Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Industrial Water Treatment Chemicals
Industrial Water Treatment Chemicals
Uploaded by
hashir zaman0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views4 pagesHard water contains calcium and magnesium ions that can lead to scaling in pipes and decrease the life of metal pipes. Total dissolved solids and total suspended solids are measures of inorganic and organic particles in water. Acidic water can corrode metal pipes by reacting to form metal salts and hydrogen gas, while basic water reacts with organic compounds. Industrial water should have low scaling and corrosion between a pH of 5.5-6.5. Temperature increases corrosion rates by accelerating chemical reactions, though protective metal oxide layers can form at high pH to decrease corrosion. Common water treatment chemicals used in industries include biocides, scale inhibitors, iron removers, corrosion inhibitors, acids, hypochlorite, and coagul
Original Description:
Original Title
Industrial Water treatment Chemicals
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHard water contains calcium and magnesium ions that can lead to scaling in pipes and decrease the life of metal pipes. Total dissolved solids and total suspended solids are measures of inorganic and organic particles in water. Acidic water can corrode metal pipes by reacting to form metal salts and hydrogen gas, while basic water reacts with organic compounds. Industrial water should have low scaling and corrosion between a pH of 5.5-6.5. Temperature increases corrosion rates by accelerating chemical reactions, though protective metal oxide layers can form at high pH to decrease corrosion. Common water treatment chemicals used in industries include biocides, scale inhibitors, iron removers, corrosion inhibitors, acids, hypochlorite, and coagul
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views4 pagesIndustrial Water Treatment Chemicals
Industrial Water Treatment Chemicals
Uploaded by
hashir zamanHard water contains calcium and magnesium ions that can lead to scaling in pipes and decrease the life of metal pipes. Total dissolved solids and total suspended solids are measures of inorganic and organic particles in water. Acidic water can corrode metal pipes by reacting to form metal salts and hydrogen gas, while basic water reacts with organic compounds. Industrial water should have low scaling and corrosion between a pH of 5.5-6.5. Temperature increases corrosion rates by accelerating chemical reactions, though protective metal oxide layers can form at high pH to decrease corrosion. Common water treatment chemicals used in industries include biocides, scale inhibitors, iron removers, corrosion inhibitors, acids, hypochlorite, and coagul
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Industrial water
Acid water is corrosive in nature
Hard water contains dissolved Ca and Mg salts, due to presence of them the boiling
point of water becomes high, lamination decreases and flow disturbs.
Hard water is water that contains calcium or magnesium mineral ions often in the form
of carbonate. These ions do not pose any health threat, but they can engage in reactions
that leave insoluble mineral deposits. Hard water mineral deposits, or scaling, is the
precipitation of minerals which form lime scale. Scale can clog pipes and can decrease
the life of metal pipes.
High TDS, more hardness, more scaling & more chances of corrosion at high temp.
Hardness in water can be removed by Lime-soda, Zeolite & Ion exchange methods etc.
Soft water doesn’t contain hardness producing Ca and Mg ions but contain Na ions and
microorganism.
Deionsed water doesn’t contain any ions including hardness causing cations but contain
microorganism.
Distilled water doesn’t contain any ions and microorganism since distilled water is
obtained by condensing the vapors of boiling water.
Water has high heat capacity and thermal conductivity than air therefore water can
exchange more heat than air.
Total dissolved solids (TDS) are inorganic salts and small amounts of organic matter
present in solution in water. Whereas, Total Suspended Solids (TSS) are solids
in water that can be trapped by a filter.
Acidic water can react with metal produce a metal salt and hydrogen gas bubbles which
can be dangerous if gas is trapped inside pipe then it can pressurized metal pipe to blow
up.
Base water especially reacts with organic compounds.
Industrial water should have less scaling and corrosion
Industrial water pH range should be 5.5-6.5.
More acidity of water more is the corrosion. But if the pH is very low the hydrogen ion
liberates hydrogen gas instead of water.
Corrosion due to high pH is more dangerous than acidic corrosion as it can cause cracks
in the equipment (a phenomenon known as Caustic embrittlement). The tubes of the
overhead exchangers will become like dry wood and break into large pieces which are
extremely difficult to fix.
Corrosion slows down due to the presence of oxides/hydroxides on the surface, forming
the passive layer (film).
Immunity zone, where the metal does not react with the environment, or react is such a
small rate that any change into oxide is negligible.
