Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 viewsEfm4, CH 13
Efm4, CH 13
Uploaded by
毛煌This document discusses cash flow estimation and risk analysis for capital budgeting projects. It covers estimating relevant cash flows, including operating cash flows, changes in net working capital, and terminal values. It also discusses conceptual issues in cash flow estimation like free cash flows, timing of cash flows, and sunk costs. The document provides an example of analyzing an expansion project, project S, which requires equipment purchases and will generate cash flows over four years. It also discusses analyzing a replacement project, project R, comparing a new efficient machine to an old one. Finally, it covers the three types of project risk: stand-alone, corporate, and market risk, and methods for risk analysis like sensitivity analysis, scenario analysis, and Monte Carlo simulation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Cash Flow Estimation and Risk AnalysisDocument60 pagesCash Flow Estimation and Risk AnalysisAJ100% (2)
- SWOT AnalysisDocument15 pagesSWOT AnalysisTadesse Dinku100% (1)
- Basic Capital BudgetingDocument42 pagesBasic Capital BudgetingMay Abia100% (2)
- Earned Value Project Management (Fourth Edition)From EverandEarned Value Project Management (Fourth Edition)Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- Chapter 13Document34 pagesChapter 13Aryan JainNo ratings yet
- HMM 409 Project Management Unit - 2Document46 pagesHMM 409 Project Management Unit - 2Shivam SinghNo ratings yet
- Project Finance: Valuing Unlevered ProjectsDocument41 pagesProject Finance: Valuing Unlevered ProjectsKelsey GaoNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument24 pagesCapital BudgetingHassaan NasirNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Estimation and Risk AnalysisDocument52 pagesCash Flow Estimation and Risk AnalysisHeather Cabahug100% (1)
- Cash Flow Estimation and Capital BudgetingDocument29 pagesCash Flow Estimation and Capital BudgetingShehroz Saleem QureshiNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document63 pagesCH 11Duc Tai NguyenNo ratings yet
- Ch11 RevisedDocument33 pagesCh11 RevisedNhân TrầnNo ratings yet
- CASH FLOW ESTIMATION Week 6Document30 pagesCASH FLOW ESTIMATION Week 6adulmi325No ratings yet
- FIN2004 - 2704 Week 10 SlidesDocument61 pagesFIN2004 - 2704 Week 10 SlidesNguyen DzungNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting - December 2015Document19 pagesCapital Budgeting - December 2015apoorv jindalNo ratings yet
- 4 - Cash Flow EstimationDocument11 pages4 - Cash Flow Estimationdestinyrocks88No ratings yet
- Cash Flow Estimation and Risk AnalysisDocument39 pagesCash Flow Estimation and Risk AnalysisRanyDAmandaNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting - Adv IssuesDocument21 pagesCapital Budgeting - Adv IssuesdixitBhavak DixitNo ratings yet
- A. The Importance of Capital BudgetingDocument16 pagesA. The Importance of Capital BudgetingManish ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Multinational Capital BudgetingDocument19 pagesMultinational Capital BudgetingHania Doll100% (1)
- Hellpfull 10 11Document18 pagesHellpfull 10 11Mehran MumtazNo ratings yet
- International Capital BudgetingDocument43 pagesInternational Capital BudgetingRammohanreddy RajidiNo ratings yet
- S7-Capital BudgetingDocument78 pagesS7-Capital BudgetingShaheer BaigNo ratings yet
- DR 6 UryutfyutfutduDocument13 pagesDR 6 UryutfyutfutduWisnu1201091No ratings yet
- Acf302: Corporate Finance: Capital Budgeting and Valuation With Leverage - Part IDocument43 pagesAcf302: Corporate Finance: Capital Budgeting and Valuation With Leverage - Part IXue Meng LuNo ratings yet
- Final Project Cash FlowsDocument25 pagesFinal Project Cash FlowsLalit Sondhi100% (1)
- Capital Budgeting - Part 1Document6 pagesCapital Budgeting - Part 1Aurelia RijiNo ratings yet
- 29th Aug 2023 Final Complex Investment DecisionsDocument15 pages29th Aug 2023 Final Complex Investment DecisionsKunal KadamNo ratings yet
