Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 viewsIssues
Issues
Uploaded by
Ian BergadoEpithelial tissues form protective boundaries and allow for absorption and secretion. Connective tissues bind other tissues together and provide storage and defense. Muscular tissues enable movement and support structures. Nervous tissues transmit electrical signals to allow for communication in the nervous system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Four Types of Tissue: Austin Sebastian Stem 12-2 HeaDocument5 pagesFour Types of Tissue: Austin Sebastian Stem 12-2 HeaAustin SebastianNo ratings yet
- Human Body OrganizationDocument11 pagesHuman Body OrganizationCay C. CordovaNo ratings yet
- That Means That Underlying The Cells That Are The Cellular Component of The Epithelial TissueDocument3 pagesThat Means That Underlying The Cells That Are The Cellular Component of The Epithelial TissueDivine HernandezNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue Hand-Out Bio 101Document3 pagesAnimal Tissue Hand-Out Bio 101Amor Panopio MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Specificatio N: Tissues: Epithelial: Simple (CuboidalDocument22 pagesSpecificatio N: Tissues: Epithelial: Simple (CuboidalFatma AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Human TissuesDocument7 pagesHuman Tissuesapi-269312030No ratings yet
- Exercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreDocument9 pagesExercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreMaria MarmitaNo ratings yet
- Types of Animal TissueDocument5 pagesTypes of Animal TissueDebiprasad GhoshNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReportingDocument8 pagesAnaphy ReportingRushyl Angela FaeldanNo ratings yet
- Nselec TissueDocument6 pagesNselec TissueClaire funtilarNo ratings yet
- Cell: Vertebrate Body OrganizationDocument11 pagesCell: Vertebrate Body OrganizationSyuri MustikaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Types of Animal TissuesDocument12 pagesFundamental Types of Animal TissuesBriana Franshay Aguilar SiotingNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues and Human TissuesDocument8 pagesAnimal Tissues and Human Tissuesismail.hassanineNo ratings yet
- ReferencesDocument2 pagesReferenceswilson chandigaNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument17 pagesAnimal TissuesMuskan Shree100% (1)
- Animal TissueDocument32 pagesAnimal TissueIan Kerby Sollano100% (1)
- Lesson Proper For Week 7Document5 pagesLesson Proper For Week 7Merlyn NavarroNo ratings yet
- 1 Cell Biology IntroductionDocument2 pages1 Cell Biology IntroductionMariam AymanNo ratings yet
- Body Tissues: Tissue Matrix MuscleDocument8 pagesBody Tissues: Tissue Matrix Muscle9. Hoàng Mai ChiNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue ReviewerDocument4 pagesAnimal Tissue ReviewerAli NamialusNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument3 pagesTissuebuliemissy89No ratings yet
- Gebbs PDFDocument44 pagesGebbs PDFsshoaib346No ratings yet
- TissuesDocument33 pagesTissuesAnonymous imF0MCd9UNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues 1. EpithelialDocument3 pagesAnimal Tissues 1. EpithelialRogeimar Claire MangomayaoNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument13 pagesAnimal TissuesYudatami TiaraNo ratings yet
- Tissues Level OrganizationDocument60 pagesTissues Level OrganizationHilman YusriNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument4 pagesTissuesJaveria ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Cell Types and ModificationDocument68 pagesCell Types and ModificationHannah VillocenoNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 5: Body Covering and ProtectionDocument8 pagesAssignment # 5: Body Covering and ProtectionJefferNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresDocument58 pagesLesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresPhoenixNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument1 pageAnimal TissuesIan BergadoNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Soft Tissue Mechanics The Soft Tissues of The Body:: Kripa's Notes.Document14 pagesUnit Iv Soft Tissue Mechanics The Soft Tissues of The Body:: Kripa's Notes.Kripa NNo ratings yet
- Httpseducacionadistancia - Juntadeandalucia.escentroscadizpluginfile - Php671451mod resourcecontent2UNIT2032C.20ORGANIDocument38 pagesHttpseducacionadistancia - Juntadeandalucia.escentroscadizpluginfile - Php671451mod resourcecontent2UNIT2032C.20ORGANIjuanfernandezhormigaNo ratings yet
- Tissues Part 2Document4 pagesTissues Part 2Monika Mehan100% (1)
- Tissue Repair 2023PH17Document11 pagesTissue Repair 2023PH172023ph17No ratings yet
- Answer Sheet For ActivitiesDocument7 pagesAnswer Sheet For ActivitiesAlanah JaneNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument61 pagesStructural Organisation in AnimalsGanesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Is Cell Important For HumansDocument2 pagesIs Cell Important For HumansniallevetriscaNo ratings yet