Temperature accelerates all the processes involved in corrosion. One would expect that
the corrosion rate steadily increases with temperature. Since the corrosion rate was
raised due to the oxygen diffusion on the metal surface, therefore, at low pH protective
films do not occur. The situation changes markedly when solubility of salt was exceeded,
typically at high pH. In that case, increased temperature accelerates rapidly the kinetics
of precipitation and protective film formation, decreasing the corrosion rate. The peak
in the corrosion rate was usually seen between 50 and 80C depending on water
chemistry and dynamic condition.
Magnetite (Fe3O4) is called saturated iron oxide, it is a chemical of iron and oxygen thus
it is an oxide. If there is not enough oxygen in water to finalize the oxidation, then
magnetite (Fe3O4) forms, instead of more common rust (Fe2O3). Magnetite is black
layer deposited on metallic surface (metal pipe). This black layer make the pipe inert
against new corrosion, the black layer is almost like a passivation. This black layer
doesn’t let MIC (microbiologically induced corrosion which harm to steel surfaces. Once
magnetite is exposed to enough oxygen, the black layer disappears after a short time and
forms normal rust again.
Red oxide is used in paints and primers as a rust preventive. If traces of rust are present
on an iron surface, red oxide paint will adhere (stick), because it interacts with the
surface by forming chemical bonds. Other methods are Tin plating, Galvanization (Zinc
plating), Coating, Enameling and Copper plating
Passivation is a technique of a light coat of a protective material, such as metal oxide, to
create a shell against corrosion.
Sodium Nitrite use as a Corrosion Inhibitor for Mild Steel (MS).
BIOCIDE act against bacteria and used to control other micro-organisms such as fungi
in water.
Iron level in water system should be <1.50ppm in MS pipes.
Dispersants Effectively disperses iron, clay, and zinc deposits, and is used extensively
in cooling water systems.
Sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) normally called as HYPO is a compound that can be
effectively used for water purification. It is used on a large scale for surface purification,
bleaching, odor removal and water disinfection.
Due to the presence of caustic soda in sodium hypo chlorite, the pH of the water is
increased. When sodium hypo chlorite dissolves in water, two substances form, which
play a role in for oxidation and disinfection. These are hypochlorous acid (HOCl) and
the less active hypochlorite ion (OCl-). The pH of the water determines how much
hypochlorous acid is formed. While sodium hypochlorite is used, hydrochloric acid
(HCl) is used to lower the pH. Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) can be used as an alternative for
acetic acid. Less harmful gasses are produced when sulfuric acid is used. Sulfuric acid is
a strong acid that strongly reacts with bases and that is very corrosive
Hypochlorite can be used to prevent algae and shellfish growth in cooling towers.
MAXIGUARD (SCALE & CORROSION INHIBITOR)
MAXIGARD may be used with waters that have hardness contamination, provided the
total hardness levels are less than 170 ppm or as otherwise recommended by the engine
manufacturer, whichever is less. The chloride level in the cooling system should be limited
to 100 ppm or as otherwise recommended by the engine manufacturer, whichever is less.
Benefits
Protects against variable metal corrosion
Reduces corrosion due to cavitation
Maintains heat transfer effectiveness
Helps prevent overheating caused by sludge and mineral scale deposits Reduces
cleaning and maintenance costs
Stabilizes cooling water pH
Chemical products name used for water treatment in industries by different companies.
R-25 (biocide)
R-95 (scale & corrosion inhibitor)
Aquaprime 808 (iron removal)
Aquaprime 2005, Maxi guard (anti corrosion) (maintain nitrate level and prevent
oxidation)
R-25, R-95, R-3100, HYPO (uses to decreases scaling & TDS)
H2SO4 (uses to maintain PH)
You might also like
