedNo ratings yet
- ISRM Programa FINAL WEBDocument78 pagesISRM Programa FINAL WEBalexis romeroNo ratings yet
- NSCP Seismic Provisions and STAAD Seismic Design LoadsDocument10 pagesNSCP Seismic Provisions and STAAD Seismic Design LoadsJaid HedrianaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Geology: MD Farhad Hasan, Hossam Abuel-Naga, E.-C. LeongDocument10 pagesEngineering Geology: MD Farhad Hasan, Hossam Abuel-Naga, E.-C. LeongFernando Andrés Ortega JiménezNo ratings yet
- Group7 q2w8 Comets and AsteroidsDocument23 pagesGroup7 q2w8 Comets and AsteroidsYassy TalibNo ratings yet
- 1994 - Mahalinga-Iyer-Consolidation and Shear Strength Properties of A Lateritic SoilDocument11 pages1994 - Mahalinga-Iyer-Consolidation and Shear Strength Properties of A Lateritic SoilnsanieleNo ratings yet
- A Further Examination of The Nature of Dispersive Soils in Natal, South Africa Bell 2000Document13 pagesA Further Examination of The Nature of Dispersive Soils in Natal, South Africa Bell 2000Suraj BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- REPORT - Mr. R. BALU MANI, TIRUPURDocument8 pagesREPORT - Mr. R. BALU MANI, TIRUPURkannaNo ratings yet
- La SereneDocument95 pagesLa SereneAllysa RedondoNo ratings yet
- Ural Mountains PDFDocument17 pagesUral Mountains PDFAnonymous BeoWLI3D7QNo ratings yet
- 4 - Espallardo-Ortiz (Geological Maps - PPT)Document30 pages4 - Espallardo-Ortiz (Geological Maps - PPT)Estelle Joy OrtizNo ratings yet
- Budget-of-Work-Earth ScienceDocument3 pagesBudget-of-Work-Earth Sciencejoei ArqueroNo ratings yet
- 17-Core Subject-Science 11-Earth - Life Science-Q1-Module 17Document20 pages17-Core Subject-Science 11-Earth - Life Science-Q1-Module 17BruceNo ratings yet
- McBride 1963Document6 pagesMcBride 1963cobagame terbaruNo ratings yet
- Polar Dinosaurs and Biotas of The Early CreatacceousDocument40 pagesPolar Dinosaurs and Biotas of The Early CreatacceousTayssa MarquesNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes: © Boardworks LTD 2003Document29 pagesVolcanoes: © Boardworks LTD 2003Crisanta GanadoNo ratings yet
- EhsjxhfngDocument32 pagesEhsjxhfngVenus CaringalNo ratings yet
- Chinese Silver Market 2012Document26 pagesChinese Silver Market 2012Nestor Alejandro HillarNo ratings yet
- Case Study of A Drainage BasinDocument8 pagesCase Study of A Drainage BasinGrace KamauNo ratings yet
- Geo AssignmentDocument30 pagesGeo Assignmentaabhash bhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Rock TypesDocument2 pagesRock TypesSahar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Earth's Sixth Mass Extinction EventDocument6 pagesEarth's Sixth Mass Extinction EventLeon RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Cyclic Steam StimulationDocument48 pagesCyclic Steam StimulationMohamed ElkumatiNo ratings yet
EALSFinals
EALSFinals
Uploaded by
Hannah Estebar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesThis document summarizes different types of energy resources and waste management. It discusses renewable and nonrenewable energy resources like fossil fuels, nuclear energy, geothermal energy, hydroelectric energy, wind energy, and solar energy. It also covers different types of waste like solid waste, liquid waste, and gaseous waste. Some key laws around environmental protection and waste management in the Philippines are mentioned. The recycling process and different waste disposal methods are briefly outlined.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes different types of energy resources and waste management. It discusses renewable and nonrenewable energy resources like fossil fuels, nuclear energy, geothermal energy, hydroelectric energy, wind energy, and solar energy. It also covers different types of waste like solid waste, liquid waste, and gaseous waste. Some key laws around environmental protection and waste management in the Philippines are mentioned. The recycling process and different waste disposal methods are briefly outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesEALSFinals
EALSFinals
Uploaded by
Hannah EstebarThis document summarizes different types of energy resources and waste management. It discusses renewable and nonrenewable energy resources like fossil fuels, nuclear energy, geothermal energy, hydroelectric energy, wind energy, and solar energy. It also covers different types of waste like solid waste, liquid waste, and gaseous waste. Some key laws around environmental protection and waste management in the Philippines are mentioned. The recycling process and different waste disposal methods are briefly outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Earth Science: Energy Resources + Soil
Energy - capacity to do work. RA 8749 ALSO KNOWN AS THE PHILIPPINE
Resource - general term referring to any item CLEAN AIR ACT OF 1999.
