Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GENERAL MATHEMATICS Reviewer Note #2
GENERAL MATHEMATICS Reviewer Note #2
Uploaded by
Ristan RectoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GENERAL MATHEMATICS Reviewer Note #2
GENERAL MATHEMATICS Reviewer Note #2
Uploaded by
Ristan RectoCopyright:
Available Formats
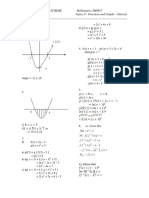
GENERAL Step 2 (4points): f(x) → f-1(x)
1. f(x) = {(1, 3), (3,1), (7,2)} ← One to one Function
MATHEMATICS F
E
f(x) = {(3, 1), (1,3), (2,1)} ✓
Module 5.2: Exponential Function
2. f(x) = {(1, 3), (3, 1), (1, 2)}
D
f-1 doesn’t exist
F(x) = 2 3x+1 C
A B
f(x) = 2x+3
Step 1 (6 points)
1. y = 2x+3
x -2 -1 0 1 2 3
2. x = 2y+3
f(x) 0.03125 0.25 2 16 128 1024
3. 2y = -x+3
or y
Step 3 (5 points) -2 -2
Let x = -2 Let x = -1 Let x = 0 4. f-1 = x-3
f(x) = 23(-2)+1 f(x) = 23(-1)+1 f(x) = 23(0)+1
f(x) = 2-6+1 f(x) = 2-3+1 f(x) = 20+1 Domain: {x|x ∈ ℝ} / (-∞, +∞) 2
f(x) = 2-5 f(x) = 2-2 f(x) = 21
f(x) = 0.03125 f(x) = 0.25 f(x) = 2 Range: {y|y ∈ ℝ > 0} / (0, +∞)
Let x = 1 Let x = 2 Let x = 3 X – Intercept: none
3(1)+1 3(2)+1 3(3)+1
f(x) = 2 f(x) = 2 f(x) = 2
f(x) = 23+1 f(x) = 26+1 f(x) = 29+1 Y – Intercept: (0, 2)
f(x) = 24 f(x) = 27 f(x) = 210
Horizontal Asymptote: none, y=0, x-axis
f(x) = 16 f(x) = 128 f(x) = 1024
A 0.03125
B 0.25
C 2
D 16
E 128
F 1024
Module 6: Inverse Function
You might also like
- GED Math Lessons Practice Problems Workbook (PDFDrive)Document357 pagesGED Math Lessons Practice Problems Workbook (PDFDrive)Guo QiangNo ratings yet
- Takashi Math Tutorials Ans Key (2019)Document72 pagesTakashi Math Tutorials Ans Key (2019)Experimental BeXNo ratings yet
- Takashi Math Tutorials (2021)Document25 pagesTakashi Math Tutorials (2021)Experimental BeXNo ratings yet
- ECON 104: Mathematics For Economics SMU School of Economics Fall 2021 Homework AssignmentsDocument19 pagesECON 104: Mathematics For Economics SMU School of Economics Fall 2021 Homework AssignmentsExperimental BeXNo ratings yet
- 7 For Math For Econ Fall2021Document16 pages7 For Math For Econ Fall2021Experimental BeXNo ratings yet
- ECON 104: Mathematics For Economics SMU School of Economics Fall 2021 Homework AssignmentsDocument20 pagesECON 104: Mathematics For Economics SMU School of Economics Fall 2021 Homework AssignmentsExperimental BeXNo ratings yet
- Problems Set 7Document2 pagesProblems Set 7Panduleni Hamalwa IVNo ratings yet
- January 2022 ExamDocument6 pagesJanuary 2022 ExamjidsjijsdwdNo ratings yet
- Assignment Functions 1Document6 pagesAssignment Functions 1Ishita Bharambe (Ish)No ratings yet
- Deriválja A Következı Függvényeket!Document2 pagesDeriválja A Következı Függvényeket!András BenedekNo ratings yet
- DerivadasDocument3 pagesDerivadaswwfcctkxkbNo ratings yet
- VersionA 1225 Test3 Final AnswersDocument6 pagesVersionA 1225 Test3 Final AnswersIsma QadNo ratings yet
- Fitxa de DerivadesDocument6 pagesFitxa de Derivadesstepano carmoñaNo ratings yet
- Applied CALC 2nd Edition Frank Wilson Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesApplied CALC 2nd Edition Frank Wilson Solutions Manual 1eugenehallgqdcsamwtn100% (34)
- Applied CALC 2nd Edition Frank Wilson Solutions Manual 1Document41 pagesApplied CALC 2nd Edition Frank Wilson Solutions Manual 1daisy100% (38)
