Professional Documents
Culture Documents
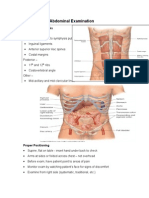
ABDOMEN
ABDOMEN
Uploaded by
Zin Lim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views13 pagesThe document provides instructions for assessing a patient's abdomen through inspection, auscultation, percussion, and palpation. It describes preparing the patient and necessary equipment. It then outlines the specific steps and assessments to perform for each part of the abdominal exam, including inspecting the skin, listening for bowel sounds, percussing to determine dullness or tympanic notes, and palpating the abdomen and internal organs. The goal is to evaluate for any abnormalities, masses, tenderness, or organ enlargement.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides instructions for assessing a patient's abdomen through inspection, auscultation, percussion, and palpation. It describes preparing the patient and necessary equipment. It then outlines the specific steps and assessments to perform for each part of the abdominal exam, including inspecting the skin, listening for bowel sounds, percussing to determine dullness or tympanic notes, and palpating the abdomen and internal organs. The goal is to evaluate for any abnormalities, masses, tenderness, or organ enlargement.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views13 pagesABDOMEN
ABDOMEN
Uploaded by
Zin LimThe document provides instructions for assessing a patient's abdomen through inspection, auscultation, percussion, and palpation. It describes preparing the patient and necessary equipment. It then outlines the specific steps and assessments to perform for each part of the abdominal exam, including inspecting the skin, listening for bowel sounds, percussing to determine dullness or tympanic notes, and palpating the abdomen and internal organs. The goal is to evaluate for any abnormalities, masses, tenderness, or organ enlargement.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 13
hello every one i am flor mae g.
idao from ateneo de
davao university your student nurse for today, so for
todays video im going to perform assessing the abdomen
return demonstration
assessment of the abdomen consist of inspection,
auscultation, percussion and palpation the physical
examination of the abdomen is the key step in the
evaluation of abdominal complaints such as pain,
distension, enlarged organs or masses
prior to the conduct of the procedure first thing to do is to
review clients previous medcal records if available ( start
looking to the chart)
next is to prepare the necessary equipments needed to
conserve time and energy
the equipments that im going to use includes a tape
measure for the measurement for the patients abdominal
girth, a sharp object such as this ruler for the
hypersensitivity test, and ofcourse a stethoscope to listen
for patients bowel sounds
now perform hand hygiene to prevent the microorganism
from spreading
good morning sir i am flormae your student nurse for today
and may i see your wrist bond sir please state your full
name, your birthday please, ok thank you verymuch sir
so today ill be assessing your abdomen which means ill
have to expose your abdomen, ill have to listen for your
bowelsounds and also feel for your internal organs will that
be alright, okay
is it okay to close the door so no one from outside will be
able to disturb you while were doing the assessment, okay
before we start i encourage you to void first so it will be
much comfortable with you while were doing the
assessment.
ensure that the patient has emptied his bladder prior to the
conduct of the procedure because a full bladder can make
the examination uncomfortable, and it can be reduce the
accuracy of the bundle height measurement
now position the client to the supine position with the arms
folded over his chest or just by lying at his side and then
place ta pillow underneath the patients knees, this position
ensures abdominal muscle relaxation to avoid putting
additional pressure on the patients abdomen
now cover the upper and lower body parts of the patient
leaving only the abdomen exposed from the sephoid
process down to just above the symphysis pubis ( start
exposing the abdomen)
sir do you feel and pain in your abdomen, okay so ill begin
inspecting your abdomen first
begin with the inspection of the abdominal skin
characteristics assess for abdominal skin temperature
collar ( start pindot ) note for any vascularities, striae or
stretch marks and also note for any scars lessions or
rashes and if there is any document for its history and its
location by quadrant
now inspect the umbilical location color and contour the
umbilical skin tones is similar the surrounding skin tones
or even pinkish it should be recessed inverted or
protruding no more than .5 centimeters and it should be
round and conical and now also observe for any presence
of masses or bulges suggesting ventral hernia which is
any protrusion of the intestine or other tissues through a
weakness or gap in the abdominal wall.