which is used for a specific purpose. RA 9275 ALSO KNOWN AS THE CLEAN WATER ACT.
Energy resource - anything that can be used RA 9003 OR THE SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT ACT.
as a source of energy. Nuclear reaction - occurs when atoms of one
Renewable resources - can be replenished or species of a chemical element are transformed
regenerated. into atoms of another species.
Nonrenewable resources - cannot be Fission - splitting of heavy atoms into
replenished or regenerated. Resources that lighter atoms.
humans mostly relied on since industrial Fusion - combination of two light atoms to
revolution. form heavier atom.
Examples of industrial revolution: Nuclear energy - the heat the fission and
- Steam engines fusion makes.
- Chimneys Atomic explosion - the event that happens
- Trains when nuclear reaction is not controlled.
Republic Act 9513 - Renewable Act of 2008. Bataan Nuclear Powerplant (BNPP) - built in
Governs the development, utilization, and 1976 at Morong, Bataan.
commercialization of energy resource in the Geothermal energy - one source of energy in
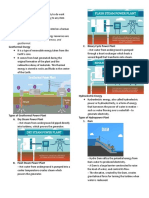
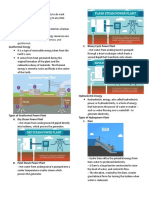
Philippines. the earth’s system is its internal heat.
Fossil fuel - world’s primary energy Geothermal gradients - rate of temperature
resources. Comes from the remains of with depth.
prehistoric plants and animals that died Hydroelectric energy - gravity is essential
million years ago. to hydroelectric energy. An object at rest in
Example of fossil fuels: a higher elevation has a gravitational
- Gas potential energy.
- Petroleum Kinetic energy - when it moves to lower
- Coal elevation, the potential energy transforms to
Coal - formed from the remains of plants that kinetic energy.
once grew in swamps and adjacent forests Hydropower - power elevated from falling
million years ago. water or fast running water.
Peat - precursor of coal containing 50% Penstock - the large pipe or tunnel where
carbon. Transformed into coal at burial depth water flows to reach the turbine.
of 4 to 10km. RA 7156 - Mini Hydro law
Natural gas - mixture of naturally-occurring San Roque Dam - located in Pangasinan. The
light hydrocarbons composed mostly of methane. largest hydroelectric dam in the Philippines
Forms from the remains of ancient with the height of 200 meters.
microorganisms, as well as plant and animal Ocean powers - ocean water has a vast
matter. potential to generate energy by using other
Hydraulic fracturing - also called fracking. sources of power.
It is the drilling process to get natural gas. Types of ocean power:
Petroleum - comes from the Latin word petra Tidal barrages
that means rock. Naturally-occurring liquid Tidal fences
composed of complex hydrocarbons, and is Tidal turbines
found in geological formation underneath the Wind energy - is the movement of air caused
Earth’s crust. by differences in atmospheric pressure.
Petroleum - a fossil fuel derived from large Air - static. The gaseous mixture, water
quantities of microscopic aquatic organisms vapour and dust particles in our atmosphere,
such as algae and planktons. which we breath.
Kerogen - waxy material that organic matters Wind - when the air moves. Horizontal motion
turn into when faced with increasing pressure of air, due to the pressure difference
and temperature. between to places.
