Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Definition Chapter 4+9-14
Definition Chapter 4+9-14
Uploaded by
ZAIN LATIFOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Definition Chapter 4+9-14
Definition Chapter 4+9-14
Uploaded by
ZAIN LATIFCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter # 4 (Quadratic Equations)
Quadratic Equation: An equation of second degree polynomial in a certain variable is
called
Quadratic Equation.
e.g. 2 2 2 x x x x x − = = + + = 4 0, 5 – 7 0, 5 0.
Equation of type 2
Ax bx c + + = 0 where a b c = = ≠ 0 is called standard form of Quadratic
Equation.
Solution of Quadratic Equation: (i) Factorization (ii) Quadratic Formula (iii)
Completing Square.
Exponential Equation: Equations in which variable occur in exponents.
e.g. 2
x
and 5
x
Reciprocal Equation: An equation which remains unchanged when x is replaced by 1
X
, is called a
Reciprocal equation.
Radical Equation: Equation involving radical expression of the variable is called radical
equation.
Example 2 3 7 x x + + − = .
Remainder Theorem: If a polynomial f x( ) of degree n ≥1 is divided by ( x a − ) till no x
term
Exits in the remainder then f a( ) is remainder .
Polynomial function: A polynomial in x is an expression of the form
1
110…,0nn
Nnnnaxaxaxaa–
++++≠−
Where n is a non-negative integer and the coefficients
1 0 , ,…,
Nn
Aaa–
Are real numbers. It can be considered as a polynomial function of x.
Factor Theorem: The polynomial ( x a − )is a factor of the polynomial f x( )if and only if
F x( ) = 0 .
Chapter # 9,10,11,12,13,14 (Trigonometry)
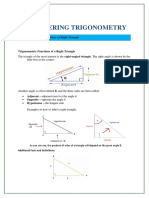
Trigonometry: The word trigonometry has been derived from three Greek words Trei
(three) Goni (angles) and Metron (measurement). Its mean measurement of triangle.
Angle: Two rays with common starting point from an angle is called an angle.
Degree: If the circumference of circle is divided into 360 equal parts in length, the angle
subtended By one part at the centre of the circle is called a degree.
Allied angles: The angles associated with basic angles of measure θ to the right angle
or its Multiple are called allied angles. The angles of measure 90 , 180 , 270 , 360 ± ± ±
± θ θ θ θAre known as allied angles.
Period: period is the smallest positive number which, when added to the original
circular measure Of the angle, gives the same value of the function.
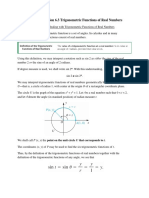
Circular system (Radians): A radian is the measure of the central angle of an arc of a
circle whose Length is equal to the radius of the circle.
Sexagesimal system: The system of measurement in which the angle is measured in
degree, and its Sub-units, minutes and seconds is called the Sexagesimal system.
Example 16 40 34 ′ ′′
Period of Trigonometric Function: The smallest positive number which when added
to the Original circular measurement of the angle gives same value of function is called
period.
Example 2π is period of sine function as sin sin ( ) α π α + = 2 .
Trigonometry equation: The equation, containing at least one trigonometry function
are called Trigonometry equation.
Example:Sinx cosx tanx = − = 2 / 7, 0
Oblique Triangles:A triangle, which is not right, is called anoblique triangle.
Circum-Circle: The circle passes through the three vertices of a triangle is called
circum-circle.
In-Circle:A circle drawn inside a triangle touching its three sides is called its inscribed
circle or in-Circle.
Escribed Circles:A circle, which touches one side of the triangle externally and the
other two Produced sides, is called an escribed circle or ex-circle or e-circle.
Trigonometric function:The equation, containing at least one trigonometric function,
are called Trigonometric function.