- Applied Calc 2Nd Edition Frank Wilson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesApplied Calc 2Nd Edition Frank Wilson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFarthur.brown523100% (20)
- Integrales Indefinidas I: X X X X FDocument4 pagesIntegrales Indefinidas I: X X X X FSara DiSuNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: MTHE01P03Document15 pagesMathematics: MTHE01P03Mohamed FathyNo ratings yet
- 201 NYA 05 Dec2013Document4 pages201 NYA 05 Dec2013rhl5761No ratings yet
- وظيفة منزلية 1 دالة ناطقةDocument1 pageوظيفة منزلية 1 دالة ناطقةOuarezguia sofianeNo ratings yet
- Week 8 Fourier SeriesDocument11 pagesWeek 8 Fourier SeriesLuqman NHNo ratings yet
- Cal2 FE Sem3 1516Document4 pagesCal2 FE Sem3 1516Thảo Nguyễn Thị ThanhNo ratings yet
- Type of Relation 1.2 Functions 1.4 Inverse FunctionDocument3 pagesType of Relation 1.2 Functions 1.4 Inverse Function纪泽勇No ratings yet
- UNIT # 03 Function: Check Your GraspDocument7 pagesUNIT # 03 Function: Check Your GraspritziscoolNo ratings yet
- Derivative WorksheetDocument2 pagesDerivative WorksheetbeadeleeNo ratings yet
- Inverse Functions PowerPointDocument14 pagesInverse Functions PowerPointLaundry VendingNo ratings yet
- Seminar 1. Derivarea Funct Iilor Reale de o Variabil A Real A (Recapitulare)Document5 pagesSeminar 1. Derivarea Funct Iilor Reale de o Variabil A Real A (Recapitulare)Zvy MazelNo ratings yet
- Tut 4 Graphing TechniquesDocument20 pagesTut 4 Graphing TechniquesselmerparisNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1A (FET) Test 2 First OppDocument6 pagesMathematics 1A (FET) Test 2 First Opppaulosmandlazi8No ratings yet
- Lab 08Document2 pagesLab 08honhathao2805No ratings yet
- ListaS6 CalculoA 2020-2Document2 pagesListaS6 CalculoA 2020-2Yasmin SeloisNo ratings yet
- Multivariable Func +partial Derrivative Çalışma SorularıDocument13 pagesMultivariable Func +partial Derrivative Çalışma Soruları247rxg9qr8No ratings yet
- Functions and LimitsDocument5 pagesFunctions and Limitsanywrites31No ratings yet
- XII - Adv & Main (HA04) - 08042024 (Relations Func - 240409 - 230319Document4 pagesXII - Adv & Main (HA04) - 08042024 (Relations Func - 240409 - 230319sharmavatsal346No ratings yet
- College Algebra 4Th Edition Blitzer Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesCollege Algebra 4Th Edition Blitzer Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFgloria.owens760100% (16)
- College Algebra 4th Edition Blitzer Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesCollege Algebra 4th Edition Blitzer Solutions Manual 1leonardkennedypaoicfbkxd100% (28)
- I Hoja3 18 SolDocument10 pagesI Hoja3 18 SolsempiNo ratings yet
- Revisão de Funções e ComposiçõesDocument2 pagesRevisão de Funções e Composiçõesmarinaalmondes16No ratings yet
- 45 An Algorithm For Curve SketchingDocument4 pages45 An Algorithm For Curve SketchingDan AvrukhNo ratings yet
- 103 Worksheet ContinuityDocument2 pages103 Worksheet ContinuityJohnmark LiboonNo ratings yet
- 1st EXAM - Differential CalculusDocument4 pages1st EXAM - Differential CalculusAemie FerrerNo ratings yet
- QA20091 Em2 28 - 1Document3 pagesQA20091 Em2 28 - 1api-25895802No ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 SolutionsDocument8 pagesWorksheet 3 SolutionsXuze ChenNo ratings yet
