Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LecturesNotes (MEE122) 78
LecturesNotes (MEE122) 78
Uploaded by
mhd slmnCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Exercise Problems: By: Kristel Shane R. Lenon SPL Ce-5B (Inc)Document25 pagesExercise Problems: By: Kristel Shane R. Lenon SPL Ce-5B (Inc)Kristel Lenon0% (2)
- Tutorial Chapter 03 - Conservation of Energy - AnswerDocument6 pagesTutorial Chapter 03 - Conservation of Energy - AnswerMukhzin Rashid100% (3)
- Tutorial Chapter 03 - QuestionsDocument2 pagesTutorial Chapter 03 - QuestionsMarzs MarNo ratings yet
- Fluid 52Document1 pageFluid 52mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Inflow Device - ProductionDocument9 pagesInflow Device - Productionmfazaeli40No ratings yet
- Homework of Chapter (4.2,4.3) : Dead Line: Saturday (24/3/2018)Document5 pagesHomework of Chapter (4.2,4.3) : Dead Line: Saturday (24/3/2018)aditya divyadarshiNo ratings yet
- Exercise Sheet 6Document4 pagesExercise Sheet 6Gonçalo GuerreiroNo ratings yet
- Sheet 6Document3 pagesSheet 6Hussien El-masryNo ratings yet
- Solution of Sheet No.2 (Blank)Document14 pagesSolution of Sheet No.2 (Blank)محمد خريبطNo ratings yet
- Tutorial QN 6-10Document6 pagesTutorial QN 6-10clarence limNo ratings yet
- Fluid 4Document1 pageFluid 4mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Sheet No1Document5 pagesSheet No1Ismail SakrNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.2Document5 pagesAssignment No.2Nonsikelelo GobozaNo ratings yet
- Lec-11 (Hydraulics of Water Distribution System)Document30 pagesLec-11 (Hydraulics of Water Distribution System)Muhammad MateenNo ratings yet
- UGNA3023 Report 1Document12 pagesUGNA3023 Report 1Shawn OngNo ratings yet
- Assignment#1Document4 pagesAssignment#1hishamlashennNo ratings yet
- Garcia Lopez Sebastian Homework05Document6 pagesGarcia Lopez Sebastian Homework05Sebastián García LópezNo ratings yet
- Lec4. Practical Applications of Bernoulli Equation By. Engr - Wendhel Q.LDocument5 pagesLec4. Practical Applications of Bernoulli Equation By. Engr - Wendhel Q.Ljames PrincipeNo ratings yet
- HYDR 225 TUTORIAL 3 FRIDAY 20TH May 2022Document4 pagesHYDR 225 TUTORIAL 3 FRIDAY 20TH May 2022Khabane LelokaNo ratings yet
- Boundary Layer Theory Problems Sheet - I - 2017 - 18Document1 pageBoundary Layer Theory Problems Sheet - I - 2017 - 18Abhyuday SharmaNo ratings yet
- CE443 04 GritDocument17 pagesCE443 04 GritPasunkiliNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 1-2022Document6 pagesSheet - 1-2022Ismail SakrNo ratings yet
- "To Determine C of Venturimeter and Hence Calibrate It": Experiment # 11Document3 pages"To Determine C of Venturimeter and Hence Calibrate It": Experiment # 11Kamran AliNo ratings yet
- Lec-11 (Hydraulics of Water Distribution System)Document29 pagesLec-11 (Hydraulics of Water Distribution System)Bint e HawaNo ratings yet
- Lec-11 (Hydraulics of Water Distribution System)Document29 pagesLec-11 (Hydraulics of Water Distribution System)Bint e HawaNo ratings yet
- Storm-Drainage - On RunoffDocument20 pagesStorm-Drainage - On Runoffrosalesapril0214No ratings yet
- Irrigation Basic HydraulicsDocument27 pagesIrrigation Basic Hydraulicsaz4049581No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Governing Laws and Principles: Self Evaluation Questions and AnswersDocument22 pagesLecture 4 - Governing Laws and Principles: Self Evaluation Questions and AnswersMohamedNo ratings yet
- Rr210201 Hydraulics and Hydraulic MachineryDocument8 pagesRr210201 Hydraulics and Hydraulic MachinerySRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- AssumptionsDocument1 pageAssumptionsKerlos SaeedNo ratings yet
- ADocument1 pageAIago GrossNo ratings yet
- Fluid ProblemsDocument6 pagesFluid ProblemsAlaa ShammaaNo ratings yet
- Rr220301 Mechanics of FluidsDocument8 pagesRr220301 Mechanics of Fluidslibrarian_abitNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Needle ValveDocument23 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Needle Valvemet-calcNo ratings yet
- Exercise Problems On Pipe FlowDocument2 pagesExercise Problems On Pipe FlowArina Priyanka VedaswariNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Chapter-4Document7 pagesFluid Mechanics: Chapter-4Ahmed SuhailNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Chapter-4Document7 pagesFluid Mechanics: Chapter-4Ahmed SuhailNo ratings yet
