Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-1
CurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-1
Uploaded by
Shreyansh ChauhanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Topic 1.2 FormativeDocument3 pagesTopic 1.2 FormativeHamza Farhan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- ERTEKIN - & - ATIK - 2015 - Sustainable Markets - Motivating Factors, Barriers, and Remedies For Mobilization of Slow FashionDocument17 pagesERTEKIN - & - ATIK - 2015 - Sustainable Markets - Motivating Factors, Barriers, and Remedies For Mobilization of Slow FashionEstudanteSaxNo ratings yet
- CurrentDocument12 pagesCurrentrajvanshiaditya549No ratings yet
- KCET 2019 Question Paper PhysicsDocument10 pagesKCET 2019 Question Paper PhysicsDarshan LNo ratings yet
- JEE MAIN 2-7 SRDocument11 pagesJEE MAIN 2-7 SRNINE EDUCATIONNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics Book Back Questions New BookDocument28 pages12th Physics Book Back Questions New BookangelinerosedeborahNo ratings yet
- QP PhysicsDocument6 pagesQP Physicsdurga charanNo ratings yet
- Pre Board 1 PhysicsDocument6 pagesPre Board 1 PhysicsMohit KumarNo ratings yet
- BSCPH 102Document11 pagesBSCPH 102Umar MirNo ratings yet
- Uploads1645599553DPP - 5 (JEE Main & Adv.) Current Electricity, Wheat Stone Bridge, Symmetric CircuitsDocument24 pagesUploads1645599553DPP - 5 (JEE Main & Adv.) Current Electricity, Wheat Stone Bridge, Symmetric Circuitsbirupakshyapradhan62No ratings yet
- Electric-Current Class NotesDocument34 pagesElectric-Current Class NotesPraxxmNo ratings yet
- 8.physics - Class XII - CPBE 2023Document11 pages8.physics - Class XII - CPBE 2023EMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNo ratings yet
- 12 TH Physics S9Document7 pages12 TH Physics S9Yashvir KillzNo ratings yet
- Physics Final 22Document7 pagesPhysics Final 22AYAN SINGHNo ratings yet
- CH 3 - MCQ QN AloneDocument34 pagesCH 3 - MCQ QN Alonexefayo4337No ratings yet
- 7.prelim - Physics-2022-QnDocument10 pages7.prelim - Physics-2022-QnEMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNo ratings yet
- Vidyalankar-Question Paper MHT-CET 2017 Phy-Chem PDFDocument14 pagesVidyalankar-Question Paper MHT-CET 2017 Phy-Chem PDFDeadly RiderzNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Question PaperDocument18 pages12 Physics Question PaperRahul AryavartiNo ratings yet
- Xii QP Physics VSTDocument5 pagesXii QP Physics VSTkrishnapradhani091No ratings yet
- Holiday HomeworkDocument6 pagesHoliday Homeworks74355470No ratings yet
- UnitTest - D03 Aug 2023 (1) K.Document61 pagesUnitTest - D03 Aug 2023 (1) K.krishgj19ab3232No ratings yet
- Electric CurrentDocument22 pagesElectric Currentmoon007000No ratings yet
- Physics QP Ag 2023 PB-1 Set-1Document6 pagesPhysics QP Ag 2023 PB-1 Set-1Rayan SinghNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Sample Question Paper-1 Phyiscs 2022-23Document7 pagesClass Xii Sample Question Paper-1 Phyiscs 2022-23Anonymous NV7nnJDeNo ratings yet
- Physics Sample Papers 2022-23 QPDocument42 pagesPhysics Sample Papers 2022-23 QPOJASisLiveNo ratings yet
- 12th Physic One MarksDocument17 pages12th Physic One MarksKirthik Reshan.S 12'A'No ratings yet
- REOT - 14, Dropper Afternoon, (30 - 01 - 2023)Document6 pagesREOT - 14, Dropper Afternoon, (30 - 01 - 2023)nolifermxx6261No ratings yet
- Revision DPP - JEE Advance - DPP-3 - P - DPP-3 - DPP - 03 PDFDocument11 pagesRevision DPP - JEE Advance - DPP-3 - P - DPP-3 - DPP - 03 PDFvijay kakarlaNo ratings yet