now to observe for abdominal symmetry while the patient
lies supine on the bed sit bedside the client and look
across the abdomen at a level slightly higher than the
patients abdomen ( start looking )
and the stand at the foot of the bed and observe for
abdominal symmetry ( start observing)
so the abdomen is normally flat rounded or scaphoid in
which is seen in thin adults and it should be evenly
rounded and symmetrical so while doing the inspection
also observe for abdominal respiratory movements aortic
pulsations and peristalsis
(stand patient) measure the patients abdominal around by
placing a measuring tape around the patients abdomen
( start measure) at the level of the umbilicus
so the abdominal girth should be measured at the same
time of the day ideally in the morning just after voiding
now auscultation of the patients vowel sounds
ok sir im going to proceed to a listening over your
abdomen, I just want to ask when did you last eat, okay
recent intake may have increased the peristaltic activity,
warm hands and the diaphragm of the stethoscope to
avoid startling the patient of the coldness of the
stethoscope ,now auscultate all four abdominal quadrants
for at least 1minute each starting from the right lower
quadrant and the proceeding to a clockwise pattern
noting for the intensity pitch and frequency of the vowel
sounds ( start stet)
now listen for the vascular sounds use the bell of the
stethoscope and listen for brewee over the abdominal
aorta, renal iliac and femoral arteries ( start stet )
now to listen for peritoneal friction rod use diaphragm of
the stethoscope to listen for friction rod over the liver and
spleen ( start stet )
proceeding now to the percussion patients abdomen
because several areas in each in the four quadrants to
determine presence of tympani or dullness, tympani is a
high pitch musical sound that indicates a hollow space
filled by air and dullness suggests fluid or feces (start
percussing)
now percuss for the vertical liver span at the midclavicular
line so from the right lower quadrant along the mid
clavicular line percuss upwards towards the liver and note
the note the change from tympani to dullness and mark
this point ( start percussing)
now percuss on the right mid clavicular line on the area of
the lung resonance around the third intercoastal space
and percuss downwards to the liver note the change from
lung resonance to liver dullness mark this ( start
percussing )
now for vertical liver span at the mid sternal line starting
just above the umbilicus purpose upward toward the liver
and note the change from tympani to dullness and mark
this point ( start percussing )
now for the upper border start percussion at the body of
the sternum along the third intercoastal space and
perhaps downwards until the tone changes from flat to the
liver dullness ( start percussing )
now measure the distance between the two points ( start
measuring )
a normal liver span at the mid clavicular line is about 6-12
centimeters and the normal liver span along the midsternal
line is 4-8 centimeters
to assess for liver descent ask the patient to take a deep
breath and hold it while percussing the right lower
quadrant towards the liver and note the change from
tympani to dullness and mark this point, ok sir I need you
to take a deep breath and hold it please( start percussing )
ok you can exhale.