You might also like
- Trigo IdentitiesDocument29 pagesTrigo IdentitiesKunalKaushikNo ratings yet
- Cartesian PlaneDocument39 pagesCartesian PlaneBol Mën NhialNo ratings yet
- Assignment in Algebra and TrigoDocument14 pagesAssignment in Algebra and TrigoDaryl Anne NolascoNo ratings yet
- Basic Trigonometry ReviewerDocument6 pagesBasic Trigonometry ReviewerKarl Benedict Chua100% (1)
- YaywyeyfoDocument9 pagesYaywyeyfoClaire GubatNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry SBDocument25 pagesTrigonometry SBReema ChitaliaNo ratings yet
- Electronics: Integrals and RMS Signals: BackgroundDocument34 pagesElectronics: Integrals and RMS Signals: BackgroundAngelina Florisa ApriliaNo ratings yet
- LarCalcETF7e 01 04calculusDocument45 pagesLarCalcETF7e 01 04calculusDerviş Hasan SubaşıNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument2 pagesTrigonometrydiamondNo ratings yet
- Lecture11 Trigonometric Functions of Acute AnglesDocument6 pagesLecture11 Trigonometric Functions of Acute Anglesmarchelo_cheloNo ratings yet
- Jhun JhunDocument7 pagesJhun Jhunjhunjhun ricablancaNo ratings yet
- Review in Plane TrigonometryDocument51 pagesReview in Plane TrigonometryDoone Heart Santander CabuguasNo ratings yet
- Interpolation DefinitionDocument8 pagesInterpolation Definitionapi-126876773No ratings yet
- Units and MeasurementsDocument12 pagesUnits and MeasurementsImranHashmiNo ratings yet
- Number (Calculation and Equations)Document10 pagesNumber (Calculation and Equations)winda lestariNo ratings yet
- Fungsi TrigonometriDocument110 pagesFungsi TrigonometriM IkhsanNo ratings yet
- Section 4.2 PCDocument20 pagesSection 4.2 PCmarons inigoNo ratings yet
- Section 4.2 PCDocument20 pagesSection 4.2 PCMyla Mae BalalaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4-8 Stem 1BDocument15 pagesLesson 4-8 Stem 1BJune Patricia AraizNo ratings yet
- ACT Test: Trigonometry, Logarithms, and MatricesDocument12 pagesACT Test: Trigonometry, Logarithms, and MatricesRaymond BarglowNo ratings yet
- Module 5 TrigonometryDocument0 pagesModule 5 TrigonometryManish MishraNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument13 pagesTrigonometryMary Lee Operiano ElementoNo ratings yet
- q391 Assignment LawrenzaquinoDocument50 pagesq391 Assignment LawrenzaquinoReuNo ratings yet
- Synergetics in The PlaneDocument27 pagesSynergetics in The PlaneIan BeardsleyNo ratings yet
- Non-Perpendicular Resultant CalculationsDocument9 pagesNon-Perpendicular Resultant Calculationsangelinayin322No ratings yet
- Lesson 2: The Trigonometric Functions by Thomas E. PriceDocument38 pagesLesson 2: The Trigonometric Functions by Thomas E. PriceVed Prakash PantNo ratings yet
- Pre Cal Exam Quarter 2Document6 pagesPre Cal Exam Quarter 2Hannah Balais100% (1)
- TrigonometryDocument2 pagesTrigonometrydummkopfworkNo ratings yet
- Week VIDocument5 pagesWeek VIninoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus / Math Notes (Unit 9 of 22)Document17 pagesPre-Calculus / Math Notes (Unit 9 of 22)OmegaUserNo ratings yet
- SEM 1 MCA 11 MathematicsDocument379 pagesSEM 1 MCA 11 MathematicsMalatesh HavanagiNo ratings yet
- Math 2: Lazaro, Mark Vincent J. BS CriminologyDocument13 pagesMath 2: Lazaro, Mark Vincent J. BS CriminologyArrojo Rhiane Hilary MaeNo ratings yet
- Complex NumbersDocument42 pagesComplex NumbersNjabulo MdlaloseNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric, Calculus and AlgebraDocument3 pagesTrigonometric, Calculus and Algebraraybors2No ratings yet
- List of Trigonometric Identities - wikiPEDIADocument26 pagesList of Trigonometric Identities - wikiPEDIAAmiya Ranjan MalikNo ratings yet
- Module I TrigoDocument6 pagesModule I TrigoAteng FordNo ratings yet
- Basic Functions and The Right TriangleDocument15 pagesBasic Functions and The Right TriangleChetan Tolia100% (1)
- Precal Study GuideDocument2 pagesPrecal Study GuideJP SatterfieldNo ratings yet
- What Is A Complementary AngleDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Complementary Angleapi-126876773No ratings yet
- All Trignometric Formula'sDocument14 pagesAll Trignometric Formula'sVivek Singh100% (3)
- PREC 2nd Quarter APBDocument6 pagesPREC 2nd Quarter APBJae JinNo ratings yet
