Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fetal Heart Tones
Fetal Heart Tones
Uploaded by
Christian Clyde N. JakosalemCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ENT Question PaperDocument12 pagesENT Question Paperasokk40% (5)
- Renr Practice Test BDocument13 pagesRenr Practice Test BAaron Wallace75% (8)
- Cit0008e 2Document1 pageCit0008e 2deepteck000No ratings yet
- Method For IV Heparin CalculationDocument3 pagesMethod For IV Heparin CalculationDerricka CrosbyNo ratings yet
- Bates' Guide To Physical Examination and History Taking, 12th EditionDocument9 pagesBates' Guide To Physical Examination and History Taking, 12th Editionmanes50% (2)
- Mechanical Ventilation 2015Document18 pagesMechanical Ventilation 2015Nauman GilaniNo ratings yet
- Generic: Hydromorphone (SC) Brand Name: DilaudidDocument1 pageGeneric: Hydromorphone (SC) Brand Name: DilaudidPreet ChahalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Flash CardsDocument5 pagesNursing Flash CardsJan Clarisse RamosNo ratings yet
- NCM100 RUBRIC Complete Bed BathDocument2 pagesNCM100 RUBRIC Complete Bed BathMARK JOSHUA ALFARONo ratings yet
- 12 Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pages12 Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- Final 641 NodayDocument9 pagesFinal 641 Nodaynatalie nodayNo ratings yet
- ObsGyn - OSCE NotesDocument69 pagesObsGyn - OSCE NotesMatt McCannNo ratings yet
- Anti Arrythemic DrugsDocument30 pagesAnti Arrythemic DrugsAsif Ali LashariNo ratings yet
- 4.3 InfectiousDocument29 pages4.3 InfectiousJohn Anthony de GùzmanNo ratings yet
- Administering Intramuscular InjectionDocument3 pagesAdministering Intramuscular InjectionJela Jane ArcalNo ratings yet
- Case Log FNP 1Document6 pagesCase Log FNP 1natalie nodayNo ratings yet
- Icu FlowsheetDocument4 pagesIcu FlowsheetdedeandikaNo ratings yet
- PsychaitryDocument421 pagesPsychaitrylaraib emadNo ratings yet
- Case Log TotalsDocument6 pagesCase Log Totalsnatalie nodayNo ratings yet
- GSK Sotrovimab Fact Sheet For HCP 12222021Document34 pagesGSK Sotrovimab Fact Sheet For HCP 12222021Jillian SmithNo ratings yet
- Streptococcal PharyngitisDocument28 pagesStreptococcal PharyngitissylviaNo ratings yet
- MS Eent (Nle)Document3 pagesMS Eent (Nle)Maginalyn CangasNo ratings yet
- MI MEDIC CARDS - Reference MaterialDocument26 pagesMI MEDIC CARDS - Reference MaterialAylinNo ratings yet
- I Summary Family MedicineDocument185 pagesI Summary Family MedicineModa ModyNo ratings yet
- Sec D - Intervention of Common Signs & SymptomsDocument30 pagesSec D - Intervention of Common Signs & SymptomsCheryl OrtizNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Cardiac EmergencyDocument30 pagesModule 4 - Cardiac EmergencyElaine AntonetteNo ratings yet
- ArrythmiaDocument31 pagesArrythmialubnaNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 (11F)Document15 pagesNCM 112 (11F)Justine April YbanezNo ratings yet
- Daily Rounds in IcuDocument59 pagesDaily Rounds in IcutuulipNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Nursing Skills Procedure On GI, Endo-Metab Concept (A)Document18 pagesModule 3 Nursing Skills Procedure On GI, Endo-Metab Concept (A)Nashebah A. BatuganNo ratings yet
- Ebp Paper Final Draft2Document38 pagesEbp Paper Final Draft2natalie nodayNo ratings yet
- Basic Ecg: A Report By: Clinical Clerk Mary Hazel TeDocument74 pagesBasic Ecg: A Report By: Clinical Clerk Mary Hazel TeHazel Arcosa100% (1)
- Medical Disorder During PregnancyDocument310 pagesMedical Disorder During PregnancyRitbano AhmedNo ratings yet
