Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biologia A Color
Biologia A Color
Uploaded by
Jorge Andres Vasquez AvilaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Essentials of Biology 5th Edition Mader Test BankDocument25 pagesEssentials of Biology 5th Edition Mader Test BankEdwardBrooksqcoi100% (54)
- Power Point Presentation of Bio Chem SIWESDocument13 pagesPower Point Presentation of Bio Chem SIWESUmar Ridwan saniNo ratings yet
- HCT 12 PDFDocument12 pagesHCT 12 PDFdoha73039944No ratings yet
- CellsDocument9 pagesCellsjasmineNo ratings yet
- Organelle With Solution 2022-23Document1 pageOrganelle With Solution 2022-23LuLaMejorNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument5 pages2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionIRDINA ADLIN BINTI FIRDAUS MoeNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles and Its StucturesDocument7 pagesCell Organelles and Its StucturesHailey Eisleen LazaroNo ratings yet
- Basic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismDocument2 pagesBasic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismkikomagsaysayNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Structure & FunctionDocument4 pagesCell Organelles Structure & FunctionDaniel ChinNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument72 pagesThe Cellbir.email013No ratings yet
- Cell NotesDocument7 pagesCell NotesBrohi NadeemNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and Functions Review ANSWER KEYDocument7 pagesCell Structures and Functions Review ANSWER KEY김꽁쥬No ratings yet
- Cellular Structure - AP BiologyDocument9 pagesCellular Structure - AP Biologyejung26No ratings yet
- MicroDocument5 pagesMicrotahashahzad9901No ratings yet
- Modx Week 1 Lec-NDocument16 pagesModx Week 1 Lec-NANGELA FRANCESS DE LEONNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology and Diagnostic Intro To CytogeneticsDocument6 pagesMolecular Biology and Diagnostic Intro To Cytogeneticselijah montefalcoNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganelleDocument9 pagesCell OrganelleGwencytech DomingoNo ratings yet
- Chromasomal Basis of HeredityDocument9 pagesChromasomal Basis of Heredityplmbsbio1No ratings yet
- Activity 1Document4 pagesActivity 1sharksiedNo ratings yet
- Cell - Histology Trans Part 1&2Document6 pagesCell - Histology Trans Part 1&2Mark AbrazaldoNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document4 pagesActivity 1sharksiedNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab Oral Recitation 1-7Document10 pagesAnaphy Lab Oral Recitation 1-7Niña C.No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Organic Vs Inorganic CompoundsDocument16 pagesCarbohydrates: Organic Vs Inorganic CompoundsTsu Wei Chua100% (5)
- Cell Organelles Activiities - Ainaratorres3fDocument2 pagesCell Organelles Activiities - Ainaratorres3fAinaraNo ratings yet
- Organelle Present/Absent Description FunctionDocument5 pagesOrganelle Present/Absent Description FunctionTania BacsinNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument1 pageBiologyGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument1 pageCell OrganellesshrinithielangumanianNo ratings yet
- Bmed 105 Cells and Tissues (Notes)Document14 pagesBmed 105 Cells and Tissues (Notes)Jobelle MalihanNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Structure: The Cell Membrane, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, and Everything in BetweenDocument1 pageAnimal Cell Structure: The Cell Membrane, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, and Everything in Between04Annisa PutrianeNo ratings yet
- Human HistologyDocument128 pagesHuman HistologyBreane Denece LicayanNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 3Document7 pagesGen Bio Module 3Jann Ranniel PanlilioNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 (The Cell)Document6 pagesActivity 2 (The Cell)Sophia VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Study NotesDocument134 pagesIB Biology Study NotesManav Parikh100% (3)
