Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inst Tmah
Inst Tmah
Uploaded by
Zia UddinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Inst Tmah
Inst Tmah
Uploaded by
Zia UddinCopyright:
Available Formats
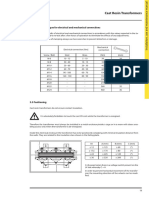
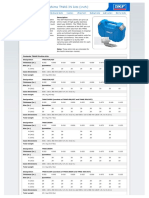
Horizontal adjustment tool TMAH series
Application Description
Performing shaft alignment requires the The TMAH are available to suit seven
horizontal and vertical adjustment of the common metric bolt sizes. They are not
motor. Vertical adjustment can easily be available to suit imperial bolt sizes.
done by using the SKF TMAS shims. Each TMAH will enable the user to adjust
two bolts of one side of the motor at the
The horizontal adjustment of the motor same time.
can be difficult and often requires the
use of heavy hammers, pry or crow bars
or brute force. These tools contrast with
the precision achieved by the SKF Shaft
Alignment Tools (TKSA 20 or TKSA 40)
and SKF Machinery Shims TMAS.
The TMAH uses a special eccentric
socket arrangement that enables rotary
movement to be translated to linear
A 2 x Eccentric sockets
movement at the motor foot. The result
is a precise and controllable horizontal E Adjustment nut
movement of the motor to the desired
alignment position making the C 2 x positioning rods
adjustment easier and safer. (includes B + D)
D Pin
Characteristics
B Dot mark
Welded jack-bolt assemblies are no
longer required to move each motor
foot horizontally. This also eliminates
the need to repair the jack-bolts due
to rust or corrosion. Make sure the TMAH’s height is
Quick and easy to fit, operate and compatible with the motor feet design.
remove. The TMAH does not stay on The height of the TMAH is given on
the motor. column H of the table below.
Enables accurate horizontal
adjustment movements of 25 microns The spanner size to loosen or tighten the
or less, suitable for laser alignment motor foot bolt (F) is different from the
equipment accuracy. spanner size to operate the TMAH
Is a complementary product to SKF eccentric socket (G)
TMAS machinery alignment shims.
Available to suit a wide range of
metric bolt head sizes, making it
suitable for many different types of
electric motors.
Virtually eliminates the risk of
damaging the motor feet.
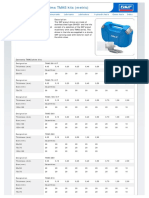
Dimensions
Designation A B C D E F G H
mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm
TMAH 13 14 31 14–17 21–50 95 13 17 20
TMAH 17 20 43 20–22 22–55 107 17 24 21
TMAH 19 23 52 24–26 22–82 137 19 30 27
TMAH 24 23 52 24–26 22–82 137 24 30 27
TMAH 30 35 70 30–32 38–134 187 30 36 39
TMAH 36 35 70 30–32 38–134 187 36 36 39
TMAH 46 44 89 40–43 48–156 229 46 46 45
Designation A B C D E F G H
in. in. in. in. in. in. in. in.