- PlanningDocument56 pagesPlanningManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Glucose TestingDocument5 pagesGlucose TestingMoira Julianne Serognas BrigoliNo ratings yet
- Research Tools Group E-2Document7 pagesResearch Tools Group E-2Preeti ChouhanNo ratings yet
- NURS702 Critique 2Document9 pagesNURS702 Critique 2natalie nodayNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument7 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDashhh RamirezNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Catheterization FemaleDocument3 pagesChecklist For Catheterization FemaleCheran DeviNo ratings yet
- W1 L2 PneumoniaDocument57 pagesW1 L2 PneumoniaAnas FikriNo ratings yet
- Intrauterine Growth RestrictionDocument13 pagesIntrauterine Growth RestrictionAnca AdamNo ratings yet
- Proliferation Phase: Corpus AlbicansDocument18 pagesProliferation Phase: Corpus AlbicansJOHN CARL GOMEZNo ratings yet
- COPD ExacerbationsDocument57 pagesCOPD ExacerbationsÁýáFáŕőúgNo ratings yet
- Principles of Dialysis: Hemodialysis Nurse Training CourseDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Dialysis: Hemodialysis Nurse Training CourseCj MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Pharma NotesDocument18 pagesPharma Notesseanne kskwkwkaNo ratings yet
- Best Practice in ShockDocument30 pagesBest Practice in ShockFoungZanz D. LuffyzNo ratings yet
- Livro Acesso VenosoDocument302 pagesLivro Acesso VenosoDaniele MoraesNo ratings yet
- SBAR WorksheetDocument3 pagesSBAR Worksheet6bigstar9No ratings yet
- Use of Restraint and Seclusion in The Emergency Department - Psychiatric TimesDocument10 pagesUse of Restraint and Seclusion in The Emergency Department - Psychiatric TimesKaren C. ManoodNo ratings yet
- Pantent Ductus ArteriosusDocument26 pagesPantent Ductus ArteriosusAmmar AlnajjarNo ratings yet
- Technologies Designed To Help Improve Patients OutcomeDocument53 pagesTechnologies Designed To Help Improve Patients OutcomeHarby Ongbay AbellanosaNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Care AduanaDocument36 pagesAntenatal Care AduanalaarnieNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Fetal Outcomes in Patients With Previous Caesarean Section Undergoing Trial of Vaginal BirthDocument14 pagesMaternal and Fetal Outcomes in Patients With Previous Caesarean Section Undergoing Trial of Vaginal BirthIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- History, Physical Examination and Preventive Health CareDocument9 pagesHistory, Physical Examination and Preventive Health CareChristine Evan HoNo ratings yet
- Medical ManagementDocument6 pagesMedical ManagementYORO MIKE ANGELO O.No ratings yet
- CARDOS NAUSEA FDAR-formatDocument3 pagesCARDOS NAUSEA FDAR-formatGabrielle CardosNo ratings yet
- Webinar ACLSDocument52 pagesWebinar ACLSNurhasanahNo ratings yet
- High Risk in NewbornDocument35 pagesHigh Risk in NewbornCaren AsdfNo ratings yet
- Illicit Use of Drugs Among The Youth and Adults in The Frances Baard Region Northern Cape, South AfricaDocument10 pagesIllicit Use of Drugs Among The Youth and Adults in The Frances Baard Region Northern Cape, South AfricaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Bates' Visual Guide To Physical Examination Vol. 7: Head, Eyes, and EarsDocument9 pagesBates' Visual Guide To Physical Examination Vol. 7: Head, Eyes, and EarsArlene DaroNo ratings yet
- Procedure-Nasogastric Tube InsertionDocument22 pagesProcedure-Nasogastric Tube Insertionmohamad dildarNo ratings yet
- Icu Adult and PaedsDocument2 pagesIcu Adult and PaedsPrashin RocharamNo ratings yet
