Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lec 1 Part 3 Xmind
Lec 1 Part 3 Xmind
Uploaded by
Ahmad AbuelgasimOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lec 1 Part 3 Xmind
Lec 1 Part 3 Xmind
Uploaded by
Ahmad AbuelgasimCopyright:
Available Formats
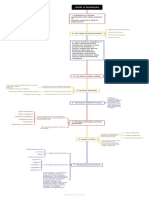
he Role of
T
Information Systems
in Business
• Emerging mobile digital platform
1 - How information systems are
• Growing business use of “big data”
transforming business
• Growth in cloud computing
• Internet has drastically reduced costs of
operating on global scale
2- Globalization opportunities • Increases in foreign trade, outsourcing
• Presents both challenges and opportunities
Information technology capital investment,
defined as hardware, software, and
communications - Information Technology
3
equipment, grew from 14 percent to 33 Capital Investment
percent of all invested capital between 1999
and 2013.
• Significant business relationships are
digitally enabled and mediated
- In the emerging, fully digital
4 • Core business processes are accomplished
firm: through digital networks
• Key corporate assets are managed digitally
- Digital firms offer greater
5
• Time shifting, space shifting flexibility in organization and
management
• Ability to use information technology and
- Growing interdependence
6
between: • Ability to implement corporate strategies
and achieve corporate goals
In contemporary systems there is a growing
interdependence between a firm’s
information systems and its business
capabilities. Changes in strategy, rules, and - The Interdependence Between
7
business processes increasingly require
changes in hardware, software, databases,
Organizations and
and telecommunications. Often, what the Information Technology:
organization would like to do
depends on what its systems will permit it to
do
• Improvement of efficiency to attain higher
profitability
1. Operational Excellence:
• Information systems, technology an
important tool in achieving greater efficiency
and productivity
describes how company produces, delivers,
• Business model:
and sells product or service to create wealth
• Information systems and technology a
.New products, services, and business
2
major enabling tool for new products,
models:
services, business models
• Examples: Apple’s iPad, Google’s Android
OS, and Netflix
• Example: High-end hotels that use
• Serving customers well leads to customers computers to track customer preferences
returning, which raises revenues and profits. and used to monitor and customize
environment
3. Customer and supplier intimacy:
• Example: JCPenney’s information system
• Intimacy with suppliers allows them to
which links sales records to contract
provide vital inputs, which lowers costs.
manufacturer
• Managers must use forecasts, best guesses,
luck
• Overproduction, underproduction
- Firms invest in information
8
systems in order to achieve six • Without accurate information: • Results in: • Misallocation of resources
strategic business objectives:
• Poor response times
4. Improved Decision Making • Poor outcomes raise costs, lose customers
1. Achieve operational excellence
• Example: Verizon’s Web-based digital
2. Develop new products and services dashboard to provide managers with real-
time data on customer complaints, network
performance, line outages, and so on
3. Attain customer intimacy and service
he six strategic business
T
objectives: –Delivering better performance
4. Improve decision making
–Charging less for superior products
5. Promote competitive advantage
–Responding to customers and suppliers in
6. Ensure survival real time
5.competitive advantage
– Achieving any of the previous four
business objectives represents the
achievement of a competitive advantage as
well
– Examples: Apple, Walmart
• Information technologies as necessity of
business
6. survival • Industry-level changes
• Example: Citibank’s introduction of ATMs
he study of information systems deals with
T
- Contemporary Approaches to
9
issues and insights contributed from
technical and behavioral disciplines Information Systems
• Emphasizes mathematically based models
• Technical approach
• Computer science, management science,
operations research
• Behavioral issues (strategic business
integration, implementation, etc.)