TMAH 13 0.55 1.22 0.55–0.67 0.83–1.97 3.74 0.51 0.67 0.79
TMAH 17 0.79 1.69 0.79–0.87 0.87–2.17 4.21 0.67 0.94 0.83
TMAH 19 0.90 2.05 0.94–1.02 0.87–3.23 5.39 0.75 1.18 1.06
TMAH 24 0.90 2.05 0.94–1.02 0.87–3.23 5.39 0.94 1.18 1.06
TMAH 30 1.38 2.75 1.18–1.25 1.50–5.28 7.36 1.18 1.42 1.53
TMAH 36 1.38 2.75 1.18–1.25 1.50–5.28 7.36 1.42 1.42 1.53
TMAH 46 1.73 3.50 1.57–1.69 1.89-6.14 9.02 1.81 1.81 2.16
SKF Maintenance Products Date of issue: 2012-11-05
You might also like
- Steering CalculationsDocument9 pagesSteering CalculationsAshik Naidu83% (6)
- Nissan Y61 Engine MechanicalDocument65 pagesNissan Y61 Engine Mechanicalblumng100% (2)
- MF CX330 Tier3 GBDocument281 pagesMF CX330 Tier3 GBjose luis baldiviezo olmosNo ratings yet
- Cardan Shaft Catalog From STDocument6 pagesCardan Shaft Catalog From STAHMAD SAIFULLAH100% (1)
- Product List Hyundai-210: Sr. No. O.E. Part No. Description Assy Name Undercarriage PartsDocument1 pageProduct List Hyundai-210: Sr. No. O.E. Part No. Description Assy Name Undercarriage PartsMahendra Tyre Works RaigarhNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 12 Exercise - ProblemsDocument3 pagesChapter # 12 Exercise - ProblemsZia UddinNo ratings yet
- Case Excavator Crawler Cx330 Tier3 TrainingDocument20 pagesCase Excavator Crawler Cx330 Tier3 Trainingcynthia100% (62)
- Actuator TorqDocument16 pagesActuator TorqSEPTADONAI TRISNANo ratings yet
- MODULES 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 8.0, 10.0 PinionsDocument8 pagesMODULES 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 8.0, 10.0 PinionsROHAN SHENDENo ratings yet
- Zucchini - Cast - Resin - Transformeon - Use - and - Maintenance - Manual 13Document1 pageZucchini - Cast - Resin - Transformeon - Use - and - Maintenance - Manual 13SYURINo ratings yet
- 00-2017 New-2017.04.14 NewDocument187 pages00-2017 New-2017.04.14 NewDesmond OeiNo ratings yet
- Technical Manual - Alligator CouplersDocument8 pagesTechnical Manual - Alligator CouplersStelian ConstantinescuNo ratings yet
- Suntech Babbitt Cata 18-19Document7 pagesSuntech Babbitt Cata 18-19ARKA technocorpNo ratings yet
- Eljay RC BrochureDocument3 pagesEljay RC Brochurekev YNo ratings yet
- P 7426 SC A4 - CeusDocument2 pagesP 7426 SC A4 - CeusHKC EQUIPEMENTSNo ratings yet
- DiseñoVigasCimentación (Con Muros) - Grupo2Document38 pagesDiseñoVigasCimentación (Con Muros) - Grupo2EVELYN BURBANONo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Cylinders CHDocument8 pagesHydraulic Cylinders CHStoianovici CristianNo ratings yet
- A4af3 A4bf2 SDocument53 pagesA4af3 A4bf2 Sjnansley33% (3)
- 123Document2 pages123Wabco AutoNo ratings yet
- Vane Motor Cartridge UnlockedDocument3 pagesVane Motor Cartridge UnlockedSamuel Lopez BenitesNo ratings yet
- INV016-ELE-MC-001 M1 Cuadro de CargasDocument29 pagesINV016-ELE-MC-001 M1 Cuadro de CargasMIERWEN PALACIOS ARANDANo ratings yet
- Hitachi SCX 1200-2 PDFDocument0 pagesHitachi SCX 1200-2 PDFleokareyxoxoersNo ratings yet
- Inova Ball Joints JBDocument2 pagesInova Ball Joints JBSympatyagaNo ratings yet
- Product Datasheet - Helical Gear ReducerDocument7 pagesProduct Datasheet - Helical Gear ReducerTrisna RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Analog Panel & Switchboard Meters - Dimension: Models Refer A B C D E F Ext. Box Drawing DrawingDocument1 pageAnalog Panel & Switchboard Meters - Dimension: Models Refer A B C D E F Ext. Box Drawing DrawingAnonymous SDeSP1No ratings yet