Oil window - the deeper, the better the Winds with strengths and speed:
petroleum quality. Petroleum forms within the Gust - short-duration, high-speed
specific depth, pressure, and temperature
Breeze - low wind
range.
Gale - High-speed, long-term
Thermal cracking - process where the oil is
transformed to natural gas because of the Storm/Hurricane - high-speed with water
increase of temperature in oil window. Mechanical power - can be produced from wind
Environmental Laws: flows or air current.
Wind farm - collection of individual wind
RA 9513 ALSO KNOWN AS THE RENEWABLE
turbines. Built onshore in flat areas,
ENERGY ACT OF 2008.
usually near coastlines.
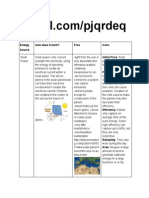
Solar energy - energy coming from the sun.
Earth Science: Energy Resources + Soil
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) - involves Agricultural waste (liquid) - raising hog,
mirror, lenses, and tracking system that livestock & post harvest waste.
focuses light into a receiver and generates Domestic waste - wastes from bathing, laundry,
heat. cleaning, washing, & other kitchen cooking.
Photovoltaic - also known as solar cell. Industrial wastewater - food, dairy, pulp,
Refers to the direct conversion of light into paper, & textile industry carries organic
electricity at the atomic level. matters.
Wafer - solar cells consists of semiconductor Sewage - septic tanks
materials (usually silicon) made into sheets Effects of liquid waste:
called wafer. Water pollution
Three types of Human waste: Depletion of oxygen in water affects
1. Solid waste fishes.
2. Liquid waste Can cause sickness/death
3. Gas waste Gaseous waste - affects air pollution.
Solid waste - all discarded household, Acid rain - corrodes cement and metal.
commercial waste, nonhazardous institutional Clean Air Act of 1999 - management of gaseous
and industrial wastes, street sweeping, waste.
construction debris, agricultural waste, & Universal Recycle Symbol - promotes proper
other nontoxic/nonhazardous solid waste. waste disposal.
RA 9003 - Ecological Solid Waste Management Gary Anderson - design the universal recycle
Act of 2000 symbol
Effects of solid waste: Mobius strip - unending single-sided looped
Land pollution surface
Affect plant growth Earth Hour - turning off of lights for 1 hour.
Serve as breeding place for disease- Volcanism - A phenomena which molten rocks
carrying animal (magma) are erupted from the Earth’s interior
Cause aesthetic degradation of the onto the surface.
environment Volcano - series of vents on Earth’s surface.
Lower the quality of the land Vent - where magma, ash, & gases are released.
Ways to manage solid waste: Crater - mouth on the vent.
Reduce - limiting the amount of waste. Caldera - large cauldron-like hollow that
Reuse - recovery of materials with the forms shortly after the emptying of a magma
intention of reusing it. chamber in a volcanic eruption.
Recycle - using a material to another Apolaki - a volcanic crater with a diameter
purpose. of 150 kilometers (93 mi), making it the
Waste reduction: world's largest caldera. Discovered by Jenny
Manufacturing products with less Anne Barretto.
packaging. Active volcano - 600-1000 years
Bringing reusable bag for packaging. Dormant volcano - 1000 years inactive but has
the possibility to erupt.
Choosing reusable products such as cloth
Extinct volcano - 10 000 years and are unlike
napkins.
to erupt.
Reusing plastic and glass containers.
PHIVOLCS - Philippine Institute of
Backyard composting. Volcanology and Seismology or Surian ng
Donating unused items. Pilipinas sa Bulkanolohiya at Sismolohiya.
Recycling Process: Pacific Ring of Fire - 70% of volcanic
Segregation - separation activity came from here.
Collection - removal of solid waste from the Convergent volcano - As two tectonic plates
source. collide, the slabs of rocks descend into the
Production of new product - original product mantle. The heat generated by this mechanism
loses identity. facilitates the formation of magma.
