Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Automata Theory
Automata Theory
Uploaded by
Kanwal UbaidaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Module 1 - PART 2Document63 pagesModule 1 - PART 2Hema ReddyNo ratings yet
- HW1 Solutions 2017 Spring PDFDocument6 pagesHW1 Solutions 2017 Spring PDFApoorva PanchalNo ratings yet
- Finite Automata: Reading: Chapter 2Document48 pagesFinite Automata: Reading: Chapter 2Pro HammadNo ratings yet
- FiniteAutomata AnimDocument41 pagesFiniteAutomata Animmavoho1719No ratings yet
- Pset2 SolutionsDocument5 pagesPset2 Solutionsaniketgupta3001No ratings yet
- Finite Automata With - TransitionsDocument5 pagesFinite Automata With - TransitionsatulNo ratings yet
- MG 02 1 FiniteAutomata AnimDocument12 pagesMG 02 1 FiniteAutomata AnimSanny Era Eliza SiallaganNo ratings yet
- COL352 hw1Document4 pagesCOL352 hw1pratik pranavNo ratings yet
- Formal Languages, Automata and ComputabilityDocument59 pagesFormal Languages, Automata and ComputabilityMahnoor KhandwaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Theory of Computation: Part II: Computability TheoryDocument42 pagesIntroduction To The Theory of Computation: Part II: Computability Theoryocy12100% (1)
- Lecture 2 - 3 - First Order ResponsesDocument31 pagesLecture 2 - 3 - First Order ResponsesLiyana HalimNo ratings yet
- 3 FiniteAutomata AnimDocument39 pages3 FiniteAutomata AnimRajdeep RandhawaNo ratings yet
- Non-Deterministic Finite AutomataDocument36 pagesNon-Deterministic Finite AutomataS.K. RoyNo ratings yet
- Formal Languages, Automata, and ComputabilityDocument27 pagesFormal Languages, Automata, and ComputabilityNehru VeerabatheranNo ratings yet
- Formal Definition Equivalence With Finite Automaton Generalized Nondeterministic Finite AutomatonDocument14 pagesFormal Definition Equivalence With Finite Automaton Generalized Nondeterministic Finite AutomatonShabab Israk PiasNo ratings yet
- Regular ExpressionDocument14 pagesRegular ExpressionMD Robiul Awal ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform OdeDocument24 pagesLaplace Transform OdeUmer KhanNo ratings yet
- RMI Vol17 (2001)Document652 pagesRMI Vol17 (2001)lucivandolopesNo ratings yet
- Compiler Design CA1Document10 pagesCompiler Design CA1Debasis GaraiNo ratings yet
- Establish Indices For FFT Operations: Shortlin - MCD 1 1/23/2011 3:56 PMDocument8 pagesEstablish Indices For FFT Operations: Shortlin - MCD 1 1/23/2011 3:56 PMSharifNo ratings yet
- DFA Construction IdeasDocument4 pagesDFA Construction IdeasInderpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit V (TM) - Part1nDocument24 pagesUnit V (TM) - Part1nStuti GuptaNo ratings yet
- APP Unit 5Document86 pagesAPP Unit 5anirudh3369No ratings yet
- Appndx D Mae175Document26 pagesAppndx D Mae175JAyNo ratings yet
- Study Note of Theory of ComputationDocument21 pagesStudy Note of Theory of Computationarik_cjNo ratings yet
- 09 Z TransformDocument34 pages09 Z TransformBhaskarNo ratings yet
- Theory of Automata6&7Document39 pagesTheory of Automata6&7zawad aliNo ratings yet
- Finite Automata Formal Languages: Operations On SentencesDocument20 pagesFinite Automata Formal Languages: Operations On SentencesBhaskar Rao PNo ratings yet
- Notation To Specify A Language: Theory of Computation - Regular ExpressionsDocument23 pagesNotation To Specify A Language: Theory of Computation - Regular ExpressionsHimañshu BhattNo ratings yet
- Unit-Ii Regular Expressions and Languages DefinitionDocument34 pagesUnit-Ii Regular Expressions and Languages DefinitionGanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chap 3Document39 pagesChap 3yeabsira gashawNo ratings yet
- Nfa To ReDocument5 pagesNfa To Reprateek lilhareNo ratings yet
- Finite Autometa PDFDocument40 pagesFinite Autometa PDFsahuashishcsNo ratings yet
