Professional Documents
Culture Documents
QM - Chapter 4 (MCQ'S)
QM - Chapter 4 (MCQ'S)
Uploaded by
arslanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
QM - Chapter 4 (MCQ'S)
QM - Chapter 4 (MCQ'S)
Uploaded by
arslanCopyright:
Available Formats
RISE School of Accountancy (Islamabad & Rawalpindi) Quantitative Methods (PRC-02) MCQ’s
Chapter 4: Linear Programming
1. An employer recruits experienced (x) and fresh workmen (y) for his firm under the condition that he cannot
employ more than 9 people, x and y can be related by the inequality:
(a) x + y 9 (b) x + y 9, x 0, y 0
(c) x + y 9, x 0, y 0 (d) None of these
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2. On the average, an experienced person does 5 units of work while a fresh recruit does 3 units of work daily
and the employer has to maintain an output of at least 30 units of work per day. This situation can be expressed
as:
(a) 5x + 3y 30 (b) 5x + 3y > 30
(c) 5x + 3y 30, x 0, y 0 (d) None of these
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------------
3. The rules and regulations demand that the employer should employ not more than 5 experienced hands to 1
fresh one. This fact can be expressed as:
(a) y x/5 (b) 5y x
(c) x 5y (d) None of these
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
4. The union however forbids him to employ less than 2 experienced person to each fresh person. This situation
can be expressed as:
(a) x y/2 (b) y x/2
(c) y x/2 (d) x > 2y
------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ---------------------------------------------------------
5. The graph to express the inequality x + y 9 is:
(a) (b)
(c) (d) None of these
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
M. Bilal Kamran Page 1
RISE School of Accountancy (Islamabad & Rawalpindi) Quantitative Methods (PRC-02) MCQ’s
6. The graph to express the inequality 5x + 3y 30 is:
(a) (b)
(c) (d) None of these
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
1
y
7. The graph to express the inequality 2 x is indicated by:
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
8. L1: 5x + 3y = 30, L2: x + y = 9, L3: y = x/3, L4: y = x/2
The common region (shaded part) shown in the diagram refers to:
(a) 5x + 3y 30 (b) 5x + 3y 30
x + y 9 x + y 9
y 1/5x y x/3
y x/2 y x/2
x 0, y 0
M. Bilal Kamran Page 2
RISE School of Accountancy (Islamabad & Rawalpindi) Quantitative Methods (PRC-02) MCQ’s
(c) 5x + 3y 30 (d) None of these
x + y 9
y x/3
y x/2
x 0, y 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
9. The region indicated by the shading in the graph is expressed by inequalities:
(a) x1 + x2 2 (b) x1 + x2 2
2x1 + 2x2 8 x2 x1 + x2 4
x1 0, x2 0
(c) x1 + x2 2 (d) x1 + x2 2
2x1 + 2x2 8 2x1 + 2x2 > 8
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
10. If A is the number of batsmen and B is the number of bowlers, the inequality constraint that the number of
batsmen must be no more than 50% of the total players is:
(a) A B (c) BA
(b) A B (d) A B
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
11. A firm manufactures two products. The products must be processed through one department. Product A
requires 6 hours per unit, and product B requires 3 hours per unit. Total production time available for the
coming week is 60 hours. There is a restriction in planning the production schedule, as total hours used in
producing the two products cannot exceed 60 hours. This situation can be expressed as:
M. Bilal Kamran Page 3
RISE School of Accountancy (Islamabad & Rawalpindi) Quantitative Methods (PRC-02) MCQ’s
Y Y
20 ● 20 ●
15 15
10 10
(a) (b)
5 5
● ● X ● ● X
5 10 5 10
20
15 ●
10
(c) (d) None of these
5
● ● X
5 10
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
12. A manufacturer produce two products P and Q which must pass through the same processes in departments
A and B having weekly production capacities of 240 hours and 100 hours respectively. Product P needs 4 hours
in department A and 2 hours in department B. Product Q requires 3 hours and 1 hour respectively, in
department A and B. Profit yields for product P is Rs.700 and for Q is Rs.500. The manufacturer wants to
maximize the profit with the given set of inequalities. The objective function and all the constraints are:
(a) Z = 700x + 500y (b) Z = 700x + 500y
2x + 3y 240 4x + 3y 240
2x + y 100 2x + y 100
x, y 0 x, y 0
(c) Z = 700x + 500y (d) None of these
4x + 3y 240
2x + y 100
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
13. A dietician wishes to mix together two kinds of food so that the vitamin content of the mixture is at least 9
units of vitamin A, 7 units of vitamin B, 10 units of vitamin C and 12 units of vitamin D. The vitamin content
per Kg. of each food is shown below:
A B C D
Food I: 2 1 1 2
Food II: 1 1 2 3
Assuming x units of food I is to be mixed with y units of food II the situation can be expressed as:
M. Bilal Kamran Page 4
RISE School of Accountancy (Islamabad & Rawalpindi) Quantitative Methods (PRC-02) MCQ’s
(a) 2x + y 9 (b) 2x + y 30
x + y 7 x + y 7
x + 2y 10 x + 2y 10
2x + 3y 12 x + 3y 12
x > 0, y > 0
(c) 2x + y 9 (d) None of these
x + y 7
x + y 10
x + 3y 12
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
14. Graphs of four equations are drawn below:
L1: 2x + y = 9, L2: x + y = 7, L3: x + 2y = 10, L4: x + 3y = 12
The common region (shaded part) indicated on the diagram is expressed by the set of inequalities.