- Synthesis of Pentaaminechlorocobalt (III) ChlorideDocument7 pagesSynthesis of Pentaaminechlorocobalt (III) Chloridecrybaby75% (12)
- Gravimetric Determination of Nickel Using Dimethylglyoxime GokulDocument4 pagesGravimetric Determination of Nickel Using Dimethylglyoxime GokulHarshilGarg88% (8)
- Handbook of Industrial Water TreatmentDocument6 pagesHandbook of Industrial Water TreatmentArunish Mangla0% (2)
- Acid CorrosionDocument26 pagesAcid CorrosionTamer Abd ElrasoulNo ratings yet
- Project XDocument14 pagesProject XMRIDUL DESAINo ratings yet
- C3 PDFDocument39 pagesC3 PDFAbdulsalam MaaNo ratings yet
- Rougin GDocument7 pagesRougin GSanjay Singh MewarNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Corrosion: 8.1.1 Environmental Factors and Their EffectsDocument6 pagesAtmospheric Corrosion: 8.1.1 Environmental Factors and Their EffectsOvaid MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Rouging in Pharmaceutical Water Systems (IVT 2015)Document6 pagesRouging in Pharmaceutical Water Systems (IVT 2015)julianpellegrini860No ratings yet
- CorrosionDocument9 pagesCorrosionMygroup 5544No ratings yet
- InhibitorDocument33 pagesInhibitorMohd SyazwanNo ratings yet
- Water PurificationDocument56 pagesWater Purificationniloykumarnandi01No ratings yet
- CorosionDocument15 pagesCorosionHazel PiniliNo ratings yet
- Boiler Water Treatment-6 HrsDocument13 pagesBoiler Water Treatment-6 HrsRahul JoshiNo ratings yet
- Why Is Rusting An Undesirable PhenomenonDocument4 pagesWhy Is Rusting An Undesirable PhenomenonVon Jezzrel Jumao-asNo ratings yet
- LimitationsDocument10 pagesLimitationsCamaya RumbleNo ratings yet
- Discussion of RustingDocument15 pagesDiscussion of RustingShamil Azha Ibrahim0% (1)
- Corrosion in MetalsDocument5 pagesCorrosion in MetalsPratama ZetoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CorrosionDocument74 pagesIntroduction To CorrosionAmrinder BhartiNo ratings yet
- Boiler Water Treatment and TestDocument56 pagesBoiler Water Treatment and TestRayhaan Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Why Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandWhy Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- To Study The Effect of Metal Coupling On Rate of CorrosionDocument13 pagesTo Study The Effect of Metal Coupling On Rate of CorrosionHimanshu54% (13)
- To Study The Effect of Metal Coupling On The Rusting of Iron.Document12 pagesTo Study The Effect of Metal Coupling On The Rusting of Iron.Heaven Pal100% (1)
- Rusting of Iron - Explanation, Chemical Reaction, PreventionDocument3 pagesRusting of Iron - Explanation, Chemical Reaction, PreventiondikshaNo ratings yet
- Rusting of IrDocument14 pagesRusting of IrRohit MishraNo ratings yet
- R 482Document9 pagesR 482Andre Osmond Nugraha SimorangkirNo ratings yet
- Causes of CorrosionDocument5 pagesCauses of CorrosionmeshahanNo ratings yet
- Why Is TSPDocument4 pagesWhy Is TSPAbhi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Course Work 2Document6 pagesCorrosion Course Work 2Charles NtaNo ratings yet
- Influencia Del Inhibidor en Decapado QuimicoDocument2 pagesInfluencia Del Inhibidor en Decapado QuimicodavmedclNo ratings yet
- Corrosion of PipesDocument22 pagesCorrosion of PipesSonali JahagirdarNo ratings yet
- RustDocument6 pagesRustanon_86163638No ratings yet
- Acid Mine Drainage: Kantilal Meena Roll No. 13154007 (IDD) 4 Year (8 Semester)Document25 pagesAcid Mine Drainage: Kantilal Meena Roll No. 13154007 (IDD) 4 Year (8 Semester)abhiramNo ratings yet
- S Block NcertDocument7 pagesS Block NcertStock CheckNo ratings yet
- CW Treatment in HWPDocument6 pagesCW Treatment in HWPSivakumar NagarathinamNo ratings yet
- CorrosionDocument33 pagesCorrosionirfanlarikhotmailcom100% (1)
- Aeration and Water SofteningDocument8 pagesAeration and Water SofteningKarl TimtimNo ratings yet
- Amtec Guide To CorrosionDocument16 pagesAmtec Guide To CorrosionsgttomasNo ratings yet
- What Is Corrosion ES 022017Document5 pagesWhat Is Corrosion ES 022017sergioNo ratings yet
- EPPWT HandoutDocument47 pagesEPPWT HandoutBhargav ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- CorrosionDocument2 pagesCorrosionM Abdullah Khalid ArvgsmNo ratings yet