- Title of The Activity: Connective Tissue Objectives:: Ground SubstanceDocument3 pagesTitle of The Activity: Connective Tissue Objectives:: Ground SubstanceKristine PangahinNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument12 pagesImmune SystemCasper Irra Marcos100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The NailDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Nailtaniannet latorreNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Study QuestionsDocument13 pagesModule 1 Study QuestionsLuna AstanehNo ratings yet
- Biology 25: Human Biology: Prof. Gonsalves Los Angeles City College Loosely Based On Mader's Human Biology, 7 EditionDocument42 pagesBiology 25: Human Biology: Prof. Gonsalves Los Angeles City College Loosely Based On Mader's Human Biology, 7 EditionRhaine EstebanNo ratings yet
- 01 Animal TissueDocument8 pages01 Animal TissueRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Abella, Franz Karl - Zoology Reviewer Pt. 1Document4 pagesAbella, Franz Karl - Zoology Reviewer Pt. 1Franz AbellaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument1 pageEpithelial TissueSamuel MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Tissues Animal Tissues: Tissue Is A Cellular Organizational Level Intermediate Between Cells andDocument5 pagesChapter-6 Tissues Animal Tissues: Tissue Is A Cellular Organizational Level Intermediate Between Cells andMonika MehanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology Study Guide Test 1Document15 pagesAnatomy Physiology Study Guide Test 1Jennifer BrownNo ratings yet
- 1-Epithelial Tissue 2-Connective Tissue 3-Muscle Tissue 4-Nervous Tissues Epithelial TissueDocument8 pages1-Epithelial Tissue 2-Connective Tissue 3-Muscle Tissue 4-Nervous Tissues Epithelial TissuekawiNo ratings yet
- Types of Cells Types of TissuesDocument1 pageTypes of Cells Types of TissuesNicole Audrey Ignacio DuqueNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Notes 2022Document3 pagesAnatomy Notes 2022Julianne LinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology LabDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Labشهد إياد0% (1)
- Why Human Beings Are Considered Complex Organisms Group 5Document37 pagesWhy Human Beings Are Considered Complex Organisms Group 5Nuraini Zul100% (3)
- M 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument39 pagesM 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in Animalsamarendrar87No ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 1 MarkDocument4 pagesLaboratory Activity 1 MarkJerome JanNo ratings yet
- Nadiyah Farhah Salsabila - Animal TissueDocument2 pagesNadiyah Farhah Salsabila - Animal TissueNadiyah SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Anatomof. T1 Reconocim. 1.3.2 1.4Document7 pagesAnatomof. T1 Reconocim. 1.3.2 1.4salchicha pokemonNo ratings yet
- 3 Animal Tissues Structure and FunctionDocument16 pages3 Animal Tissues Structure and FunctionIce ShadowNo ratings yet
- TX Bio Ch30Document48 pagesTX Bio Ch30Mario Alberto Mora OrtizNo ratings yet
Issues
Issues
Uploaded by
Ian Bergado0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageEpithelial tissues form protective boundaries and allow for absorption and secretion. Connective tissues bind other tissues together and provide storage and defense. Muscular tissues enable movement and support structures. Nervous tissues transmit electrical signals to allow for communication in the nervous system.
Original Description:
Animals
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEpithelial tissues form protective boundaries and allow for absorption and secretion. Connective tissues bind other tissues together and provide storage and defense. Muscular tissues enable movement and support structures. Nervous tissues transmit electrical signals to allow for communication in the nervous system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageIssues
Issues
Uploaded by
Ian BergadoEpithelial tissues form protective boundaries and allow for absorption and secretion. Connective tissues bind other tissues together and provide storage and defense. Muscular tissues enable movement and support structures. Nervous tissues transmit electrical signals to allow for communication in the nervous system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
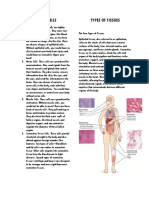
Animal Tissues
1. Describe the functions of each type of tissues.
Epithelial Tissues
Epithelium forms boundaries between different environments, so nearly all
substances must pass through it. As an interface tissue, epithelium acts in many ways,
including: Protection against radiation, desiccation, toxins, and physical trauma. The
digestive tract lining absorbs substances in distinct ways. Control and excretion of chemicals
between underlying tissues and the body cavity. Glandular epithelium secretes hormones
into the bloodstream. Ducts deliver sweat, mucus, enzymes, and other products. The
detection of sensation.