(a) 2x + y 9 (b) 2x + y 9
x + y 7 x + y 7
x + 2y 10 x + 2y 10
x + 3y 12 x + 3y 12
(c) 2x + y 9 (d) None of these
x + y 7
x + 2y 10
x + 3y 12
x 0, y 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
15. The common region satisfied by the inequalities
L1: 3x + y 6
L2: x + y 4
L3: x + 3y 6
L4: x + y 6
is indicated by:
M. Bilal Kamran Page 5
RISE School of Accountancy (Islamabad & Rawalpindi) Quantitative Methods (PRC-02) MCQ’s
(a) (b)
(c) (d) None of these
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
16. A firm makes two types of products: Type A and Type B. The profit on product A is Rs.20 each and that on
product B is Rs.30 each. Both types are processed on three machines M1, M2 and M3. The time required in
hours by each product and total time available in hours per week on each machine are as follow:
Machine Product A Product B Available Time
M1 3 3 36
M2 5 2 50
M3 2 6 60
The constraints can be formulated taking x1 = number of units A and x2 = number of unit of B as:
(a) x1 + x2 12 (b) 3x1 + 3x2 36
5x1 + 2x2 50 5x1 + 2x2 50
2x1 + 6x2 60 2x1 + 6x2 60
x1 0, x2 0
(c) 3x1 + 3x2 36 (d) None of these
5x1 + 2x2 50
2x1 + 6x2 60
x1 0, x2 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
17. The set of inequalities
L1: x1 + x2 12,
L2: 5x1 + 2x2 50
L3: x1 + 3x2 30
x1 0 and x2 0
is represented by:
M. Bilal Kamran Page 6
RISE School of Accountancy (Islamabad & Rawalpindi) Quantitative Methods (PRC-02) MCQ’s
(a) (b)
(c) (d) None of these
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
18. The common region satisfying the set of inequalities x 0, y 0, L1: x + y 5,
L2: x + 2y 8 and L3: 4x + 3y 12 is indicated by:
(a) (b)
(c) (d) None of these
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
19. A manufacturer produces two products X1 and X2. Resources available for the production of these two
items are restricted to 200 support staff hours, 320 machine hours and 280 labour hours. X1 requires for its
production 1 support staff hour, 1 machine hour and 2 labour hours. X2 requires 1 support staff hour, 2 machine
hours and 0.8 labour hour. X1 yields Rs.300 profit per unit and X2 yields Rs.200 profit per unit. The
manufacturer wants to determine the profit maximizing weekly output of each product while operating within
the set of resource limitations. Situation of the above data in the form of equations and inequalities is:
M. Bilal Kamran Page 7
RISE School of Accountancy (Islamabad & Rawalpindi) Quantitative Methods (PRC-02) MCQ’s