- Tcom005n PDFDocument41 pagesTcom005n PDFS.K. RoyNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 FiniteAutomataDocument39 pagesUNIT 1 FiniteAutomataVathyasamNo ratings yet
- Formal LanguagesDocument47 pagesFormal LanguagesSourav RoyNo ratings yet
- CS 321 HW2Document5 pagesCS 321 HW2Daniel GohNo ratings yet
- Laplace and Inverse TransformsDocument40 pagesLaplace and Inverse TransformsDheerajOmprasadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 First Order SystemsDocument26 pagesLecture 3 First Order SystemsZena wNo ratings yet
- What It IsDocument2 pagesWhat It IsABHISHEK KUMARNo ratings yet
- 20.07. mkg1 Automata PDFDocument53 pages20.07. mkg1 Automata PDFmukesh guptaNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Computation Part IIDocument113 pagesThe Theory of Computation Part IImjn0107No ratings yet
- Flat Module 5Document11 pagesFlat Module 5Priya RanaNo ratings yet
- Deterministic Finite Automata (DFA)Document19 pagesDeterministic Finite Automata (DFA)xigon53558No ratings yet
- 02 FiniteAutomata PDFDocument7 pages02 FiniteAutomata PDFApoorva NaikNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform Converges Fourier TransformDocument14 pagesLaplace Transform Converges Fourier TransformSupriyaNo ratings yet
- PLL Technique 2Document25 pagesPLL Technique 2Preeti MishraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document45 pagesChapter 4Mohammad AliffuddinNo ratings yet
- Formal Languages - Lec6 - P1Document23 pagesFormal Languages - Lec6 - P1ahmed.teka446No ratings yet
- 01 Nfa To RegDocument5 pages01 Nfa To Regmariamelabd42No ratings yet
- Laplace HadyDocument52 pagesLaplace HadyT ANo ratings yet
- Lec 03Document45 pagesLec 03Cyrus LiNo ratings yet
- Turning Machine: Unit-VDocument23 pagesTurning Machine: Unit-VVenkata Rao SNo ratings yet
- Theory of Automata NotesDocument29 pagesTheory of Automata NotesMuhammad Arslan RasoolNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform Solution of ODEsDocument2 pagesLaplace Transform Solution of ODEsbedodsonNo ratings yet
- Laplace HadyDocument50 pagesLaplace HadyIhwan FauziNo ratings yet
- 3 DfaDocument23 pages3 DfaHassan AlsayedNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Summary 1 Topic: Review Conditional Zero, First and Second: General ExplanationDocument6 pagesSummary 1 Topic: Review Conditional Zero, First and Second: General ExplanationJaime G. MendozaNo ratings yet
- Direct & Indirect SpeechDocument7 pagesDirect & Indirect SpeechDebela AbidhuNo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument5 pagesEnglish GrammarRalucaNo ratings yet
- EMD CARMELTE SCHOOL FOUNDATION INC 2nd PrelimDocument4 pagesEMD CARMELTE SCHOOL FOUNDATION INC 2nd PrelimNikolai NoronNo ratings yet
- Second Language Acquisition HandoutsDocument10 pagesSecond Language Acquisition HandoutsmounaNo ratings yet
- Mandarin For All-1Document7 pagesMandarin For All-1aleeya syahirahNo ratings yet
- Speech Communities and Languages in HK: En3591 Hong Kong Language and SocietyDocument42 pagesSpeech Communities and Languages in HK: En3591 Hong Kong Language and SocietyMuqdas hayatNo ratings yet
- Year 4 J Comp and Spelling Third Term Examination J 2023Document7 pagesYear 4 J Comp and Spelling Third Term Examination J 2023finney gabrielsNo ratings yet
- Khroskyabs LanguageDocument14 pagesKhroskyabs LanguageRicardoNo ratings yet
- Animal-Onomatopoeia-Worksheet MR BrownDocument1 pageAnimal-Onomatopoeia-Worksheet MR BrownKatjaNo ratings yet
- O FFNTST: ShouldDocument2 pagesO FFNTST: ShouldmielpopsglekNo ratings yet
- X SeralDocument7 pagesX SeralOana-Violeta Si Cornel SelaruNo ratings yet
- EAPP Module 1 Week 1 - L. ArenilloDocument9 pagesEAPP Module 1 Week 1 - L. ArenilloLeigh Afable100% (1)