- 2.8 SKILL Financial AnalysisDocument63 pages2.8 SKILL Financial AnalysisYared AssefaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Corporate Finance, 2/e: Robert Parrino, Ph.D. David S. Kidwell, Ph.D. Thomas W. Bates, PH.DDocument56 pagesFundamentals of Corporate Finance, 2/e: Robert Parrino, Ph.D. David S. Kidwell, Ph.D. Thomas W. Bates, PH.DNguyen Thi Mai Lan100% (1)
- 3.3 Project Feasibility StudyDocument20 pages3.3 Project Feasibility Studydawit tibebuNo ratings yet
- MBA Lec - Capital BudgetingDocument85 pagesMBA Lec - Capital BudgetingNathasha RathnayakeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document41 pagesChapter 5Project MgtNo ratings yet
- InternshipDocument17 pagesInternshipHimanshu Sekhar GuruNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument26 pagesCapital BudgetingGowryshankar SumatharanNo ratings yet
- EBF 2054 Capital BudgetingDocument48 pagesEBF 2054 Capital BudgetingizzatiNo ratings yet
- Capital Investment DecisionspptDocument24 pagesCapital Investment DecisionspptDeepika PantNo ratings yet
- 2017 2018 Eup 222 Sem 1 Project Finance Topic Outcome 1Document49 pages2017 2018 Eup 222 Sem 1 Project Finance Topic Outcome 1NNadiah IsaNo ratings yet
- Part 4 Capital BudgetingDocument5 pagesPart 4 Capital BudgetingToulouse18No ratings yet
- FINA2010 Financial Management: Lecture 5: Capital Budgeting IIDocument54 pagesFINA2010 Financial Management: Lecture 5: Capital Budgeting IImoonNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument11 pagesCapital BudgetingSumit AroraNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting: Kavishe W.FDocument39 pagesCapital Budgeting: Kavishe W.FThomasaquinos Gerald Msigala Jr.No ratings yet
- Risk in Capital BudgetingDocument17 pagesRisk in Capital BudgetingSabit Ahmed Aleem100% (1)
- Cu Capital BudgetingDocument22 pagesCu Capital BudgetingHarshita ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument18 pagesCapital BudgetingYash ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting DecisionsDocument28 pagesCapital Budgeting DecisionsMoshmi MazumdarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 CASH FLOW ESTIMATION-1 - 15713Document20 pagesLecture 4 CASH FLOW ESTIMATION-1 - 15713Furqan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Session 06Document27 pagesSession 06Jaya RoyNo ratings yet
- PPCH 08Document41 pagesPPCH 08Nady SouzaNo ratings yet
- 10.cap+budgeting Cash Flows-1Document20 pages10.cap+budgeting Cash Flows-1Navid GodilNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Project Management 7Document31 pagesUnit 7 Project Management 7chuchuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Project Cash FlowsDocument28 pagesChapter 9 Project Cash FlowsGovinda AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Cash Flow Estimation and Risks AnalysisDocument45 pagesChapter 12: Cash Flow Estimation and Risks AnalysisElizabeth Espinosa ManilagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Cash Flow Estimation and Risks AnalysisDocument45 pagesChapter 12: Cash Flow Estimation and Risks AnalysisElizabeth Espinosa ManilagNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Unit 2 Study Guide StudentsDocument8 pagesCorporate Finance Unit 2 Study Guide StudentsJust for Silly UseNo ratings yet
- Week 9 Notes OnCapital BudgetingDocument13 pagesWeek 9 Notes OnCapital BudgetingAnonymous O5asZmNo ratings yet
- Teoria Financial Management IIDocument83 pagesTeoria Financial Management IIMANUEL GONZÁLEZNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document37 pagesLecture 8Tesfaye ejetaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Managerial Finance: Capital Budgeting and Cash Flow PrinciplesDocument37 pagesPrinciples of Managerial Finance: Capital Budgeting and Cash Flow PrinciplesJoshNo ratings yet
- Applied Corporate Finance. What is a Company worth?From EverandApplied Corporate Finance. What is a Company worth?Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Investments Profitability, Time Value & Risk Analysis: Guidelines for Individuals and CorporationsFrom EverandInvestments Profitability, Time Value & Risk Analysis: Guidelines for Individuals and CorporationsNo ratings yet
- Darwin Capuno PT 2 Las 4Document3 pagesDarwin Capuno PT 2 Las 4Darwin CapunoNo ratings yet
- News Release 2 Araw NG KasambahayDocument1 pageNews Release 2 Araw NG KasambahayjulyenfortunatoNo ratings yet