(a) Z = 300x + 200y (b) Z = 300x + 200y
x + y 200 x + y 200
x + 2y 320 3x + 2y 320
2x + 0.8y 280 2x + 0.8y 280
x 0, y 0 x 0, y 0
(c) Z = 300x + 200y (d) None of these
x + y 200
x + 2y 320
2x + 0.8y 280
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
20. A factory is planning to buy some machine to produce boxes and has a choice of B-1 or B-9 machines.
Rs.9.6 million has been budgeted for the purchase of machines. B-1 machines costing Rs.0.3 million each
require 25 hours of maintenance and produce 1,500 units a week. B-9 machines costing Rs.0.6 million each
require 10 hour of maintenance and produce 2,000 units a week. Each machine needs 50 square meters of floor
area. Floor area of 1,000 square meters and maintenance time of 400 hours are available each week. Since all
production can be sold, the factory management wishes to maximize output. Situation of above data in the form
of objective function and constraints is:
(a) Z = 1500x + 2000y (b) Z = 1500x + 2000y
0.3x + 0.6y 9.6 0.3x + 0.6y 9.6
25x + 10y 400 25x + 10y 400
50x + 50y 1000 50x + 50y 1000
x 0, y 0 x 0, y 0
(c) Z = 1500x + 2000y (d) Z = 1500x + 2000y
0.3x + 0.6y 9.6 0.3x + 0.6y 9.6
25x + 10y 400 25x + 10y 400
50x + 50y 1000 50x + 50y 1000
x 0, y 0 x 0, y 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
21. A company produces two products a and b. Production of A will be at least five times the production of B.
This situation can be expressed as:
(a) b≥5a (b) b≤5a
(c) a≤5b (d) a≥5b
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
22. A manufacturer produces two products A and B. Each unit of A requires 3kg of raw material and 2 labour
hours whereas each unit of B requires 2kg or raw material and 2 labour hours. Total raw material available is
200kg whereas total labour hours available are 150 hours. This situation can be expressed as:
(a) 3a+2b ≥ 200 and 2a+2b ≥ 150 (b) 3a+2b ≤ 200 and 2a+2b ≤ 150
(a) 3a+2b ≤ 150 and 2a+2b ≤ 200 (a) 3a+2b ≥ 150 and 2a+2b ≥ 200
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
23. Inequalities x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0 suggest that feasible region will be in _____ quadrant.
(a) 1st (b) 2nd
(c) 3rd (d) 4th
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
M. Bilal Kamran Page 8
RISE School of Accountancy (Islamabad & Rawalpindi) Quantitative Methods (PRC-02) MCQ’s
24. Which of the following values of x and y does not satisfy the inequality 2x+3y ≤ 6
(a) (1,1) (b) (0,1)
(c) (3,1) (d) (1,0)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
25. A machine can work for 16 hours per day at most. It takes 4 hours to produce one unit of product A and 8
hours to produce one unit of product B. This information can be expressed as:
(a) 4a+8b ≤ 16 (b) 4a+8b ≥ 16
(c) 4a+8b = 16 (d) Not possible to express information
------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ---------------------------------------------------------
26. Which of the following constraint will have a feasible region with coordinate (2, 3) in it?
(a) 10x+5y ≤ 40 (b) 10x+5y ≤ 30
(c) 10x+5y ≤ 10 (d) 10x+5y ≤ 20
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
27. Pharma limited produces two medicines. Each of which requires two types of raw material with following
details:
Product A(kg/unit) Product B(kg/unit) Total available (kg)
Raw material X 2 3 120
Raw material Y 4 6 360
Form appropriate constraints as per above information
(a) 2a+3b ≤ 120 and 4a+6b ≤ 360 (b) 2x+4y ≤ 120 and 3x+6y ≤ 360
(c) 4a+6b ≤ 120 and 2a+3b ≤ 360 (a) 2x+3y ≤ 120 and 4a+6b ≤ 360
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
28. The maximum number of constraints while solving a business problem using linear programming is
(a) 1 (b) 2
(c) 3 (d) there is no specific limit
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
29. Feasible region is a _____
(a) Region which satisfies all given constraints
(b) Region which is in first quadrant
(c) Region above the last mentioned constraint
(d) Always below all the constraints in a given scenario
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
30. Corner point theorem states _____
(a) Optimal solution is at one of the corners of feasible region.
(b) Optimal solution is within feasible region.
(c) Profit is maximum at all corners of a feasible region.
(d) Revenue is maximum at all corners of a feasible region.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
31. Linear programming model can be used for _____
(a) Profit maximization (b) Cost minimization
(c) Both (d) None
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
32. For the following set of inequalities and objective function. Identify the optimal solution using corner point
theorem
M. Bilal Kamran Page 9
RISE School of Accountancy (Islamabad & Rawalpindi) Quantitative Methods (PRC-02) MCQ’s
Constraints
i. x≥0
ii. y ≥0
iii. x+y ≤ 8
Objective function
Profit = 10x+2y
(a) (8, 0) (b) (0, 8)
(c) (4, 4) (d) (0, 0)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
33. For the following set of inequalities and objective function. Identify the optimal solution using corner point
theorem
Constraints
i. x≥0
ii. y ≥0
iii. 2x+y ≤ 8
iv. 2x+2y ≤ 10
Objective function
Profit = 10x+2y
(a) (0, 8) (b) (5, 0)
(c) (0, 5) (d) (8, 0)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
34. For the following set of inequalities and objective function. Identify the optimal solution using corner point
theorem
Constraints
i. x≥1
ii. y ≥2
iii. x+y ≤ 8
Objective function
Cost = 10x+2y
(a) (0, 0) (b) (1, 2)
(c) (2, 1) (d) (0, 0)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- --------
35. Identify the redundant constraint from the following set of constraints:
i. x+y ≤ 6
ii. x≥0
iii. y ≥0
iv. 4x+2y ≤ 8
(a) 4x+2y ≤ 8 (b) x≥0
(c) y≥0 (d) x+y ≤ 6
36. A company wants to make product A which will contain both chemical x and chemical y. The product must
contain at least 1 unit of x and 2 units of y. The company has to be careful that total of x and y units in the
product must not exceed 8 units.