now measure the distance between the border and the
right coastal margin along the midclavicular line ( start
measuring )
to assess for the spleen and evaluate for splenomegaly
reposition the patient in a right sided lying position with left
knee flexed and identify the left anterior axillary line ( start
assisting the patient )
to assess the sides of the spleen, percuss the left anterior
chest wall roughly from the border of the cardiac dullness
at the sixth rib to the anterior axillary line down to the
coastal margin ( start percussing while talking)
percuss the lower interspace in the left anterior axillary line
and ask the client to take a deep breath and percuss again
( start percussing )
Perform the liver blood percussion to assess for liver
tenderness place the right hand flat against the lower
anterior rib cage (start putting it) and then use the ulnar
surface of the left hand to strike right hand( start striking)
ok sir do you any pain
Perform the kidney punch to assess for kidney tenderness
reposition the patient in a sitting position and then place
the left hand at the coastal vertebral over the 12th rib use
the ulnar side of the right Fist to strike against the left hand
and ask for anything ( start striking) and do on the other
side
Test for a scientist test for shifting dullness while the
patient lying supine on the bed percuss the planks of the
patient from the bed towards the umbilicus noting the
change from dullness to tympani and mark this (start
percussing)
now reposition the patient to a side lying position and
perhaps the abdomen from the bed upward and noting for
the change from dullness to tympani ( start assessing the
client to roll in his side) ( start percussing)
so for fluid wave test while the client is lying in a supine
position, ask the patient to press the edges of his hand
firmly down the midline of his abdomen ( ask the patient
sir I need you to place your hand here and press it down
please thank you, and then tap one flank sharply with
finger tips to fill for a fluid wave transmitted across the
abdomen to the opposite flank) ( start pressing)
perform light palpation to assess for tenderness and
presence of mass with client lying relaxed in a supine
position begin with a light systematic palpation of all four
quadrants or nine regions (start palpating) using the finger
pads initially avoiding any areas that the patient had
identified as painful and then observe for reports of pain,
tenderness, guarding behavior and masses
perform the palpation which is done to feel for the internal
organs and masses ( start palpating) compress the
abdomen to a maximum of five to six centimeter using the
palmer surface of the hands and initially avoiding the
painful areas and palpated for muscle resistance or
masses
perform moderate palpation at umbilical ring noting for any
presence of masses, swelling, nodules, granulation to
assess tenderness and presence of mass ( start palpating)
palpation of the abdominal aorta use both hands to deeply
palpate the pedestrian slightly to the left midline( start
palpating)
now palpate for the liver to assess for liver contour surface
presence of nodule, tenderness, and irregularity, place the
left hand under the clients back at the level of the 11th and
12th ribs while the right hand is laid parallel to the right
coastal margin with fingertips pointing towards clients lead
( start palpating) instruct the client to take a deep breath
then compress the fingertips upward and inward to the
lower border of the liver and assess for contour surface
presence of nodules, tenderness and irregularity ( start
take a deep breath )
now perform the hooking technique stand at the clients
right side facing his feet, press in and upward the coastal
margin with your fingertips and ask the patient to take a
deep breath gently and firmly pull inward and upward with
the fingers palpate for the liver edge as it descends to
meet the fingers nothing to contour surface presence of
nodules, tenderness, and irregularity, sir can you please
take a deep breath (start palpating)
percuss the spleen and assess for splenomegaly stand at
the patient’s right side and reach over the patients
abdomen with the left hand under the posterior lower ribs
and pull u gently place the right hand below the left coastal