- DPP - 01 - Current ElectricityDocument4 pagesDPP - 01 - Current ElectricityDavid MillerNo ratings yet
- 10.Physics-Class XII-QP - ISML - CPBE 2023Document6 pages10.Physics-Class XII-QP - ISML - CPBE 2023EMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument36 pagesCurrent ElectricityT. TNo ratings yet
- Quiz Enthuse SaturdayDocument4 pagesQuiz Enthuse Saturdayyashwant bhaduNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics All Book Back One Mark (EM)Document10 pages12 Physics All Book Back One Mark (EM)azeezsharique4No ratings yet
- Physics - Detailed SolutionsDocument25 pagesPhysics - Detailed SolutionsPoorni RenuNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 2 Word FileDocument12 pagesSample Paper 2 Word FileAtul DubeyNo ratings yet
- Physics PQ2Document7 pagesPhysics PQ2David BamNo ratings yet
- Physics Practice Paper - 02Document9 pagesPhysics Practice Paper - 02bajpaianubhav58538No ratings yet
- 2023 Physics Board PaperDocument11 pages2023 Physics Board Papershivkarnwal2No ratings yet
- Details: General InstructionsDocument9 pagesDetails: General InstructionsAakriti RoyNo ratings yet
- PH Sample Paper 3 UnsolvedDocument9 pagesPH Sample Paper 3 UnsolvedApSWgxmwNo ratings yet
- Selfstudys Com FileDocument28 pagesSelfstudys Com Filedhariharan38No ratings yet
- Arihant Sample Paper Term 1 Class 12 PhysicsDocument17 pagesArihant Sample Paper Term 1 Class 12 PhysicsHitesh Yadav100% (1)
- Electric CurrentDocument2 pagesElectric CurrentAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics: Class II IIT-JEE Achiever 2022 - 23 Solution To CET Worksheet - 03 Topics Current ElectricityDocument22 pagesPhysics: Class II IIT-JEE Achiever 2022 - 23 Solution To CET Worksheet - 03 Topics Current ElectricityNaman KaradennavarNo ratings yet
- Board Test Phy Paper-3Document9 pagesBoard Test Phy Paper-3shrawantiyaNo ratings yet
- Board Test Phy Paper-3Document9 pagesBoard Test Phy Paper-3shrawantiyaNo ratings yet
- CRP PH 4 JEE MAIN-rDocument20 pagesCRP PH 4 JEE MAIN-rkunalbestNo ratings yet
- Physics XII - Set 3Document6 pagesPhysics XII - Set 3ashishgambhir1986No ratings yet
- Phy - Paper - 1 (QP) (New)Document4 pagesPhy - Paper - 1 (QP) (New)yadnyabhandari4No ratings yet
- 262C SANKALP12345 (XII) Mains1 02.07.2023Document16 pages262C SANKALP12345 (XII) Mains1 02.07.2023Laxmi RawatNo ratings yet
- Mock PB 23-1Document11 pagesMock PB 23-1Kshitij YadavNo ratings yet
- Physics Kcet 2023Document12 pagesPhysics Kcet 2023Prajwal MNo ratings yet
- CBSE Set 2 (2.4-4.1)Document2 pagesCBSE Set 2 (2.4-4.1)keystonevp8No ratings yet
- This Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingDocument18 pagesThis Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingvarunkohliinNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity PYQ SDocument5 pagesCurrent Electricity PYQ Spatiminati2020No ratings yet
- CBSE Set 1 (2.4-4.1)Document2 pagesCBSE Set 1 (2.4-4.1)keystonevp8No ratings yet
- Physics Set ADocument21 pagesPhysics Set AnayanasuzanneNo ratings yet
- Physics Test GeneratorDocument17 pagesPhysics Test GeneratorTweety PreetyNo ratings yet
- Physics 3rd Sec EgyptDocument39 pagesPhysics 3rd Sec Egyptabdelrahman mohamedNo ratings yet
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 MergedDocument8 pages1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 MergedSanyam SinghNo ratings yet