If the cost of each unit of x and y is 10 and 2 respectively, formulate constraints and objective function
respectively.
M. Bilal Kamran Page 10
RISE School of Accountancy (Islamabad & Rawalpindi) Quantitative Methods (PRC-02) MCQ’s
(a) Constraints (b) Constraints
i. x ≥ 1 i. x ≥ 1
ii. y ≥2 ii. y ≥2
iii. x+y ≤ 8 iii. x+y ≤ 8
Objective function Objective function
Cost = 10x+2y Cost = 2x+10y
(c) Constraints (d) Constraints
i. x ≥ 0 i. x ≥ 1
ii. y ≥0 ii. y ≥2
iii. x+y ≤ 8 iii. x+y ≤ 2
Objective function Objective function
Cost = 10x+2y Cost = 10x+2y
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
37. A company produces two types of cola drinks. Each of which requires two types of raw material with
following details:
Product A(kg/unit) Product B(kg/unit) Total available (kg)
Raw material X 3 4 480
Raw material Y 2 6 540
How many units of each type of cola drink may be produced to maximise the profit, if the profit on each unit of
A and B is Rs 1,800 and Rs. 6,300 respectively?
(a) (72, 66) (b) (0, 90)
(c) (160, 0) (d) (66, 72)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
38. For the following constraints:
i. x+y ≥ 40
ii. x+y ≤ 10
(a) There is no feasible region (b) One feasible region
(c) Two feasible regions (d) Three feasible regions
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
39. Minimum number of constraints to draw a feasible region is/are:
(a) 1 (b) 2
(c) 3 (d) 4
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ---------------
40. A bounded feasible region will:
(a) Have both maximum and minimum value (b) Have maximum value only
(c) Have minimum value only (d) None of these
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
41. Y ≤ X will have a feasible region: __
(a) Above Y axis only (b) Below Y axis only
(c) Above X axis only (d) Below or on the line Y=X
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
M. Bilal Kamran Page 11
RISE School of Accountancy (Islamabad & Rawalpindi) Quantitative Methods (PRC-02) MCQ’s
42. Product passes through two departments A and B which have a capacity of 1120 hours and 1400 hours The
Product X requires 4 hours in department A and 7 hours in department B, the product Y requires 5 hours in
department A and 8 hours in department B. The constraints representing the above data:
a) 4x+5y ≤ 1120 and 7x+8y ≤ 1400 c) 7x+5y ≤ 1400 and 8x+4y ≤ 1120
b) 4x+7y ≤ 1400 and 5x+8y ≤ 1120 d) 7x+8y ≤ 1120 and 4x+5y ≤ 1400
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
43. A factory produces two products x and y. Each product passes through two departments A and B which
have a capacity of 1120 hours and 1400 hours The Product X requires 7 hours in department A and 4 hours in
department B, the product Y requires 8 hours in department A and 5 hours in department B. The constraints
representing the above data:
a) 7x+4y ≤ 1120 and 8x+5y ≤ 1400 c) 7x+5y ≤ 1400 and 8x+4y ≤ 1120
b) 7x+8y ≤ 1400 and 4x+5y ≤ 1120 d) 7x+8y ≤ 1120 and 4x+5y ≤ 1400
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
44. A factory produces two products x and y. Each product passes through two departments M and N which
have a capacity of 1120 hours and 1400 hours The Product A requires 7 hours in department M and 4 hours in
department N, the product B requires 8 hours in department M and 5 hours in department N. The constraints
representing the above data:
a) 7A+4B ≤ 1120 and 8A+5B ≤ 1400 c) 7A+5B ≤ 1400 and 8A+4B ≤ 1120
b) 7A+8B ≤ 1400 and 4A+5B ≤ 1120 d) 7A+8B ≤ 1120 and 4A+5B ≤ 1400
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
45. A factory produces two products x and y. Each product passes through two departments A and B which
have a capacity of 1,100 hours and 1,400 hours The Product X requires 4 hours in department A and 5 hours in
department B, the product Y requires 7 hours in department A and 8 hours in department B. The profit margin
on x and y is Rs. 500 and Rs. 700 respectively. Objective function related to the given situation will be:
a) 1100x+1400y c) 600x+700y
b) 500x+700y d) 660,000x+980,000y
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
46. A company earns profit of Rs 250 and Rs 375 per unit on product X and Y respectively. Find the maximum
profit that the company could earn if the company is subject to the following constraints:
4x+2y ≤ 25,000
3x+2y ≤ 20,000
a) Rs 1,666,667 c) Rs 3,750,000
b) Rs 2,187,500 d) Rs 4,687,500
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
47. A company makes and sells two products X and Y. the contribution per unit is Rs 250 for product X and
375 for product Y. due to various constraints, the company cannot make more than 750 units of X and 500 units
of Y in a month. If x represents the number of product X, y represents the number of product Y and C
represents contribution, which of the following relationship represents maximum contribution?