- Module 10 Inflation RevDocument12 pagesModule 10 Inflation RevGumiNo ratings yet
- Internship Report PELDocument60 pagesInternship Report PELsara-bashir-8426No ratings yet
- Week-12 Financial Analysis EUAC, Gradient and Capitalized Cost AnalysisDocument15 pagesWeek-12 Financial Analysis EUAC, Gradient and Capitalized Cost AnalysisMustajab KhanNo ratings yet
- Ps 3Document2 pagesPs 3King LeonidusNo ratings yet
- PRMG 135 - Ass. 01 Answering GuidanceDocument1 pagePRMG 135 - Ass. 01 Answering GuidanceMohammed SaadNo ratings yet
- Mitc Gold RCPDocument6 pagesMitc Gold RCPu4rishiNo ratings yet
- Quiz Week 2 No AnswerDocument10 pagesQuiz Week 2 No AnswerKatherine EderosasNo ratings yet
- TF 00000049Document2 pagesTF 00000049chkzaNo ratings yet
- Research On Sustainable Development of Textile Industrial Clusters in The Process of GlobalizationDocument5 pagesResearch On Sustainable Development of Textile Industrial Clusters in The Process of GlobalizationSam AbdulNo ratings yet
- Douglas Robert Brown - The Food Service Manager's Guide To Creative Cost Cutting - Over 2,001 Innovative and Simple Ways To Save Your Food Service Operation Thousands by Reducing Expenses-Atlantic PubDocument170 pagesDouglas Robert Brown - The Food Service Manager's Guide To Creative Cost Cutting - Over 2,001 Innovative and Simple Ways To Save Your Food Service Operation Thousands by Reducing Expenses-Atlantic PubTemo BeasNo ratings yet
- Econ 2Document11 pagesEcon 2Marcos PittmanNo ratings yet
- Textile Business PlanDocument3 pagesTextile Business PlanJoshua Anim100% (2)
- De Dollar Is at I On AnonymousDocument36 pagesDe Dollar Is at I On AnonymousTanmaye ShagotraNo ratings yet
- BPE-60312 Sept 2020 - MARKET ANALYSISDocument26 pagesBPE-60312 Sept 2020 - MARKET ANALYSISAntonio MoncayoNo ratings yet
- Manuals For Participants PDFDocument5 pagesManuals For Participants PDFindra alverdianNo ratings yet
- SFM Formulae PDFDocument255 pagesSFM Formulae PDFpiyush bansalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 MonitoringDocument37 pagesChapter 11 MonitoringRana LaeeqNo ratings yet
- Introduction Page For LNMCBMDocument3 pagesIntroduction Page For LNMCBMShivam KumarNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment ERP-2021 KduDocument10 pagesIndividual Assignment ERP-2021 KduPradeep AnuradhaNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Tbch09 578d492668ce2Document40 pagesDokumen - Tips Tbch09 578d492668ce2lei veraNo ratings yet
- Golden ABC Inc.Document7 pagesGolden ABC Inc.Ivy Mhae SantiaguelNo ratings yet
- Sbi LifeDocument16 pagesSbi LifesahilNo ratings yet
- Sustainable RegenerationDocument72 pagesSustainable RegenerationDipayan BhowmikNo ratings yet
- Flexible Budget Examples Chapter 18Document9 pagesFlexible Budget Examples Chapter 18Surbhi JainNo ratings yet
- Pricing and Revenue Management in A Supply Chain: True/FalseDocument16 pagesPricing and Revenue Management in A Supply Chain: True/FalseHaris AmirNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Built Environment: The Role of Quantity SurveyorsDocument6 pagesSustainable Built Environment: The Role of Quantity SurveyorsChanna KariyawasamNo ratings yet
- 4.1 The Role of MarketingDocument23 pages4.1 The Role of MarketingDanae Illia GamarraNo ratings yet
Efm4, CH 13
Efm4, CH 13
Uploaded by
毛煌0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views11 pagesThis document discusses cash flow estimation and risk analysis for capital budgeting projects. It covers estimating relevant cash flows, including operating cash flows, changes in net working capital, and terminal values. It also discusses conceptual issues in cash flow estimation like free cash flows, timing of cash flows, and sunk costs. The document provides an example of analyzing an expansion project, project S, which requires equipment purchases and will generate cash flows over four years. It also discusses analyzing a replacement project, project R, comparing a new efficient machine to an old one. Finally, it covers the three types of project risk: stand-alone, corporate, and market risk, and methods for risk analysis like sensitivity analysis, scenario analysis, and Monte Carlo simulation.
