Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WK 17.valeriano
WK 17.valeriano
Uploaded by
VALERIANO TRISHA0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views5 pages Risk for Leukemias are After 6 Independent: Independent: After 6
Pale skin, infection cancers of the hours of 1. Monitor Protect patient hours of
fatigued, related to blood forming nursing vital signs from potential nursing
enlarged deficient tissues. White interven every 4 hours sources interven
lymph primary blood cells tions the 2. Assess for pathogens or tions the
nodes, defenses may be patient signs and infection patient was
petechiae, produced in will: symptoms of able to:
bru
Original Description:
Original Title
wk 17.valeriano
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document Risk for Leukemias are After 6 Independent: Independent: After 6
Pale skin, infection cancers of the hours of 1. Monitor Protect patient hours of
fatigued, related to blood forming nursing vital signs from potential nursing
enlarged deficient tissues. White interven every 4 hours sources interven
lymph primary blood cells tions the 2. Assess for pathogens or tions the
nodes, defenses may be patient signs and infection patient was
petechiae, produced in will: symptoms of able to:
bru
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views5 pagesWK 17.valeriano
WK 17.valeriano
Uploaded by
VALERIANO TRISHA Risk for Leukemias are After 6 Independent: Independent: After 6
Pale skin, infection cancers of the hours of 1. Monitor Protect patient hours of
fatigued, related to blood forming nursing vital signs from potential nursing
enlarged deficient tissues. White interven every 4 hours sources interven
lymph primary blood cells tions the 2. Assess for pathogens or tions the
nodes, defenses may be patient signs and infection patient was
petechiae, produced in will: symptoms of able to:
bru
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
1.
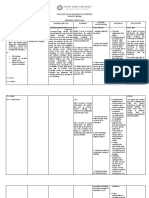
Make a table to differentiate the 4 common types of leukemia: Acute lymphocytic leukemia
(ALL), Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), Acute myeloid leukemia (AML), and Chronic
myeloid leukemia (CML) according to incidence, physiologic alterations, clinical manifestations,
management, and prognosis
Acute Chronic Chronic Myeloid Chronic Myeloid
Lymphocytic Lymphocytic Leukemia (AML) Leukemia (CML)
Leukemia (ALL) Leukemia (CLL)
Incidence The average A US study AML is About 15% of all
person’s lifetime published in uncommon, leukemia is
risk of getting 2004 estimates making up about CML. This year,
ALL is about 1 in the worldwide 1% of cancers. an estimated
1,000. The risk incidence of CLL This year, an 9,110 people
is slightly higher to be between estimated (5,150 men and
in males than in <1 and 5.5 per 20,240 people of 3,960 women) in
females and 100,000 people all ages (11,230 the United
higher in whites (24). The men and boys Stated will be
than in African highest and 9,010 diagnosed with
Americans. Most incidence rates women and CML. Most of
cases of ALL in 2004 were girls) in the these will be
occur in found to be in United States adults, with an
children, but Australia, US, will be average age of
most deaths Ireland and Italy diagnosed with diagnosis of 64
from ALL (about AML. AML is the years. About
4 out of 5) occur second most 50% of cases
in adults. common type of are found in
leukemia people older
diagnosed in than 64
adult and
children but
most cases
occur in adults
Physiologic Acute Chronic (AML). In CML is a stem
Alterations Lymphocytic Lymphocytic myeloid cells, cell disease
Leukemia Leukemia is the myeloblast is characterized by
occurs as a distinguished by an immature the
bone marrow the clonal reservoir of accumulation of
cell makes DNA proliferation of white blood myeloid
mistakes. The CD5+ CD23+ B cells. This precursor cells
errors instruct Cells in the myeloblast may in the bone
the cell to begin blood, bone experience a marrow and
expanding and marrow and genetic blood. This cells
splitting while a secondary alteration that exhibits a