- AEE 211-Hw05-2023-2-Rev 2Document7 pagesAEE 211-Hw05-2023-2-Rev 2AlexanderNo ratings yet
- NAME 409 Pump MathsDocument10 pagesNAME 409 Pump Mathsisrat jahanNo ratings yet
- Continuity and Energy Equation TutorialDocument2 pagesContinuity and Energy Equation TutorialmujunaidphdNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Learning ManualDocument8 pagesHydraulics Learning ManualJebone Stein Web JuarbalNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 2 Incompressible Flow 2022-1Document26 pagesLecture Notes 2 Incompressible Flow 2022-1Slindokuhle ThandoNo ratings yet
- Determination of Friction Factor of Pipe Lines: Al Habeeb College of Engineering & TechnologyDocument3 pagesDetermination of Friction Factor of Pipe Lines: Al Habeeb College of Engineering & TechnologyAsrar UddinNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Machinery (QB)Document26 pagesFluid Mechanics and Machinery (QB)KARTHICK MNo ratings yet
- Ke-103944 8Document1 pageKe-103944 8KhalidNo ratings yet
- VENTURIMETERDocument10 pagesVENTURIMETERKrishan PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Jntuworld: R09 Set No. 2Document9 pagesJntuworld: R09 Set No. 2saiteja1234No ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Needle Valve Closing Flow Against The Direction of Movement of The PistonDocument23 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Needle Valve Closing Flow Against The Direction of Movement of The Pistonmet-calcNo ratings yet
- Piping System in Building: Asst. Prof. Channarong AsavatesanupapDocument59 pagesPiping System in Building: Asst. Prof. Channarong AsavatesanupapIatan AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Mee3221 Mee4205Document18 pagesMee3221 Mee4205Lim WcNo ratings yet
- Example ExtraDocument7 pagesExample Extraaland pshtiwanNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 6 PumpsDocument3 pagesSheet - 6 PumpsS.A. BeskalesNo ratings yet
- Assignment#3Document3 pagesAssignment#3hishamlashennNo ratings yet
- Sesion 5 FLOW MEASUREMENTDocument32 pagesSesion 5 FLOW MEASUREMENTmuh amarNo ratings yet
- ChemEngineering 02 00019 v2Document14 pagesChemEngineering 02 00019 v2Amine HamaouiNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1 (Flow Through Pipes) ModifiedDocument2 pagesSheet 1 (Flow Through Pipes) ModifiedS.A. BeskalesNo ratings yet
- FM Test 1 - ADocument1 pageFM Test 1 - Asankarsuper83No ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsFrom EverandEnhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Presentation Chapter 04.1 4Document1 pagePresentation Chapter 04.1 4mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Ucmp MCQDocument10 pagesUnit 4 Ucmp MCQmhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Interoduction 3Document1 pageModule 1 Interoduction 3mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Mid 2Document13 pagesTest Bank Mid 2mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Advance Manufacturing Processes MCQ S 1 PDFDocument18 pagesAdvance Manufacturing Processes MCQ S 1 PDFmhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Presentation Chapter 04.1 7 PDFDocument1 pagePresentation Chapter 04.1 7 PDFmhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Advanced Machine ProcessesDocument7 pagesAdvanced Machine Processesmhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Interoduction 8Document1 pageModule 1 Interoduction 8mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Interoduction 7Document1 pageModule 1 Interoduction 7mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Interoduction 9Document1 pageModule 1 Interoduction 9mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Interoduction 4Document1 pageModule 1 Interoduction 4mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Interoduction 6Document1 pageModule 1 Interoduction 6mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Interoduction 5Document1 pageModule 1 Interoduction 5mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 76Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 76mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 79Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 79mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 89Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 89mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 77Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 77mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 75Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 75mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 74Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 74mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 86Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 86mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Fluid 52Document1 pageFluid 52mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 72Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 72mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 84Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 84mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 73Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 73mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 71Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 71mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 87Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 87mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 88Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 88mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 85Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 85mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 82Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 82mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Fluid 8Document1 pageFluid 8mhd slmnNo ratings yet
LecturesNotes (MEE122) 78
LecturesNotes (MEE122) 78
Uploaded by
mhd slmnOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LecturesNotes (MEE122) 78
LecturesNotes (MEE122) 78
Uploaded by
mhd slmnCopyright:
Available Formats
78
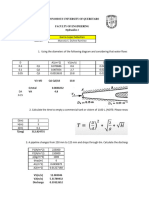
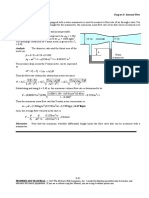
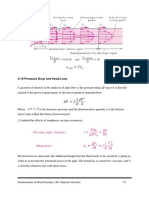
Example 2
Water at 10C (=999.7 kg/m3 and =1.307 x10-3 kg/m s) is flowing steadily in a 0.20-
cm-diameter, 15-mlong pipe at an average velocity of 1.2 m/s. Determine (a) the pressure
drop, (b) the head loss, and (c) the pumping power requirement to overcome this pressure
drop.
= 999.7 kg/m3 and = 1.30710-3 kg/ms, V = 1.2 m/s
Assumptions 1 The flow is steady and incompressible. 2 The entrance effects are negligible,
and thus the flow is fully developed. 3 The pipe involves no components such as bends,
valves, and connectors. 4 The piping section involves no work devices such as pumps and
turbines.
Water D = 0.2 cm
1.2 m/s
L = 15 m
Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics (Dr. Hameed Alawadi) 78
You might also like
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Exercise Problems: By: Kristel Shane R. Lenon SPL Ce-5B (Inc)Document25 pagesExercise Problems: By: Kristel Shane R. Lenon SPL Ce-5B (Inc)Kristel Lenon0% (2)
- Tutorial Chapter 03 - Conservation of Energy - AnswerDocument6 pagesTutorial Chapter 03 - Conservation of Energy - AnswerMukhzin Rashid100% (3)
- Tutorial Chapter 03 - QuestionsDocument2 pagesTutorial Chapter 03 - QuestionsMarzs MarNo ratings yet
- Fluid 52Document1 pageFluid 52mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Inflow Device - ProductionDocument9 pagesInflow Device - Productionmfazaeli40No ratings yet
- Homework of Chapter (4.2,4.3) : Dead Line: Saturday (24/3/2018)Document5 pagesHomework of Chapter (4.2,4.3) : Dead Line: Saturday (24/3/2018)aditya divyadarshiNo ratings yet
- Exercise Sheet 6Document4 pagesExercise Sheet 6Gonçalo GuerreiroNo ratings yet
- Sheet 6Document3 pagesSheet 6Hussien El-masryNo ratings yet
- Solution of Sheet No.2 (Blank)Document14 pagesSolution of Sheet No.2 (Blank)محمد خريبطNo ratings yet
- Tutorial QN 6-10Document6 pagesTutorial QN 6-10clarence limNo ratings yet
- Fluid 4Document1 pageFluid 4mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Sheet No1Document5 pagesSheet No1Ismail SakrNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.2Document5 pagesAssignment No.2Nonsikelelo GobozaNo ratings yet
- Lec-11 (Hydraulics of Water Distribution System)Document30 pagesLec-11 (Hydraulics of Water Distribution System)Muhammad MateenNo ratings yet