- BIO104E - Laboratory Activity (The Cell)Document5 pagesBIO104E - Laboratory Activity (The Cell)Stephen AzaresNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle and Parts Review Table - Chapter 6 Organelle/Cell Function Structure Plant/Animal/Proka Ryote?Document3 pagesCell Organelle and Parts Review Table - Chapter 6 Organelle/Cell Function Structure Plant/Animal/Proka Ryote?Lehman042No ratings yet
- CellDocument36 pagesCellwnslthmangulad05No ratings yet
- Asa Double-Membraned Eukaryotic Cell Organelle That Contains The Genetic Material. The Nucleus Has Two Major Functions: It Stores The Cell's Genetic Material, or DnaDocument1 pageAsa Double-Membraned Eukaryotic Cell Organelle That Contains The Genetic Material. The Nucleus Has Two Major Functions: It Stores The Cell's Genetic Material, or DnaMary Pauline G. CamposNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument5 pagesChapter 3 - Cell Structures and Their Functionsllena llenaNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument1 pageAnimal CellBenju Arios TamayoNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of Cells: RibosomesDocument6 pagesStructure and Functions of Cells: RibosomesShakib al molik100% (1)
- Quiz Fms 1 Questions and Answers 1. Describe The Organelle of The Cell (Cytoplasm and Its Components & The Functions of Each Organelles)Document12 pagesQuiz Fms 1 Questions and Answers 1. Describe The Organelle of The Cell (Cytoplasm and Its Components & The Functions of Each Organelles)deaNo ratings yet
- Sel Dan JaringanDocument1 pageSel Dan JaringanBakhitah Nurul100% (1)
- Cells and TissuesDocument8 pagesCells and TissuesA R F I J U LNo ratings yet
- Ph1F1-PhBioSCi1a-Activity 2-Individual-GloriaDocument7 pagesPh1F1-PhBioSCi1a-Activity 2-Individual-GloriaAllysa GloriaNo ratings yet
- Neve CellDocument5 pagesNeve CellAaron WallaceNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Membrane and DivisionDocument15 pagesCell Structure Membrane and DivisionRawdatul JannahNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 - Cell Parts & FunctionDocument23 pagesLESSON 2 - Cell Parts & FunctionThe DarkCrafter 423No ratings yet
- Hematopoiesis HandoutsDocument10 pagesHematopoiesis HandoutsEmmanuel Tristan OlarteNo ratings yet
- Is The of Life. It Is of And: Cell AND Cell Basic Unit Composed Different Structures Each HasDocument6 pagesIs The of Life. It Is of And: Cell AND Cell Basic Unit Composed Different Structures Each HasShaweh TogononNo ratings yet
- Cells: Hap - Cell BiologyDocument8 pagesCells: Hap - Cell BiologyKyle LumingkitNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument25 pagesCellsAshwika RajanNo ratings yet
- CELL-STRUCTURE Cell StructureDocument5 pagesCELL-STRUCTURE Cell StructureJacqueline Rose Alipo-onNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell StructureDocument24 pagesEukaryotic Cell StructureKarolina RyśkiewiczNo ratings yet
- Chem 104D MidtermsDocument27 pagesChem 104D MidtermsCASTAÑEDA, Jameela AnneNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 - CellDocument9 pagesWorksheet 1 - CellDiva putri DamayantiNo ratings yet
- Cell ReviewerDocument7 pagesCell ReviewerMar LagmayNo ratings yet
- CellFunctions PlantCellDocument1 pageCellFunctions PlantCellHENNESA JOYCE ALABANo ratings yet
- Plant Cell 1Document1 pagePlant Cell 1Reina JaneNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Endomembrane System, Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, Cytoskeleton and Extracellular ComponentsDocument65 pagesThe Cell: Endomembrane System, Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, Cytoskeleton and Extracellular ComponentsMeljean Kalaw CastilloNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles & Their Functions 1112Document7 pagesCell Organelles & Their Functions 1112Amrul Zlalu AdaNo ratings yet
- (Organelles & Cellular Structures) H1 Bio NotesDocument11 pages(Organelles & Cellular Structures) H1 Bio Notesblah blehNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Prokaryotic Animal Plant Functions: Danong, Maria Alexandria Sustiguer, JezielDocument4 pagesCell Structure Prokaryotic Animal Plant Functions: Danong, Maria Alexandria Sustiguer, Jeziel[REDACTED]No ratings yet