stable cell will lymphoid tissues prevents the cell distinct
normally avoid (CLL). Gene from maturing abnormality in
dividing and expression and the gene
eventually die. profiling and differentiating encoding the
As a result, phenotypic tests translocation of
blood cell growth indicate that CLL chromosomes 9
becomes is likely and 22
abnormal. originated from
CD5+ B cells
similar to those
found in healthy
adult blood
Clinical •Felt exhausted •Deficiency •Fatigue •Defects
Manifestation •Suffering from •Exhaustion •Defects •Exhausted
nausea •Loss of weight • Feeling cold •Perspire at
•Experienced •The chills High •Experienced night
•lightheadednes fever Sweating lightheadedness •Weight loss
•Lack of breath at night or dizziness •Bone ache
•A thin peel •Enlarged lymp •Lack of breath (caused by
•Chronic nodes (often felt leukemia cells
diseases that do as lumps under that migrate
not resolve or do the skin) from the marrow
not recur •Abdominal pain cavity to the
•Surface or a feeling of bone surface or
bruishing (with “fullness” into the joint)
little red or •Spleen
purple spots); enlargement
•Bleeding, such (feeling as a
as frequent or mass below the
severe feminine left side of the
nosebleeds, ribcage)
bleeding gums
or menstrual
bleeding that is
excessive
Managements Treatments may If your doctor Treatment The standard
include: determines your depends on the treatment for
Chronic subtype of AML chronic phase
Chemotherapy, Lymphocytic and may include CML is a
which uses Leukemia is the following: tyrosine kinase
drugs to kill progressing or is inhibitor (TKI)
cancer cells, is in the •Combination like imatinib
typically used as intermediate or chemotherapy (Gleevec),
an induction advanced •Targeted nilotinib
therapy for stages, your therapy with (Tasigna),
children and treatment monoclonal dasatinib
adults with options may antibodies (Sprycel), or
Acute include: •Stem cell bosutinib
Lymphocytic transplant using (Bosulif).
Leukemia. Chemotherapy. the patient’s
Targeted drug. stem cells or If the first drug
Immunotherapy. donor stem cells stops working or
Bone marrow •Arsenic trioxide it never really
transplant therapy worked well at
• A clinical trial all, the dose
of arsenic may be
trioxide therapy increased or
followed by stem another TKI
cell transplant might be tried
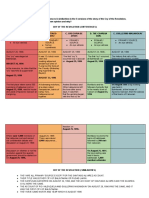
2. Formulate a Nursing Care Plan for a patient with Acute Leukemia
NCP:ACUTE LEUKEMIA
Nursing Nursing Background Nursing Nursing Rationale Evaluation
Assessme Diagnosis Knowledge Planning Intervention
nt
Subjective: Risk for Leukemias After 6 Independent Independent: After 6
“Nagkaka infection are cancer of hours of Place the Protect patient hours of
pasa po ako related to the blood nursing patient in a from potential nursing
nang hindi deficient forming interventi private room. sources interventio
ko alam at primary tissues. on s the Limited pathogens or n s the
biglaan po defenses White blood patient visitors as infection patient was
ako cells may be will: indicated. able to:
nangayayat produced in identify Prohibits use identify
” as excessive actions to of live plants actions to
verbalized amounts and prevent or cut prevent or
by the are unable to or reduce flowers. reduce the
patient work properly the risk Restrict fresh risk for
which for fruits and infection
Objective: weakens the infection vegetables or
•Skin pallor immune make sure
•Irritability system they are
washed or
T:37.5 peeled
P:80
R:18 Require good Prevent cross
BP:110/80 hand examination
washing or reduce risk
protocol for for infection
all personnel
and visitors
Encourage Prevent stasis
frequent of respiratory
turning and secretions,
deep reducing risk
breathing of atelectasis
or pneumonia
Inspect skin May indicate
for tender local infection
erythematous
ares, open
wounds,
Cleanse skin
with
antibacterial
solutions
Promote Promotes
good perineal cleanliness,
hygiene. reducing risk
Examine of perianal
perianal area abscess;
at least daily enhances
during acute circulation and
illness and healing.