Waste disposal methods: Andesitic - magma generated at the subduction
1. Mulch & Compost - simplest method zone.
2. Landfill - cheapest and most convenient. Hotspots - These are columns of mantle
3. Incineration - waste material is turned materials that begin to melt as they rise to
into gas. lower pressure and shallower depths.
Incinerator - machine used in incineration Volcanic Materials:
Composting - method of allowing the natural Gases - Volcanic eruption emits a variety of
process of decomposition. gases.
Compost - mucus-like material. Lava – It refers to magma that flows out to
RA 9512 - National Environment Awareness and the earth’s surface.
Education Act of 2008 Viscosity – resistance to flow.
Liquid waste - wastes in water
Earth Science: Energy Resources + Soil
Pyroclastic – (tephra) Solid particles thrown Earthquake Intensity Scale - developed by the
out in volcanic eruption. Philippine Institute of Volcanology and
Volcanic blocks – large angular volcanic Seismology, is used in reporting earthquake
rocks like pumice that have sizes greater intensities.
than 64 mm in diameter. Largest earthquake - Celebes Sea (Magnitude
Lapilli – medium-sized particles between 2 mm 8.3)
and 64 mm in size. Deadliest earthquake - Moro Gulf (Magnitude 8)
Volcanic ash – consists of small particles
less than 2 mm in diameter.
Volcanic dust – consists of very small
particles that is less than 0.25 mm in
diameter.
Lahar - mixture of ash and water.
Nuee ardantes - (Glowing cloud) highly
destructive, fast-moving, incandescent mass
of gas-enveloped particles that is associated
with certain types of volcanic eruptions.
Ash-flow tuff - An ash flow releases most of
its gases when it stops flowing. It leaves
behind a mixture of volcanic ash and rock
fragments.
Earthquake - vibration on the surface of
Earth resulting from the sudden release of
energy.
Elastic rebound theory - first theory to
satisfactorily explain earthquakes.
Fault - crack on earth’s crust.
Fracture - forms in rocks when earthquake
occur.
Normal fault - moves down.
Reverse fault - goes up.
Strike-slip fault - horizontal direction.
Focus/Hypocenter - where rock ruptures.
Epicenter - point directly above focus.
Seismic waves - waves of energy that travel
through the Earth's layers, and are a result
of earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, magma
movement, large landslides and large man-made
explosions that give out low-frequency
acoustic energy.
Active fault - where we expect displacement
to occur.
Inactive fault - structures we identify but
do not expect displacement.
Body waves - within the interior of the earth.
Primary waves - back & forth in parallel
direction.
Secondary waves - back & forth in
perpendicular direction.
Surface waves - travels along the earth’s
surface.
Rayleigh waves - ripple up and down.
Love waves - snake like movement.
Seismograph - detects the movement of ground
from earthquake.
Seismogram - records of seismograph.
Magnitude - number of size that indicate the
relative size of energy released during an
earthquake.
Intensity - amount of damage brought by an
earthquake.
Mercalli Intensity Scale - Giuseppe Mercalli.
Used to record the intensity of an earthquake.
