Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prefixes Used in The SI System
Prefixes Used in The SI System
Uploaded by
toanvmpetrologxOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prefixes Used in The SI System
Prefixes Used in The SI System
Uploaded by
toanvmpetrologxCopyright:
Available Formats
SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY 9
Table 1.3 Prefixes used in the SI System
Multiple Prefix Symbol
10–24 yocto y
10–21 zepto z
–18
10 atto a
–15
10 femto f
–12
10 pico p
–9
10 nano n
10 –6
micro µ
10–3 milli m
10–2 centi c
–1
10 deci d
10 deca da
2
10 hecto h
3
10 kilo k
6
10 mega M
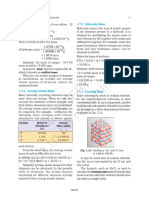
Fig. 1.5 Analytical balance
109 giga G
1012 tera T
15
SI system, volume has units of m3. But again,
10 peta P
in chemistry laboratories, smaller volumes are
1018 exa E used. Hence, volume is often denoted in cm3
21
10 zeta Z or dm3 units.
24
10 yotta Y A common unit, litre (L) which is not an SI
unit, is used for measurement of volume of
1.3.4 Mass and Weight
liquids.
Mass of a substance is the amount of matter 1 L = 1000 mL , 1000 cm3 = 1 dm3
present in it, while weight is the force exerted
by gravity on an object. The mass of a Fig. 1.6 helps to visualise these relations.
substance is constant, whereas, its weight
may vary from one place to another due to
change in gravity. You should be careful in
using these terms.
The mass of a substance can be determined
accurately in the laboratory by using an
analytical balance (Fig. 1.5).
The SI unit of mass as given in Table 1.1 is
kilogram. However, its fraction named as gram
(1 kg = 1000 g), is used in laboratories due to
the smaller amounts of chemicals used in
chemical reactions.
1.3.5 Volume
Volume is the amont of space occupied by a Fig. 1.6 Different units used to express
substance. It has the units of (length)3. So in volume
2022-23
You might also like
- Pre-Season Wrestling Strength ProgramDocument25 pagesPre-Season Wrestling Strength Programalex waeghe100% (2)
- Full Download Solution Manual For Thermodynamics An Engineering Approach 9th Edition Yunus Cengel Michael Boles PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Solution Manual For Thermodynamics An Engineering Approach 9th Edition Yunus Cengel Michael Boles PDF Full Chapteruniteacerichgsib90% (20)
- Thors Power Program Deadlift Gospel Microsoft ExcelDocument14 pagesThors Power Program Deadlift Gospel Microsoft ExceltomNo ratings yet
- 6 Day PPL Split For Strength and Hypertrophy PDFDocument7 pages6 Day PPL Split For Strength and Hypertrophy PDFAnkit Sharma100% (1)
- Presentation: Group 3: Cruz, Tristen de Leon, Rico Dela Pena, Meanna Durante, MadelaineDocument11 pagesPresentation: Group 3: Cruz, Tristen de Leon, Rico Dela Pena, Meanna Durante, MadelaineMarilou MacasinagNo ratings yet
- D3739-US Rev D EZIII Technical Manual0Document72 pagesD3739-US Rev D EZIII Technical Manual0raguilar1abc1No ratings yet
- Blending Plant Operations Audit ProtocolDocument18 pagesBlending Plant Operations Audit ProtocolshisokarNo ratings yet
- Basic Laboratory TechniquesDocument9 pagesBasic Laboratory TechniquesannaNo ratings yet
- SI UnitsDocument2 pagesSI UnitsChastine CruzNo ratings yet
- CHEM 1111 Experiment 1 Lab Report Basic Laboratory TechniquesDocument16 pagesCHEM 1111 Experiment 1 Lab Report Basic Laboratory TechniquesDARYLL WAYNE MATUTINONo ratings yet
- Measurement of Physical QuantitiesDocument2 pagesMeasurement of Physical QuantitiesEarl CalingacionNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheets: Quarter 1, 1st Week, Lesson 1Document3 pagesLearning Activity Sheets: Quarter 1, 1st Week, Lesson 1Almar Jade DagayloanNo ratings yet