- Derivative Worksheet 1Document1 pageDerivative Worksheet 1Kasun TudugalaNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus Colley 4th Edition Solutions ManualDocument51 pagesVector Calculus Colley 4th Edition Solutions ManualSharonScottdizmr100% (56)
- Wa0011.Document6 pagesWa0011.Bryan CaesarNo ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus Practice Midterm 2 Solutions Prof. FedorchukDocument5 pagesMultivariable Calculus Practice Midterm 2 Solutions Prof. FedorchukraduNo ratings yet
- Recognition Patterns: Jean Carlo Grandas Franco March 2020Document9 pagesRecognition Patterns: Jean Carlo Grandas Franco March 2020Jean Carlo GfNo ratings yet
- Differentiation RevisionDocument4 pagesDifferentiation RevisionMyureshwaranNo ratings yet
- I. Illustrate The Tangent Line To The Graph of A Function at A Given PointDocument5 pagesI. Illustrate The Tangent Line To The Graph of A Function at A Given Pointrandom potatoNo ratings yet
- Math101-MT-2 Summer 2022 SolutionsDocument4 pagesMath101-MT-2 Summer 2022 SolutionsmohammadhoseinzeinaliNo ratings yet
- Derivative 1Document7 pagesDerivative 1patch23298990No ratings yet
- ?ملخص يرتب لك عقلكDocument90 pages?ملخص يرتب لك عقلكalyazih.hamedNo ratings yet
- HW 5Document3 pagesHW 5Kiran AdhikariNo ratings yet
- TALLER #3 Funciones de Varias VariablesDocument7 pagesTALLER #3 Funciones de Varias Variablesmiguel rojas tonuscoNo ratings yet
- Extra HW - Calculus - Chapter 2Document3 pagesExtra HW - Calculus - Chapter 2siriNo ratings yet
- MATH 122 Critical PointsDocument4 pagesMATH 122 Critical PointsEzekiel PeterNo ratings yet
- Functions and Their Graphs: 2.2 The Graph of A FunctionDocument5 pagesFunctions and Their Graphs: 2.2 The Graph of A FunctionRicardo PlasenciaNo ratings yet
- Differentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDifferentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- EARTH & LIFE SCIENCE Reviewer Note #2Document3 pagesEARTH & LIFE SCIENCE Reviewer Note #2Ristan RectoNo ratings yet
- GENERAL MATHEMATICS Reviewer Note #1Document1 pageGENERAL MATHEMATICS Reviewer Note #1Ristan RectoNo ratings yet
- EARTH & LIFE SCIENCE Reviewer Note #3Document2 pagesEARTH & LIFE SCIENCE Reviewer Note #3Ristan RectoNo ratings yet
- EARTH & LIFE SCIENCE Reviewer Note #2.5Document3 pagesEARTH & LIFE SCIENCE Reviewer Note #2.5Ristan RectoNo ratings yet
- Old ReviewersDocument5 pagesOld ReviewersRistan RectoNo ratings yet
- Old ReviewersDocument2 pagesOld ReviewersRistan RectoNo ratings yet
- Old ReviewersDocument2 pagesOld ReviewersRistan RectoNo ratings yet
- Old ReviewersDocument2 pagesOld ReviewersRistan RectoNo ratings yet
- Old ReviewersDocument2 pagesOld ReviewersRistan RectoNo ratings yet
- Connection Design As Per Bs en 1993-1-8:2005Document3 pagesConnection Design As Per Bs en 1993-1-8:2005waquarstrNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Theories of Failure: Introduction: Due To Large Numbers of Examples of Compound Stresses MetDocument23 pagesUnit IV Theories of Failure: Introduction: Due To Large Numbers of Examples of Compound Stresses MetMohtasham NaeemNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors Basics1 2013Document30 pagesSemiconductors Basics1 2013SriHariKalyanBNo ratings yet
- Multi-Media Fluid MechanicsDocument6 pagesMulti-Media Fluid MechanicsOmar Al-AniNo ratings yet
- Swep Report - WriteDocument23 pagesSwep Report - WriteDavid AkomolafeNo ratings yet