You might also like
- Chrome Ore Beneficiation Challenges and Oppurtunities-A Review-Y. Rama Murthy, Sunil Kumar Tripathy, C. Raghu KumarDocument6 pagesChrome Ore Beneficiation Challenges and Oppurtunities-A Review-Y. Rama Murthy, Sunil Kumar Tripathy, C. Raghu KumarSudikondala PurushothamNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 What Is Renewable EnergyDocument4 pagesLesson 1 What Is Renewable Energyangelicamariz.tanNo ratings yet
- Makapasar Sa Sci CutieDocument18 pagesMakapasar Sa Sci CutieChristian MonterroyoNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Definitions - The Carbon Cycle and Energy Security - Edexcel Geography A-LevelDocument3 pagesGlossary of Definitions - The Carbon Cycle and Energy Security - Edexcel Geography A-LevelLeo GreenwoodNo ratings yet
- Renewable Nonrenewable Solar Electricity Wind Geothermal Biomass HydropowerDocument18 pagesRenewable Nonrenewable Solar Electricity Wind Geothermal Biomass HydropowermannuNo ratings yet
- GEOG Nature Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesGEOG Nature Lecture NotesVincent CheungNo ratings yet
- Energy Resources - Non-Renewable Energy ResourcesDocument60 pagesEnergy Resources - Non-Renewable Energy ResourcesMarco Antonio MatanguihanNo ratings yet
- Impacts - Considering The Effects On The: Oleum OilDocument4 pagesImpacts - Considering The Effects On The: Oleum OilKrisha DimailigNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument19 pagesElectricityAdie Alie PumpNo ratings yet
- Fossil Fuel: Non-Renewable Energy Renewable Energy Biomass Hydropower Wind PowerDocument33 pagesFossil Fuel: Non-Renewable Energy Renewable Energy Biomass Hydropower Wind PowerJoyce Ann SosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Energy Resources PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 3 - Energy Resources PDFNicoleNo ratings yet
- Oil & Gas ConsumptionDocument35 pagesOil & Gas ConsumptionSuleiman BaruniNo ratings yet
- Solar, Wind, Water (Hydro), Biomass, and Geothermal.: Energy ResourcesDocument16 pagesSolar, Wind, Water (Hydro), Biomass, and Geothermal.: Energy ResourcesjenduekieNo ratings yet
- Solar, Wind, Water (Hydro), Biomass, and Geothermal.: Energy ResourcesDocument16 pagesSolar, Wind, Water (Hydro), Biomass, and Geothermal.: Energy ResourcesjenduekieNo ratings yet
- Ts Day 5Document20 pagesTs Day 5api-350193855No ratings yet
- Renewable and Non-Renewable Energy and ResourcesDocument7 pagesRenewable and Non-Renewable Energy and ResourcesChristine Rizza Ablao NavarroNo ratings yet
- Sourses of EnergyDocument5 pagesSourses of EnergyArshid WaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Energy ResourcesDocument24 pagesLesson 6 Energy ResourcesDanilo Sare IIINo ratings yet
- Es Chapter 3Document19 pagesEs Chapter 3Itsme lieliesNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Nonrenewable EnergyDocument10 pagesRenewable and Nonrenewable EnergyElaine RoseNo ratings yet
- Goal:: Letter MatrixDocument1 pageGoal:: Letter MatrixPint EraNo ratings yet
- ESN Reporting FinalDocument109 pagesESN Reporting FinalJose Miguel RuizNo ratings yet
- Toyol EnergyDocument1 pageToyol EnergyzinilNo ratings yet
- Earth Science S-WPS OfficeDocument14 pagesEarth Science S-WPS OfficeBai Johaira BenitoNo ratings yet
- Energy Source How Does It Work? Pros Cons Solar PowerDocument13 pagesEnergy Source How Does It Work? Pros Cons Solar Powerapi-272945780No ratings yet
- Renewable ResourcesDocument5 pagesRenewable ResourcessumitrochakrabortiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 and 16 Enviro SciDocument4 pagesChapter 15 and 16 Enviro SciAnonymous oTtlhPNo ratings yet
- JC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: TOPIC: Energy Resources (Part 1)Document11 pagesJC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: TOPIC: Energy Resources (Part 1)Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Worksheet Week 3Document4 pagesScience 9 Worksheet Week 3Jaybie Tejada100% (1)