provide sitz Conserves
baths energy for
healing,
cellular
regeneration
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan Group 3 C2e s2Document5 pagesNursing Care Plan Group 3 C2e s2Frian MariñasNo ratings yet
- Cell Unit TestDocument2 pagesCell Unit Testapi-385753111No ratings yet
- WK 16 Valeriano Colon CancerDocument2 pagesWK 16 Valeriano Colon CancerVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- WK 16 Cerv Can ValerianoDocument2 pagesWK 16 Cerv Can ValerianoVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- VRTS114 Final Exam-1Document2 pagesVRTS114 Final Exam-1ivy bernalNo ratings yet
- CT ColonDocument2 pagesCT Colonjaijai magbanuaNo ratings yet
- PRIORITY 2: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Excessive or Thick Secretions Tree Secondary To PneumoniaDocument4 pagesPRIORITY 2: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Excessive or Thick Secretions Tree Secondary To PneumoniaElay Pedroso100% (1)
- Course Task 7 Dengue Fever, Filariasis, Malaria and EncephalitisDocument4 pagesCourse Task 7 Dengue Fever, Filariasis, Malaria and EncephalitisBunnie AlphaNo ratings yet
- Study-Guide - 4 Chn2 2nd PartDocument6 pagesStudy-Guide - 4 Chn2 2nd PartFrancis Lawrence AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Tumangan Ma. Estela Leonor Angelap Proj1m1Document10 pagesTumangan Ma. Estela Leonor Angelap Proj1m1Mela TumanganNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired SocialDocument5 pagesNCP Impaired SocialPau-pau BasiNo ratings yet
- Identify A Teacher You Might Had in The Past Who Think Was A Good Teacher But Do NotDocument4 pagesIdentify A Teacher You Might Had in The Past Who Think Was A Good Teacher But Do NotAriaNo ratings yet
- VIII - PMHN Role As A Member of The Research TeamDocument15 pagesVIII - PMHN Role As A Member of The Research Teamlester lopezNo ratings yet
- Sheehan SyndromeDocument15 pagesSheehan SyndromeRaul DoctoNo ratings yet
- Application of Research in Nursing Leadership and ManagementDocument25 pagesApplication of Research in Nursing Leadership and ManagementLee BuelaNo ratings yet
- Doctor's OrderDocument3 pagesDoctor's OrderStephen S. PadayhagNo ratings yet
- Medical Ward - Discharge PlanDocument5 pagesMedical Ward - Discharge Plandon7dane100% (1)
- PoliomyelitisDocument28 pagesPoliomyelitisshanel18No ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMaria Fatima MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Hospital Policy and Information ManualDocument1 pageHospital Policy and Information ManualDarren CariñoNo ratings yet
- Acute AppendicitisDocument23 pagesAcute AppendicitisSandie Daniel GabalunosNo ratings yet
- 4 Nursing Research Alpha 2017Document8 pages4 Nursing Research Alpha 2017Nicole DimarucutNo ratings yet
- Case 6Document7 pagesCase 6Angel MayNo ratings yet
- Endometrial Adenocarcinoma A Tahbso CaseDocument78 pagesEndometrial Adenocarcinoma A Tahbso CaseJohn Mark Obrero100% (1)
- Simple Schematic Diagram of PneumoniaDocument1 pageSimple Schematic Diagram of PneumoniaTyrel LozanoNo ratings yet
- Week 14 - CD Course Task 8Document1 pageWeek 14 - CD Course Task 8Rochelle TenederoNo ratings yet
- NCP, PL, DPDocument6 pagesNCP, PL, DPJazel Algara JompillaNo ratings yet
- Evidence-Based Nursing: I. Clinical QuestionDocument4 pagesEvidence-Based Nursing: I. Clinical QuestionRay Jorge MarmetoNo ratings yet
- Deficient KnowledgeDocument3 pagesDeficient KnowledgeCalimlim KimNo ratings yet
- Gordon's Typology of 11 Functional Health PatternDocument12 pagesGordon's Typology of 11 Functional Health PatternJ. ishtelleNo ratings yet
- Gordon ChristianDocument1 pageGordon ChristianChristian Rodison Maningas100% (1)
- Step-By-step Description of HemodialysisDocument11 pagesStep-By-step Description of Hemodialysisprakash_smileyNo ratings yet
- Nursing MGT For StrokeDocument7 pagesNursing MGT For StrokeRubijen NapolesNo ratings yet
- Vitamin K (Phytomenadione) 2016: Indication Action Drug Type Trade Name Presentation Dosage / IntervalDocument3 pagesVitamin K (Phytomenadione) 2016: Indication Action Drug Type Trade Name Presentation Dosage / IntervalDeni Yuda Adi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Colonic Diverticular DiseaseDocument8 pagesEpidemiology and Pathophysiology of Colonic Diverticular DiseaseAnonymous Hz5w55No ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument11 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationYzel Vasquez AdavanNo ratings yet
- Mental Health AssessmentDocument1 pageMental Health AssessmentyasminNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues and Data Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues and Data Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationPaul Cubacub100% (1)