- From Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.From EverandFrom Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.No ratings yet
- Pharm - Biotechnology - Question BankDocument8 pagesPharm - Biotechnology - Question BankujjwalNo ratings yet
- Apego, Estabilidad y Cambio A Lo Largo Del Ciclo VitallDocument16 pagesApego, Estabilidad y Cambio A Lo Largo Del Ciclo VitallJai ParedesNo ratings yet
- Gene Structure and Function Regulation of Gene Expression - Part 1Document29 pagesGene Structure and Function Regulation of Gene Expression - Part 1Ana AbuladzeNo ratings yet
- Maths Maths Maths Maths: VIDAAT (2023-2024) Proposed SyllabusDocument6 pagesMaths Maths Maths Maths: VIDAAT (2023-2024) Proposed SyllabusOneShotNo ratings yet
- Immunohistochemical Uterus RatsDocument7 pagesImmunohistochemical Uterus RatsTika IndraNo ratings yet
- Human Activities That Affect The EcosystemDocument2 pagesHuman Activities That Affect The EcosystemRondel Forjes33% (3)
- Ria ImmunoassayDocument10 pagesRia ImmunoassayDinkey SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pathogenic Gram Positive BacteriaDocument34 pagesPathogenic Gram Positive BacteriaFahimRazmandehNo ratings yet
- SWH AQA Revision Guide Biology 1Document42 pagesSWH AQA Revision Guide Biology 1afshinNo ratings yet
- The Origins of Genome Complexity: Science December 2003Document6 pagesThe Origins of Genome Complexity: Science December 2003Ramadhan AkmalNo ratings yet
- 7 Chapter 7 T-Cell Maturation, Activation, and DifferentiationDocument34 pages7 Chapter 7 T-Cell Maturation, Activation, and DifferentiationMekuriya BeregaNo ratings yet
- Desmoid Tumor PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesDesmoid Tumor Pathophysiologyjo_annamae4413No ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris XiiDocument6 pagesBahasa Inggris Xiinurmala sariNo ratings yet
- Hematology 2011 Kaplan 51 61 PDFDocument11 pagesHematology 2011 Kaplan 51 61 PDFhiran.reisNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: Transcription & TranslationDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis: Transcription & TranslationtshahriyarNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetics: By: Jeffrey L. Leal, MDDocument25 pagesLocal Anesthetics: By: Jeffrey L. Leal, MDmemelandNo ratings yet
- Animal BehaviorDocument11 pagesAnimal Behaviorwanna_be_friend2005No ratings yet
- Enzyme ImmunoassayDocument84 pagesEnzyme Immunoassayabby_cantuba78% (9)
- Definition of Terms: Herbaceous Plant Costaceae Brazil Bahia Espirito SantoDocument1 pageDefinition of Terms: Herbaceous Plant Costaceae Brazil Bahia Espirito SantoAshly Jamiah DelRosario ManatoNo ratings yet
- A Reappraisal of CTLA-4 Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer ImmunotherapyDocument17 pagesA Reappraisal of CTLA-4 Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer ImmunotherapyKRUBAKARAN MUTHUSAMYNo ratings yet
- 1SC0 1BF Que 20201107Document20 pages1SC0 1BF Que 20201107Thasanya AlgamaNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Restoration: Made By-Anshika KushwahaDocument10 pagesEcosystem Restoration: Made By-Anshika KushwahaShubhamNo ratings yet
- Antisense Technology 7th SemDocument17 pagesAntisense Technology 7th SemSavita GoyalNo ratings yet
- Nature - Can Gene Editing Cure HIV or Hep BDocument3 pagesNature - Can Gene Editing Cure HIV or Hep BrichyaggaNo ratings yet
- 1 Study Guide - Unit 2Document3 pages1 Study Guide - Unit 2slimjimonfire5682No ratings yet
- Schmittgen 2008Document8 pagesSchmittgen 2008Gina PistolNo ratings yet
- Vacuna Hepatitis BDocument2 pagesVacuna Hepatitis Bluis alejandro rodriguez moraNo ratings yet
Biologia A Color
Biologia A Color
Uploaded by
Jorge Andres Vasquez AvilaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biologia A Color
Biologia A Color
Uploaded by
Jorge Andres Vasquez AvilaCopyright:
Available Formats
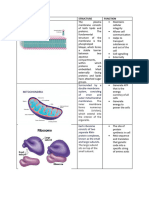
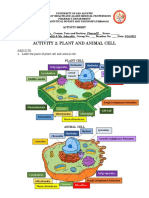
Figure 6.