- Notes TeacherenergyunitDocument15 pagesNotes Teacherenergyunitapi-213591933No ratings yet
- 3 Energy ResourcesDocument21 pages3 Energy ResourcesJessica May DimeNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction To Energy ScienceDocument42 pagesModule 1: Introduction To Energy ScienceNishita Waghmare50% (2)
- Understanding Climate Change GlossaryDocument1 pageUnderstanding Climate Change GlossaryBomdzele Eric JuniorNo ratings yet
- Handout 2.10.f PDFDocument3 pagesHandout 2.10.f PDFToru -No ratings yet
- Harnessing Energy From Different SourcesDocument3 pagesHarnessing Energy From Different SourcesMARVIN HILARIONo ratings yet
- Harnessing Energy From Different SourcesDocument3 pagesHarnessing Energy From Different SourcesMARVIN HILARIONo ratings yet
- Module 3Document15 pagesModule 3SumanpalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Energy SourcesDocument28 pagesChapter 9 Energy SourcesJung HoonNo ratings yet
- Commercial ApplicationsDocument6 pagesCommercial ApplicationsAaryaman Rathi (Yr. 21-23)No ratings yet
- ESPERE Climate EncyclopaediaDocument52 pagesESPERE Climate EncyclopaediaLayla Ratna AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Coal EnergyDocument4 pagesCoal Energytisya95No ratings yet
- ELEC AssignmentDocument5 pagesELEC AssignmentMiko Ong TanNo ratings yet
- 20bscagh065 Siddharth ChakrabortyDocument21 pages20bscagh065 Siddharth ChakrabortySiddharth ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- PhysciDocument27 pagesPhyscisophia lizarondoNo ratings yet
- Wind and Other Renewable Energy SourcesDocument25 pagesWind and Other Renewable Energy SourcesVarun Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Alternative EnergyDocument59 pagesAlternative Energynecessio200No ratings yet
- Name: Class: Subject:: M.Saad Baig Vi-A ScienceDocument6 pagesName: Class: Subject:: M.Saad Baig Vi-A ScienceM Fahad BaigNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Disaster Management: Near-Surface Disposal:-CoalDocument2 pagesNuclear Disaster Management: Near-Surface Disposal:-CoalRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document6 pagesUnit 6Ernie CoachNo ratings yet
- Sources of Energy: Chapter - 14Document9 pagesSources of Energy: Chapter - 14milind dhamaniyaNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension Exercise Subjects: Geography & English Sources of Renewable Energy"Document4 pagesReading Comprehension Exercise Subjects: Geography & English Sources of Renewable Energy"etwinningNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 End of Year Exam CoverageDocument27 pagesGrade 6 End of Year Exam CoverageMouza Al ArimiNo ratings yet
- 1940 - F23 - L19 - Climate Change - 1Document32 pages1940 - F23 - L19 - Climate Change - 1ashwingupta88077No ratings yet
- Week 4 Lecture For StudentsDocument52 pagesWeek 4 Lecture For StudentsKevin De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- What Is Non-Renewable EnergyDocument5 pagesWhat Is Non-Renewable EnergyRida FatimaNo ratings yet
- Energy Sources JustificationDocument13 pagesEnergy Sources Justificationapi-272862164No ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument16 pagesEnergy ResourcesBhaskar TiwariNo ratings yet
- Envi Sci ReportDocument4 pagesEnvi Sci ReportMyra Dionela SorianoNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Sources - Wave, Geothermal and Biomass Energy Edition : Environment Books for Kids | Children's Environment BooksFrom EverandRenewable Energy Sources - Wave, Geothermal and Biomass Energy Edition : Environment Books for Kids | Children's Environment BooksNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Renewable Energy Sources : Environment Books for Kids | Children's Environment BooksFrom EverandAn Introduction to Renewable Energy Sources : Environment Books for Kids | Children's Environment BooksNo ratings yet