• Behavioral approach
• Psychology, economics, sociology
• Optimal organizational performance
achieved by jointly optimizing both social
and technical systems used in production
10- Studying Information Systems • Sociotechnical view
• Helps avoid purely technological approach
• Combines computer science, management
• Management Information Systems science, operations research, and
practical orientation with behavioral issues
• Suppliers of hardware and software
In a sociotechnical perspective, the
performance of a system is optimized when • Business firms
both the technology and • Four main actors
the organization mutually adjust to each • Managers and employees
other until a satisfactory fit is obtained
• Firm’s environment (legal, social, cultural
context)
You might also like
- Digital TransformationDocument22 pagesDigital TransformationJohn Ekpikhe100% (4)
- Digital Capability Framework OverviewDocument7 pagesDigital Capability Framework OverviewKieran O'HeaNo ratings yet
- The Digitalization Triumvirate: How Incumbents Survive: 1. The Incumbent S CurseDocument2 pagesThe Digitalization Triumvirate: How Incumbents Survive: 1. The Incumbent S CursejennyxzxzNo ratings yet
- The Language of Technical Writing and Practical Problems Regarding Style in Technical CommunicationDocument6 pagesThe Language of Technical Writing and Practical Problems Regarding Style in Technical CommunicationQueen ValleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Information Management IDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Information Management IAidan LitargoNo ratings yet
- lsc38 - d4 - Top Ten Trends Impacting Infrastructure and Operat - 607085 - 342846Document26 pageslsc38 - d4 - Top Ten Trends Impacting Infrastructure and Operat - 607085 - 342846Jose SerranoNo ratings yet
- MBA - PGDPM - IKM - Webinar - 1 - UpdatedDocument61 pagesMBA - PGDPM - IKM - Webinar - 1 - UpdatedmengesiprettyNo ratings yet
- 5 Keys For SuccessDocument19 pages5 Keys For SuccessneerleoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Introduction To Digital TransformationDocument12 pagesLecture 2 - Introduction To Digital TransformationNguyễn Văn TàiNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document2 pagesActivity 2Gu SionNo ratings yet
- Digital TransformationDocument20 pagesDigital TransformationGaetano DisNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Introduction To Digital TransformationDocument11 pagesLecture 2 - Introduction To Digital TransformationQuỳnh MaiNo ratings yet
- MBA - PGDPM - IKM - Webinar - 2Document78 pagesMBA - PGDPM - IKM - Webinar - 2mengesiprettyNo ratings yet
- Role of Chief Data OfficerDocument16 pagesRole of Chief Data Officerkallepalli100% (3)
- IT Strategy Illustrative ExampleDocument29 pagesIT Strategy Illustrative ExampleRanita91No ratings yet
- Mckinsey 2016 Digital-By-Default-A-Guide-To-Transforming-Government-FinalDocument13 pagesMckinsey 2016 Digital-By-Default-A-Guide-To-Transforming-Government-FinaldividerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Information Management Iim NckuDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Information Management Iim NckuAidan LitargoNo ratings yet
- Cloud PDFDocument104 pagesCloud PDFLakshay KapoorNo ratings yet
- Nokia Es Phases of MobilityDocument7 pagesNokia Es Phases of Mobilityalonelover91No ratings yet
- Digital Media SatelliteDocument8 pagesDigital Media SatellitejimwestNo ratings yet
- Persona Cards and Value Prompters, New Back Office UserDocument10 pagesPersona Cards and Value Prompters, New Back Office UserlrreNo ratings yet
- The Evolving Role of Information Systems and Technology in Organizations: A Strategic PerspectiveDocument4 pagesThe Evolving Role of Information Systems and Technology in Organizations: A Strategic Perspectivej financeNo ratings yet
- Ch1 MisDocument24 pagesCh1 MisMusaeed AljaaidiNo ratings yet
- IT and Is in BusinessDocument25 pagesIT and Is in BusinessJonathanNo ratings yet
- IBM Global Business Services Executive RDocument20 pagesIBM Global Business Services Executive RAlbertoNo ratings yet
- DT Group 8Document3 pagesDT Group 8SHUBHAM AKOLENo ratings yet
- MIS Case 2Document16 pagesMIS Case 2Saurabh SreekumarNo ratings yet