- 6.XII Physics Question PaperDocument8 pages6.XII Physics Question PaperEMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- CurrentElectricity Exercise-3Document5 pagesCurrentElectricity Exercise-3Shreyansh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- CurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-4Document3 pagesCurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-4Shreyansh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- CurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-3Document3 pagesCurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-3Shreyansh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- CurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-2Document2 pagesCurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-2Shreyansh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 12 DPP 08D Carboxylic AcidDocument7 pages12 DPP 08D Carboxylic AcidShreyansh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Types of Bread Suited For SandwichesDocument4 pagesTypes of Bread Suited For SandwichesMARY JOY VILLARUEL75% (4)
- Trump, GOP Reset After Tensions: For PersonalDocument54 pagesTrump, GOP Reset After Tensions: For PersonalstefanoNo ratings yet
- Managing Interdependence: Social Responsibility and EthicsDocument21 pagesManaging Interdependence: Social Responsibility and EthicsSalman MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- Types of RoofDocument37 pagesTypes of RoofBRAIN OF AN ARCHITECT100% (1)
- NEXO Dory-User Guide-V2.11-EnDocument19 pagesNEXO Dory-User Guide-V2.11-Enandrygonzalez00No ratings yet
- Manual NCM 117 LabDocument57 pagesManual NCM 117 LabCristhel Mae C. RosalesNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower LessonsDocument26 pagesCooling Tower Lessonssmidhum7470100% (1)
- Radiation Measurements: Zhipeng Wang, Shuming Xing, Kun Wang, Sunjun Jin, Jian Zhang, Fuyou FanDocument7 pagesRadiation Measurements: Zhipeng Wang, Shuming Xing, Kun Wang, Sunjun Jin, Jian Zhang, Fuyou FanÖzgür Kara (OncoHealth)No ratings yet
- Nocchi Pentair Pompe VLRDocument14 pagesNocchi Pentair Pompe VLRThomas MyszkaNo ratings yet
- 9 Home Remedies To Get Rid of Dandruff NaturallyDocument9 pages9 Home Remedies To Get Rid of Dandruff NaturallyMr. MeNo ratings yet
- PACSA 2012 Invitation Program RegFormDocument6 pagesPACSA 2012 Invitation Program RegFormCherie DyNo ratings yet
- Ged 101 Activity 4Document2 pagesGed 101 Activity 4Ranzel CruzatNo ratings yet
- Florence Gilbao: ProfileDocument1 pageFlorence Gilbao: ProfileFLORENCE GILBAONo ratings yet
- HVT Tennis Strategy 2015Document11 pagesHVT Tennis Strategy 2015Vibhav SinghNo ratings yet
- TRIP Moving South Carolina Forward Report September 2021Document21 pagesTRIP Moving South Carolina Forward Report September 2021WMBF NewsNo ratings yet
- Assignment01 2023Document2 pagesAssignment01 2023Nthabeleng GaringNo ratings yet
- Utilization of Excel in Solving Structural Analysis ProblemsDocument13 pagesUtilization of Excel in Solving Structural Analysis ProblemsGnkds100% (1)
- David Sm13 PPT 10Document27 pagesDavid Sm13 PPT 10Ahmed Yousufzai100% (1)
- Esbd - Unit IDocument39 pagesEsbd - Unit IpallaviNo ratings yet
- 16 - Math and Logic GamesDocument3 pages16 - Math and Logic Gamesmozam haqNo ratings yet
- Foundation Semester 1 Phonics and HFWs School Version Home Version 4Document4 pagesFoundation Semester 1 Phonics and HFWs School Version Home Version 4Sum Soo PinNo ratings yet
- Project:SASEC Mugling-Pokhara Highway Improvement Phase I Project (SMPHIP) Contract No. SMPHIP/OCB/MAP/2 Contractor: Anhui Kaiyuan Highway and Bridge Co. LTDDocument4 pagesProject:SASEC Mugling-Pokhara Highway Improvement Phase I Project (SMPHIP) Contract No. SMPHIP/OCB/MAP/2 Contractor: Anhui Kaiyuan Highway and Bridge Co. LTDugrasen chaudharyNo ratings yet