- UGNA3023 Report 1Document12 pagesUGNA3023 Report 1Shawn OngNo ratings yet
- Assignment#1Document4 pagesAssignment#1hishamlashennNo ratings yet
- Garcia Lopez Sebastian Homework05Document6 pagesGarcia Lopez Sebastian Homework05Sebastián García LópezNo ratings yet
- Lec4. Practical Applications of Bernoulli Equation By. Engr - Wendhel Q.LDocument5 pagesLec4. Practical Applications of Bernoulli Equation By. Engr - Wendhel Q.Ljames PrincipeNo ratings yet
- HYDR 225 TUTORIAL 3 FRIDAY 20TH May 2022Document4 pagesHYDR 225 TUTORIAL 3 FRIDAY 20TH May 2022Khabane LelokaNo ratings yet
- Boundary Layer Theory Problems Sheet - I - 2017 - 18Document1 pageBoundary Layer Theory Problems Sheet - I - 2017 - 18Abhyuday SharmaNo ratings yet
- CE443 04 GritDocument17 pagesCE443 04 GritPasunkiliNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 1-2022Document6 pagesSheet - 1-2022Ismail SakrNo ratings yet
- "To Determine C of Venturimeter and Hence Calibrate It": Experiment # 11Document3 pages"To Determine C of Venturimeter and Hence Calibrate It": Experiment # 11Kamran AliNo ratings yet
- Lec-11 (Hydraulics of Water Distribution System)Document29 pagesLec-11 (Hydraulics of Water Distribution System)Bint e HawaNo ratings yet
- Lec-11 (Hydraulics of Water Distribution System)Document29 pagesLec-11 (Hydraulics of Water Distribution System)Bint e HawaNo ratings yet
- Storm-Drainage - On RunoffDocument20 pagesStorm-Drainage - On Runoffrosalesapril0214No ratings yet
- Irrigation Basic HydraulicsDocument27 pagesIrrigation Basic Hydraulicsaz4049581No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Governing Laws and Principles: Self Evaluation Questions and AnswersDocument22 pagesLecture 4 - Governing Laws and Principles: Self Evaluation Questions and AnswersMohamedNo ratings yet
- Rr210201 Hydraulics and Hydraulic MachineryDocument8 pagesRr210201 Hydraulics and Hydraulic MachinerySRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- AssumptionsDocument1 pageAssumptionsKerlos SaeedNo ratings yet
- ADocument1 pageAIago GrossNo ratings yet
- Fluid ProblemsDocument6 pagesFluid ProblemsAlaa ShammaaNo ratings yet
- Rr220301 Mechanics of FluidsDocument8 pagesRr220301 Mechanics of Fluidslibrarian_abitNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Needle ValveDocument23 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Needle Valvemet-calcNo ratings yet
- Exercise Problems On Pipe FlowDocument2 pagesExercise Problems On Pipe FlowArina Priyanka VedaswariNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Chapter-4Document7 pagesFluid Mechanics: Chapter-4Ahmed SuhailNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Chapter-4Document7 pagesFluid Mechanics: Chapter-4Ahmed SuhailNo ratings yet
- AEE 211-Hw05-2023-2-Rev 2Document7 pagesAEE 211-Hw05-2023-2-Rev 2AlexanderNo ratings yet
- NAME 409 Pump MathsDocument10 pagesNAME 409 Pump Mathsisrat jahanNo ratings yet
- Continuity and Energy Equation TutorialDocument2 pagesContinuity and Energy Equation TutorialmujunaidphdNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Learning ManualDocument8 pagesHydraulics Learning ManualJebone Stein Web JuarbalNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 2 Incompressible Flow 2022-1Document26 pagesLecture Notes 2 Incompressible Flow 2022-1Slindokuhle ThandoNo ratings yet
- Determination of Friction Factor of Pipe Lines: Al Habeeb College of Engineering & TechnologyDocument3 pagesDetermination of Friction Factor of Pipe Lines: Al Habeeb College of Engineering & TechnologyAsrar UddinNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Machinery (QB)Document26 pagesFluid Mechanics and Machinery (QB)KARTHICK MNo ratings yet
- Ke-103944 8Document1 pageKe-103944 8KhalidNo ratings yet
- VENTURIMETERDocument10 pagesVENTURIMETERKrishan PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Jntuworld: R09 Set No. 2Document9 pagesJntuworld: R09 Set No. 2saiteja1234No ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Needle Valve Closing Flow Against The Direction of Movement of The PistonDocument23 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Needle Valve Closing Flow Against The Direction of Movement of The Pistonmet-calcNo ratings yet