8 exploring eukaryotic Cells
Animal Cell (cutaway view of generalized cell)
Nuclear envelope: double
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER): network membrane enclosing the
of membranous sacs and tubes; active in nucleus; perforated by
membrane synthesis and other synthetic pores; continuous with ER
Flagellum: motility and metabolic processes; has rough
structure present in (ribosome-studded) and smooth regions Nucleolus: nonmembranous
some animal cells, structure involved in production
composed of a cluster of of ribosomes; a nucleus has NUCLEUS
Rough ER Smooth ER
microtubules within an one or more nucleoli
extension of the plasma
membrane Chromatin: material consisting
of DNA and proteins; visible in
a dividing cell as individual
Centrosome: region condensed chromosomes
where the cell’s
microtubules are
initiated; contains a
pair of centrioles Plasma membrane:
membrane
enclosing the cell
CYTOSKELETON:
reinforces cell’s shape;
functions in cell movement;
components are made of
protein. Includes:
Microfilaments
Intermediate filaments
Ribosomes (small brown
Microtubules dots): complexes that
make proteins; free in
cytosol or bound to
rough ER or nuclear
Microvilli:
envelope
projections that
increase the cell’s
surface area Golgi apparatus: organelle active
in synthesis, modification, sorting,
and secretion of cell products
Peroxisome: organelle with
various specialized metabolic
Lysosome: digestive
functions; produces hydrogen
organelle where
peroxide as a by-product and
macromolecules are
then converts it to water
hydrolyzed
Mitochondrion: organelle where
cellular respiration occurs and
most ATP is generated BioFlix® animation: tour of an animal Cell
Parent 1 μm
10 μm
cell
Cell wall
Animal Cells
Fungal Cells
Buds Vacuole
Cell
5 μm
Nucleus
Nucleolus Nucleus
Yeast cells: reproducing by budding
(above, colorized SEM) and a single cell
Human cells from lining of uterus (colorized TEM) (right, colorized TEM) Mitochondrion
100 Unit two The Cell
Plant Cell (cutaway view of generalized cell)
Nuclear envelope Rough
NUCLEUS endoplasmic
Nucleolus
reticulum
Chromatin
Smooth
endoplasmic
reticulum
Ribosomes (small brown dots)
Central vacuole: prominent organelle
in older plant cells; functions include storage,
breakdown of waste products, and hydrolysis
Golgi apparatus of macromolecules; enlargement of the
vacuole is a major mechanism of plant growth
Microfilaments
CYTOSKELETON
Microtubules
Mitochondrion
Peroxisome
Chloroplast: photosynthetic
Plasma membrane organelle; converts energy of
sunlight to chemical energy
stored in sugar molecules
Cell wall: outer layer that maintains
cell’s shape and protects cell from
mechanical damage; made of cellulose,
other polysaccharides, and protein Plasmodesmata: cytoplasmic BioFlix® animation: tour of a Plant Cell
channels through cell walls Video: turgid Elodea
that connect the cytoplasms Video: Chlamydomonas
Wall of adjacent cell
of adjacent cells
Cell Flagella
1 μm
5 μm
Unicellular Eukaryotes
8 μm
Cell wall
Nucleus
Plant Cells
Chloroplast
Mitochondrion Nucleolus
Nucleus Vacuole
Nucleolus
Unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas Chloroplast
Cells from duckweed (Spirodela oligorrhiza), (above, colorized SEM; right, colorized
a floating plant (colorized TEM) TEM) Cell wall
chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell 101
You might also like
- Essentials of Biology 5th Edition Mader Test BankDocument25 pagesEssentials of Biology 5th Edition Mader Test BankEdwardBrooksqcoi100% (54)
- Power Point Presentation of Bio Chem SIWESDocument13 pagesPower Point Presentation of Bio Chem SIWESUmar Ridwan saniNo ratings yet
- HCT 12 PDFDocument12 pagesHCT 12 PDFdoha73039944No ratings yet
- CellsDocument9 pagesCellsjasmineNo ratings yet