- Digital Capability Framework Overview 3Document9 pagesDigital Capability Framework Overview 3Kieran O'HeaNo ratings yet
- ITIS362 Chapter 1Document9 pagesITIS362 Chapter 1mst112003No ratings yet
- UC21NA-D2TD040-Berhad-Ubina-PI-System-DGA-PI-Vision-CustomDocument18 pagesUC21NA-D2TD040-Berhad-Ubina-PI-System-DGA-PI-Vision-CustomJochen JungNo ratings yet
- Management of Digital TransformationDocument26 pagesManagement of Digital TransformationGaurav Tale100% (2)
- U1 DigitizationDocument7 pagesU1 Digitization15 Sai KiranNo ratings yet
- 05 Digital Economy-2Document8 pages05 Digital Economy-2Michael BotisNo ratings yet
- IT Gov 2Document23 pagesIT Gov 2Sanjay DahalNo ratings yet
- DigiDocument2 pagesDigiLp NgNo ratings yet
- Flyer v3Document2 pagesFlyer v3Herjuno Bagus WicaksonoputroNo ratings yet
- IT Management DPADocument32 pagesIT Management DPAplpictimatecNo ratings yet
- Lect 1Document47 pagesLect 1SiaBeng SAINS BANo ratings yet
- Operational Excellence Goes Digital 29 07 FinalDocument15 pagesOperational Excellence Goes Digital 29 07 FinalJack HuseynliNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document18 pagesTopic 1maryam nabilahNo ratings yet
- Digital Strategy-1Document24 pagesDigital Strategy-1Vijay KashettiNo ratings yet
- Flevy 125Document21 pagesFlevy 125RADWAN RAHATNo ratings yet
- CIO BrochureDocument4 pagesCIO BrochurealexymutkNo ratings yet
- ITIL Leader Cram Card (v1)Document13 pagesITIL Leader Cram Card (v1)Baghirov RuslanNo ratings yet
- Technology (IT)Document13 pagesTechnology (IT)wasay aliNo ratings yet
- Workforce TransformationDocument28 pagesWorkforce TransformationKhánh LinhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Presentation HandoutsDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Presentation HandoutsTheslynessNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Chapter 1 Information Systems in Global Business TodayDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Chapter 1 Information Systems in Global Business TodayNguyễn BìnhNo ratings yet
- Deloitte IT Governance SurveyDocument20 pagesDeloitte IT Governance Surveymrehan2k2No ratings yet
- It Assess Infrastructure Readiness For Digital Transformation StoryboDocument21 pagesIt Assess Infrastructure Readiness For Digital Transformation StoryboSasa VujovicNo ratings yet
- Mdim - Icbit Brochure 2020Document6 pagesMdim - Icbit Brochure 2020bando007No ratings yet
- Midbs Unit 1: Prof. Shrikumar M Lean Operations and Systems School of Business and ManagementDocument47 pagesMidbs Unit 1: Prof. Shrikumar M Lean Operations and Systems School of Business and ManagementChintoo KalyanadurgamNo ratings yet
- Building Without Barriers: Do You Own, Operate, Construct or Maintain Physical Built Assets?Document10 pagesBuilding Without Barriers: Do You Own, Operate, Construct or Maintain Physical Built Assets?Unknown020No ratings yet
- The Path To Digital Transformation: Where IT Leaders StandDocument17 pagesThe Path To Digital Transformation: Where IT Leaders StandSAmpleNo ratings yet
- CIO Business ValueDocument11 pagesCIO Business ValueRajesh RayNo ratings yet
- Bab 2 Computing ToolsDocument14 pagesBab 2 Computing Toolsuvuvevwe osasNo ratings yet
- How To Find and Maximize Digital Value in Any M&A DealDocument7 pagesHow To Find and Maximize Digital Value in Any M&A DealAlfred DonkorNo ratings yet
- NSSE 2011 Nirmalya Applications of SEDocument48 pagesNSSE 2011 Nirmalya Applications of SEAbhinav GauravNo ratings yet
- Digital Maturity: Take a Journey of a Thousand Miles from Functioning to DelightFrom EverandDigital Maturity: Take a Journey of a Thousand Miles from Functioning to DelightNo ratings yet
- Digital Capability: Building Lego Like Capability Into Business CompetencyFrom EverandDigital Capability: Building Lego Like Capability Into Business CompetencyNo ratings yet
- The Business-Oriented CIO: A Guide to Market-Driven ManagementFrom EverandThe Business-Oriented CIO: A Guide to Market-Driven ManagementNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 Part 1 XmindDocument1 pageLec 3 Part 1 XmindAhmad AbuelgasimNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Part 2 XmindDocument1 pageLec 2 Part 2 XmindAhmad AbuelgasimNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Part 2 XmindDocument1 pageLec 1 Part 2 XmindAhmad AbuelgasimNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Part 1 XmindDocument1 pageLec 1 Part 1 XmindAhmad AbuelgasimNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Part 1 XmindDocument1 pageLec 2 Part 1 XmindAhmad AbuelgasimNo ratings yet