- Advanced-Physics-Reviewer 4th-Quarter Perio LTDocument4 pagesAdvanced-Physics-Reviewer 4th-Quarter Perio LTKermit GooeyNo ratings yet
- Sporlan TXV Bulletin 10-91Document19 pagesSporlan TXV Bulletin 10-91seanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 Alternating Current CircuitsDocument14 pagesChapter 18 Alternating Current CircuitsKELLY NGU SHU YI MoeNo ratings yet
- O5k500 00 - en Us IfmDocument3 pagesO5k500 00 - en Us IfmNhi LinNo ratings yet
- Fabrication - of - Solar - Milk - Cooler FinalDocument22 pagesFabrication - of - Solar - Milk - Cooler Finalemiro denisNo ratings yet
- Activity 7 5 1Document4 pagesActivity 7 5 1Nicole MendozaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Examination: Subject: Physics 2 (Fluid Mechanics and Thermal Physics) (ID: PH014IU)Document3 pagesMidterm Examination: Subject: Physics 2 (Fluid Mechanics and Thermal Physics) (ID: PH014IU)Anh TrầnNo ratings yet
- Structure of the Hydrated Α-Al2O3 (0001) SurfaceDocument6 pagesStructure of the Hydrated Α-Al2O3 (0001) SurfaceYunzhe DuNo ratings yet
- Single-Layer Drying Characteristics and COLOUR Kinetics of RED CHILLIDocument10 pagesSingle-Layer Drying Characteristics and COLOUR Kinetics of RED CHILLIaivangtrNo ratings yet
- Engineering Properties (Al O) : 94% Aluminum Oxide Mechanical Units of Measure SI/Metric (Imperial)Document7 pagesEngineering Properties (Al O) : 94% Aluminum Oxide Mechanical Units of Measure SI/Metric (Imperial)Hendy SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - Phys 131: 0 1 1 2 2 Gauge 0Document1 pageFormula Sheet - Phys 131: 0 1 1 2 2 Gauge 0eNo ratings yet
- 6.32 A Solar Cell Used in Eskimo Point The Intensity of Light Arriving at A Point On Earth, WhereDocument6 pages6.32 A Solar Cell Used in Eskimo Point The Intensity of Light Arriving at A Point On Earth, Wheresamuel laurentiusNo ratings yet
- Maths Infinity: (Agni 3.0 Batch)Document13 pagesMaths Infinity: (Agni 3.0 Batch)varad1unacademyNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Momentum and Impulse: Example 1Document18 pages6.1 Momentum and Impulse: Example 1JH Garciano Posa100% (1)
- RCC 100 Important Questions 39Document33 pagesRCC 100 Important Questions 39Engr Mehdi BugtiNo ratings yet
- Math 8 Q1 Week 1 Factoring CompletelyDocument2 pagesMath 8 Q1 Week 1 Factoring CompletelyKara BanzonNo ratings yet
- Temperature, Internal Energy and HeatDocument15 pagesTemperature, Internal Energy and HeatShafqat HussainNo ratings yet
- Brett Haggerty: TexasDocument8 pagesBrett Haggerty: TexasSamuel Ch. G.No ratings yet
- A Sine Bar Is A Tool Used To Measure Angles in MetalworkingDocument16 pagesA Sine Bar Is A Tool Used To Measure Angles in MetalworkingPiu KunduNo ratings yet
- Admin - Docs - Updated CCB List English - OCT 2017Document22 pagesAdmin - Docs - Updated CCB List English - OCT 2017Bheemendra NarayanNo ratings yet
- TFM - Xueting ZhangDocument208 pagesTFM - Xueting ZhangJavierNo ratings yet
- Delta Function - From Wolfram MathWorldDocument8 pagesDelta Function - From Wolfram MathWorldjaswinder singhNo ratings yet
- Karl Pearson's Coefficient of Correlation: FormulaDocument2 pagesKarl Pearson's Coefficient of Correlation: FormulaAnupriyaNo ratings yet
- IMP IMP Unit - 4 SurveyDocument107 pagesIMP IMP Unit - 4 SurveySHAIK MURTHUJAVALINo ratings yet