Original Description:
Original Title
efm4, ch 13
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses cash flow estimation and risk analysis for capital budgeting projects. It covers estimating relevant cash flows, including operating cash flows, changes in net working capital, and terminal values. It also discusses conceptual issues in cash flow estimation like free cash flows, timing of cash flows, and sunk costs. The document provides an example of analyzing an expansion project, project S, which requires equipment purchases and will generate cash flows over four years. It also discusses analyzing a replacement project, project R, comparing a new efficient machine to an old one. Finally, it covers the three types of project risk: stand-alone, corporate, and market risk, and methods for risk analysis like sensitivity analysis, scenario analysis, and Monte Carlo simulation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views11 pagesEfm4, CH 13
Efm4, CH 13
Uploaded by
毛煌This document discusses cash flow estimation and risk analysis for capital budgeting projects. It covers estimating relevant cash flows, including operating cash flows, changes in net working capital, and terminal values. It also discusses conceptual issues in cash flow estimation like free cash flows, timing of cash flows, and sunk costs. The document provides an example of analyzing an expansion project, project S, which requires equipment purchases and will generate cash flows over four years. It also discusses analyzing a replacement project, project R, comparing a new efficient machine to an old one. Finally, it covers the three types of project risk: stand-alone, corporate, and market risk, and methods for risk analysis like sensitivity analysis, scenario analysis, and Monte Carlo simulation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 11
Chapter 13
Cash Flow Estimation and
Risk Analysis
Relevant Cash Flows
Types of Risk
Risk Analysis
NPV Profiles for Project S and L
Determining Project Value
• Estimate relevant cash flows
– Calculating annual operating cash
flows.
– Identifying changes in net operating
working capital.
– Calculating terminal cash flows: after-
tax salvage value and recovery of
NOWC.
0 1 2 3 4
Initial OCF1 OCF2 OCF3 OCF4
Costs +
Terminal
CFs
FCF0 FCF1 FCF2 FCF3 FCF4
Conceptual Issues in Cash
Flow Estimation
Free Cash Flow
Timing of Cash Flows
Incremental Cash Flows
Expansion Projects and Replacement
Projects
Sunk Cost - 已經發生並且無論專案
項目被接受還是拒絕都無法收回的
現金支出。
Opportunity Costs - 如果某些資產
不用於新專案項目下,該資產可以
獲得的最佳回報(獲利)。
Externalities (公司/環境的外部成本)
Cannibalization (蠶食; IBM/PC)
Complementary (iPod/iTunes)
Environmental Externalities
(Government Regulations/Rules)
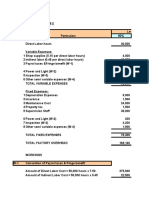
Analysis of an Expansion Project
• Project S will require Allied to purchase $900,000
of equipment in 2017(t=0)
• Inventory will increase by $175,000 and accounts
payable will rise by $75,000. All other working
capital components will stay the same, so the
change in net operating working capital (NOWC) is
$100,000 at t 0.
• The project will last for four years. The company
forecasts the following sales: 2,685,000 units in
2018; 2,600,000 units in 2019; 2,525,000 units
in 2020; and 2,450,000 units in 2021. Each unit
will sell for $2.
• The fixed cost of producing the product is $2
million each year, and the variable cost of
producing each unit will rise from $1.018 in 2018
to $1.221 in 2021.
• The company will use accelerated depreciation,
however, the CFO is also interested in seeing how
the project’s value would change if it instead used
straight-line depreciation.
• When the project is completed in 2021 t 4 , the
company expects that it will be able to salvage the
equipment for $50,000 and that it will fully
recover the NOWC of $100,000.
• The estimated tax rate is 40%.
• Based on the perceived risk, the project’s WACC is
estimated to be 10%.
Cash Flow Estimation and
Analysis for Expansion Project S
Replacement Analysis
• Evaluate a replacement decision on both
a new, highly efficient machine
(depreciated on an accelerated basis)
and the old machine (depreciated on a
straight-line basis).
• The key inputs used in the analysis. No
additional operating working capital is
needed.