- DOMINO Pizza Case StudyDocument2 pagesDOMINO Pizza Case StudyAhmad AbuelgasimNo ratings yet
- مذكرات حول التكتلات الإقليمية الصادق ضؤ البيتDocument119 pagesمذكرات حول التكتلات الإقليمية الصادق ضؤ البيتAhmad AbuelgasimNo ratings yet
- Sqs DGDocument192 pagesSqs DGluong tranNo ratings yet
- Importance of CRM in B2B Markets-Key Account ManagementDocument8 pagesImportance of CRM in B2B Markets-Key Account ManagementSoumyaNo ratings yet
- Sap MM Real Time Interview Ques - UnknownDocument131 pagesSap MM Real Time Interview Ques - UnknownSanketKubalNo ratings yet
- BUS B328F Assignment 1 Lean CanvasDocument1 pageBUS B328F Assignment 1 Lean CanvasMohammed Ameer EjazNo ratings yet
- 7 Snowflake Reference Architectures For Application BuildersDocument13 pages7 Snowflake Reference Architectures For Application BuildersMaria PilarNo ratings yet
- The Everything Store Jeff Bezos and The Age of Amazon-Notebook (PDFDrive)Document24 pagesThe Everything Store Jeff Bezos and The Age of Amazon-Notebook (PDFDrive)Roman TilahunNo ratings yet
- Release Notes For iVMS-4200 VS - V1.3.1Document8 pagesRelease Notes For iVMS-4200 VS - V1.3.1Marcos Ramos MotaNo ratings yet
- CPP106-MODULE - 9 - 2ndSEM - Data - Modelling (1) (20230504171831)Document9 pagesCPP106-MODULE - 9 - 2ndSEM - Data - Modelling (1) (20230504171831)Ivan HermosillaNo ratings yet
- Retreeb: Ethical Payment SolutionsDocument24 pagesRetreeb: Ethical Payment SolutionsJoseNo ratings yet
- DevelopmentThatPays Scrumban CheatSheet 3 - 0Document1 pageDevelopmentThatPays Scrumban CheatSheet 3 - 0Hamed KamelNo ratings yet
- Data Connector Report 1Document34 pagesData Connector Report 1GeorgeSidirasNo ratings yet
- Register OAF Page in Oracle ApplicationsDocument9 pagesRegister OAF Page in Oracle ApplicationsMostafa TahaNo ratings yet
- Invest India PDFDocument171 pagesInvest India PDFManoj BhojNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument18 pagesCloud ComputingPiyush GargNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1.2 44-47Document4 pagesCase Study 1.2 44-47AraNo ratings yet
- Post Graduate Program in Product ManagementDocument16 pagesPost Graduate Program in Product ManagementSushil KumarNo ratings yet
- SAP Chapter 4 - Purchasing ProcessDocument47 pagesSAP Chapter 4 - Purchasing ProcessmsjoyceroxaneNo ratings yet
- Cobot Programming For Collaborative Industrial Tasks: An OverviewDocument37 pagesCobot Programming For Collaborative Industrial Tasks: An OverviewSayantan RahaNo ratings yet
- GMC India - Competition Timeline (Round 1)Document7 pagesGMC India - Competition Timeline (Round 1)Rishabh JainNo ratings yet
- Vmware Advanced Design Exam GuideDocument10 pagesVmware Advanced Design Exam GuideJuliano PereiraNo ratings yet
- Principles of Auditing Other Assurance Services 19Th Edition Whittington Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesPrinciples of Auditing Other Assurance Services 19Th Edition Whittington Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFAndrewRobinsonixez100% (11)
- Academic Integrity Policy:: CIS 310 - Excel AssignmentDocument18 pagesAcademic Integrity Policy:: CIS 310 - Excel AssignmentRoberto RossiNo ratings yet
- Beware. FAKE Offer LetterDocument2 pagesBeware. FAKE Offer LetterKkRider KolkataNo ratings yet
- Vsphere With KubernetesDocument12 pagesVsphere With Kubernetesleroy23No ratings yet
- Test OneDocument11 pagesTest Onealum jacobNo ratings yet
- The Problem and Its Setting: City College of CalambaDocument61 pagesThe Problem and Its Setting: City College of CalambaKate ManaigNo ratings yet
- advancedOrderEntry AOM Manual v4 1 PDFDocument289 pagesadvancedOrderEntry AOM Manual v4 1 PDFTino PiazzardiNo ratings yet
- ITSU3008 Project 1 Project Title: Student ID and Student NamesDocument5 pagesITSU3008 Project 1 Project Title: Student ID and Student Namesyatin gognaNo ratings yet
- Ax My Perfect ResumeDocument7 pagesAx My Perfect Resumekpcvpkjbf100% (2)