Connective Tissue
The collagen fiber microfibrils and elastin bind bones and other tissues together. The
fat they store in their tissues is classified as adipose. They help in repairing tissues. They
prevent the organs from being damaged by mechanical shocks. The organs also help in
defense. Additionally, they allow organs to resist stretching and tearing forces.
Muscular Tissue
It helps in movement and locomotion. It supports the bones and other structures. It is
responsible for peristalsis and parturition.
Nervous Tissues
The transmission of electric signals across the tissue forms the nervous system’s
communication network. Gray matter, which contains the synapses, is essential for
processing information in the CNS. The white matter in the CNS, composed of myelinated
axons, facilitates and connects gray matter areas. The action potential nerve impulses are
carried by nerve tissue containing myelinated axon bundles.
You might also like
- Four Types of Tissue: Austin Sebastian Stem 12-2 HeaDocument5 pagesFour Types of Tissue: Austin Sebastian Stem 12-2 HeaAustin SebastianNo ratings yet
- Human Body OrganizationDocument11 pagesHuman Body OrganizationCay C. CordovaNo ratings yet
- That Means That Underlying The Cells That Are The Cellular Component of The Epithelial TissueDocument3 pagesThat Means That Underlying The Cells That Are The Cellular Component of The Epithelial TissueDivine HernandezNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue Hand-Out Bio 101Document3 pagesAnimal Tissue Hand-Out Bio 101Amor Panopio MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Specificatio N: Tissues: Epithelial: Simple (CuboidalDocument22 pagesSpecificatio N: Tissues: Epithelial: Simple (CuboidalFatma AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Human TissuesDocument7 pagesHuman Tissuesapi-269312030No ratings yet
- Exercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreDocument9 pagesExercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreMaria MarmitaNo ratings yet
- Types of Animal TissueDocument5 pagesTypes of Animal TissueDebiprasad GhoshNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReportingDocument8 pagesAnaphy ReportingRushyl Angela FaeldanNo ratings yet
- Nselec TissueDocument6 pagesNselec TissueClaire funtilarNo ratings yet
- Cell: Vertebrate Body OrganizationDocument11 pagesCell: Vertebrate Body OrganizationSyuri MustikaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Types of Animal TissuesDocument12 pagesFundamental Types of Animal TissuesBriana Franshay Aguilar SiotingNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues and Human TissuesDocument8 pagesAnimal Tissues and Human Tissuesismail.hassanineNo ratings yet
- ReferencesDocument2 pagesReferenceswilson chandigaNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument17 pagesAnimal TissuesMuskan Shree100% (1)
- Animal TissueDocument32 pagesAnimal TissueIan Kerby Sollano100% (1)
- Lesson Proper For Week 7Document5 pagesLesson Proper For Week 7Merlyn NavarroNo ratings yet
- 1 Cell Biology IntroductionDocument2 pages1 Cell Biology IntroductionMariam AymanNo ratings yet
- Body Tissues: Tissue Matrix MuscleDocument8 pagesBody Tissues: Tissue Matrix Muscle9. Hoàng Mai ChiNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue ReviewerDocument4 pagesAnimal Tissue ReviewerAli NamialusNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument3 pagesTissuebuliemissy89No ratings yet
- Gebbs PDFDocument44 pagesGebbs PDFsshoaib346No ratings yet
- TissuesDocument33 pagesTissuesAnonymous imF0MCd9UNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues 1. EpithelialDocument3 pagesAnimal Tissues 1. EpithelialRogeimar Claire MangomayaoNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument13 pagesAnimal TissuesYudatami TiaraNo ratings yet
- Tissues Level OrganizationDocument60 pagesTissues Level OrganizationHilman YusriNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument4 pagesTissuesJaveria ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Cell Types and ModificationDocument68 pagesCell Types and ModificationHannah VillocenoNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 5: Body Covering and ProtectionDocument8 pagesAssignment # 5: Body Covering and ProtectionJefferNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresDocument58 pagesLesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresPhoenixNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument1 pageAnimal TissuesIan BergadoNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Soft Tissue Mechanics The Soft Tissues of The Body:: Kripa's Notes.Document14 pagesUnit Iv Soft Tissue Mechanics The Soft Tissues of The Body:: Kripa's Notes.Kripa NNo ratings yet