• Data applicable to both machines:
Sales revenues, remain constant $ 2,500
Expected life of the new and old machines
4 years; WACC for the analysis 10%; Tax
rate 40%
• Data for old machine:
Market (salvage) value of the old machine
today $ 400; Old labor, materials, and
other costs per year $ 1,000; Old
machine’s annual depreciation $ 100
• Data for new machine:
Cost of new machine $ 2,000; New labor,
materials, and other costs per year $ 400
Replacement Project R
Three Types of Project Risk
• Stand-alone Risk :
The project’s total risk, uncertainty about its
cash flows.
Usually measured by standard deviation (or
coefficient of variation).
However, it ignores the firm’s diversification
among projects and investors’ diversification
among firms.
• Corporate Risk
The project’s risk when considering the firm’s
other projects, i.e., diversification within the
firm.
Corporate risk is a function of the project’s
NPV and standard deviation and its
correlation with the returns on other firm
projects.
• Market Risk
the riskiness of the project as seen by a well
diversified stockholder who recognizes (a) that
the project is only one of the firm’s assets and
(b) that the firm’s stock is but one part of his
or her stock portfolio.
The project’s market risk is measured by its
effect on the firm’s beta coefficient.
Stand-Alone Risk
Sensitivity Analysis
• Percentage change in NPV
resulting from a given percentage
change in an input variable, other
things held constant.
Sensitivity Graph for Project S
Scenario Analysis for
Project S
Monte Carlo simulation
You might also like
- Cash Flow Estimation and Risk AnalysisDocument60 pagesCash Flow Estimation and Risk AnalysisAJ100% (2)
- SWOT AnalysisDocument15 pagesSWOT AnalysisTadesse Dinku100% (1)
- Basic Capital BudgetingDocument42 pagesBasic Capital BudgetingMay Abia100% (2)
- Earned Value Project Management (Fourth Edition)From EverandEarned Value Project Management (Fourth Edition)Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- Chapter 13Document34 pagesChapter 13Aryan JainNo ratings yet
- HMM 409 Project Management Unit - 2Document46 pagesHMM 409 Project Management Unit - 2Shivam SinghNo ratings yet
- Project Finance: Valuing Unlevered ProjectsDocument41 pagesProject Finance: Valuing Unlevered ProjectsKelsey GaoNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument24 pagesCapital BudgetingHassaan NasirNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Estimation and Risk AnalysisDocument52 pagesCash Flow Estimation and Risk AnalysisHeather Cabahug100% (1)
- Cash Flow Estimation and Capital BudgetingDocument29 pagesCash Flow Estimation and Capital BudgetingShehroz Saleem QureshiNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document63 pagesCH 11Duc Tai NguyenNo ratings yet
- Ch11 RevisedDocument33 pagesCh11 RevisedNhân TrầnNo ratings yet
- CASH FLOW ESTIMATION Week 6Document30 pagesCASH FLOW ESTIMATION Week 6adulmi325No ratings yet
- FIN2004 - 2704 Week 10 SlidesDocument61 pagesFIN2004 - 2704 Week 10 SlidesNguyen DzungNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting - December 2015Document19 pagesCapital Budgeting - December 2015apoorv jindalNo ratings yet
- 4 - Cash Flow EstimationDocument11 pages4 - Cash Flow Estimationdestinyrocks88No ratings yet
- Cash Flow Estimation and Risk AnalysisDocument39 pagesCash Flow Estimation and Risk AnalysisRanyDAmandaNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting - Adv IssuesDocument21 pagesCapital Budgeting - Adv IssuesdixitBhavak DixitNo ratings yet
- A. The Importance of Capital BudgetingDocument16 pagesA. The Importance of Capital BudgetingManish ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Multinational Capital BudgetingDocument19 pagesMultinational Capital BudgetingHania Doll100% (1)
- Hellpfull 10 11Document18 pagesHellpfull 10 11Mehran MumtazNo ratings yet
- International Capital BudgetingDocument43 pagesInternational Capital BudgetingRammohanreddy RajidiNo ratings yet
- S7-Capital BudgetingDocument78 pagesS7-Capital BudgetingShaheer BaigNo ratings yet
- DR 6 UryutfyutfutduDocument13 pagesDR 6 UryutfyutfutduWisnu1201091No ratings yet