- Piping System in Building: Asst. Prof. Channarong AsavatesanupapDocument59 pagesPiping System in Building: Asst. Prof. Channarong AsavatesanupapIatan AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Mee3221 Mee4205Document18 pagesMee3221 Mee4205Lim WcNo ratings yet
- Example ExtraDocument7 pagesExample Extraaland pshtiwanNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 6 PumpsDocument3 pagesSheet - 6 PumpsS.A. BeskalesNo ratings yet
- Assignment#3Document3 pagesAssignment#3hishamlashennNo ratings yet
- Sesion 5 FLOW MEASUREMENTDocument32 pagesSesion 5 FLOW MEASUREMENTmuh amarNo ratings yet
- ChemEngineering 02 00019 v2Document14 pagesChemEngineering 02 00019 v2Amine HamaouiNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1 (Flow Through Pipes) ModifiedDocument2 pagesSheet 1 (Flow Through Pipes) ModifiedS.A. BeskalesNo ratings yet
- FM Test 1 - ADocument1 pageFM Test 1 - Asankarsuper83No ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsFrom EverandEnhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Presentation Chapter 04.1 4Document1 pagePresentation Chapter 04.1 4mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Ucmp MCQDocument10 pagesUnit 4 Ucmp MCQmhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Interoduction 3Document1 pageModule 1 Interoduction 3mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Mid 2Document13 pagesTest Bank Mid 2mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Advance Manufacturing Processes MCQ S 1 PDFDocument18 pagesAdvance Manufacturing Processes MCQ S 1 PDFmhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Presentation Chapter 04.1 7 PDFDocument1 pagePresentation Chapter 04.1 7 PDFmhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Advanced Machine ProcessesDocument7 pagesAdvanced Machine Processesmhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Interoduction 8Document1 pageModule 1 Interoduction 8mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Interoduction 7Document1 pageModule 1 Interoduction 7mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Interoduction 9Document1 pageModule 1 Interoduction 9mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Interoduction 4Document1 pageModule 1 Interoduction 4mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Interoduction 6Document1 pageModule 1 Interoduction 6mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Interoduction 5Document1 pageModule 1 Interoduction 5mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 76Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 76mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 79Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 79mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 89Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 89mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 77Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 77mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 75Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 75mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 74Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 74mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 86Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 86mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Fluid 52Document1 pageFluid 52mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 72Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 72mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 84Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 84mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 73Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 73mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 71Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 71mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 87Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 87mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 88Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 88mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 85Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 85mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 82Document1 pageLecturesNotes (MEE122) 82mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Fluid 8Document1 pageFluid 8mhd slmnNo ratings yet