- Writing 3Document8 pagesWriting 3Оля ГурьяноваNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Iii Schools Division of Tarlac ProvinceDocument33 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Iii Schools Division of Tarlac Provincebaldo yellow4No ratings yet
- Simple Past Tense BookletDocument7 pagesSimple Past Tense BookletAfifah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Types of Pronouns Personal Object Possessive Adjectives Possessive Pronouns Reflexive PronounsDocument3 pagesTypes of Pronouns Personal Object Possessive Adjectives Possessive Pronouns Reflexive PronounsFano UwUNo ratings yet
- Stylistics 2 A Short History of StylisticsDocument31 pagesStylistics 2 A Short History of StylisticsOtmane en nasiriNo ratings yet
- Presentation BAHASA INGGRISDocument12 pagesPresentation BAHASA INGGRISCok AmiNo ratings yet
- Random - Definition of Random by Merriam-Webster PDFDocument11 pagesRandom - Definition of Random by Merriam-Webster PDFinsomnium1227No ratings yet
- 218.764 - 2019 Assignment 1Document2 pages218.764 - 2019 Assignment 1Suresh GovindarajNo ratings yet
- Sílabos - Ingles III-ISAMDocument4 pagesSílabos - Ingles III-ISAMtrafaelNo ratings yet
- Reduced Participle Clauses Grammar Drills Grammar Guides 130210Document2 pagesReduced Participle Clauses Grammar Drills Grammar Guides 130210yusacoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - MotivationDocument3 pagesLesson Plan - Motivationapi-644318070No ratings yet
- 01 Reported StatementsDocument6 pages01 Reported StatementsVleyZ1XNo ratings yet
- Syntax: Dependent/Subordinate ClausesDocument4 pagesSyntax: Dependent/Subordinate ClausesLe PhucNo ratings yet
- Linguistics, Penguin: Module 2 Unit 2 Error Analysis 1Document7 pagesLinguistics, Penguin: Module 2 Unit 2 Error Analysis 1Dedeh KurniasihNo ratings yet
- Gimas Olympiad 2054Document13 pagesGimas Olympiad 2054rqvlog13No ratings yet
- English Phonetics and PhonologyDocument24 pagesEnglish Phonetics and PhonologyMirela MoiseNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 English Most Essential Learning Competencies MELCsDocument4 pagesGrade 5 English Most Essential Learning Competencies MELCsTeresa saiconNo ratings yet
Automata Theory
Automata Theory
Uploaded by
Kanwal UbaidaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Automata Theory
Automata Theory
Uploaded by
Kanwal UbaidaCopyright:
Available Formats
Automata Cheat Sheet
by Vipera via cheatography.com/128346/cs/25093/
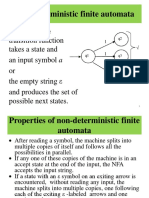
DFA (Deterministic Finite Automaton) NFA to DFA Conversion (cont) Regular Expressions
Automaton Repres‐ M=(Q,Σ,δ,q0,F) 3. Set every DFA state as accepting if it L(r1+r2) = L(r1) ∪ L(r2)
entation contains an accepting state from the NFA L(r1•r2) = L(r1)L(r2)
Q: Set of states {q0,q1,q2} The language for the NFA (M) and DFA (M') L(r1*) = (L(r1))*
Σ: input alphabet {a,b} & ε ∉ Σ are equivalent
L(a) = {a}
L(M)=L(M')
δ: transition δ(q,x)=q'
Precedence: * → + → • → +
function
Properties of Regex
q0: initial state NFA to Regular Language
L1 ∪ L2 Initial state has two ε transi‐
F: set of accepting {q2} 1. Transform each transition into regex (e.g.
tions, one to L1 and one to
states (a,b) is a+b
L2
Language of L(M)={ w∈Σ* : δ* 2. Remove each state one by one, until you
L1L2 L1 accept state tranitions
Automaton (q0,w)∈F} are left with the initial and accepting state
(ε) to L2 initial state
Languages are regular if a DFA exists for 3. Resulting regular expression: r = r1*
L1* New initial state transitions
that language. r2(r4+r3r1*r2)* where:
to L1 initial state. New
DFA: Each state has one transition for r1: initial → initial
accept state transitions (ε)
evrey alphabet r2: initial → accepting
from L1 accept state. Initial
to accept state transition r3: accepting → initial
NFA (Non-deterministic Finite r4: accepting → accepting
transitions (ε) and vice
Automaton)
versa.