- Httpseducacionadistancia - Juntadeandalucia.escentroscadizpluginfile - Php671451mod resourcecontent2UNIT2032C.20ORGANIDocument38 pagesHttpseducacionadistancia - Juntadeandalucia.escentroscadizpluginfile - Php671451mod resourcecontent2UNIT2032C.20ORGANIjuanfernandezhormigaNo ratings yet
- Tissues Part 2Document4 pagesTissues Part 2Monika Mehan100% (1)
- Tissue Repair 2023PH17Document11 pagesTissue Repair 2023PH172023ph17No ratings yet
- Answer Sheet For ActivitiesDocument7 pagesAnswer Sheet For ActivitiesAlanah JaneNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument61 pagesStructural Organisation in AnimalsGanesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Is Cell Important For HumansDocument2 pagesIs Cell Important For HumansniallevetriscaNo ratings yet
- Title of The Activity: Connective Tissue Objectives:: Ground SubstanceDocument3 pagesTitle of The Activity: Connective Tissue Objectives:: Ground SubstanceKristine PangahinNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument12 pagesImmune SystemCasper Irra Marcos100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The NailDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Nailtaniannet latorreNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Study QuestionsDocument13 pagesModule 1 Study QuestionsLuna AstanehNo ratings yet
- Biology 25: Human Biology: Prof. Gonsalves Los Angeles City College Loosely Based On Mader's Human Biology, 7 EditionDocument42 pagesBiology 25: Human Biology: Prof. Gonsalves Los Angeles City College Loosely Based On Mader's Human Biology, 7 EditionRhaine EstebanNo ratings yet
- 01 Animal TissueDocument8 pages01 Animal TissueRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Abella, Franz Karl - Zoology Reviewer Pt. 1Document4 pagesAbella, Franz Karl - Zoology Reviewer Pt. 1Franz AbellaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument1 pageEpithelial TissueSamuel MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Tissues Animal Tissues: Tissue Is A Cellular Organizational Level Intermediate Between Cells andDocument5 pagesChapter-6 Tissues Animal Tissues: Tissue Is A Cellular Organizational Level Intermediate Between Cells andMonika MehanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology Study Guide Test 1Document15 pagesAnatomy Physiology Study Guide Test 1Jennifer BrownNo ratings yet
- 1-Epithelial Tissue 2-Connective Tissue 3-Muscle Tissue 4-Nervous Tissues Epithelial TissueDocument8 pages1-Epithelial Tissue 2-Connective Tissue 3-Muscle Tissue 4-Nervous Tissues Epithelial TissuekawiNo ratings yet
- Types of Cells Types of TissuesDocument1 pageTypes of Cells Types of TissuesNicole Audrey Ignacio DuqueNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Notes 2022Document3 pagesAnatomy Notes 2022Julianne LinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology LabDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Labشهد إياد0% (1)
- Why Human Beings Are Considered Complex Organisms Group 5Document37 pagesWhy Human Beings Are Considered Complex Organisms Group 5Nuraini Zul100% (3)
- M 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument39 pagesM 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in Animalsamarendrar87No ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 1 MarkDocument4 pagesLaboratory Activity 1 MarkJerome JanNo ratings yet
- Nadiyah Farhah Salsabila - Animal TissueDocument2 pagesNadiyah Farhah Salsabila - Animal TissueNadiyah SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Anatomof. T1 Reconocim. 1.3.2 1.4Document7 pagesAnatomof. T1 Reconocim. 1.3.2 1.4salchicha pokemonNo ratings yet
- 3 Animal Tissues Structure and FunctionDocument16 pages3 Animal Tissues Structure and FunctionIce ShadowNo ratings yet
- TX Bio Ch30Document48 pagesTX Bio Ch30Mario Alberto Mora OrtizNo ratings yet