- GAT Formulas: Results On TriangleDocument15 pagesGAT Formulas: Results On TrianglekzrdurNo ratings yet
- Geec 107 - Module IiDocument30 pagesGeec 107 - Module IiMarooning ManNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry BasicsDocument8 pagesTrigonometry BasicsFrecel OsoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions of Real NumbersDocument20 pagesTrigonometric Functions of Real Numbersteachergirl2009No ratings yet
- Learning Journal 7Document2 pagesLearning Journal 7azadaNo ratings yet
- Mathematical & EducationalSayings 081311Document3 pagesMathematical & EducationalSayings 081311pfredaNo ratings yet
- Definite Integral and Area Under Curves: FXDX y FXDocument2 pagesDefinite Integral and Area Under Curves: FXDX y FXSubrahmanyam SanaNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus TrigonometryDocument77 pagesPre Calculus TrigonometryTeacher JasonNo ratings yet
- B2 Module 1 Lesson 2Document11 pagesB2 Module 1 Lesson 2Kate RellitaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric RatioDocument17 pagesTrigonometric RatioApex InstituteNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument13 pagesTrigonometryjobmajuneNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other Polygons with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other Polygons with AnswersNo ratings yet
- RM 900ib (E) 04Document2 pagesRM 900ib (E) 04Cere_CericNo ratings yet
- Math 125 - Exam 1 SolutionsDocument9 pagesMath 125 - Exam 1 SolutionsPhuc DangNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry FormulasDocument3 pagesTrigonometry Formulasakshat yadavNo ratings yet
- AC CircuitDocument210 pagesAC CircuitRagilNo ratings yet
- Kinematics - NEETDocument25 pagesKinematics - NEETAlok SinghNo ratings yet
- Handson Technology: 775 Ball Bearing DC MotorDocument13 pagesHandson Technology: 775 Ball Bearing DC MotorArif KusumaNo ratings yet
- HttpsDocument38 pagesHttpssmileforeverNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument4 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelkeysNo ratings yet
- Module in Trigonometry MidtermsDocument45 pagesModule in Trigonometry MidtermsEUGENE D. GABRIEL, MSENo ratings yet
- Untitled 203Document4 pagesUntitled 203Aditya jainNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document91 pagesModule 5Rejean Faith MallariNo ratings yet
- MATHS ProjectDocument40 pagesMATHS ProjectShrija Padhi100% (1)
- SATUANDocument1 pageSATUANagungcsyNo ratings yet
- Plane and Spherical Trigo - With SolutionDocument80 pagesPlane and Spherical Trigo - With SolutionNala A.No ratings yet
- Dae Electronics RevisedDocument221 pagesDae Electronics RevisedJunaid AhsanNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machine Kme 603Document3 pagesTheory of Machine Kme 603georgianrupesh3217No ratings yet
- Topical Al-Mat-P1 Source FileDocument473 pagesTopical Al-Mat-P1 Source FileBoiboiboi BoiNo ratings yet
- Examples Mec31 1Document6 pagesExamples Mec31 1Aihnee OngNo ratings yet
- Calculus - Radian - Measure Unit 5 Lesson 1Document22 pagesCalculus - Radian - Measure Unit 5 Lesson 1Zeinab RamadanNo ratings yet
- Rover ConstructionDocument19 pagesRover ConstructionNicolas Del BuonoNo ratings yet
- 전자기학 1장 솔루션Document13 pages전자기학 1장 솔루션이재하No ratings yet
- Tutorial Lengkap Phy 143 (Edit)Document22 pagesTutorial Lengkap Phy 143 (Edit)Aten AzharNo ratings yet
- GeoGebra en ManualDocument419 pagesGeoGebra en ManualInes Apituley Sopacua100% (1)
- 07 WavesDocument23 pages07 Wavesfisica2No ratings yet
- Aalborg Universitet: Hansen, Rico HjermDocument291 pagesAalborg Universitet: Hansen, Rico Hjermsantiago gNo ratings yet
- Flag This Store This Question: Report Problem With Question Send Your ReferenceDocument57 pagesFlag This Store This Question: Report Problem With Question Send Your ReferenceKarthik ReddyNo ratings yet
- System of UnitsDocument9 pagesSystem of UnitsHoney AliNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions in The Unit CircleDocument10 pagesTrigonometric Functions in The Unit CircleDerick John PalapagNo ratings yet
- Radian Measure Worksheet 1Document4 pagesRadian Measure Worksheet 1Joseph AngNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On A LevelDocument55 pagesRevision Notes On A LevelZainab PeerbuxNo ratings yet