a) C=250x+375y c) C=500x+125y
b) C=750x+500y d) C=3x+1.33y
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
M. Bilal Kamran Page 12
RISE School of Accountancy (Islamabad & Rawalpindi) Quantitative Methods (PRC-02) MCQ’s
48. A company makes and sells two products X and Y. the related information is as follows:
X Y
Contribution per unit (Rs.) 450 375
Maximum sales demand per month 2,800 1,200
Direct labour hour per unit 2 5
Machine hours per unit 6 7
A total of 10,000 direct labour hours and 22,000 machine hours are available per month. Which of the following
objective function (Z) and set of constraints represents the above situation?
a) Z=450x+375y c) Z=450x-375y
x ≤ 2,800 x ≤ 2,800
2x+5y ≤ 22,000 2x-5y ≤ 22,000
y ≤ 1,200 y ≤ 1,200
b) Z=450x+375y d) Z=450x+375y
x ≤ 2,800 x ≤ 1,800
2x+5y ≤ 10,000 2x+5y ≤ 12,000
y ≤ 1,200 y ≤ 1,200
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
49. New product. The fixed cost of manufacturing and marginal cost per unit are estimated at Rs 500,000 and
Rs 400 respectively. The capacity of the plant is 75,000 units and marketing department has indicated that the
entire production can be sold at a price of Rs 650 per unit. Determine the total profit function
a) 250x – 500,000 c) 75,000 – 500,000
b) 650x – 500,000 d) 650x2 – 250x – 500,000
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
50. Tooba furniture (TF) manufacture chairs (C) and tables (T). the sale price and cost of production of the two
articles are as follows:
Article Sale price Cost of Production
Amount in Rs.
C 850 700
T 1,300 1,200
Manufacturing time is 3 and 4 labour hours for each chair and table respectively. TF has a labour force of 20
workers and each worker can work a maximum of 180 hours. The total funds available for manufacturing are
Rs. 4 million. The objective function (Z) and the constraints representing the given scenario are:
a) Z=100C+150T c) Z=700C+1,200T
700x+1200y ≤ 4,000,000 700x+1200y ≤ 4,000,000
3x+4y ≤ 3,600 3x+4y ≤ 180
b) Z=150C+100T d) Z=850C+1,300T
700x+1200y ≤ 4,000,000 700x+1200y ≤ 4,000,000
3x+4y ≤ 3,600 3x+4y ≤ 3,600
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
51. A company owns a machine which runs for 208 hours a month. The machine is used to make two parts X
and Y. each part X takes 1 hour of machine time and each part Y takes 2 hours of machine time. If x represents
M. Bilal Kamran Page 13
RISE School of Accountancy (Islamabad & Rawalpindi) Quantitative Methods (PRC-02) MCQ’s
the number of part X made in a month and y represents the number of part Y made in a month, which of t he
following statements/ inequalities is correct?
a) The company could make any quantity of X and Y but the total machine hours in a month cannot exceed 208.