- Organelle With Solution 2022-23Document1 pageOrganelle With Solution 2022-23LuLaMejorNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument5 pages2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionIRDINA ADLIN BINTI FIRDAUS MoeNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles and Its StucturesDocument7 pagesCell Organelles and Its StucturesHailey Eisleen LazaroNo ratings yet
- Basic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismDocument2 pagesBasic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismkikomagsaysayNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Structure & FunctionDocument4 pagesCell Organelles Structure & FunctionDaniel ChinNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument72 pagesThe Cellbir.email013No ratings yet
- Cell NotesDocument7 pagesCell NotesBrohi NadeemNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and Functions Review ANSWER KEYDocument7 pagesCell Structures and Functions Review ANSWER KEY김꽁쥬No ratings yet
- Cellular Structure - AP BiologyDocument9 pagesCellular Structure - AP Biologyejung26No ratings yet
- MicroDocument5 pagesMicrotahashahzad9901No ratings yet
- Modx Week 1 Lec-NDocument16 pagesModx Week 1 Lec-NANGELA FRANCESS DE LEONNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology and Diagnostic Intro To CytogeneticsDocument6 pagesMolecular Biology and Diagnostic Intro To Cytogeneticselijah montefalcoNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganelleDocument9 pagesCell OrganelleGwencytech DomingoNo ratings yet
- Chromasomal Basis of HeredityDocument9 pagesChromasomal Basis of Heredityplmbsbio1No ratings yet
- Activity 1Document4 pagesActivity 1sharksiedNo ratings yet
- Cell - Histology Trans Part 1&2Document6 pagesCell - Histology Trans Part 1&2Mark AbrazaldoNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document4 pagesActivity 1sharksiedNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab Oral Recitation 1-7Document10 pagesAnaphy Lab Oral Recitation 1-7Niña C.No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Organic Vs Inorganic CompoundsDocument16 pagesCarbohydrates: Organic Vs Inorganic CompoundsTsu Wei Chua100% (5)
- Cell Organelles Activiities - Ainaratorres3fDocument2 pagesCell Organelles Activiities - Ainaratorres3fAinaraNo ratings yet
- Organelle Present/Absent Description FunctionDocument5 pagesOrganelle Present/Absent Description FunctionTania BacsinNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument1 pageBiologyGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument1 pageCell OrganellesshrinithielangumanianNo ratings yet
- Bmed 105 Cells and Tissues (Notes)Document14 pagesBmed 105 Cells and Tissues (Notes)Jobelle MalihanNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Structure: The Cell Membrane, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, and Everything in BetweenDocument1 pageAnimal Cell Structure: The Cell Membrane, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, and Everything in Between04Annisa PutrianeNo ratings yet
- Human HistologyDocument128 pagesHuman HistologyBreane Denece LicayanNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 3Document7 pagesGen Bio Module 3Jann Ranniel PanlilioNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 (The Cell)Document6 pagesActivity 2 (The Cell)Sophia VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Study NotesDocument134 pagesIB Biology Study NotesManav Parikh100% (3)
- BIO104E - Laboratory Activity (The Cell)Document5 pagesBIO104E - Laboratory Activity (The Cell)Stephen AzaresNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle and Parts Review Table - Chapter 6 Organelle/Cell Function Structure Plant/Animal/Proka Ryote?Document3 pagesCell Organelle and Parts Review Table - Chapter 6 Organelle/Cell Function Structure Plant/Animal/Proka Ryote?Lehman042No ratings yet