- Marine CorrosionDocument10 pagesMarine CorrosionAngel DivyaNo ratings yet
- SchoolDocument17 pagesSchoolEjaz ul Haq kakarNo ratings yet
- Rusting of IronDocument11 pagesRusting of Ironharsh100% (1)
- Training Cooling Tower Treatment ChemicalsDocument127 pagesTraining Cooling Tower Treatment ChemicalsparagNo ratings yet
- Passivation and De-Passivation of Mild Steel SampleDocument3 pagesPassivation and De-Passivation of Mild Steel SampleRaza AliNo ratings yet
- Corrosion: by Mrs - Rajeshree PanigrahiDocument80 pagesCorrosion: by Mrs - Rajeshree PanigrahiRajeshree PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Importance of Sequestering Agent in Textile ProcessingDocument2 pagesImportance of Sequestering Agent in Textile ProcessingKushagradhi DebnathNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Sawinder Singh Sr. Manager (Prod.)Document36 pagesPresented By: Sawinder Singh Sr. Manager (Prod.)JitendraSinghNo ratings yet
- CMT555 - Alteration of EnvironmentDocument10 pagesCMT555 - Alteration of EnvironmentLina LynxNo ratings yet
- Potassium: Physical PropertiesDocument6 pagesPotassium: Physical PropertiesJihad Ibrahim AYNo ratings yet
- Corrosion of Carbon SteelDocument3 pagesCorrosion of Carbon Steelvandanak_mechNo ratings yet
- Rusting of IronDocument19 pagesRusting of IronGokulakrishnan JawaharNo ratings yet
- Influence of The Inhibitor On The Chemical Pickling of MetalsDocument2 pagesInfluence of The Inhibitor On The Chemical Pickling of MetalsdavmedclNo ratings yet
- ChemistrypracticalDocument16 pagesChemistrypractical8rg48v4zgfNo ratings yet
- Corrosion PDFDocument13 pagesCorrosion PDFDiwakar NigamNo ratings yet
- Boiler Water TreatmentDocument80 pagesBoiler Water TreatmentRAJINDER HANSNo ratings yet
- Technical Bulletin: Pickling Methods For Duplex Stainless SteelDocument3 pagesTechnical Bulletin: Pickling Methods For Duplex Stainless SteelPhoenix KukuruyukNo ratings yet
- Tarnish and Corrosion: DefinitionsDocument3 pagesTarnish and Corrosion: DefinitionsangelrasNo ratings yet
- Skip To ContentDocument66 pagesSkip To ContentnarutoNo ratings yet
- Acids - Bases & Salts (S.2 SJB)Document35 pagesAcids - Bases & Salts (S.2 SJB)Maku MichaelNo ratings yet
- Boiler Phosphate TreatmentDocument4 pagesBoiler Phosphate TreatmentSilvina C. Gómez Correa0% (1)
- FYP RUBRICS Final Evaluation (BSC Electrical)Document5 pagesFYP RUBRICS Final Evaluation (BSC Electrical)hashir zamanNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower DetailsDocument3 pagesCooling Tower Detailshashir zamanNo ratings yet
- v5 S23 ClassesDocument52 pagesv5 S23 Classeshashir zamanNo ratings yet
- Lab Final ExamDocument1 pageLab Final Examhashir zamanNo ratings yet
- FYP Notification1Document1 pageFYP Notification1hashir zamanNo ratings yet
- StandardsDocument2 pagesStandardshashir zamanNo ratings yet
- Attendance SheetDocument5 pagesAttendance Sheethashir zamanNo ratings yet
- v5 S23 TeachersDocument43 pagesv5 S23 Teachershashir zamanNo ratings yet
- InfoDocument4 pagesInfohashir zamanNo ratings yet
- DC LinkDocument1 pageDC Linkhashir zamanNo ratings yet
- IGBT With FWDDocument2 pagesIGBT With FWDhashir zamanNo ratings yet
- HU - Approved - Bloom's Taxonomy - Affective Domain and Psychomotor DomainDocument9 pagesHU - Approved - Bloom's Taxonomy - Affective Domain and Psychomotor Domainhashir zamanNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere and Plasma InformationDocument3 pagesAtmosphere and Plasma Informationhashir zamanNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Motor DetailDocument1 page3 Phase Motor Detailhashir zamanNo ratings yet
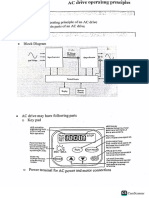
- VFD Lab ManualDocument74 pagesVFD Lab Manualhashir zamanNo ratings yet
- FYP Report Template v6 UpdatedDocument19 pagesFYP Report Template v6 Updatedhashir zamanNo ratings yet
- Outcome Based Education (OBE)Document51 pagesOutcome Based Education (OBE)hashir zamanNo ratings yet
- Attendance SheetDocument7 pagesAttendance Sheethashir zamanNo ratings yet
- Faculty Goals 2022-23 M Hashir Zaman 1005156Document25 pagesFaculty Goals 2022-23 M Hashir Zaman 1005156hashir zamanNo ratings yet