b) x+2y<208 represents the boundary of maximum production in a month
c) y ≤ 208 if x=0, represents the maximum production of Y in a month
d) both (a) and (b)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
52. If 3x+7 ≥ x+5 ≥ 5x – 3, then the inequality holds when x lies in the range
a) 7 ≤ x ≤ – 3 c) 3 ≤ x ≤ 5
b) 5 ≥ x ≥ 7 d) 2 ≥ x ≥ – 1
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
53. If 3x+7 ≤ 5x – 3, then the inequality holds when x lies in the range
a) Less than or equal to 7 c) Less than or equal to 5
b) Greater than or equal to 5 d) Greater than or equal to 2
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
54. 2x + 7< 5x – 3 Which value of x will satisfy
a) x ≥ 5 c) x <2
b) x ≤ 7 d) None
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
55. 4x+3y ≤ 9, 2x+6y ≤ 4, while x ≤ 0, y ≤ 0 find redundant constraints
a) 4x+3y≤9 c) Both equations
b) 2x+6y ≤ 4 d) No equations
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
56. Which of the following is a redundant constraint?
L1 5x + 3y < 9,000 L3 x < 1,000
L2 3x + 2y < 8,400 L4 y < 1,000
a) L-1 c) L-3
b) L-2 d) none
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
57. High grade concrete contains 10 kg of gravel and 5 kg of cement, while each bag of low grade concrete
contains 12 kg of gravel and 3 kg of cement. There are 1,920 kg of gravel and 780 kg of cement currently
available. The manufacturer can make a profit of Rs. 1.20 on each bag of the high grade and Rs. 1.00 on each
bag of low grade concrete. Then the number of bags of low grade, high grade and the maximum profit are
respectively:
a) 60,120,240 c) 60,120,204
b) 120,60,240 d) 120,60,204
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------------------
58. A factory produced two products X and Y in two departments A(production) and B(packing). Capacity of
each department is 1100 and 1420 hours respectively. The product X requires 4 hours in department A and 5
hours in department B, the product Y requires 7 hours in department A and 8 hours in department B. wha t are
the constraints
a) 5x+4y≤1100 b) 4x+5y≤1100
7x+8Y ≤1420 7x+8Y ≤1420
X,y≥0 X,y≥0
M. Bilal Kamran Page 14
RISE School of Accountancy (Islamabad & Rawalpindi) Quantitative Methods (PRC-02) MCQ’s
c) 4x+7y≤1100 d) None of these
5x+8Y ≤1420
X, y ≥ 0
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------
M. Bilal Kamran Page 15
You might also like
- 0 Ecuatii ExpDocument1 page0 Ecuatii ExpMimi2007No ratings yet
- Final Exam G8 P1Document4 pagesFinal Exam G8 P1Omar AbdallaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam G7 p1Document3 pagesFinal Exam G7 p1Omar AbdallaNo ratings yet
- 1T00717Document3 pages1T00717B 87 VISHWAKARMA AAKASH ACHCHHELALNo ratings yet
- C TestDocument115 pagesC Testapi-26090714No ratings yet
- Worksheet-Bridge Course Class Iv Maths Competen Cy - Forming Numbers and UnderstandingDocument2 pagesWorksheet-Bridge Course Class Iv Maths Competen Cy - Forming Numbers and UnderstandingNisha SomasekharanNo ratings yet
- Xi Mathematics PastpaperDocument72 pagesXi Mathematics PastpapersalmanNo ratings yet
- Saz5cDocument7 pagesSaz5cSan Dinakar DheenaNo ratings yet
- BBA BS Accounting Finance BS Social Sciences Test PDFDocument15 pagesBBA BS Accounting Finance BS Social Sciences Test PDFHafsah AnwarNo ratings yet
- Questions BankDocument5 pagesQuestions BankAjitNo ratings yet
- Factorial Design-PrpDocument21 pagesFactorial Design-Prpbhargav patelNo ratings yet
- Regional Unified Numeracy TestDocument3 pagesRegional Unified Numeracy TestLenchen M. ArconNo ratings yet
- Math 204 Final v1 Spring 2018-2019 PDFDocument11 pagesMath 204 Final v1 Spring 2018-2019 PDFJad Abou AssalyNo ratings yet
- Sem-Vii Comp CBGS PDFDocument20 pagesSem-Vii Comp CBGS PDFTHE GAMING CHANNELNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus Group Quiz 5.1 - 5.3: X (1 - Sin X)Document4 pagesPre-Calculus Group Quiz 5.1 - 5.3: X (1 - Sin X)madisonNo ratings yet