margin pressed in I toward the spleen ask the patient to
take a deep breath then press inward and upward using
the right hand as the left hand provided support, begin
palpation below the coastal margin and try to feel the tipp
or edge of the spleen as it comes down to meet the
fingertips note for any tenderness and assess the splenic
contour ( start palpating) sir can you please take a deep
breath 2x,
repeat the procedure with the client lying on the right side
lying on the right side with legs somewhat flex of the hips
and knees as needed, (assist the patient to roll on the
side) ( start palpating with inhale and exhale)
palpate the kidneys to assess for kidney enlargement
stand at the patients right side lace the left hand under the
patients right posterior flank and the right hand at the right
coastal margin at the mid clavicular line instruct the client
to take a deep breath and compress the fingers during
peak inspiration and then ask him to exhale and hold his
breath briefly and gradually release the pressure of the
right hand to feel the right kidney sleeping beneath the
fingers ( start palpating ) ask to take a deep breath and
hold the breath
palpate the left kidney with the procedure reverse, state
the urinary bladder begin palpating at the synthesis pubis
and move upward and outward to estimate the bladder
borders ( began palpating)
as for the appendicitis or peritoneal irritation rebound
tenderness or Bloomberg sign palpate deeply at 90
degrees into the abdomen halfway between the umbilicus
and the anterior iliac crest or the muck burnish point then
suddenly release the pressure ( start palpating ) listen and
watch the clients expression of pain as the client to
describe which hurt more the pressing in or the releasing
and where on the abdomen the pain occur ( start palpating
) okay sir did you feel pain while I was pressing your
abdomen (no) did you feel pain when I released
oppressing your abdomen (no) okay
pain induced or worsened by withdrawal is rebound
tenderness suggesting peritoneal inflammation
now for the referred rebound tenderness or rubs inside
palpate deeply in the left lower quadrant and quickly
release the pressure ( start palpating ) okay sir did you
feel any pain while I was pressing your abdomen (no) did
you feel pain when I release pressing your abdomen ( no )
okay
pain in the lower quadrant during pressure in the left lower
quadrant is positive of promising signs suggesting acute
appendicitis
test for soa was sign reposition the patient in a right lying
position and then hyperextend the right leg, ( start testing)
okay sir tell me if you feel any pain, you feel pain (no) okay
pain in the right lower quadrant or the soa sign is
associated with the irritation of the iliopsoas muscles due
to appendicitis
test for obturators sign, now support the clients knee and
ankle and flex the hip and leg and rotate the leg internally
and externally ( start testing )
pain in the right lower quadrant indicates irritation of the
obturator muscle due to appendicitis or perforated
appendix
hypersensitivity test using a sharp objects stroke the
patients abdomen (palpate while talking) do this several
times and note for any complaints of pain, sir are you
feeling a pain in your abdomen (no)
pain or an exaggerated sensation felt on the right lower
quadrant is a positive skin hypersensitivity test and may
indicate an appendicitis
test for murphy’s sign or test for cholecystitis, press your
fingertips under the liver border at the right coastal margin
and ask the client to inhale deeply and note for any
increase in painful (ask the patient to inhale deeply and tell
me if you feel a pain and begun the test)
a positive murphy sign is when pain occurs when
examiner’s hand comes in contact with the gallbladder
okay sir now that were done with the assessment of your
abdomen here is the summary of what we have just done
okay
so upon inspection your skin is uniform in color no rashes,
no lesions, no scars and your umbilicus or your navel is
midline and inverted which is pretty normal your abdomen
is symmetrical and upon auscultation of your bowel
sounds while I was listening to your abdomen the sounds
are pretty normal and I hear no brewees or venus hum
while I was measuring for your liver size on your liver span