- Steering System: Service Data and Specifications (SDS) ............ 2Document12 pagesSteering System: Service Data and Specifications (SDS) ............ 2Юра ПетренкоNo ratings yet
- E Mindman Product FeatureDocument56 pagesE Mindman Product Featurey8889jvt2kNo ratings yet
- Siemens Flow SwitchDocument6 pagesSiemens Flow Switcheng.abdullrahmanNo ratings yet
- Trutorq AegisDocument12 pagesTrutorq AegisJuan Peñaloza CortésNo ratings yet
- Datasheet KMDocument1 pageDatasheet KMAlexander DíazNo ratings yet
- Cat - Standard.ing Mav 1061Document1 pageCat - Standard.ing Mav 1061Aaron SoteloNo ratings yet
- Brazo Grua para Bomba NG 100Document2 pagesBrazo Grua para Bomba NG 100Lucía Salazar de TeránNo ratings yet
- All Torque & Conversion Chart HYTORC MXTDocument18 pagesAll Torque & Conversion Chart HYTORC MXTnadiya.anggraeni123No ratings yet
- Md310 Quick ManualDocument55 pagesMd310 Quick ManualHitesh PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Metal Bellows Coupling I: Series KMDocument1 pageMetal Bellows Coupling I: Series KMIsmael RiosNo ratings yet
- Massey Ferguson MF 178 TRACTORS (FR) Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 957368)Document15 pagesMassey Ferguson MF 178 TRACTORS (FR) Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 957368)bvk29800220% (1)
- Tightening Torque, HT90 Caution: Service InformationDocument2 pagesTightening Torque, HT90 Caution: Service InformationAngga Budi PratamaNo ratings yet
- Asae s278.6 Enganche Rapido Modificado 7Document4 pagesAsae s278.6 Enganche Rapido Modificado 7Policarpio Mamani HuchaniNo ratings yet
- MASTIL 20WHE 163966-68 G25TV-4C 10000 REF - EPMT0231 (Ord. P16M016073)Document5 pagesMASTIL 20WHE 163966-68 G25TV-4C 10000 REF - EPMT0231 (Ord. P16M016073)Neoz CuandonNo ratings yet
- MSA VLL Installation InstructionsDocument13 pagesMSA VLL Installation InstructionsDavid Chaparro AguilarNo ratings yet
- Parts Catalog For Engine 150 HP - Sea Pro SN 2b482084 - 2b482085 - BakamlaDocument115 pagesParts Catalog For Engine 150 HP - Sea Pro SN 2b482084 - 2b482085 - BakamlaPussarpras KamlaNo ratings yet
- TM31 ServicemanualDocument48 pagesTM31 ServicemanualVic3501No ratings yet
- ESAB ExtractPage20-21cDocument8 pagesESAB ExtractPage20-21cDries VandezandeNo ratings yet
- Motorcycle ISSUE NO.: M-4-0453 Date: May 22, 2008: 1 OF 6Document6 pagesMotorcycle ISSUE NO.: M-4-0453 Date: May 22, 2008: 1 OF 6mattprcsoportNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Card: Piston Type Steering GearsDocument10 pagesCatalogue Card: Piston Type Steering GearsSenol SeidaliNo ratings yet
- WExcav DrivelinesDocument3 pagesWExcav Drivelinesarmando del carpioNo ratings yet
- Especificación QC2 - Martin InglésDocument2 pagesEspecificación QC2 - Martin InglésAntonio Mena MiñoNo ratings yet
- Minimum Pressure-Thermostatic ValveDocument2 pagesMinimum Pressure-Thermostatic ValveНариман ТусупбековNo ratings yet
- Heavy-Duty Slide 2 For Heavy LoadsDocument2 pagesHeavy-Duty Slide 2 For Heavy LoadsawemetalNo ratings yet
- TOQUES Mms.Document4 pagesTOQUES Mms.jose diego vallejos llamoNo ratings yet
- VALEO TM43 - ServicemanualDocument41 pagesVALEO TM43 - ServicemanualAnonymous 9xvU1FNo ratings yet
- A6V10094175 - Flow Switch For Use in Hydraulic Systems QVE1900 - deDocument2 pagesA6V10094175 - Flow Switch For Use in Hydraulic Systems QVE1900 - deRadu HereaNo ratings yet
- Yanmar Ym135 330 Shop ManualDocument6 pagesYanmar Ym135 330 Shop Manualedna100% (49)
- Sucker Rod Pump Surface Units CatalogDocument32 pagesSucker Rod Pump Surface Units CatalogAlbertoNo ratings yet