- Hydrolithological Investigation For Near-Surface ADocument10 pagesHydrolithological Investigation For Near-Surface AEdilson LourencoNo ratings yet
- L3&4 - Geology and Landscapes WorksheetDocument6 pagesL3&4 - Geology and Landscapes WorksheetCelia KilzieNo ratings yet
- Tugas WorkSheet Webinar ELKPDDocument7 pagesTugas WorkSheet Webinar ELKPDIrma ShintaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Rate of Penetration (ROP) Prediction in Drilling Using Physics-Based and Data-Driven ModelsDocument30 pagesAnalysis of Rate of Penetration (ROP) Prediction in Drilling Using Physics-Based and Data-Driven ModelsChinedu NwabuezeNo ratings yet
- 2017 Val Dufeu From Macro To Micro-Archaeology. An Introduction To Geo-Archaeology and SoilDocument15 pages2017 Val Dufeu From Macro To Micro-Archaeology. An Introduction To Geo-Archaeology and SoilSERGIO GIRALDO ARIASNo ratings yet
- Stratigraphy and Depositional Setting of The LateDocument18 pagesStratigraphy and Depositional Setting of The LateRodrigo Requelme BorjaNo ratings yet
- Origin of Oceans:: When The Super Continent Pangaea Broke IntoDocument28 pagesOrigin of Oceans:: When The Super Continent Pangaea Broke IntoRafia SaeedNo ratings yet
- ISRM Programa FINAL WEBDocument78 pagesISRM Programa FINAL WEBalexis romeroNo ratings yet
- NSCP Seismic Provisions and STAAD Seismic Design LoadsDocument10 pagesNSCP Seismic Provisions and STAAD Seismic Design LoadsJaid HedrianaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Geology: MD Farhad Hasan, Hossam Abuel-Naga, E.-C. LeongDocument10 pagesEngineering Geology: MD Farhad Hasan, Hossam Abuel-Naga, E.-C. LeongFernando Andrés Ortega JiménezNo ratings yet
- Group7 q2w8 Comets and AsteroidsDocument23 pagesGroup7 q2w8 Comets and AsteroidsYassy TalibNo ratings yet
- 1994 - Mahalinga-Iyer-Consolidation and Shear Strength Properties of A Lateritic SoilDocument11 pages1994 - Mahalinga-Iyer-Consolidation and Shear Strength Properties of A Lateritic SoilnsanieleNo ratings yet
- A Further Examination of The Nature of Dispersive Soils in Natal, South Africa Bell 2000Document13 pagesA Further Examination of The Nature of Dispersive Soils in Natal, South Africa Bell 2000Suraj BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- REPORT - Mr. R. BALU MANI, TIRUPURDocument8 pagesREPORT - Mr. R. BALU MANI, TIRUPURkannaNo ratings yet
- La SereneDocument95 pagesLa SereneAllysa RedondoNo ratings yet
- Ural Mountains PDFDocument17 pagesUral Mountains PDFAnonymous BeoWLI3D7QNo ratings yet
- 4 - Espallardo-Ortiz (Geological Maps - PPT)Document30 pages4 - Espallardo-Ortiz (Geological Maps - PPT)Estelle Joy OrtizNo ratings yet
- Budget-of-Work-Earth ScienceDocument3 pagesBudget-of-Work-Earth Sciencejoei ArqueroNo ratings yet
- 17-Core Subject-Science 11-Earth - Life Science-Q1-Module 17Document20 pages17-Core Subject-Science 11-Earth - Life Science-Q1-Module 17BruceNo ratings yet
- McBride 1963Document6 pagesMcBride 1963cobagame terbaruNo ratings yet
- Polar Dinosaurs and Biotas of The Early CreatacceousDocument40 pagesPolar Dinosaurs and Biotas of The Early CreatacceousTayssa MarquesNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes: © Boardworks LTD 2003Document29 pagesVolcanoes: © Boardworks LTD 2003Crisanta GanadoNo ratings yet
- EhsjxhfngDocument32 pagesEhsjxhfngVenus CaringalNo ratings yet
- Chinese Silver Market 2012Document26 pagesChinese Silver Market 2012Nestor Alejandro HillarNo ratings yet
- Case Study of A Drainage BasinDocument8 pagesCase Study of A Drainage BasinGrace KamauNo ratings yet
- Geo AssignmentDocument30 pagesGeo Assignmentaabhash bhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Rock TypesDocument2 pagesRock TypesSahar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Earth's Sixth Mass Extinction EventDocument6 pagesEarth's Sixth Mass Extinction EventLeon RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Cyclic Steam StimulationDocument48 pagesCyclic Steam StimulationMohamed ElkumatiNo ratings yet