at the midclavicular line here I measured it is 7
centimeters and while I was measuring for your liver at the
mid sternal line it is measured at five centimeters which
falls within the normal range
upon percussion and palpation there were no tenderness,
no masses, no bulges, and no swelling overall your
abdomen is doing pretty good
do you any questions or clarifications
overall your abdomen is doing really good but before I
leave I just like give you some advice how to keep your
abdominal internal organs healthy okay
so first is as much as possible avoid from drinking too
much alcohol or hard liquor because it may cause damage
to your liver and instead of drinking alcohol might as well
increase your fluid intake such as water to flush out
unwanted residues in your liver and in your bladder in your
intestines
and if you have any urge to pee then do not hold back or
do not delay because holding back your pee might cause
the bacteria to multiply and can cause serious diseases
such as urinary tract infection
that is all do you have any questions or clarifications
perhaps
that is all thank you very much for your cooperation
perform hand hygiene and document findings
You might also like
- Abdominal Examination - OSCE SkillsDocument5 pagesAbdominal Examination - OSCE SkillsMastura IsmailNo ratings yet
- Os 206: Pe of The Abdomen - ©spcabellera, Upcm Class 2021Document4 pagesOs 206: Pe of The Abdomen - ©spcabellera, Upcm Class 2021Ronneil BilbaoNo ratings yet
- Non Deliverable ForwardDocument17 pagesNon Deliverable ForwardManish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Yoga Nidra Masterclass Training Notes 1 PDFDocument4 pagesYoga Nidra Masterclass Training Notes 1 PDFMino Zo SydneyNo ratings yet
- Abdomen ScriptDocument14 pagesAbdomen Scriptadrian nakilaNo ratings yet
- Session 6 - Performing Abdominal ExaminationDocument33 pagesSession 6 - Performing Abdominal ExaminationOtsward OwdenNo ratings yet
- Abdomen PE ChecklistDocument6 pagesAbdomen PE ChecklistJulienne Sanchez-SalazarNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan AbdomenDocument91 pagesPemeriksaan AbdomenEndah Cahaya SufianyNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Exam StepsDocument4 pagesAbdominal Exam StepsRonaldoNo ratings yet
- Semester 1 Physical Examination Skills Lab Handout Abdominal Exam IDocument4 pagesSemester 1 Physical Examination Skills Lab Handout Abdominal Exam IFlowerNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination Algorithm - SurgeryDocument6 pagesPhysical Examination Algorithm - Surgeryzynna.abadiNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Examination ProcedureDocument5 pagesAbdominal Examination ProcedureAnamul hossainNo ratings yet
- Abdomen AssessmentDocument7 pagesAbdomen AssessmentJordan SingaNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment - Yuli PutriDocument4 pagesPhysical Assessment - Yuli PutriIkadek AgustianaNo ratings yet
- LI - Physical Examination - AbdomenDocument6 pagesLI - Physical Examination - AbdomenTravis DonohoNo ratings yet
- AbdomenDocument7 pagesAbdomenShayne Lyrrie Pajela100% (1)
- Abdominal Assessment 3Document41 pagesAbdominal Assessment 3Leonilyn Dagoplo RN100% (1)
- 3 Session 3 - AbdominalExamDocument15 pages3 Session 3 - AbdominalExamjhk0428No ratings yet
- Bates Physical Exam Video NotesDocument3 pagesBates Physical Exam Video Notesdulcedeleche12359No ratings yet
- Abdominal Assessment VideoDocument4 pagesAbdominal Assessment VideoAmber Nicole HubbardNo ratings yet
- Preparation: Palpation INSPECTION Inspect Abdomen ForDocument2 pagesPreparation: Palpation INSPECTION Inspect Abdomen FornicoscribdNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Abdomen: Prepared By: Mary Ann F. Rubio, RN, MNDocument54 pagesAssessing The Abdomen: Prepared By: Mary Ann F. Rubio, RN, MNWilma Acorin OrillinedaNo ratings yet
- Internal MedicineDocument5 pagesInternal MedicineManickanadarajah VanoNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan AbdomenDocument46 pagesPemeriksaan AbdomenPrystia_RNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal AssessmentDocument82 pagesGastrointestinal Assessmentkristine_silangNo ratings yet