- Final Exam G7 P2Document5 pagesFinal Exam G7 P2Omar AbdallaNo ratings yet
- 1S00255C7 PDFDocument19 pages1S00255C7 PDFSimran SurveNo ratings yet
- Final 204 PDFDocument9 pagesFinal 204 PDFibrahim fadelNo ratings yet
- Reaction DiffusionDocument33 pagesReaction DiffusionAzeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Class VIII Mathematics Worksheet 3Document3 pagesClass VIII Mathematics Worksheet 3Pooja AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Jhu M D A Wohdmk Fomd Fïka J Provincial Department of Education - NWPDocument6 pagesJhu M D A Wohdmk Fomd Fïka J Provincial Department of Education - NWPAnura Prasantha RamanayakeNo ratings yet
- 1T00727Document2,758 pages1T00727Pratik DhandeNo ratings yet
- Complete PastpaperDocument82 pagesComplete Pastpapersecret studentNo ratings yet
- 1T00144ECA4GDocument10 pages1T00144ECA4GRekha JadhavNo ratings yet
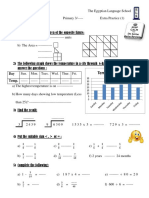
- Temprature Degree: Day Temp.Document1 pageTemprature Degree: Day Temp.Adam Amr ElgoharyNo ratings yet
- Sample 1 MsDocument7 pagesSample 1 MsjobyvallikunnelNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Economics Notes - III For V Sem: A. Diagram Discussion Economic RelationshipDocument6 pagesMathematical Economics Notes - III For V Sem: A. Diagram Discussion Economic RelationshipAngad 2K19-PE-012No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledVipul Vaibhav MahajanNo ratings yet
- Class IV Maths Quarterly RevisionDocument10 pagesClass IV Maths Quarterly RevisionVimal B JainNo ratings yet
- ProgrammingWithSMathStudio2012 PDFDocument30 pagesProgrammingWithSMathStudio2012 PDFMarioNo ratings yet
- CA2RDocument189 pagesCA2RAllRounderNo ratings yet
- 856 EconomicsDocument4 pages856 Economicsayushii kapurNo ratings yet
- Bos 43674 MTPFNDQ 3Document16 pagesBos 43674 MTPFNDQ 3Jagpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Revisions - Model Exams 2023Document7 pagesRevisions - Model Exams 2023Haytham SaadNo ratings yet
- Mock Test Maths 2021Document17 pagesMock Test Maths 2021Manthan JadhavNo ratings yet
- 1T01427Document23 pages1T01427triotics3No ratings yet
- ProblemDocument18 pagesProblemFikre Ayele100% (1)
- Business Mathematics and Statistics PDFDocument392 pagesBusiness Mathematics and Statistics PDFSM Friend85% (74)
- Assignment - 1Document41 pagesAssignment - 1ZelalemBenayewNo ratings yet
- Cal Apps Study PacketDocument60 pagesCal Apps Study PacketAustin JosephNo ratings yet
- Q1: Choose The Correct Answer From The BracketsDocument1 pageQ1: Choose The Correct Answer From The Bracketsحمزة عبد الهادي حسونNo ratings yet
- Anexo Graderias PDFDocument80 pagesAnexo Graderias PDFklanpunkNo ratings yet
- Business Studies 9 ........... (Cambridge) : Monthlytest October 2020Document7 pagesBusiness Studies 9 ........... (Cambridge) : Monthlytest October 2020Mohamed MubarakNo ratings yet
- 1T00161Document437 pages1T00161Rohan JadhavNo ratings yet
- DS Updated PDF QuestionsDocument35 pagesDS Updated PDF Questionsdiksha1920dangdeNo ratings yet
- 1T00161 1Document235 pages1T00161 1Rohan JadhavNo ratings yet
- Computer Science IIDocument9 pagesComputer Science IIThasanya ThanuliNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Aptitude - Chain RuleDocument26 pagesQuantitative Aptitude - Chain RuleKiran GadkariNo ratings yet
- Math - G11 - T1 - I, II Ans - 2020Document6 pagesMath - G11 - T1 - I, II Ans - 2020dulmeth bandaraNo ratings yet
- Or ObjectivesDocument22 pagesOr ObjectivesKAYNo ratings yet
- BBA BS Accounting FinanceDocument15 pagesBBA BS Accounting Financeadeelali849714No ratings yet
- Quantitative Group Assignment-Answer2Document18 pagesQuantitative Group Assignment-Answer2Asegid H/meskelNo ratings yet
- rr311303 Operations ResearchDocument9 pagesrr311303 Operations ResearchSRINIVASA RAO GANTA100% (1)
- Mba Past Papers IbaDocument19 pagesMba Past Papers IbaM Burhan SafiNo ratings yet
- QMS - Question Bank - 2013Document99 pagesQMS - Question Bank - 2013Syed Haseeb Naqvi0% (1)