- QF-1100-MN-002 Whistle Blowing Policy and Procedure ManualDocument6 pagesQF-1100-MN-002 Whistle Blowing Policy and Procedure ManualPratiek RaulNo ratings yet
- How Do Society Shape Science and How Did Science Shape SocietyDocument2 pagesHow Do Society Shape Science and How Did Science Shape SocietyReenigne OcgnasNo ratings yet
- AtrazineDocument22 pagesAtrazineapi-257409369No ratings yet
- Kohls Et Al - 2011Document11 pagesKohls Et Al - 2011chysaNo ratings yet
- DiagnoseDocument25 pagesDiagnosesambathnatarajanNo ratings yet
- 2010 Calgary Census ResultsDocument124 pages2010 Calgary Census ResultsCalgary HeraldNo ratings yet
CurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-1
CurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-1
Uploaded by
Shreyansh ChauhanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-1
CurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-1
Uploaded by
Shreyansh ChauhanCopyright:
Available Formats
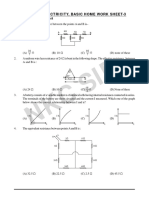
CURRENT ELECTRICITY, BASIC HOME WORK SHEET-1
Drift Velocity and Resistance
1. Two wires each of radius of cross section r but of different malerials are connected together end to
end (in series). If the densities of charge carries in the two wires are in the ratio 1:4, the drift velocity
of electrons in the two wires will be in the ratio :
(A) 1 : 2 (B) 2 : 1 (C) 4 : 1 (D) 1 : 4
2. A current I flows through a uniform wire of diameter d when the mean electron drift velocity is v. The
same current will flow through a wire of diameter d/2 made of the same material if the mean drift velocity
of the electron is :
(A) v/4 (B) v/2 (C) 2v (D) 4v
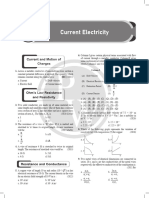
3. A wire a non-uniform cross-section as shown in figure. A steady current flows through it. The drift
speed of electron at points P and Q is vP and vQ :
P Q
IR
S
(A) vP = vQ (B) vP < vQ (C) vP > vQ (D) data insufficient
4. Three copper wires have their lengths in the ratio 5 : 3 : 1 and their masses are in the ratio 1 : 3 :
5. Their electrical resistance will be in the ratio :
C
(A) 5 : 3 : 1 (B) 1 : 3 : 5 (C) 125 : 15 : 1 (D) 1 : 15 : 125
5. A reactangular carbon block has dimensions 1.0 cm × 1.0 cm × 50 cm. Resistances are measured,
first across two square ends and then across two rectangular ends, respectively. If resistivity of carbon
K
is 3.5 × 10–5 - m, then values of measured resistances respectively are :
N 1cm
1cm
50cm
(A) 17.5 × 10–2 , 7 × 10–5 (B) 7 × 10–5 , 7.5 × 10–2
(C) 17.5 × 10–4 , 7 × 10–7 (D) 7.5 , 7 × 10–2
6. A wire of resistance R is stretched to double its length. Its new resistance is
(A) R (B) R/2 (C) 4R (D) R/4
7. The resistance of a wire is 5 at 50 ºC and 6 at 100 ºC. The resistance of the wire of 0 ºC will
be-
(A) 2 (B) 1 (C) 4 (D) 3
ANSWERS
HOME WORK SHEET-1
1. C 2. D 3. C 4. C 5. A
6. C 7. B
You might also like
- Topic 1.2 FormativeDocument3 pagesTopic 1.2 FormativeHamza Farhan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- ERTEKIN - & - ATIK - 2015 - Sustainable Markets - Motivating Factors, Barriers, and Remedies For Mobilization of Slow FashionDocument17 pagesERTEKIN - & - ATIK - 2015 - Sustainable Markets - Motivating Factors, Barriers, and Remedies For Mobilization of Slow FashionEstudanteSaxNo ratings yet
- CurrentDocument12 pagesCurrentrajvanshiaditya549No ratings yet
- KCET 2019 Question Paper PhysicsDocument10 pagesKCET 2019 Question Paper PhysicsDarshan LNo ratings yet