Formal Definition M=(Q,Σ,Δ,S,F) Proving Regularity with Pumping
L1R Reverse all transitions.
Lemma
Q: Set of states {q0,q1,q2} (reverse) Make initial state accepting
Σ: input alphabet {a,b} state and vice versa. Prove than an infinite language L is not
regular:
Δ: transition Δ(q,x)={q1,q2,...} !(L1) Accepting states become
function (include ε) Complement non-accepting and vice 1. Assume L is regular
versa 2. The pumping lemma should hold for L
S: initial states {q0}
L1 ∩ L2 !( !(L1) ∪ !(L2) ) 3. Use the pumping lemma to obtain a
F: set of accepting {q2}
states P.S. To turn multiple states to one accept contradiction:
Language of L(M) = {w1,w2,...,wn} state in an NFA, just add a new accept a. Let m be the critical length for L
Automaton state, and add transition to the old accept b. Choose a particular string w∈L which
states with language ε. satisfies the length condition |w|≥m
NFA: Each state can have different
transition with the same language output c. Write w=xyz
Intersection DFA1 ∩ DFA2
d. Show that w'=xyi z∉L for some i≠1
NFA to DFA Conversion Transitions DFA M: (q1,p1)→a→‐
M1: (q2,p2)
1. Set initial state of NFA to initial state of
q1→a→q2
DFA
M2:
2. Take the states in the DFA, and compute
p1→a→p2
in the NFA what the union Δ of those states
Initial State DFA M: (q0,p0)
for each letter in the alphabet and add them
M1: q0
as new states in the DFA.
For example if (q0,a) takes you to {q1,q2} M2: p0
add a state {q1,q2}. If there isn't one, the Accept State DFA M: (qi,pj) , (qi,pk)
add state null M1: qi
M2: pj,pk
By Vipera Published 11th December, 2020. Sponsored by CrosswordCheats.com
cheatography.com/vipera/ Last updated 12th December, 2020. Learn to solve cryptic crosswords!
Page 1 of 1. http://crosswordcheats.com
You might also like
- Module 1 - PART 2Document63 pagesModule 1 - PART 2Hema ReddyNo ratings yet
- HW1 Solutions 2017 Spring PDFDocument6 pagesHW1 Solutions 2017 Spring PDFApoorva PanchalNo ratings yet
- Finite Automata: Reading: Chapter 2Document48 pagesFinite Automata: Reading: Chapter 2Pro HammadNo ratings yet
- FiniteAutomata AnimDocument41 pagesFiniteAutomata Animmavoho1719No ratings yet
- Pset2 SolutionsDocument5 pagesPset2 Solutionsaniketgupta3001No ratings yet
- Finite Automata With - TransitionsDocument5 pagesFinite Automata With - TransitionsatulNo ratings yet
- MG 02 1 FiniteAutomata AnimDocument12 pagesMG 02 1 FiniteAutomata AnimSanny Era Eliza SiallaganNo ratings yet
- COL352 hw1Document4 pagesCOL352 hw1pratik pranavNo ratings yet
- Formal Languages, Automata and ComputabilityDocument59 pagesFormal Languages, Automata and ComputabilityMahnoor KhandwaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Theory of Computation: Part II: Computability TheoryDocument42 pagesIntroduction To The Theory of Computation: Part II: Computability Theoryocy12100% (1)
- Lecture 2 - 3 - First Order ResponsesDocument31 pagesLecture 2 - 3 - First Order ResponsesLiyana HalimNo ratings yet
- 3 FiniteAutomata AnimDocument39 pages3 FiniteAutomata AnimRajdeep RandhawaNo ratings yet
- Non-Deterministic Finite AutomataDocument36 pagesNon-Deterministic Finite AutomataS.K. RoyNo ratings yet
- Formal Languages, Automata, and ComputabilityDocument27 pagesFormal Languages, Automata, and ComputabilityNehru VeerabatheranNo ratings yet
- Formal Definition Equivalence With Finite Automaton Generalized Nondeterministic Finite AutomatonDocument14 pagesFormal Definition Equivalence With Finite Automaton Generalized Nondeterministic Finite AutomatonShabab Israk PiasNo ratings yet
- Regular ExpressionDocument14 pagesRegular ExpressionMD Robiul Awal ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform OdeDocument24 pagesLaplace Transform OdeUmer KhanNo ratings yet
- RMI Vol17 (2001)Document652 pagesRMI Vol17 (2001)lucivandolopesNo ratings yet