- Abdomenal Exam HandoutDocument4 pagesAbdomenal Exam HandoutAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- DR - Serwan HX - ExDocument3 pagesDR - Serwan HX - ExDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Lung and ThoraxDocument4 pagesLung and ThoraxKrysstal GerongaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Exam: Order of Exam Is Critical. Auscultate BEFORE Palpating!Document14 pagesAbdominal Exam: Order of Exam Is Critical. Auscultate BEFORE Palpating!RomanNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Examination For PSIII Edited-1Document33 pagesAbdominal Examination For PSIII Edited-1myarjddbzNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Examination-1Document88 pagesAbdominal Examination-1naveen kumar kushwahaNo ratings yet
- LWW BATES 13 Abdomen Transcript FINALDocument6 pagesLWW BATES 13 Abdomen Transcript FINALmuhammad Babar50% (2)
- (Unedit) Assessment of The Abdomen PRDocument12 pages(Unedit) Assessment of The Abdomen PRdayniellecutamoraNo ratings yet
- Abdomen Physical ExaminationDocument2 pagesAbdomen Physical ExaminationHildaSilvi WNo ratings yet
- Assessment of AbdomenDocument16 pagesAssessment of AbdomenjoslinjohnNo ratings yet
- No. Description of Actions To Be Done Score 0 1 2Document3 pagesNo. Description of Actions To Be Done Score 0 1 2Adiprayogo LiemenaNo ratings yet
- GI History and Abdominal ExamDocument113 pagesGI History and Abdominal ExamTokichaw AwokeNo ratings yet
- Examination of The AbdomenDocument19 pagesExamination of The AbdomenAllen AykayNo ratings yet
- Abdominal AssessmentDocument59 pagesAbdominal AssessmentSIR ONE100% (1)
- Skill: Assessing The Thorax and LungsDocument3 pagesSkill: Assessing The Thorax and LungsKathrina AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Abdominal AssessmentDocument6 pagesAbdominal AssessmentRhelina MinNo ratings yet
- LymphaticDocument52 pagesLymphaticlemuel_queNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Examination: Before Examining The PatientDocument4 pagesAbdominal Examination: Before Examining The PatientrebeccaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Assessment TechniquesDocument3 pagesAbdominal Assessment TechniquesRex CaasiNo ratings yet
- Abdomenal Exam HandoutDocument5 pagesAbdomenal Exam HandoutNesma AdelNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Script v3Document7 pagesGastrointestinal Script v3Ray ChangNo ratings yet
- Neurological Examination of The Limbs TextDocument8 pagesNeurological Examination of The Limbs Textvidur_talrejaNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Abdomen: Psik Fikes UmmDocument12 pagesPemeriksaan Abdomen: Psik Fikes UmmAbd RahmanNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Examination PDFDocument3 pagesAbdominal Examination PDFHadid AliNo ratings yet
- Abdominal PEPDocument7 pagesAbdominal PEPRandy TurnerNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Abdomen: Dr. Suhaemi, SPPD, FinasimDocument179 pagesPemeriksaan Abdomen: Dr. Suhaemi, SPPD, FinasimiroelnafialyskaNo ratings yet
- Osce Abdominal ExaminationDocument1 pageOsce Abdominal ExaminationNairobipaeds Madakitari WatotoNo ratings yet
- Inspection, Auscultation, Palpation, and Percussion of The AbdomenDocument16 pagesInspection, Auscultation, Palpation, and Percussion of The AbdomenKaye ExeveaNo ratings yet
- 1.2.7 Abdominal Exam - SendDocument65 pages1.2.7 Abdominal Exam - Senddanielndaa51No ratings yet
- HA Lec 16Document10 pagesHA Lec 16Althea Sachi CruzNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Assessment: Normal FindingsDocument10 pagesAbdominal Assessment: Normal FindingsMiden AlbanoNo ratings yet
- SCRIPT - ASSESSMENT (AutoRecovered)Document5 pagesSCRIPT - ASSESSMENT (AutoRecovered)Angela Shaine CruzNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Examination UMYDocument181 pagesAbdominal Examination UMYMspitha LiaNo ratings yet
- Retdem AbdomenDocument1 pageRetdem AbdomenCharlize PareNo ratings yet
- NursingDocument49 pagesNursingMarieNo ratings yet