- JEE MAIN 2-7 SRDocument11 pagesJEE MAIN 2-7 SRNINE EDUCATIONNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics Book Back Questions New BookDocument28 pages12th Physics Book Back Questions New BookangelinerosedeborahNo ratings yet
- QP PhysicsDocument6 pagesQP Physicsdurga charanNo ratings yet
- Pre Board 1 PhysicsDocument6 pagesPre Board 1 PhysicsMohit KumarNo ratings yet
- BSCPH 102Document11 pagesBSCPH 102Umar MirNo ratings yet
- Uploads1645599553DPP - 5 (JEE Main & Adv.) Current Electricity, Wheat Stone Bridge, Symmetric CircuitsDocument24 pagesUploads1645599553DPP - 5 (JEE Main & Adv.) Current Electricity, Wheat Stone Bridge, Symmetric Circuitsbirupakshyapradhan62No ratings yet
- Electric-Current Class NotesDocument34 pagesElectric-Current Class NotesPraxxmNo ratings yet
- 8.physics - Class XII - CPBE 2023Document11 pages8.physics - Class XII - CPBE 2023EMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNo ratings yet
- 12 TH Physics S9Document7 pages12 TH Physics S9Yashvir KillzNo ratings yet
- Physics Final 22Document7 pagesPhysics Final 22AYAN SINGHNo ratings yet
- CH 3 - MCQ QN AloneDocument34 pagesCH 3 - MCQ QN Alonexefayo4337No ratings yet
- 7.prelim - Physics-2022-QnDocument10 pages7.prelim - Physics-2022-QnEMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNo ratings yet
- Vidyalankar-Question Paper MHT-CET 2017 Phy-Chem PDFDocument14 pagesVidyalankar-Question Paper MHT-CET 2017 Phy-Chem PDFDeadly RiderzNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Question PaperDocument18 pages12 Physics Question PaperRahul AryavartiNo ratings yet
- Xii QP Physics VSTDocument5 pagesXii QP Physics VSTkrishnapradhani091No ratings yet
- Holiday HomeworkDocument6 pagesHoliday Homeworks74355470No ratings yet
- UnitTest - D03 Aug 2023 (1) K.Document61 pagesUnitTest - D03 Aug 2023 (1) K.krishgj19ab3232No ratings yet
- Electric CurrentDocument22 pagesElectric Currentmoon007000No ratings yet
- Physics QP Ag 2023 PB-1 Set-1Document6 pagesPhysics QP Ag 2023 PB-1 Set-1Rayan SinghNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Sample Question Paper-1 Phyiscs 2022-23Document7 pagesClass Xii Sample Question Paper-1 Phyiscs 2022-23Anonymous NV7nnJDeNo ratings yet
- Physics Sample Papers 2022-23 QPDocument42 pagesPhysics Sample Papers 2022-23 QPOJASisLiveNo ratings yet
- 12th Physic One MarksDocument17 pages12th Physic One MarksKirthik Reshan.S 12'A'No ratings yet
- REOT - 14, Dropper Afternoon, (30 - 01 - 2023)Document6 pagesREOT - 14, Dropper Afternoon, (30 - 01 - 2023)nolifermxx6261No ratings yet
- Revision DPP - JEE Advance - DPP-3 - P - DPP-3 - DPP - 03 PDFDocument11 pagesRevision DPP - JEE Advance - DPP-3 - P - DPP-3 - DPP - 03 PDFvijay kakarlaNo ratings yet
- DPP - 01 - Current ElectricityDocument4 pagesDPP - 01 - Current ElectricityDavid MillerNo ratings yet
- 10.Physics-Class XII-QP - ISML - CPBE 2023Document6 pages10.Physics-Class XII-QP - ISML - CPBE 2023EMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument36 pagesCurrent ElectricityT. TNo ratings yet
- Quiz Enthuse SaturdayDocument4 pagesQuiz Enthuse Saturdayyashwant bhaduNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics All Book Back One Mark (EM)Document10 pages12 Physics All Book Back One Mark (EM)azeezsharique4No ratings yet
- Physics - Detailed SolutionsDocument25 pagesPhysics - Detailed SolutionsPoorni RenuNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 2 Word FileDocument12 pagesSample Paper 2 Word FileAtul DubeyNo ratings yet