- Description:: Materials/ Equipment NeededDocument6 pagesDescription:: Materials/ Equipment NeededMarc Renz R. ChanNo ratings yet
- NPI Process RecordingDocument7 pagesNPI Process RecordingChristine ElbanbuenaNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument4 pagesNCP Impaired Gas ExchangevanNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Nursing Act of 2002Document8 pagesThe Philippine Nursing Act of 2002Reyhan FloresNo ratings yet
- COPARDocument21 pagesCOPAREdra VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases ReviewerDocument12 pagesCommunicable Diseases ReviewerClarissa GuifayaNo ratings yet
- Idc NCPDocument14 pagesIdc NCPEnrique BabierraNo ratings yet
- Seizure Disorders and Management in Primary Health CareDocument83 pagesSeizure Disorders and Management in Primary Health CareChidi MbatuegwuNo ratings yet
- NMAT Social Science Practice Questions Set 2Document7 pagesNMAT Social Science Practice Questions Set 2thea kyla angelaNo ratings yet
- KAren LFD ManangoDocument2 pagesKAren LFD ManangoKaren Joyce Costales MagtanongNo ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument361 pagesCombinepdfBULARON, Gerry Mar ANo ratings yet
- Renal MedsurgDocument14 pagesRenal MedsurgCliff Lois ╭∩╮⎷⎛⎝⎲⏝⏝⎲⎠⎷⎛╭∩╮ Ouano100% (1)
- Drug Study (Uterine Atony)Document14 pagesDrug Study (Uterine Atony)Violy CabigatNo ratings yet
- RRL DizonDocument2 pagesRRL DizonAlaiza AvergonzadoNo ratings yet
- Crizotinib Improves ProgressionDocument3 pagesCrizotinib Improves ProgressionIsabella RoselliniNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 Nursing DiagnosisDocument6 pagesNCP 1 Nursing DiagnosisJosh BlasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study and NCP For StrokeDocument7 pagesDrug Study and NCP For Strokegateway1119No ratings yet
- Hemo Glucose TestDocument3 pagesHemo Glucose TestrocheNo ratings yet
- NCP ExamplesDocument1 pageNCP Examplesapi-316414872No ratings yet
- Topic 2 (Informatics - Communication Technologies in The Critical Care Units)Document2 pagesTopic 2 (Informatics - Communication Technologies in The Critical Care Units)Ghianx Carlox PioquintoxNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Parathyroid Adenoma, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Parathyroid Adenoma, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 33-LeukemiaDocument21 pagesLecture 33-LeukemiaYasir KareemNo ratings yet
- Bone Cancer (Osteosarcoma) : Carolea Casas & Brittany HogueDocument222 pagesBone Cancer (Osteosarcoma) : Carolea Casas & Brittany Hoguegiggs_libraNo ratings yet
- HE G2scriptDocument10 pagesHE G2scriptVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- OrganizationalBehaviorandManagementFinalExam DR - ErmitaDocument2 pagesOrganizationalBehaviorandManagementFinalExam DR - ErmitaVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Cultural Beliefs On Disease Causation in The PhilippinesDocument6 pagesCultural Beliefs On Disease Causation in The PhilippinesVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- PainDocument7 pagesPainVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Final Group Assignment MhgapDocument4 pagesFinal Group Assignment MhgapVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- CT4 314Document2 pagesCT4 314VALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument4 pagesDiabetes MellitusVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- CT1 314Document2 pagesCT1 314VALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Foreign RRLDocument1 pageForeign RRLVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Valeriano, Nutrition ConceptDocument3 pagesValeriano, Nutrition ConceptVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Activity 4 MagpayoDocument3 pagesActivity 4 MagpayoVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- CT2 314Document1 pageCT2 314VALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- CHNN312 FinalDocument26 pagesCHNN312 FinalVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- 312 MidDocument60 pages312 MidVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- ENTH311 Business Model Plan Manuscript TemplateDocument2 pagesENTH311 Business Model Plan Manuscript TemplateVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- NCMB210 FinalDocument18 pagesNCMB210 FinalVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Electrolyte ImbalancesDocument4 pagesElectrolyte ImbalancesVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Term Paper 2022Document3 pagesTerm Paper 2022VALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Travel Agency Business Plan TATM311 QUICK ESCAPE FINALDocument59 pagesTravel Agency Business Plan TATM311 QUICK ESCAPE FINALVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Final Manuscript Cardio ChangesDocument9 pagesFinal Manuscript Cardio ChangesVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Film ReviewDocument4 pagesFilm ReviewVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- WK 16 Valeriano Colon CancerDocument2 pagesWK 16 Valeriano Colon CancerVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Valeriano, NCPDocument4 pagesValeriano, NCPVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Cu 7Document6 pagesCu 7VALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- WK 16 Cerv Can ValerianoDocument2 pagesWK 16 Cerv Can ValerianoVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Cu 8Document4 pagesCu 8VALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Cu 9Document2 pagesCu 9VALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- wk13 ValerianoDocument5 pageswk13 ValerianoVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- wk14 ValerianoDocument1 pagewk14 ValerianoVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Wk15 Breast CancerDocument3 pagesWk15 Breast CancerVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Biology: Board - Cbse Class - Xii Topic - Principles and ProcessesDocument7 pagesBiology: Board - Cbse Class - Xii Topic - Principles and ProcessesAkshat JainNo ratings yet
- Hos MCQ PDFDocument3 pagesHos MCQ PDFaminata6No ratings yet
- OsteomalaciaDocument28 pagesOsteomalaciaReginette Pisalbo ChanNo ratings yet
- Buerger DseDocument3 pagesBuerger DseLenny Ronalyn QuitorianoNo ratings yet
- Antisocial Personality DisorderDocument20 pagesAntisocial Personality DisorderAzifah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Principles of Medical Technology Practice 1 Midterm TranseesDocument19 pagesPrinciples of Medical Technology Practice 1 Midterm TranseesSean Rafael LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Hem - Lab 4 Retic - 09Document9 pagesHem - Lab 4 Retic - 09djebrutNo ratings yet
- Cerebellar AtaxiaDocument11 pagesCerebellar AtaxiaAnurag SachanNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocument82 pagesCardiovascular PhysiologyAminah Al-NafisahNo ratings yet
- Handouts For Normal PediatricsDocument54 pagesHandouts For Normal Pediatricsapi-3842758No ratings yet
- Congenital Hips DislocationDocument6 pagesCongenital Hips DislocationMar OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- ASCP Board of Certification BrochureDocument32 pagesASCP Board of Certification BrochureMark Raymund Galvez Nava60% (5)
- Current Status and Challenges of Stem Cell Treatment For Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument19 pagesCurrent Status and Challenges of Stem Cell Treatment For Alzheimer's DiseaseHelical Nail FemurNo ratings yet
- Understanding Satiation and SatietyDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Satiation and SatietyzenderiwNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument41 pagesMuscular SystemGem Rose UretaNo ratings yet
- Practical Task 2 Starfish DevelopmentDocument4 pagesPractical Task 2 Starfish DevelopmentBuhle PhaswaneNo ratings yet
- 1.mofologi Dan Sitologi Bakteri MikrobioDocument38 pages1.mofologi Dan Sitologi Bakteri MikrobiomerlindikaNo ratings yet
- Alcoholic Liver Disease: Pathogenesis and Current ManagementDocument15 pagesAlcoholic Liver Disease: Pathogenesis and Current ManagementRahelin KidoNo ratings yet
- Charmanta Sambo CV UpdatedDocument2 pagesCharmanta Sambo CV Updatedapi-625293707No ratings yet
- Yersinia Pestis Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesYersinia Pestis Practice QuestionsVibhav SinghNo ratings yet
- Hair Growth PatternDocument3 pagesHair Growth PatternDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- tmp92D8 TMPDocument244 pagestmp92D8 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- G-12 Biology, 3.4 MutationsDocument5 pagesG-12 Biology, 3.4 MutationsYohannes NigussieNo ratings yet
- Graves DiseaseDocument13 pagesGraves DiseaseGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Adoptive Immunotherapy Ludewig Hoffmann (Methods Molec Medicine 109 Humana 2005)Document517 pagesAdoptive Immunotherapy Ludewig Hoffmann (Methods Molec Medicine 109 Humana 2005)Cristian PopaNo ratings yet
- Med/Surg Chapter 45: Thyroid and Parathyroid Disorders 'Highlights'Document4 pagesMed/Surg Chapter 45: Thyroid and Parathyroid Disorders 'Highlights'Missy HaslamNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Biotechnology (BT) : Engineering MathematicsDocument2 pagesSyllabus For Biotechnology (BT) : Engineering MathematicsManoj SkNo ratings yet
- Quillen Quirks 2013Document85 pagesQuillen Quirks 2013Anand SahaNo ratings yet
- Structure of SkinDocument19 pagesStructure of SkinFiqi Lampard100% (1)