- Rle Part 1 ScriptDocument12 pagesRle Part 1 ScriptgkixNo ratings yet
- Fetal Monitoring: Condition Causes GradeDocument6 pagesFetal Monitoring: Condition Causes GradeSachin SinghNo ratings yet
- Stages of LaborDocument1 pageStages of LaborChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Complete-Head MergedDocument85 pagesComplete-Head MergedChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Postpartum CareDocument1 pagePostpartum CareChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument1 pageSkeletal SystemChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs Normal RangeDocument1 pageVital Signs Normal RangeChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Pharma MneomicsDocument30 pagesPharma MneomicselanthamizhmaranNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Handout CO2 Adverse Health Effects Fact SheetDocument1 pageModule 2 Handout CO2 Adverse Health Effects Fact Sheetdennis ovichNo ratings yet
- Consciousness Traumatic Brain Injury: Eye Opening (E)Document3 pagesConsciousness Traumatic Brain Injury: Eye Opening (E)Nathalie kate petallarNo ratings yet
- Salient Points of The Philippine Blood Banking LawsDocument76 pagesSalient Points of The Philippine Blood Banking LawsAngelica Parreñas BayonaNo ratings yet
- DermatologyDocument27 pagesDermatologydranilshindeNo ratings yet
- Hls Set Advanced Brochure en Non - UsDocument8 pagesHls Set Advanced Brochure en Non - UsAlmudena DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Overlap Syn AniDocument59 pagesOverlap Syn AniAnimesh AryaNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Thrombolysis For Acute Ischemic 2023Document19 pagesIntravenous Thrombolysis For Acute Ischemic 2023angieselene.telloNo ratings yet
- SanaPro Individual Health Insurance Presentation - 2021 - Final ENDocument12 pagesSanaPro Individual Health Insurance Presentation - 2021 - Final ENGabriela GiurgiNo ratings yet
- Recurrent Epulis GranulomatosaDocument7 pagesRecurrent Epulis GranulomatosaAnnisa ghina imaniarNo ratings yet
- Electro Surgical Catalogue 2019-20 HDDocument45 pagesElectro Surgical Catalogue 2019-20 HDECO SurgicalNo ratings yet
- Low Carbohydrate DietDocument38 pagesLow Carbohydrate DietEsther SiraitNo ratings yet
- Bakale To OffersDocument23 pagesBakale To OffersMAHADEVI GROUPNo ratings yet
- Practice Test Questions Downloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRALDocument33 pagesPractice Test Questions Downloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRALFilipino Nurses Central91% (11)
- Homeopathy For Depression Anxiety and InsomniaDocument55 pagesHomeopathy For Depression Anxiety and InsomniaSana Farooqui100% (1)
- Yersinia Pestis V Protein Epitopes Recognized by CD4 T CellsDocument8 pagesYersinia Pestis V Protein Epitopes Recognized by CD4 T CellsHerdi ArdianaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Audit in Obstetric Care (1) - Mrs. Sarla TakooDocument45 pagesNursing Audit in Obstetric Care (1) - Mrs. Sarla TakooSaritaNo ratings yet
- MERRYAN A. TOTAAN Visual Impairment SPED 214Document5 pagesMERRYAN A. TOTAAN Visual Impairment SPED 214Reynante Tugade PalisocNo ratings yet
- Cervicogenic HeadacheDocument7 pagesCervicogenic Headachemeta456No ratings yet
- Answer All The Following Short Essay Questions: (3 Questions)Document4 pagesAnswer All The Following Short Essay Questions: (3 Questions)Soad ShedeedNo ratings yet
- 2017 Certificate of Health 1Document2 pages2017 Certificate of Health 1herman syahNo ratings yet