- Physics PQ2Document7 pagesPhysics PQ2David BamNo ratings yet
- Physics Practice Paper - 02Document9 pagesPhysics Practice Paper - 02bajpaianubhav58538No ratings yet
- 2023 Physics Board PaperDocument11 pages2023 Physics Board Papershivkarnwal2No ratings yet
- Details: General InstructionsDocument9 pagesDetails: General InstructionsAakriti RoyNo ratings yet
- PH Sample Paper 3 UnsolvedDocument9 pagesPH Sample Paper 3 UnsolvedApSWgxmwNo ratings yet
- Selfstudys Com FileDocument28 pagesSelfstudys Com Filedhariharan38No ratings yet
- Arihant Sample Paper Term 1 Class 12 PhysicsDocument17 pagesArihant Sample Paper Term 1 Class 12 PhysicsHitesh Yadav100% (1)
- Electric CurrentDocument2 pagesElectric CurrentAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics: Class II IIT-JEE Achiever 2022 - 23 Solution To CET Worksheet - 03 Topics Current ElectricityDocument22 pagesPhysics: Class II IIT-JEE Achiever 2022 - 23 Solution To CET Worksheet - 03 Topics Current ElectricityNaman KaradennavarNo ratings yet
- Board Test Phy Paper-3Document9 pagesBoard Test Phy Paper-3shrawantiyaNo ratings yet
- Board Test Phy Paper-3Document9 pagesBoard Test Phy Paper-3shrawantiyaNo ratings yet
- CRP PH 4 JEE MAIN-rDocument20 pagesCRP PH 4 JEE MAIN-rkunalbestNo ratings yet
- Physics XII - Set 3Document6 pagesPhysics XII - Set 3ashishgambhir1986No ratings yet
- Phy - Paper - 1 (QP) (New)Document4 pagesPhy - Paper - 1 (QP) (New)yadnyabhandari4No ratings yet
- 262C SANKALP12345 (XII) Mains1 02.07.2023Document16 pages262C SANKALP12345 (XII) Mains1 02.07.2023Laxmi RawatNo ratings yet
- Mock PB 23-1Document11 pagesMock PB 23-1Kshitij YadavNo ratings yet
- Physics Kcet 2023Document12 pagesPhysics Kcet 2023Prajwal MNo ratings yet
- CBSE Set 2 (2.4-4.1)Document2 pagesCBSE Set 2 (2.4-4.1)keystonevp8No ratings yet
- This Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingDocument18 pagesThis Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingvarunkohliinNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity PYQ SDocument5 pagesCurrent Electricity PYQ Spatiminati2020No ratings yet
- CBSE Set 1 (2.4-4.1)Document2 pagesCBSE Set 1 (2.4-4.1)keystonevp8No ratings yet
- Physics Set ADocument21 pagesPhysics Set AnayanasuzanneNo ratings yet
- Physics Test GeneratorDocument17 pagesPhysics Test GeneratorTweety PreetyNo ratings yet
- Physics 3rd Sec EgyptDocument39 pagesPhysics 3rd Sec Egyptabdelrahman mohamedNo ratings yet
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 MergedDocument8 pages1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 MergedSanyam SinghNo ratings yet
- 6.XII Physics Question PaperDocument8 pages6.XII Physics Question PaperEMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- CurrentElectricity Exercise-3Document5 pagesCurrentElectricity Exercise-3Shreyansh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- CurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-4Document3 pagesCurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-4Shreyansh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- CurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-3Document3 pagesCurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-3Shreyansh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- CurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-2Document2 pagesCurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-2Shreyansh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 12 DPP 08D Carboxylic AcidDocument7 pages12 DPP 08D Carboxylic AcidShreyansh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Types of Bread Suited For SandwichesDocument4 pagesTypes of Bread Suited For SandwichesMARY JOY VILLARUEL75% (4)