- FYP Proposal FormDocument8 pagesFYP Proposal Formhashir zamanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document3 pagesUnit 2hashir zamanNo ratings yet
- Meaning of Adminstration ActionDocument2 pagesMeaning of Adminstration Actionhashir zamanNo ratings yet
- NHA67346 ERMS NetDocument28 pagesNHA67346 ERMS Nethashir zamanNo ratings yet
- John DoeDocument3 pagesJohn Doehashir zamanNo ratings yet
- P L D 1990 Supreme Court 1051Document7 pagesP L D 1990 Supreme Court 1051hashir zamanNo ratings yet
- PHYSICALDocument11 pagesPHYSICALhashir zamanNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Allama Iqbal: Insia AqeelDocument1 pageMuhammad Allama Iqbal: Insia Aqeelhashir zamanNo ratings yet
- Group 2 RababDocument9 pagesGroup 2 Rababhashir zamanNo ratings yet
- Annexure 2 - A Lab Assessment - OBE - BasedDocument3 pagesAnnexure 2 - A Lab Assessment - OBE - Basedhashir zamanNo ratings yet
- 2022 S C M R 1131Document4 pages2022 S C M R 1131hashir zamanNo ratings yet
- Symbols and Charges-Monoatomic IonsDocument20 pagesSymbols and Charges-Monoatomic Ionsjon_kasilagNo ratings yet
- What Is 30c8 SteelDocument3 pagesWhat Is 30c8 SteelSanjay MehtaNo ratings yet
- Basic Atomic Structure Worksheet ANSWERSDocument2 pagesBasic Atomic Structure Worksheet ANSWERSMiss RonaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Quiz AnswerDocument8 pagesChemistry Form 4 Quiz Answerkhangsiean89No ratings yet
- PTFE Chemical Compatibility Chart: Product TF1570 TF1580 TF1590 Teadit 24SH Teadit 24B TF 1510Document11 pagesPTFE Chemical Compatibility Chart: Product TF1570 TF1580 TF1590 Teadit 24SH Teadit 24B TF 1510tomasykNo ratings yet
- fourtyYearsOfcgiInChina PDFDocument7 pagesfourtyYearsOfcgiInChina PDFfdcarazoNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Chemistry Question PaperDocument4 pagesGrade 8 Chemistry Question PaperAly MaknojiyaNo ratings yet
- Anglais ScientifiqueDocument4 pagesAnglais Scientifiqueali BourenaneNo ratings yet
- FertilizerDocument14 pagesFertilizerrockyrrNo ratings yet
- Elements and CompoundsDocument8 pagesElements and CompoundsJerry De Leon TaayNo ratings yet
- Handbook Welding 6Document59 pagesHandbook Welding 6Eman HassanNo ratings yet
- Astm B456Document12 pagesAstm B456You UZBNo ratings yet
- Hard Soft Acid Base TheoryDocument41 pagesHard Soft Acid Base Theory김영철No ratings yet
- Corrosion: Standard Grade ChemistryDocument4 pagesCorrosion: Standard Grade ChemistryStashy LoteNo ratings yet
- Copper Mining and Its Alloys ProcessDocument7 pagesCopper Mining and Its Alloys ProcessBORUTO ANIMEZONENo ratings yet
- Demo Stiochiometry Question PaperDocument7 pagesDemo Stiochiometry Question PaperShilpy UmapatiNo ratings yet
- 02-Acids, Base, Salts Class 10 WorksheetDocument36 pages02-Acids, Base, Salts Class 10 WorksheetSiddharth SreeKumarNo ratings yet
- 6005 Aluminum Sheet SuppliersDocument15 pages6005 Aluminum Sheet Supplierssanghvi overseas incNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Assignment 3Document2 pagesChapter 6 - Assignment 3Arielle Emperador De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- R W C Technology BookDocument106 pagesR W C Technology BookScott TrainorNo ratings yet
- 10.3 Balancing by Half Reaction 2020Document30 pages10.3 Balancing by Half Reaction 2020Michelle NgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 Aqueous Ionic Solutions HWDocument6 pagesChapter 18 Aqueous Ionic Solutions HWAlejo CardoNo ratings yet
- MCQs 9th Class Ch#01Document5 pagesMCQs 9th Class Ch#01Muhammad yousafziaNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 Chemical Analysis Revision MatDocument4 pagesTopic 8 Chemical Analysis Revision MatMireiaNo ratings yet
- Astm A101 PDFDocument8 pagesAstm A101 PDFtrjithinrajNo ratings yet
- GB T 700-2006-Carbon Structural Steels-En&CNDocument22 pagesGB T 700-2006-Carbon Structural Steels-En&CNNespak P&M100% (1)
- Survivor Science - Chem TimeDocument2 pagesSurvivor Science - Chem TimeraiderphysicalscienceNo ratings yet
- science-9-lesson-4-nlc-Document19 pagesscience-9-lesson-4-nlc-Linden EvangelistaNo ratings yet