- CellDocument36 pagesCellwnslthmangulad05No ratings yet
- Asa Double-Membraned Eukaryotic Cell Organelle That Contains The Genetic Material. The Nucleus Has Two Major Functions: It Stores The Cell's Genetic Material, or DnaDocument1 pageAsa Double-Membraned Eukaryotic Cell Organelle That Contains The Genetic Material. The Nucleus Has Two Major Functions: It Stores The Cell's Genetic Material, or DnaMary Pauline G. CamposNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument5 pagesChapter 3 - Cell Structures and Their Functionsllena llenaNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument1 pageAnimal CellBenju Arios TamayoNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of Cells: RibosomesDocument6 pagesStructure and Functions of Cells: RibosomesShakib al molik100% (1)
- Quiz Fms 1 Questions and Answers 1. Describe The Organelle of The Cell (Cytoplasm and Its Components & The Functions of Each Organelles)Document12 pagesQuiz Fms 1 Questions and Answers 1. Describe The Organelle of The Cell (Cytoplasm and Its Components & The Functions of Each Organelles)deaNo ratings yet
- Sel Dan JaringanDocument1 pageSel Dan JaringanBakhitah Nurul100% (1)
- Cells and TissuesDocument8 pagesCells and TissuesA R F I J U LNo ratings yet
- Ph1F1-PhBioSCi1a-Activity 2-Individual-GloriaDocument7 pagesPh1F1-PhBioSCi1a-Activity 2-Individual-GloriaAllysa GloriaNo ratings yet
- Neve CellDocument5 pagesNeve CellAaron WallaceNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Membrane and DivisionDocument15 pagesCell Structure Membrane and DivisionRawdatul JannahNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 - Cell Parts & FunctionDocument23 pagesLESSON 2 - Cell Parts & FunctionThe DarkCrafter 423No ratings yet
- Hematopoiesis HandoutsDocument10 pagesHematopoiesis HandoutsEmmanuel Tristan OlarteNo ratings yet
- Is The of Life. It Is of And: Cell AND Cell Basic Unit Composed Different Structures Each HasDocument6 pagesIs The of Life. It Is of And: Cell AND Cell Basic Unit Composed Different Structures Each HasShaweh TogononNo ratings yet
- Cells: Hap - Cell BiologyDocument8 pagesCells: Hap - Cell BiologyKyle LumingkitNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument25 pagesCellsAshwika RajanNo ratings yet
- CELL-STRUCTURE Cell StructureDocument5 pagesCELL-STRUCTURE Cell StructureJacqueline Rose Alipo-onNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell StructureDocument24 pagesEukaryotic Cell StructureKarolina RyśkiewiczNo ratings yet
- Chem 104D MidtermsDocument27 pagesChem 104D MidtermsCASTAÑEDA, Jameela AnneNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 - CellDocument9 pagesWorksheet 1 - CellDiva putri DamayantiNo ratings yet
- Cell ReviewerDocument7 pagesCell ReviewerMar LagmayNo ratings yet
- CellFunctions PlantCellDocument1 pageCellFunctions PlantCellHENNESA JOYCE ALABANo ratings yet
- Plant Cell 1Document1 pagePlant Cell 1Reina JaneNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Endomembrane System, Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, Cytoskeleton and Extracellular ComponentsDocument65 pagesThe Cell: Endomembrane System, Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, Cytoskeleton and Extracellular ComponentsMeljean Kalaw CastilloNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles & Their Functions 1112Document7 pagesCell Organelles & Their Functions 1112Amrul Zlalu AdaNo ratings yet
- (Organelles & Cellular Structures) H1 Bio NotesDocument11 pages(Organelles & Cellular Structures) H1 Bio Notesblah blehNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Prokaryotic Animal Plant Functions: Danong, Maria Alexandria Sustiguer, JezielDocument4 pagesCell Structure Prokaryotic Animal Plant Functions: Danong, Maria Alexandria Sustiguer, Jeziel[REDACTED]No ratings yet