- GREAT SupremeHealth and GREAT TotalCare Brochure (Full)Document22 pagesGREAT SupremeHealth and GREAT TotalCare Brochure (Full)jingzhitanNo ratings yet
- Lidocaine Drug StudyDocument1 pageLidocaine Drug StudyVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Sample Charting (Fdar)Document3 pagesSample Charting (Fdar)Mary Beth AbelidoNo ratings yet
- Combined Science b8Document6 pagesCombined Science b8Jose ArcosNo ratings yet
- Aero MaxDocument2 pagesAero MaxKristine YoungNo ratings yet
Fetal Heart Tones
Fetal Heart Tones
Uploaded by
Christian Clyde N. JakosalemOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fetal Heart Tones
Fetal Heart Tones
Uploaded by
Christian Clyde N. JakosalemCopyright:
Available Formats
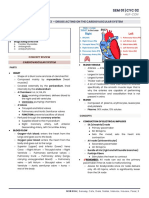
FETAL HEART TONES
CONDITION CAUSE GRADE
Fetal Tachycardia ❖ Infection ❖ Mild : > 5 BPM from baseline
❖ Dehydration ❖ Moderate: 6-25 BPM from baseline
❖ Fever ❖ Severe: < 25 BPM from baseline
❖ Fetal hypoxemia ❖ Absent : No fluctuation in fetal heart rate
❖ Anemia
❖ Prematurity
❖ Terbutaline
❖ Caffeine
❖ Epinephrine
❖ Theophylline
❖ illicit drugs
Fetal bradycardia ❖ Maternal hypotension ❖ Mild : > 5 BPM from baseline
❖ Supine hypotensive syndrome ❖ Moderate: 6-25 BPM from baseline
❖ Fetal decompression ❖ Severe: < 25 BPM from baseline
❖ Late fetal hypoxia ❖ Absent : No fluctuation in fetal heart rate
❖ Cord compression
❖ Abruptio placenta
❖ Vagal stimulation
Accelerations & Decelerations
Variability Accelerations: must be 15 BPM above the FHR baseline for 15
seconds 15x15 window
FHR drops from baseline then recovers, usually jagged and Decelerations : A decrease in FHR during uterine contraction ”
erratically shaped. Can happen at anytime during contraction mirrors contractions usually a U shape
Periodic changes : variations that occur during a contraction.
Nursing interventions : Left Side. IV bolus of fluids, O2 6l mask, ❖ Reassuring periodic changes : must be 15 BPM
Notify HCP above the FHR baseline for 15 seconds ( 15x15 window)
❖ Benign periodic changes: Early decelerations
A great way to remember this is L.I.O.N
Decreased or absent variability: Non reassuring, acute treatment Episodic changes: occur in association with medication
and monitoring are indicated. administration or analgesia
Decreased or absent variability: medications, narcotics, mag
Wandering baselines with no variability could indicate
sulfate ( preeclampsia, preterm), terbutaline, fetal sleep (
❖ Congenital defects normally 20 minute cycles), prematurity, fetal hypoxemia.
❖ Metabolic acidosis
Fetal decelerations
The nurse should administer 02 and the baby needs to be
delivered as quickly as possible.
Memory trick
Early decelerations : A decrease in FHR during uterine contraction mirrors
uterine contractions . caused by uterine squeeze
❖ FHR slows as the contraction begins
V: variable deceleration C: cord compression ❖ Lowest point coincides with the highest point ACME of the
E:early deceleration H: head compression contraction
A: acceleration O: ok ❖ Deceleration ends with the contraction
Late deceleration Placental insufficiency Late deceleration: occurs after the peak of contraction due to uteroplacental
insufficiency, pitocin, HTN, diabetes, placental abruption.
❖ Too many decelerations will indicate a need for C-section
❖ Prepare for fetal resuscitation
Variable decelerations: may indicate cord compression. Occur at different
times during a contraction, resulting in fetal HTN that causes the aortic arch
to slow the FHR. usually abrupt and sudden.