- CMD CouplingsDocument45 pagesCMD CouplingsSalgado_e_BentoNo ratings yet
- Permanent Magnet Brake. PMB SeriesDocument8 pagesPermanent Magnet Brake. PMB SeriesAshok BhatNo ratings yet
- Technical Data MJC SeriesDocument4 pagesTechnical Data MJC SeriesBenjamin MurphyNo ratings yet
- Monninghoff 546 - DatasheetDocument11 pagesMonninghoff 546 - DatasheetirfannadineNo ratings yet
- 546 DatasheetDocument11 pages546 Datasheetwilfredo mercedesNo ratings yet
- Tmsu 1Document2 pagesTmsu 1Zia UddinNo ratings yet
- NSSS Series CylinderDocument2 pagesNSSS Series CylinderZia UddinNo ratings yet
- Tksu 10Document2 pagesTksu 10Zia UddinNo ratings yet
- Tked 1Document2 pagesTked 1Zia UddinNo ratings yet
- Tmask InchDocument2 pagesTmask InchZia UddinNo ratings yet
- Inst TmasDocument2 pagesInst TmasZia UddinNo ratings yet
- Tmas InchDocument2 pagesTmas InchZia UddinNo ratings yet
- TMSP 1Document2 pagesTMSP 1Zia UddinNo ratings yet
- Inst TmaskDocument2 pagesInst TmaskZia UddinNo ratings yet
- TV712 IS CertificateDocument2 pagesTV712 IS CertificateZia UddinNo ratings yet
- Belt Aligment Tool TKBA 10 & 20Document2 pagesBelt Aligment Tool TKBA 10 & 20Zia UddinNo ratings yet
- Emotions and Moods: © 2007 Prentice Hall Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument22 pagesEmotions and Moods: © 2007 Prentice Hall Inc. All Rights ReservedZia UddinNo ratings yet
- Abcd 10 11Document1 pageAbcd 10 11Zia UddinNo ratings yet
- Personality and Values: © 2007 Prentice Hall Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument36 pagesPersonality and Values: © 2007 Prentice Hall Inc. All Rights ReservedZia UddinNo ratings yet
- Business Research Method: Case Study of Castrol IndiaDocument5 pagesBusiness Research Method: Case Study of Castrol IndiaZia UddinNo ratings yet
- Diversity in OrganizationsDocument25 pagesDiversity in OrganizationsZia UddinNo ratings yet
- Attitudes and Job Satisfaction: ThreeDocument19 pagesAttitudes and Job Satisfaction: ThreeZia UddinNo ratings yet
- Zia Uddin - EMBA-07 Disruptive TechnologyDocument3 pagesZia Uddin - EMBA-07 Disruptive TechnologyZia UddinNo ratings yet
- MA assignment-QUIZ (ONLINE)Document1 pageMA assignment-QUIZ (ONLINE)Zia UddinNo ratings yet
- What Is Organizational Behavior?Document39 pagesWhat Is Organizational Behavior?Zia UddinNo ratings yet
- MA assignment-QUIZ (ONLINE)Document1 pageMA assignment-QUIZ (ONLINE)Zia UddinNo ratings yet
- Answer:: Managerial Accounting Quiz (Online)Document5 pagesAnswer:: Managerial Accounting Quiz (Online)Zia UddinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Kanban Boards: @proofhubDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Kanban Boards: @proofhubZia UddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 12 Exercise - Problems - AnswersDocument5 pagesChapter # 12 Exercise - Problems - AnswersZia UddinNo ratings yet
- Maple Leaf Case StudyDocument30 pagesMaple Leaf Case StudyZia UddinNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 11 - Flexible Budgeting - UETDocument16 pagesCHAPTER - 11 - Flexible Budgeting - UETZia UddinNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 12 - Responsibility Accounting - UETDocument16 pagesCHAPTER - 12 - Responsibility Accounting - UETZia UddinNo ratings yet
- OM#6 - LayoutDocument69 pagesOM#6 - LayoutZia UddinNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 4 What Is Kanban - Muhammad Shoaib 2019-EMBA (Fall) - 004Document10 pagesAssignment # 4 What Is Kanban - Muhammad Shoaib 2019-EMBA (Fall) - 004Zia UddinNo ratings yet