- From Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.From EverandFrom Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.No ratings yet
- Pharm - Biotechnology - Question BankDocument8 pagesPharm - Biotechnology - Question BankujjwalNo ratings yet
- Apego, Estabilidad y Cambio A Lo Largo Del Ciclo VitallDocument16 pagesApego, Estabilidad y Cambio A Lo Largo Del Ciclo VitallJai ParedesNo ratings yet
- Gene Structure and Function Regulation of Gene Expression - Part 1Document29 pagesGene Structure and Function Regulation of Gene Expression - Part 1Ana AbuladzeNo ratings yet
- Maths Maths Maths Maths: VIDAAT (2023-2024) Proposed SyllabusDocument6 pagesMaths Maths Maths Maths: VIDAAT (2023-2024) Proposed SyllabusOneShotNo ratings yet
- Immunohistochemical Uterus RatsDocument7 pagesImmunohistochemical Uterus RatsTika IndraNo ratings yet
- Human Activities That Affect The EcosystemDocument2 pagesHuman Activities That Affect The EcosystemRondel Forjes33% (3)
- Ria ImmunoassayDocument10 pagesRia ImmunoassayDinkey SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pathogenic Gram Positive BacteriaDocument34 pagesPathogenic Gram Positive BacteriaFahimRazmandehNo ratings yet
- SWH AQA Revision Guide Biology 1Document42 pagesSWH AQA Revision Guide Biology 1afshinNo ratings yet
- The Origins of Genome Complexity: Science December 2003Document6 pagesThe Origins of Genome Complexity: Science December 2003Ramadhan AkmalNo ratings yet
- 7 Chapter 7 T-Cell Maturation, Activation, and DifferentiationDocument34 pages7 Chapter 7 T-Cell Maturation, Activation, and DifferentiationMekuriya BeregaNo ratings yet
- Desmoid Tumor PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesDesmoid Tumor Pathophysiologyjo_annamae4413No ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris XiiDocument6 pagesBahasa Inggris Xiinurmala sariNo ratings yet
- Hematology 2011 Kaplan 51 61 PDFDocument11 pagesHematology 2011 Kaplan 51 61 PDFhiran.reisNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: Transcription & TranslationDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis: Transcription & TranslationtshahriyarNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetics: By: Jeffrey L. Leal, MDDocument25 pagesLocal Anesthetics: By: Jeffrey L. Leal, MDmemelandNo ratings yet
- Animal BehaviorDocument11 pagesAnimal Behaviorwanna_be_friend2005No ratings yet
- Enzyme ImmunoassayDocument84 pagesEnzyme Immunoassayabby_cantuba78% (9)
- Definition of Terms: Herbaceous Plant Costaceae Brazil Bahia Espirito SantoDocument1 pageDefinition of Terms: Herbaceous Plant Costaceae Brazil Bahia Espirito SantoAshly Jamiah DelRosario ManatoNo ratings yet
- A Reappraisal of CTLA-4 Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer ImmunotherapyDocument17 pagesA Reappraisal of CTLA-4 Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer ImmunotherapyKRUBAKARAN MUTHUSAMYNo ratings yet
- 1SC0 1BF Que 20201107Document20 pages1SC0 1BF Que 20201107Thasanya AlgamaNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Restoration: Made By-Anshika KushwahaDocument10 pagesEcosystem Restoration: Made By-Anshika KushwahaShubhamNo ratings yet
- Antisense Technology 7th SemDocument17 pagesAntisense Technology 7th SemSavita GoyalNo ratings yet
- Nature - Can Gene Editing Cure HIV or Hep BDocument3 pagesNature - Can Gene Editing Cure HIV or Hep BrichyaggaNo ratings yet
- 1 Study Guide - Unit 2Document3 pages1 Study Guide - Unit 2slimjimonfire5682No ratings yet
- Schmittgen 2008Document8 pagesSchmittgen 2008Gina PistolNo ratings yet
- Vacuna Hepatitis BDocument2 pagesVacuna Hepatitis Bluis alejandro rodriguez moraNo ratings yet