- Advanced AutoCAD® 2017: Exercise WorkbookFrom EverandAdvanced AutoCAD® 2017: Exercise WorkbookRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Mathematics Grade 7 QuestionsDocument23 pagesMathematics Grade 7 QuestionsnurucareinternationalNo ratings yet
- Final Paper - Loftus and Palmer ExperimentDocument12 pagesFinal Paper - Loftus and Palmer ExperimentMartin BaciertoNo ratings yet
- Robust Control of A Two-Wheeled Robot : CONFIDENTIAL. Limited Circulation. For Review OnlyDocument6 pagesRobust Control of A Two-Wheeled Robot : CONFIDENTIAL. Limited Circulation. For Review OnlyChandrajit GangulyNo ratings yet
- ACM - Ds Standard Field Machine v2.0.4Document4 pagesACM - Ds Standard Field Machine v2.0.4s pradhanNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Vessel Slope RequirmentDocument2 pagesHorizontal Vessel Slope RequirmentVishal VarmaNo ratings yet
- M Qasim Electrical EngineerDocument3 pagesM Qasim Electrical EngineerqasimNo ratings yet
- TopicsDocument5 pagesTopicsAnnie MirajNo ratings yet
- Business Forecasting: by ITH PhannyDocument2 pagesBusiness Forecasting: by ITH PhannysmsNo ratings yet
- The Third Level NotesDocument28 pagesThe Third Level NotesRita MauryaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Layout Planning and Its Importance in Lean OperationsDocument12 pagesChapter 5 Layout Planning and Its Importance in Lean OperationsghaziaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Project SchedulingDocument7 pagesWeek 3 - Project Schedulingمعتز محمدNo ratings yet
- CONSOLLEDocument3 pagesCONSOLLEPeter YliNo ratings yet
- Business Research Methods: DR - Vittapu Email IDDocument31 pagesBusiness Research Methods: DR - Vittapu Email IDGizawNo ratings yet
- Pneumatics - Air CompressionDocument10 pagesPneumatics - Air CompressionNikolas FabryNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment, and Determining Control (HIRADC) Method in A University Laboratory in Surabaya, IndonesiaDocument6 pagesHazard Identification, Risk Assessment, and Determining Control (HIRADC) Method in A University Laboratory in Surabaya, IndonesiaPasta GigiNo ratings yet
- WASSCE WAEC Geography SyllabusDocument13 pagesWASSCE WAEC Geography SyllabusAMINATA THULLAHNo ratings yet
- GPS and Its ApplicationsDocument15 pagesGPS and Its ApplicationsSonal MevadaNo ratings yet
- Failure Theories - Static LoadsDocument15 pagesFailure Theories - Static LoadsMahmoud Abdelghafar ElhussienyNo ratings yet
- Air Flow Velocity Measurement Using Pitot-Static Tube (Fluid Exp 4)Document10 pagesAir Flow Velocity Measurement Using Pitot-Static Tube (Fluid Exp 4)hayder alaliNo ratings yet
- How To Make Isometric Dimension and Text in AutoCADDocument5 pagesHow To Make Isometric Dimension and Text in AutoCADgia haiNo ratings yet
- Abney LevelDocument6 pagesAbney LevelAtish Kumar86% (7)
- Conventional Tunnelling - 5.draft - 20041004Document98 pagesConventional Tunnelling - 5.draft - 20041004Aishwarya KumarNo ratings yet
- Example of Engineering ReportDocument48 pagesExample of Engineering ReportJayvee ArimbuyutanNo ratings yet
- MSC TropHEE in Technise Universitet DrarmstadtDocument2 pagesMSC TropHEE in Technise Universitet DrarmstadtdimasNo ratings yet
- 08 An Example of NN Using ReLuDocument10 pages08 An Example of NN Using ReLuHafshah DeviNo ratings yet
- 2021 JHS INSET Template For Modular/Online LearningDocument14 pages2021 JHS INSET Template For Modular/Online LearningMJ GuinacaranNo ratings yet
- EE3331C Feedback Control Systems L7: Control System Performance: Transient & Steady-StateDocument30 pagesEE3331C Feedback Control Systems L7: Control System Performance: Transient & Steady-Statepremsanjith subramaniNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 FMM Session 1Document31 pagesUnit 1 FMM Session 1Palanivel Rajan A RNo ratings yet
- PPGC - Week 1 (Politics and Governance)Document3 pagesPPGC - Week 1 (Politics and Governance)KRISTINE ANGELI BARALNo ratings yet
- COT2 FinalDocument39 pagesCOT2 FinalLJ Caylan BareteNo ratings yet