- Acf302: Corporate Finance: Capital Budgeting and Valuation With Leverage - Part IDocument43 pagesAcf302: Corporate Finance: Capital Budgeting and Valuation With Leverage - Part IXue Meng LuNo ratings yet
- Final Project Cash FlowsDocument25 pagesFinal Project Cash FlowsLalit Sondhi100% (1)
- Capital Budgeting - Part 1Document6 pagesCapital Budgeting - Part 1Aurelia RijiNo ratings yet
- 29th Aug 2023 Final Complex Investment DecisionsDocument15 pages29th Aug 2023 Final Complex Investment DecisionsKunal KadamNo ratings yet
- 2.8 SKILL Financial AnalysisDocument63 pages2.8 SKILL Financial AnalysisYared AssefaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Corporate Finance, 2/e: Robert Parrino, Ph.D. David S. Kidwell, Ph.D. Thomas W. Bates, PH.DDocument56 pagesFundamentals of Corporate Finance, 2/e: Robert Parrino, Ph.D. David S. Kidwell, Ph.D. Thomas W. Bates, PH.DNguyen Thi Mai Lan100% (1)
- 3.3 Project Feasibility StudyDocument20 pages3.3 Project Feasibility Studydawit tibebuNo ratings yet
- MBA Lec - Capital BudgetingDocument85 pagesMBA Lec - Capital BudgetingNathasha RathnayakeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document41 pagesChapter 5Project MgtNo ratings yet
- InternshipDocument17 pagesInternshipHimanshu Sekhar GuruNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument26 pagesCapital BudgetingGowryshankar SumatharanNo ratings yet
- EBF 2054 Capital BudgetingDocument48 pagesEBF 2054 Capital BudgetingizzatiNo ratings yet
- Capital Investment DecisionspptDocument24 pagesCapital Investment DecisionspptDeepika PantNo ratings yet
- 2017 2018 Eup 222 Sem 1 Project Finance Topic Outcome 1Document49 pages2017 2018 Eup 222 Sem 1 Project Finance Topic Outcome 1NNadiah IsaNo ratings yet
- Part 4 Capital BudgetingDocument5 pagesPart 4 Capital BudgetingToulouse18No ratings yet
- FINA2010 Financial Management: Lecture 5: Capital Budgeting IIDocument54 pagesFINA2010 Financial Management: Lecture 5: Capital Budgeting IImoonNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument11 pagesCapital BudgetingSumit AroraNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting: Kavishe W.FDocument39 pagesCapital Budgeting: Kavishe W.FThomasaquinos Gerald Msigala Jr.No ratings yet
- Risk in Capital BudgetingDocument17 pagesRisk in Capital BudgetingSabit Ahmed Aleem100% (1)
- Cu Capital BudgetingDocument22 pagesCu Capital BudgetingHarshita ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument18 pagesCapital BudgetingYash ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting DecisionsDocument28 pagesCapital Budgeting DecisionsMoshmi MazumdarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 CASH FLOW ESTIMATION-1 - 15713Document20 pagesLecture 4 CASH FLOW ESTIMATION-1 - 15713Furqan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Session 06Document27 pagesSession 06Jaya RoyNo ratings yet
- PPCH 08Document41 pagesPPCH 08Nady SouzaNo ratings yet
- 10.cap+budgeting Cash Flows-1Document20 pages10.cap+budgeting Cash Flows-1Navid GodilNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Project Management 7Document31 pagesUnit 7 Project Management 7chuchuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Project Cash FlowsDocument28 pagesChapter 9 Project Cash FlowsGovinda AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Cash Flow Estimation and Risks AnalysisDocument45 pagesChapter 12: Cash Flow Estimation and Risks AnalysisElizabeth Espinosa ManilagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Cash Flow Estimation and Risks AnalysisDocument45 pagesChapter 12: Cash Flow Estimation and Risks AnalysisElizabeth Espinosa ManilagNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Unit 2 Study Guide StudentsDocument8 pagesCorporate Finance Unit 2 Study Guide StudentsJust for Silly UseNo ratings yet
- Week 9 Notes OnCapital BudgetingDocument13 pagesWeek 9 Notes OnCapital BudgetingAnonymous O5asZmNo ratings yet