- AnnouncementsDocument29 pagesAnnouncementsJay-anne CruzNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Chemistry - For - Engineers - 1 - Basic - Concepts - Topic - 02 - Student - Review - On - MeasurementDocument12 pages2.2 Chemistry - For - Engineers - 1 - Basic - Concepts - Topic - 02 - Student - Review - On - MeasurementJay GrijaldoNo ratings yet
- Module 4-Principles of Measurement and Laboratory Mathematics in Clinical ChemistryDocument6 pagesModule 4-Principles of Measurement and Laboratory Mathematics in Clinical ChemistryAllyah Ross DuqueNo ratings yet
- Units DimensionsDocument18 pagesUnits DimensionsSatyajit ManeNo ratings yet
- Conversion of UnitsDocument3 pagesConversion of UnitsJonn Jhasmir MirNo ratings yet
- Che 1000 Stoichiometry Lecture Notes 2020 Academic Year 09 Mar 2021Document27 pagesChe 1000 Stoichiometry Lecture Notes 2020 Academic Year 09 Mar 2021Nathan MulunguNo ratings yet
- FinalestDocument76 pagesFinalestKristen Janna BulaNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument101 pagesGeneral ChemistryNohelia Fer GavNo ratings yet
- Genchem Lesson 2Document4 pagesGenchem Lesson 2Joeleo Aldrin SupnetNo ratings yet
- LAS 1 Units Physical Quantities Measurement Errors and UncertaintiesDocument19 pagesLAS 1 Units Physical Quantities Measurement Errors and UncertaintiesFlor de AldaNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1650888596496 6924328643841126121Document36 pagesOrca Share Media1650888596496 6924328643841126121CjeayNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Intro and Review To MathematicsDocument8 pagesUnit 1 - Intro and Review To MathematicsCelive SiendaNo ratings yet
- Calculations Used in Analytical Chemistry: Savitribai Phule Pune UniversityDocument21 pagesCalculations Used in Analytical Chemistry: Savitribai Phule Pune UniversityZari Sofia LevisteNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document17 pagesModule 1Kenth Godfrei DoctoleroNo ratings yet
- What Are The PrefixesDocument17 pagesWhat Are The PrefixesAmeer AzharNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry: AtomsDocument52 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry: AtomsSuyash A.100% (1)
- Measurements in Analytical ChemistryDocument6 pagesMeasurements in Analytical Chemistrymaya 1DNo ratings yet
- Combined ChaptersDocument218 pagesCombined Chaptersalvin adjei100% (4)
- Unit 1 ProblemsDocument5 pagesUnit 1 ProblemsFrederick NakosNo ratings yet
- MeasurementDocument7 pagesMeasurementJosh PNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument135 pagesPhysicspraveen reddyNo ratings yet
- Las 1Document33 pagesLas 1ShernanNo ratings yet
- D'unités. It Is The Most Commonly Used Metric SystemDocument7 pagesD'unités. It Is The Most Commonly Used Metric SystemZunnuraini AliyuNo ratings yet
- Quantities Are Symbolised by Italic Letters!: Measurement. Si Quantities and UnitsDocument2 pagesQuantities Are Symbolised by Italic Letters!: Measurement. Si Quantities and UnitsDane BosevNo ratings yet
- General-Physics-1 Q1 W1 M1 LDS Measurements ALG RTPDocument13 pagesGeneral-Physics-1 Q1 W1 M1 LDS Measurements ALG RTPKaye Cee GonzaloNo ratings yet
- Rmf8e Ism-Ch01 Pp1-27 CRCDocument27 pagesRmf8e Ism-Ch01 Pp1-27 CRClvravestein1No ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY For First Years of Faculties of Science, Medicine and Pharmacy Part 1Document102 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY For First Years of Faculties of Science, Medicine and Pharmacy Part 1Abeer TamimiNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument5 pagesPhysicsMxR PlaysNo ratings yet
- Admmodule - Stem - Gp12eu-Ia-1 - Lesson 1Document17 pagesAdmmodule - Stem - Gp12eu-Ia-1 - Lesson 1reivill0730No ratings yet