- Trump, GOP Reset After Tensions: For PersonalDocument54 pagesTrump, GOP Reset After Tensions: For PersonalstefanoNo ratings yet
- Managing Interdependence: Social Responsibility and EthicsDocument21 pagesManaging Interdependence: Social Responsibility and EthicsSalman MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- Types of RoofDocument37 pagesTypes of RoofBRAIN OF AN ARCHITECT100% (1)
- NEXO Dory-User Guide-V2.11-EnDocument19 pagesNEXO Dory-User Guide-V2.11-Enandrygonzalez00No ratings yet
- Manual NCM 117 LabDocument57 pagesManual NCM 117 LabCristhel Mae C. RosalesNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower LessonsDocument26 pagesCooling Tower Lessonssmidhum7470100% (1)
- Radiation Measurements: Zhipeng Wang, Shuming Xing, Kun Wang, Sunjun Jin, Jian Zhang, Fuyou FanDocument7 pagesRadiation Measurements: Zhipeng Wang, Shuming Xing, Kun Wang, Sunjun Jin, Jian Zhang, Fuyou FanÖzgür Kara (OncoHealth)No ratings yet
- Nocchi Pentair Pompe VLRDocument14 pagesNocchi Pentair Pompe VLRThomas MyszkaNo ratings yet
- 9 Home Remedies To Get Rid of Dandruff NaturallyDocument9 pages9 Home Remedies To Get Rid of Dandruff NaturallyMr. MeNo ratings yet
- PACSA 2012 Invitation Program RegFormDocument6 pagesPACSA 2012 Invitation Program RegFormCherie DyNo ratings yet
- Ged 101 Activity 4Document2 pagesGed 101 Activity 4Ranzel CruzatNo ratings yet
- Florence Gilbao: ProfileDocument1 pageFlorence Gilbao: ProfileFLORENCE GILBAONo ratings yet
- HVT Tennis Strategy 2015Document11 pagesHVT Tennis Strategy 2015Vibhav SinghNo ratings yet
- TRIP Moving South Carolina Forward Report September 2021Document21 pagesTRIP Moving South Carolina Forward Report September 2021WMBF NewsNo ratings yet
- Assignment01 2023Document2 pagesAssignment01 2023Nthabeleng GaringNo ratings yet
- Utilization of Excel in Solving Structural Analysis ProblemsDocument13 pagesUtilization of Excel in Solving Structural Analysis ProblemsGnkds100% (1)
- David Sm13 PPT 10Document27 pagesDavid Sm13 PPT 10Ahmed Yousufzai100% (1)
- Esbd - Unit IDocument39 pagesEsbd - Unit IpallaviNo ratings yet
- 16 - Math and Logic GamesDocument3 pages16 - Math and Logic Gamesmozam haqNo ratings yet
- Foundation Semester 1 Phonics and HFWs School Version Home Version 4Document4 pagesFoundation Semester 1 Phonics and HFWs School Version Home Version 4Sum Soo PinNo ratings yet
- Project:SASEC Mugling-Pokhara Highway Improvement Phase I Project (SMPHIP) Contract No. SMPHIP/OCB/MAP/2 Contractor: Anhui Kaiyuan Highway and Bridge Co. LTDDocument4 pagesProject:SASEC Mugling-Pokhara Highway Improvement Phase I Project (SMPHIP) Contract No. SMPHIP/OCB/MAP/2 Contractor: Anhui Kaiyuan Highway and Bridge Co. LTDugrasen chaudharyNo ratings yet
- QF-1100-MN-002 Whistle Blowing Policy and Procedure ManualDocument6 pagesQF-1100-MN-002 Whistle Blowing Policy and Procedure ManualPratiek RaulNo ratings yet
- How Do Society Shape Science and How Did Science Shape SocietyDocument2 pagesHow Do Society Shape Science and How Did Science Shape SocietyReenigne OcgnasNo ratings yet
- AtrazineDocument22 pagesAtrazineapi-257409369No ratings yet
- Kohls Et Al - 2011Document11 pagesKohls Et Al - 2011chysaNo ratings yet
- DiagnoseDocument25 pagesDiagnosesambathnatarajanNo ratings yet
- 2010 Calgary Census ResultsDocument124 pages2010 Calgary Census ResultsCalgary HeraldNo ratings yet