- Teoria Financial Management IIDocument83 pagesTeoria Financial Management IIMANUEL GONZÁLEZNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document37 pagesLecture 8Tesfaye ejetaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Managerial Finance: Capital Budgeting and Cash Flow PrinciplesDocument37 pagesPrinciples of Managerial Finance: Capital Budgeting and Cash Flow PrinciplesJoshNo ratings yet
- Applied Corporate Finance. What is a Company worth?From EverandApplied Corporate Finance. What is a Company worth?Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Investments Profitability, Time Value & Risk Analysis: Guidelines for Individuals and CorporationsFrom EverandInvestments Profitability, Time Value & Risk Analysis: Guidelines for Individuals and CorporationsNo ratings yet
- Darwin Capuno PT 2 Las 4Document3 pagesDarwin Capuno PT 2 Las 4Darwin CapunoNo ratings yet
- News Release 2 Araw NG KasambahayDocument1 pageNews Release 2 Araw NG KasambahayjulyenfortunatoNo ratings yet
- Module 10 Inflation RevDocument12 pagesModule 10 Inflation RevGumiNo ratings yet
- Internship Report PELDocument60 pagesInternship Report PELsara-bashir-8426No ratings yet
- Week-12 Financial Analysis EUAC, Gradient and Capitalized Cost AnalysisDocument15 pagesWeek-12 Financial Analysis EUAC, Gradient and Capitalized Cost AnalysisMustajab KhanNo ratings yet
- Ps 3Document2 pagesPs 3King LeonidusNo ratings yet
- PRMG 135 - Ass. 01 Answering GuidanceDocument1 pagePRMG 135 - Ass. 01 Answering GuidanceMohammed SaadNo ratings yet
- Mitc Gold RCPDocument6 pagesMitc Gold RCPu4rishiNo ratings yet
- Quiz Week 2 No AnswerDocument10 pagesQuiz Week 2 No AnswerKatherine EderosasNo ratings yet
- TF 00000049Document2 pagesTF 00000049chkzaNo ratings yet
- Research On Sustainable Development of Textile Industrial Clusters in The Process of GlobalizationDocument5 pagesResearch On Sustainable Development of Textile Industrial Clusters in The Process of GlobalizationSam AbdulNo ratings yet
- Douglas Robert Brown - The Food Service Manager's Guide To Creative Cost Cutting - Over 2,001 Innovative and Simple Ways To Save Your Food Service Operation Thousands by Reducing Expenses-Atlantic PubDocument170 pagesDouglas Robert Brown - The Food Service Manager's Guide To Creative Cost Cutting - Over 2,001 Innovative and Simple Ways To Save Your Food Service Operation Thousands by Reducing Expenses-Atlantic PubTemo BeasNo ratings yet
- Econ 2Document11 pagesEcon 2Marcos PittmanNo ratings yet
- Textile Business PlanDocument3 pagesTextile Business PlanJoshua Anim100% (2)
- De Dollar Is at I On AnonymousDocument36 pagesDe Dollar Is at I On AnonymousTanmaye ShagotraNo ratings yet
- BPE-60312 Sept 2020 - MARKET ANALYSISDocument26 pagesBPE-60312 Sept 2020 - MARKET ANALYSISAntonio MoncayoNo ratings yet
- Manuals For Participants PDFDocument5 pagesManuals For Participants PDFindra alverdianNo ratings yet
- SFM Formulae PDFDocument255 pagesSFM Formulae PDFpiyush bansalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 MonitoringDocument37 pagesChapter 11 MonitoringRana LaeeqNo ratings yet
- Introduction Page For LNMCBMDocument3 pagesIntroduction Page For LNMCBMShivam KumarNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment ERP-2021 KduDocument10 pagesIndividual Assignment ERP-2021 KduPradeep AnuradhaNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Tbch09 578d492668ce2Document40 pagesDokumen - Tips Tbch09 578d492668ce2lei veraNo ratings yet
- Golden ABC Inc.Document7 pagesGolden ABC Inc.Ivy Mhae SantiaguelNo ratings yet
- Sbi LifeDocument16 pagesSbi LifesahilNo ratings yet
- Sustainable RegenerationDocument72 pagesSustainable RegenerationDipayan BhowmikNo ratings yet
- Flexible Budget Examples Chapter 18Document9 pagesFlexible Budget Examples Chapter 18Surbhi JainNo ratings yet
- Pricing and Revenue Management in A Supply Chain: True/FalseDocument16 pagesPricing and Revenue Management in A Supply Chain: True/FalseHaris AmirNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Built Environment: The Role of Quantity SurveyorsDocument6 pagesSustainable Built Environment: The Role of Quantity SurveyorsChanna KariyawasamNo ratings yet
- 4.1 The Role of MarketingDocument23 pages4.1 The Role of MarketingDanae Illia GamarraNo ratings yet