- Clinical Skill ScriptDocument12 pagesClinical Skill Scriptannoying fuckerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23. Viral ExanthemsDocument19 pagesChapter 23. Viral ExanthemsZin LimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22. Infections of The Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesChapter 22. Infections of The Nervous SystemZin LimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21. Infections of The EyesDocument8 pagesChapter 21. Infections of The EyesZin LimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20. Infections of The Urinary TractDocument8 pagesChapter 20. Infections of The Urinary TractZin LimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09. Host Response To InfectionDocument51 pagesChapter 09. Host Response To InfectionZin LimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19. Sexually Transmitted InfectionsDocument19 pagesChapter 19. Sexually Transmitted InfectionsZin Lim0% (1)
- 10 Cardiovascular SystemDocument3 pages10 Cardiovascular SystemZin LimNo ratings yet
- 7 Breast and AxillaDocument2 pages7 Breast and AxillaZin LimNo ratings yet
- 9 Thorax LungsDocument2 pages9 Thorax LungsZin LimNo ratings yet
- MATH Action Plan (2022 2023)Document3 pagesMATH Action Plan (2022 2023)Kenny Ann Grace Batiancila100% (7)
- Medications For Neonatal Resuscitation Program 2011 Canadian AdaptationDocument1 pageMedications For Neonatal Resuscitation Program 2011 Canadian AdaptationrubymayNo ratings yet
- 8 (1) .Factor Endowment TheoryDocument64 pages8 (1) .Factor Endowment Theorylilianamici59No ratings yet
- Mobily Tbpo Civil SpecsDocument96 pagesMobily Tbpo Civil Specsmarwan.mohamed.mostafa2008No ratings yet
- Hand Tools and Measuring DeviceDocument86 pagesHand Tools and Measuring Devicehabtsh100% (3)
- MLD 201aDocument13 pagesMLD 201aChaucer19No ratings yet
- Metric System Common Measure Conversion Factor Common UseDocument4 pagesMetric System Common Measure Conversion Factor Common UseMarielle ChuaNo ratings yet
- UGEB2362 Course Outline 2023-24Document5 pagesUGEB2362 Course Outline 2023-24Suki PunNo ratings yet
- Buying Guide Truck Scales EN v11 Low PDFDocument80 pagesBuying Guide Truck Scales EN v11 Low PDFBồ Công AnhNo ratings yet
- SyntaxDocument9 pagesSyntaxVeronicaTurtusanNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report Pinagtigasan KinderDocument12 pagesAccomplishment Report Pinagtigasan KinderMay Anne AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Aegis - Designer and AnalyzerDocument26 pagesAegis - Designer and Analyzeropenid_S1hHcZODNo ratings yet
- Questions Energy Surfaces and Spontaneous ReactionsDocument2 pagesQuestions Energy Surfaces and Spontaneous Reactionshernys NietoNo ratings yet
- 04 Control of Reactive PowerDocument30 pages04 Control of Reactive PowersulemankhalidNo ratings yet
- Interior Design Using Augmented RealityDocument24 pagesInterior Design Using Augmented RealityHarfizzie FatehNo ratings yet
- Seven Paths To Perfection Kirpal SinghDocument52 pagesSeven Paths To Perfection Kirpal SinghjaideepkdNo ratings yet
- AP06-EV04 - Taller en Idioma Inglés Sobre Sistema de Distribución.Document8 pagesAP06-EV04 - Taller en Idioma Inglés Sobre Sistema de Distribución.juanze rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Akinlo and Asaolo, 2012 PDFDocument9 pagesAkinlo and Asaolo, 2012 PDFJason KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Dap An - DE CUONG - ANH 8Document5 pagesDap An - DE CUONG - ANH 8KienNo ratings yet
- Overview of Flexfields 58987177.doc Effective Mm/dd/yy Page 1 of 24 Rev 1Document24 pagesOverview of Flexfields 58987177.doc Effective Mm/dd/yy Page 1 of 24 Rev 1sudharshan79No ratings yet
- Noteskarts Hospital Clinical Pharmacy Sample Paper by NoteskartsDocument21 pagesNoteskarts Hospital Clinical Pharmacy Sample Paper by Noteskartsarshu98172No ratings yet
- Species Concepts PDFDocument5 pagesSpecies Concepts PDFMayhaaaNo ratings yet
- The Sophia Sun: in This Issue..Document32 pagesThe Sophia Sun: in This Issue..Gi3iBq7uAANo ratings yet
- Principal 5svbk8Document56 pagesPrincipal 5svbk8badillojdNo ratings yet
- Jury Trial Moot Problem, Bar The Lex Fiesta 2016Document22 pagesJury Trial Moot Problem, Bar The Lex Fiesta 2016ShradhaNo ratings yet
- Contin Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain-2008-Gauntlett-121-4Document4 pagesContin Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain-2008-Gauntlett-121-4Wahyu HidayatiNo ratings yet
- Floyd Electrical StatementDocument5 pagesFloyd Electrical Statementshane.ramirez1980No ratings yet
- ANSI B30.8 InterpretationDocument10 pagesANSI B30.8 InterpretationAndreyNo ratings yet