- Compiler Design CA1Document10 pagesCompiler Design CA1Debasis GaraiNo ratings yet
- Establish Indices For FFT Operations: Shortlin - MCD 1 1/23/2011 3:56 PMDocument8 pagesEstablish Indices For FFT Operations: Shortlin - MCD 1 1/23/2011 3:56 PMSharifNo ratings yet
- DFA Construction IdeasDocument4 pagesDFA Construction IdeasInderpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit V (TM) - Part1nDocument24 pagesUnit V (TM) - Part1nStuti GuptaNo ratings yet
- APP Unit 5Document86 pagesAPP Unit 5anirudh3369No ratings yet
- Appndx D Mae175Document26 pagesAppndx D Mae175JAyNo ratings yet
- Study Note of Theory of ComputationDocument21 pagesStudy Note of Theory of Computationarik_cjNo ratings yet
- 09 Z TransformDocument34 pages09 Z TransformBhaskarNo ratings yet
- Theory of Automata6&7Document39 pagesTheory of Automata6&7zawad aliNo ratings yet
- Finite Automata Formal Languages: Operations On SentencesDocument20 pagesFinite Automata Formal Languages: Operations On SentencesBhaskar Rao PNo ratings yet
- Notation To Specify A Language: Theory of Computation - Regular ExpressionsDocument23 pagesNotation To Specify A Language: Theory of Computation - Regular ExpressionsHimañshu BhattNo ratings yet
- Unit-Ii Regular Expressions and Languages DefinitionDocument34 pagesUnit-Ii Regular Expressions and Languages DefinitionGanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chap 3Document39 pagesChap 3yeabsira gashawNo ratings yet
- Nfa To ReDocument5 pagesNfa To Reprateek lilhareNo ratings yet
- Finite Autometa PDFDocument40 pagesFinite Autometa PDFsahuashishcsNo ratings yet
- Tcom005n PDFDocument41 pagesTcom005n PDFS.K. RoyNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 FiniteAutomataDocument39 pagesUNIT 1 FiniteAutomataVathyasamNo ratings yet
- Formal LanguagesDocument47 pagesFormal LanguagesSourav RoyNo ratings yet
- CS 321 HW2Document5 pagesCS 321 HW2Daniel GohNo ratings yet
- Laplace and Inverse TransformsDocument40 pagesLaplace and Inverse TransformsDheerajOmprasadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 First Order SystemsDocument26 pagesLecture 3 First Order SystemsZena wNo ratings yet
- What It IsDocument2 pagesWhat It IsABHISHEK KUMARNo ratings yet
- 20.07. mkg1 Automata PDFDocument53 pages20.07. mkg1 Automata PDFmukesh guptaNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Computation Part IIDocument113 pagesThe Theory of Computation Part IImjn0107No ratings yet
- Flat Module 5Document11 pagesFlat Module 5Priya RanaNo ratings yet
- Deterministic Finite Automata (DFA)Document19 pagesDeterministic Finite Automata (DFA)xigon53558No ratings yet
- 02 FiniteAutomata PDFDocument7 pages02 FiniteAutomata PDFApoorva NaikNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform Converges Fourier TransformDocument14 pagesLaplace Transform Converges Fourier TransformSupriyaNo ratings yet
- PLL Technique 2Document25 pagesPLL Technique 2Preeti MishraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document45 pagesChapter 4Mohammad AliffuddinNo ratings yet
- Formal Languages - Lec6 - P1Document23 pagesFormal Languages - Lec6 - P1ahmed.teka446No ratings yet
- 01 Nfa To RegDocument5 pages01 Nfa To Regmariamelabd42No ratings yet
- Laplace HadyDocument52 pagesLaplace HadyT ANo ratings yet
- Lec 03Document45 pagesLec 03Cyrus LiNo ratings yet
- Turning Machine: Unit-VDocument23 pagesTurning Machine: Unit-VVenkata Rao SNo ratings yet
- Theory of Automata NotesDocument29 pagesTheory of Automata NotesMuhammad Arslan RasoolNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform Solution of ODEsDocument2 pagesLaplace Transform Solution of ODEsbedodsonNo ratings yet
- Laplace HadyDocument50 pagesLaplace HadyIhwan FauziNo ratings yet