Measures to clarify NONreassuring FHR patterns
❖ Fetal stimulation
❖ Fetal scalp sampling
❖ Fetal scalp oximetry
You might also like
- ENT Question PaperDocument12 pagesENT Question Paperasokk40% (5)
- Renr Practice Test BDocument13 pagesRenr Practice Test BAaron Wallace75% (8)
- Cit0008e 2Document1 pageCit0008e 2deepteck000No ratings yet
- Method For IV Heparin CalculationDocument3 pagesMethod For IV Heparin CalculationDerricka CrosbyNo ratings yet
- Bates' Guide To Physical Examination and History Taking, 12th EditionDocument9 pagesBates' Guide To Physical Examination and History Taking, 12th Editionmanes50% (2)
- Mechanical Ventilation 2015Document18 pagesMechanical Ventilation 2015Nauman GilaniNo ratings yet
- Generic: Hydromorphone (SC) Brand Name: DilaudidDocument1 pageGeneric: Hydromorphone (SC) Brand Name: DilaudidPreet ChahalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Flash CardsDocument5 pagesNursing Flash CardsJan Clarisse RamosNo ratings yet
- NCM100 RUBRIC Complete Bed BathDocument2 pagesNCM100 RUBRIC Complete Bed BathMARK JOSHUA ALFARONo ratings yet
- 12 Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pages12 Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- Final 641 NodayDocument9 pagesFinal 641 Nodaynatalie nodayNo ratings yet
- ObsGyn - OSCE NotesDocument69 pagesObsGyn - OSCE NotesMatt McCannNo ratings yet
- Anti Arrythemic DrugsDocument30 pagesAnti Arrythemic DrugsAsif Ali LashariNo ratings yet
- 4.3 InfectiousDocument29 pages4.3 InfectiousJohn Anthony de GùzmanNo ratings yet
- Administering Intramuscular InjectionDocument3 pagesAdministering Intramuscular InjectionJela Jane ArcalNo ratings yet
- Case Log FNP 1Document6 pagesCase Log FNP 1natalie nodayNo ratings yet
- Icu FlowsheetDocument4 pagesIcu FlowsheetdedeandikaNo ratings yet
- PsychaitryDocument421 pagesPsychaitrylaraib emadNo ratings yet
- Case Log TotalsDocument6 pagesCase Log Totalsnatalie nodayNo ratings yet
- GSK Sotrovimab Fact Sheet For HCP 12222021Document34 pagesGSK Sotrovimab Fact Sheet For HCP 12222021Jillian SmithNo ratings yet
- Streptococcal PharyngitisDocument28 pagesStreptococcal PharyngitissylviaNo ratings yet
- MS Eent (Nle)Document3 pagesMS Eent (Nle)Maginalyn CangasNo ratings yet
- MI MEDIC CARDS - Reference MaterialDocument26 pagesMI MEDIC CARDS - Reference MaterialAylinNo ratings yet
- I Summary Family MedicineDocument185 pagesI Summary Family MedicineModa ModyNo ratings yet
- Sec D - Intervention of Common Signs & SymptomsDocument30 pagesSec D - Intervention of Common Signs & SymptomsCheryl OrtizNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Cardiac EmergencyDocument30 pagesModule 4 - Cardiac EmergencyElaine AntonetteNo ratings yet
- ArrythmiaDocument31 pagesArrythmialubnaNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 (11F)Document15 pagesNCM 112 (11F)Justine April YbanezNo ratings yet
- Daily Rounds in IcuDocument59 pagesDaily Rounds in IcutuulipNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Nursing Skills Procedure On GI, Endo-Metab Concept (A)Document18 pagesModule 3 Nursing Skills Procedure On GI, Endo-Metab Concept (A)Nashebah A. BatuganNo ratings yet
- Ebp Paper Final Draft2Document38 pagesEbp Paper Final Draft2natalie nodayNo ratings yet
- Basic Ecg: A Report By: Clinical Clerk Mary Hazel TeDocument74 pagesBasic Ecg: A Report By: Clinical Clerk Mary Hazel TeHazel Arcosa100% (1)
- Medical Disorder During PregnancyDocument310 pagesMedical Disorder During PregnancyRitbano AhmedNo ratings yet
- PlanningDocument56 pagesPlanningManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Glucose TestingDocument5 pagesGlucose TestingMoira Julianne Serognas BrigoliNo ratings yet