- Chapter 01 PDFDocument19 pagesChapter 01 PDFDiego Esteban OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry Prelims Lecture ReviewerDocument4 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Prelims Lecture ReviewerAaliyah CarlobosNo ratings yet
- Análisis EstructuralDocument82 pagesAnálisis EstructuralHernan HuancaNo ratings yet
- Session 1Document20 pagesSession 1THE SEZARNo ratings yet
- الكميات الكهربائية78564Document2 pagesالكميات الكهربائية78564bdwbd2686No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 1 - Chemical HistoryDocument9 pagesLecture Notes 1 - Chemical HistoryannmarieNo ratings yet
- The Metric SystemDocument2 pagesThe Metric SystemtaiNo ratings yet
- FM Unit ConversionDocument29 pagesFM Unit ConversionAlthaf Basha V VNo ratings yet
- XI - PPT - UNITS AND MEASUREMENT (Part 1)Document43 pagesXI - PPT - UNITS AND MEASUREMENT (Part 1)Rupali PathakNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY For First Years of Faculties of Science, Medicine and Pharmacy Part 1Document102 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY For First Years of Faculties of Science, Medicine and Pharmacy Part 1Mufaddal KaderbhaiNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Lesson 2. LLPDocument44 pagesGrade 7 Lesson 2. LLPLimuel PeñarandaNo ratings yet
- Measurement. Senior HiDocument3 pagesMeasurement. Senior HiCamille MangliwanNo ratings yet
- Measurements: Physical Quantity Name of Unit AbbreviationDocument10 pagesMeasurements: Physical Quantity Name of Unit AbbreviationLIANNE GEMIMA GIPANo ratings yet
- Chemistry Bridging WorkDocument18 pagesChemistry Bridging WorkCraftyZaidNo ratings yet
- Combine ModuleDocument97 pagesCombine ModuleleahNo ratings yet
- Units and Dimensional AnalysisDocument5 pagesUnits and Dimensional AnalysisJuan Fernando Cano LarrotaNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument16 pagesScienceshauki.mangontraNo ratings yet
- CHM131 - Chapter 1 - UnitconversionsDocument45 pagesCHM131 - Chapter 1 - UnitconversionsNotes NotesNo ratings yet
- PHY 17 - College Physics I Chapter I-Introduction To PhysicsDocument4 pagesPHY 17 - College Physics I Chapter I-Introduction To Physicsruth ranselNo ratings yet
- CHM421 - Analytical Chemistry: Topic 1: Introduction (Definition)Document29 pagesCHM421 - Analytical Chemistry: Topic 1: Introduction (Definition)Nurul Izzah KaharNo ratings yet
- UnitsDocument38 pagesUnitsyoussef.yma999No ratings yet
- Measurement LessonDocument15 pagesMeasurement LessonMatthew SonntagNo ratings yet
- 2.1. Numbers in Analytical ChemistryDocument11 pages2.1. Numbers in Analytical ChemistryJohn LopezNo ratings yet
- Physics - Summer ExercisesDocument11 pagesPhysics - Summer ExercisesDIEGO FERNANDO BARRIOS DIAZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Matter & Measurement: AP Chemistry Unit 1 Notes Chapters 1 - 3Document28 pagesChapter 1: Matter & Measurement: AP Chemistry Unit 1 Notes Chapters 1 - 3Fwaaz AlbarqiNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- The Enabling Environment in PakistanDocument1 pageThe Enabling Environment in PakistantoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Example of Calculating Molecular MassDocument1 pageExample of Calculating Molecular MasstoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate Molecular MassDocument1 pageHow To Calculate Molecular MasstoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Some Physical PropertiesDocument1 pageMeasurement of Some Physical PropertiestoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- The Importance of ChemistryDocument1 pageThe Importance of ChemistrytoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Overshot Gates For Water MeasurementDocument1 pageOvershot Gates For Water MeasurementtoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Density and TemepraturesDocument1 pageMeasurement of Density and TemepraturestoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- 3.3.1 Waveforms: Waveforms Are A Kind of Graph. Graphs Have An X-Axis, Which RunsDocument1 page3.3.1 Waveforms: Waveforms Are A Kind of Graph. Graphs Have An X-Axis, Which RunstoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Flow Totalization of LiquidDocument1 pageFlow Totalization of LiquidtoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Reference On Properties of Various Southern Diesel BlendsDocument2 pagesReference On Properties of Various Southern Diesel BlendstoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Clausen Weir Rule For Wate Measurement UtahDocument1 pageClausen Weir Rule For Wate Measurement UtahtoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- English Studying TipsDocument3 pagesEnglish Studying TipstoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Solvent Extraction OsunDocument1 pageSolvent Extraction OsuntoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Environment Management System ManualDocument5 pagesEnvironment Management System ManualtoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Physics 71 - LE1 Review Session 1S2324Document51 pagesPhysics 71 - LE1 Review Session 1S2324raoul.inocencioNo ratings yet
- Basic Engineering SciencesDocument5 pagesBasic Engineering SciencesMeet JepsyNo ratings yet
- For CheckingDocument13 pagesFor CheckingCaitlin AbadNo ratings yet
- Thomas Herzog - Roland Krippner - Werner Lang - Facade Construction Manual-DeTAIL (2017)Document352 pagesThomas Herzog - Roland Krippner - Werner Lang - Facade Construction Manual-DeTAIL (2017)merveozgurNo ratings yet
- Numeracy TestDocument14 pagesNumeracy TestJeclyn FilipinasNo ratings yet
- ECS CEMulator Manual v7.0.5Document189 pagesECS CEMulator Manual v7.0.5Dennis IsikaNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws of Motion1Document6 pagesNewtons Laws of Motion1darlei byerotNo ratings yet
- Olympiad of Metropolises, Moscow Blitz Contest, September, 5 Task 1Document20 pagesOlympiad of Metropolises, Moscow Blitz Contest, September, 5 Task 1Lazar SavicNo ratings yet
- AFA AGRICROP 7 Module 3.PDF Version 1Document38 pagesAFA AGRICROP 7 Module 3.PDF Version 1ALEX PANERIO100% (3)
- DynamicsDocument2 pagesDynamicsVon A. Damirez0% (1)
- 11 AustenDocument3 pages11 AustenCyprus Chad G. LausNo ratings yet
- The Student Hub - CSEC Physics Formula Booklet, Kerwin SpringerDocument50 pagesThe Student Hub - CSEC Physics Formula Booklet, Kerwin SpringerDaiquan StantonNo ratings yet
- PHSC Winter and Spring Learner Document 2019Document238 pagesPHSC Winter and Spring Learner Document 2019alwandeolwethu36No ratings yet
- Added Virtual Mass of Ship LewisDocument27 pagesAdded Virtual Mass of Ship LewisMd. Shahjada TarafderNo ratings yet
- Math7 Q2W2Document6 pagesMath7 Q2W2Meryl Fe P. GumeraNo ratings yet
- manualEMC 1Document27 pagesmanualEMC 1Parmeshwar Nath Tripathi25% (4)
- Dumbbell Curl Standards For Men and Women (LB)Document1 pageDumbbell Curl Standards For Men and Women (LB)David BenavidezNo ratings yet
- AHW Series Digital Weighing Scales Service ManualDocument21 pagesAHW Series Digital Weighing Scales Service ManualLuis Alberto Garcia CaychoNo ratings yet
- Batch For Steel IndustryDocument9 pagesBatch For Steel IndustryKAMALJEET SINGHNo ratings yet
- Portion Control of Sandwich and Its IngredientsDocument17 pagesPortion Control of Sandwich and Its IngredientsJoy LeddaNo ratings yet
- DLL Bread and Pastry g7 8Document71 pagesDLL Bread and Pastry g7 8AvelynJamoraNo ratings yet
- 2020 Ottawa Classic - Final Placings With OverallsDocument7 pages2020 Ottawa Classic - Final Placings With Overallsspam emailNo ratings yet
- Tohnichi Torque HandbookDocument114 pagesTohnichi Torque HandbookElJeremias100% (4)