- 3 DfaDocument23 pages3 DfaHassan AlsayedNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Summary 1 Topic: Review Conditional Zero, First and Second: General ExplanationDocument6 pagesSummary 1 Topic: Review Conditional Zero, First and Second: General ExplanationJaime G. MendozaNo ratings yet
- Direct & Indirect SpeechDocument7 pagesDirect & Indirect SpeechDebela AbidhuNo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument5 pagesEnglish GrammarRalucaNo ratings yet
- EMD CARMELTE SCHOOL FOUNDATION INC 2nd PrelimDocument4 pagesEMD CARMELTE SCHOOL FOUNDATION INC 2nd PrelimNikolai NoronNo ratings yet
- Second Language Acquisition HandoutsDocument10 pagesSecond Language Acquisition HandoutsmounaNo ratings yet
- Mandarin For All-1Document7 pagesMandarin For All-1aleeya syahirahNo ratings yet
- Speech Communities and Languages in HK: En3591 Hong Kong Language and SocietyDocument42 pagesSpeech Communities and Languages in HK: En3591 Hong Kong Language and SocietyMuqdas hayatNo ratings yet
- Year 4 J Comp and Spelling Third Term Examination J 2023Document7 pagesYear 4 J Comp and Spelling Third Term Examination J 2023finney gabrielsNo ratings yet
- Khroskyabs LanguageDocument14 pagesKhroskyabs LanguageRicardoNo ratings yet
- Animal-Onomatopoeia-Worksheet MR BrownDocument1 pageAnimal-Onomatopoeia-Worksheet MR BrownKatjaNo ratings yet
- O FFNTST: ShouldDocument2 pagesO FFNTST: ShouldmielpopsglekNo ratings yet
- X SeralDocument7 pagesX SeralOana-Violeta Si Cornel SelaruNo ratings yet
- EAPP Module 1 Week 1 - L. ArenilloDocument9 pagesEAPP Module 1 Week 1 - L. ArenilloLeigh Afable100% (1)
- Writing 3Document8 pagesWriting 3Оля ГурьяноваNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Iii Schools Division of Tarlac ProvinceDocument33 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Iii Schools Division of Tarlac Provincebaldo yellow4No ratings yet
- Simple Past Tense BookletDocument7 pagesSimple Past Tense BookletAfifah JaafarNo ratings yet
- Types of Pronouns Personal Object Possessive Adjectives Possessive Pronouns Reflexive PronounsDocument3 pagesTypes of Pronouns Personal Object Possessive Adjectives Possessive Pronouns Reflexive PronounsFano UwUNo ratings yet
- Stylistics 2 A Short History of StylisticsDocument31 pagesStylistics 2 A Short History of StylisticsOtmane en nasiriNo ratings yet
- Presentation BAHASA INGGRISDocument12 pagesPresentation BAHASA INGGRISCok AmiNo ratings yet
- Random - Definition of Random by Merriam-Webster PDFDocument11 pagesRandom - Definition of Random by Merriam-Webster PDFinsomnium1227No ratings yet
- 218.764 - 2019 Assignment 1Document2 pages218.764 - 2019 Assignment 1Suresh GovindarajNo ratings yet
- Sílabos - Ingles III-ISAMDocument4 pagesSílabos - Ingles III-ISAMtrafaelNo ratings yet
- Reduced Participle Clauses Grammar Drills Grammar Guides 130210Document2 pagesReduced Participle Clauses Grammar Drills Grammar Guides 130210yusacoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - MotivationDocument3 pagesLesson Plan - Motivationapi-644318070No ratings yet
- 01 Reported StatementsDocument6 pages01 Reported StatementsVleyZ1XNo ratings yet
- Syntax: Dependent/Subordinate ClausesDocument4 pagesSyntax: Dependent/Subordinate ClausesLe PhucNo ratings yet
- Linguistics, Penguin: Module 2 Unit 2 Error Analysis 1Document7 pagesLinguistics, Penguin: Module 2 Unit 2 Error Analysis 1Dedeh KurniasihNo ratings yet
- Gimas Olympiad 2054Document13 pagesGimas Olympiad 2054rqvlog13No ratings yet
- English Phonetics and PhonologyDocument24 pagesEnglish Phonetics and PhonologyMirela MoiseNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 English Most Essential Learning Competencies MELCsDocument4 pagesGrade 5 English Most Essential Learning Competencies MELCsTeresa saiconNo ratings yet