- Research Tools Group E-2Document7 pagesResearch Tools Group E-2Preeti ChouhanNo ratings yet
- NURS702 Critique 2Document9 pagesNURS702 Critique 2natalie nodayNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument7 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDashhh RamirezNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Catheterization FemaleDocument3 pagesChecklist For Catheterization FemaleCheran DeviNo ratings yet
- W1 L2 PneumoniaDocument57 pagesW1 L2 PneumoniaAnas FikriNo ratings yet
- Intrauterine Growth RestrictionDocument13 pagesIntrauterine Growth RestrictionAnca AdamNo ratings yet
- Proliferation Phase: Corpus AlbicansDocument18 pagesProliferation Phase: Corpus AlbicansJOHN CARL GOMEZNo ratings yet
- COPD ExacerbationsDocument57 pagesCOPD ExacerbationsÁýáFáŕőúgNo ratings yet
- Principles of Dialysis: Hemodialysis Nurse Training CourseDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Dialysis: Hemodialysis Nurse Training CourseCj MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Pharma NotesDocument18 pagesPharma Notesseanne kskwkwkaNo ratings yet
- Best Practice in ShockDocument30 pagesBest Practice in ShockFoungZanz D. LuffyzNo ratings yet
- Livro Acesso VenosoDocument302 pagesLivro Acesso VenosoDaniele MoraesNo ratings yet
- SBAR WorksheetDocument3 pagesSBAR Worksheet6bigstar9No ratings yet
- Use of Restraint and Seclusion in The Emergency Department - Psychiatric TimesDocument10 pagesUse of Restraint and Seclusion in The Emergency Department - Psychiatric TimesKaren C. ManoodNo ratings yet
- Pantent Ductus ArteriosusDocument26 pagesPantent Ductus ArteriosusAmmar AlnajjarNo ratings yet
- Technologies Designed To Help Improve Patients OutcomeDocument53 pagesTechnologies Designed To Help Improve Patients OutcomeHarby Ongbay AbellanosaNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Care AduanaDocument36 pagesAntenatal Care AduanalaarnieNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Fetal Outcomes in Patients With Previous Caesarean Section Undergoing Trial of Vaginal BirthDocument14 pagesMaternal and Fetal Outcomes in Patients With Previous Caesarean Section Undergoing Trial of Vaginal BirthIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- History, Physical Examination and Preventive Health CareDocument9 pagesHistory, Physical Examination and Preventive Health CareChristine Evan HoNo ratings yet
- Medical ManagementDocument6 pagesMedical ManagementYORO MIKE ANGELO O.No ratings yet
- CARDOS NAUSEA FDAR-formatDocument3 pagesCARDOS NAUSEA FDAR-formatGabrielle CardosNo ratings yet
- Webinar ACLSDocument52 pagesWebinar ACLSNurhasanahNo ratings yet
- High Risk in NewbornDocument35 pagesHigh Risk in NewbornCaren AsdfNo ratings yet
- Illicit Use of Drugs Among The Youth and Adults in The Frances Baard Region Northern Cape, South AfricaDocument10 pagesIllicit Use of Drugs Among The Youth and Adults in The Frances Baard Region Northern Cape, South AfricaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Bates' Visual Guide To Physical Examination Vol. 7: Head, Eyes, and EarsDocument9 pagesBates' Visual Guide To Physical Examination Vol. 7: Head, Eyes, and EarsArlene DaroNo ratings yet
- Procedure-Nasogastric Tube InsertionDocument22 pagesProcedure-Nasogastric Tube Insertionmohamad dildarNo ratings yet
- Icu Adult and PaedsDocument2 pagesIcu Adult and PaedsPrashin RocharamNo ratings yet
- Rle Part 1 ScriptDocument12 pagesRle Part 1 ScriptgkixNo ratings yet
- Fetal Monitoring: Condition Causes GradeDocument6 pagesFetal Monitoring: Condition Causes GradeSachin SinghNo ratings yet