- Alarm InterpretationDocument52 pagesAlarm Interpretationkshalawi100% (1)
- Hose Coupling - WikipediaDocument9 pagesHose Coupling - WikipediaAlberto DiazNo ratings yet
- Burks Series GNB Centrifugal Pump ManualDocument10 pagesBurks Series GNB Centrifugal Pump ManualAna MoraNo ratings yet
- Garlock GYLON Style 3545 Spec Sheet - (NA) 2016-12 enDocument1 pageGarlock GYLON Style 3545 Spec Sheet - (NA) 2016-12 enAndres Rodriguez HerreraNo ratings yet
- Paper - Lufkin - Rod Pumping Deviated WellsDocument14 pagesPaper - Lufkin - Rod Pumping Deviated WellsrolandoNo ratings yet
- Lotus Engineering Software - An Approach To Model-Based DesignDocument20 pagesLotus Engineering Software - An Approach To Model-Based DesignKrish ManglaniNo ratings yet
- Chapa Expandida Mentex e FlatexDocument5 pagesChapa Expandida Mentex e FlatexJonatans SantiagoNo ratings yet
- MT 1440 E3 Operator ManuelDocument138 pagesMT 1440 E3 Operator ManuelEmrah MertyürekNo ratings yet
- Brake Control System: SectionDocument54 pagesBrake Control System: SectionYB MOTOR Nissan - Datsun SpecialistNo ratings yet
- Service Manual SANYANG ATTILA RS-21 EFi 150Document219 pagesService Manual SANYANG ATTILA RS-21 EFi 150lainer chauxNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Bhimani HirenNo ratings yet
- Enfriador Electrico Panel Sec-2001bDocument1 pageEnfriador Electrico Panel Sec-2001braul salinasNo ratings yet
- Guyson Ultrasonic Spare Parts ListDocument1 pageGuyson Ultrasonic Spare Parts ListYoutube For EducationNo ratings yet
- Unimog Techdata U300 Euro5 1209 en PDFDocument2 pagesUnimog Techdata U300 Euro5 1209 en PDFRahmi Elsa DianaNo ratings yet
- Cooling Water Pump Station Optimization Using CFD and Physical Model TestDocument19 pagesCooling Water Pump Station Optimization Using CFD and Physical Model TestRicardo BarrosNo ratings yet
- Pump Sizing With ExercisesDocument25 pagesPump Sizing With ExercisesAkilaJosephNo ratings yet
- G1119 UsDocument212 pagesG1119 UspcrateroNo ratings yet
- Modulo 4 PDFDocument22 pagesModulo 4 PDFYorielBelloNo ratings yet
- ME 333 Final ExamDocument8 pagesME 333 Final ExamHassan Ayub KhanNo ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hours Answer All Questions Maximum: 100 MarksDocument3 pagesTime: 3 Hours Answer All Questions Maximum: 100 MarksAnonymous ZB6qyhD6No ratings yet
- An Analytical Model For The Strength Prediction of Hybrid (Boltedbonded) Composite JointsDocument9 pagesAn Analytical Model For The Strength Prediction of Hybrid (Boltedbonded) Composite Jointskhudhayer1970No ratings yet
- 7060700US-T 6.0 MAF DIR CroisillonDocument56 pages7060700US-T 6.0 MAF DIR CroisillonSan Svake Taste100% (1)
- Pipe Sizing and Pressure Drop CalculationsDocument14 pagesPipe Sizing and Pressure Drop CalculationsArindom100% (1)
- Secure and Reliable, Even Where Lubrication Is Poor: MR-D Double Seal With Diamondface in Bioculture ProductionDocument2 pagesSecure and Reliable, Even Where Lubrication Is Poor: MR-D Double Seal With Diamondface in Bioculture ProductionmunhNo ratings yet
- Erp-Pondasi Kolom Typikal R1aDocument13 pagesErp-Pondasi Kolom Typikal R1aGunawan Prc2020No ratings yet
- BESN Noir P20 TLDocument2 pagesBESN Noir P20 TLjuliushasan2No ratings yet
- The Fan BookDocument316 pagesThe Fan Booksathish kumarNo ratings yet
- Tai Lieu Thiet Ke Dai RangDocument6 pagesTai Lieu Thiet Ke Dai RangCủa Tôi Thần TuợngNo ratings yet
- HT Motor DatasheetDocument62 pagesHT Motor DatasheetShantanu Dutta100% (3)