- Stages of LaborDocument1 pageStages of LaborChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Complete-Head MergedDocument85 pagesComplete-Head MergedChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Postpartum CareDocument1 pagePostpartum CareChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument1 pageSkeletal SystemChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs Normal RangeDocument1 pageVital Signs Normal RangeChristian Clyde N. JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Pharma MneomicsDocument30 pagesPharma MneomicselanthamizhmaranNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Handout CO2 Adverse Health Effects Fact SheetDocument1 pageModule 2 Handout CO2 Adverse Health Effects Fact Sheetdennis ovichNo ratings yet
- Consciousness Traumatic Brain Injury: Eye Opening (E)Document3 pagesConsciousness Traumatic Brain Injury: Eye Opening (E)Nathalie kate petallarNo ratings yet
- Salient Points of The Philippine Blood Banking LawsDocument76 pagesSalient Points of The Philippine Blood Banking LawsAngelica Parreñas BayonaNo ratings yet
- DermatologyDocument27 pagesDermatologydranilshindeNo ratings yet
- Hls Set Advanced Brochure en Non - UsDocument8 pagesHls Set Advanced Brochure en Non - UsAlmudena DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Overlap Syn AniDocument59 pagesOverlap Syn AniAnimesh AryaNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Thrombolysis For Acute Ischemic 2023Document19 pagesIntravenous Thrombolysis For Acute Ischemic 2023angieselene.telloNo ratings yet
- SanaPro Individual Health Insurance Presentation - 2021 - Final ENDocument12 pagesSanaPro Individual Health Insurance Presentation - 2021 - Final ENGabriela GiurgiNo ratings yet
- Recurrent Epulis GranulomatosaDocument7 pagesRecurrent Epulis GranulomatosaAnnisa ghina imaniarNo ratings yet
- Electro Surgical Catalogue 2019-20 HDDocument45 pagesElectro Surgical Catalogue 2019-20 HDECO SurgicalNo ratings yet
- Low Carbohydrate DietDocument38 pagesLow Carbohydrate DietEsther SiraitNo ratings yet
- Bakale To OffersDocument23 pagesBakale To OffersMAHADEVI GROUPNo ratings yet
- Practice Test Questions Downloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRALDocument33 pagesPractice Test Questions Downloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRALFilipino Nurses Central91% (11)
- Homeopathy For Depression Anxiety and InsomniaDocument55 pagesHomeopathy For Depression Anxiety and InsomniaSana Farooqui100% (1)
- Yersinia Pestis V Protein Epitopes Recognized by CD4 T CellsDocument8 pagesYersinia Pestis V Protein Epitopes Recognized by CD4 T CellsHerdi ArdianaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Audit in Obstetric Care (1) - Mrs. Sarla TakooDocument45 pagesNursing Audit in Obstetric Care (1) - Mrs. Sarla TakooSaritaNo ratings yet
- MERRYAN A. TOTAAN Visual Impairment SPED 214Document5 pagesMERRYAN A. TOTAAN Visual Impairment SPED 214Reynante Tugade PalisocNo ratings yet
- Cervicogenic HeadacheDocument7 pagesCervicogenic Headachemeta456No ratings yet
- Answer All The Following Short Essay Questions: (3 Questions)Document4 pagesAnswer All The Following Short Essay Questions: (3 Questions)Soad ShedeedNo ratings yet
- 2017 Certificate of Health 1Document2 pages2017 Certificate of Health 1herman syahNo ratings yet
- GREAT SupremeHealth and GREAT TotalCare Brochure (Full)Document22 pagesGREAT SupremeHealth and GREAT TotalCare Brochure (Full)jingzhitanNo ratings yet
- Lidocaine Drug StudyDocument1 pageLidocaine Drug StudyVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Sample Charting (Fdar)Document3 pagesSample Charting (Fdar)Mary Beth AbelidoNo ratings yet
- Combined Science b8Document6 pagesCombined Science b8Jose ArcosNo ratings yet
- Aero MaxDocument2 pagesAero MaxKristine YoungNo ratings yet