Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BCSL45 Short Notes
BCSL45 Short Notes
Uploaded by
sahil verma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views1 pageThe document defines and describes various algorithms and algorithmic concepts including time complexity, asymptotic notation, sorting algorithms like bubble sort, selection sort, and insertion sort, searching algorithms like linear search and binary search, and additional concepts like recursion, hashing, and divide-and-conquer approaches. Key algorithms covered are quicksort, mergesort, and common sorting and searching methods. Pseudocode is also introduced as a way to represent logic in algorithms.
Original Description:
Original Title
BCSL45 short notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines and describes various algorithms and algorithmic concepts including time complexity, asymptotic notation, sorting algorithms like bubble sort, selection sort, and insertion sort, searching algorithms like linear search and binary search, and additional concepts like recursion, hashing, and divide-and-conquer approaches. Key algorithms covered are quicksort, mergesort, and common sorting and searching methods. Pseudocode is also introduced as a way to represent logic in algorithms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views1 pageBCSL45 Short Notes
BCSL45 Short Notes
Uploaded by
sahil vermaThe document defines and describes various algorithms and algorithmic concepts including time complexity, asymptotic notation, sorting algorithms like bubble sort, selection sort, and insertion sort, searching algorithms like linear search and binary search, and additional concepts like recursion, hashing, and divide-and-conquer approaches. Key algorithms covered are quicksort, mergesort, and common sorting and searching methods. Pseudocode is also introduced as a way to represent logic in algorithms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
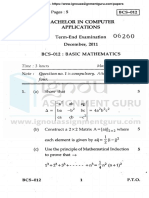
• Algorithm: sequence of steps that describe how a problem is solved.
• Time complexity of algorithm: amount of time taken by the algorithm to run.
• Asymptotic notation: mathematical notations used to describe the running time of an
algorithm.
• Big O notation: describes the limiting behavior of a function when the argument tends towards
a particular value or infinity.
• Big Theta(Θ) notation: specifies asymptotic bounds for a function f(n) and provides the average
time complexity of an algorithm.
• Big Omega(Ω) function: used to describe the performance or complexity of an algorithm.
• Recursion: process in which a function calls itself directly or in directly. Corresponding function
is called recursive function.
• Recursive function: function with repeats itself to calculate subsequent terms.
• Searching: designed to check for an element or retrieve an element from any data structure
where it is stored.
• Sorting algorithm: used to rearrange a given array or list of elements according to a comparison
operator on the elements.
• Bubble: simplest sorting algorithm. Works by repeatedly swapping the adjacent elements if they
are in wrong order.
• Selection: sorts an array by repeatedly finding the minimum element from unsorted part and
putting it at the beginning.
• Insertion: array is virtually split into sorted and unsorted part. Values from the unsorted part are
picked and placed at the correct position. Just like playing cards.
• Quick sort: array is split into subarrays and are recursively called to sort the element.
• Merge sort: repeatedly breaks down a list into several sublist unit each sublist consists of a
single element and merging those sublist in a manner that results in a sorted list.
• Linear search: it finds an element in the by searching the element sequentially until element is
found in the list.
• Binary search: finds the middle element in the list recursively until the middle element is
matched with a searched element.
• Hash algorithm: function that converts a data string into a numeric string output of a fixed
length.
• Divide-and-conquer approach: algorithm recursively breaks down a problem into 2 or more
sub-problems of the same or related type, until these become simple enough to be solved.
• Pseudo code: generic way to represent logic.
You might also like
- Csed 605 WK 10Document39 pagesCsed 605 WK 10api-695660003No ratings yet
- Linear SearchDocument11 pagesLinear SearchSafal BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- AAD AssignmentDocument20 pagesAAD Assignment1239 ShrutiNo ratings yet
- DSA Short NotesDocument4 pagesDSA Short NotesJitendra ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmsDocument32 pagesAlgorithmsKyte Valerie SamonteNo ratings yet
- Name: P Surya Narayana Subject: Summer Internship Section: K18Uw REG NO: 11802507 Course Code: Cse443 Topic: Dsa Self PacedDocument33 pagesName: P Surya Narayana Subject: Summer Internship Section: K18Uw REG NO: 11802507 Course Code: Cse443 Topic: Dsa Self PacedSURYANo ratings yet
- Data Structures and AlgorithmsDocument6 pagesData Structures and Algorithmsil.outasslaNo ratings yet
- Ict HomeworkDocument15 pagesIct HomeworkКаримов ӘділбекNo ratings yet
- Dsa Unit 5Document58 pagesDsa Unit 5VANSH BHATINo ratings yet
- AlgorithmsDocument61 pagesAlgorithmspraisechidomayaNo ratings yet
- DAA Interview Questions and AnswersDocument9 pagesDAA Interview Questions and AnswersPranjal KumarNo ratings yet
- SPPU Pattern2019 Fds Unit 2Document31 pagesSPPU Pattern2019 Fds Unit 2Keshav MahajanNo ratings yet
- 5 (Sorting (Bubble, Insertion, Quick) ) W4Document29 pages5 (Sorting (Bubble, Insertion, Quick) ) W4Asra NadeemNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmsDocument13 pagesAlgorithmsjuhi2781No ratings yet
- Sorting AlgorithmsDocument84 pagesSorting AlgorithmsDhavalNo ratings yet
- DAA Questions & AnswersDocument26 pagesDAA Questions & AnswersTusharNo ratings yet
- Algorithm Analysis - Types, Time, & ExamplesDocument2 pagesAlgorithm Analysis - Types, Time, & Examplesjohndoland19No ratings yet
- CSE 12 Sorting and SearchingDocument44 pagesCSE 12 Sorting and SearchingShengFengNo ratings yet
- CSC 425 Summary NoteDocument13 pagesCSC 425 Summary Noteayomidekelly21No ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument30 pagesChapter Twosenawagari07fNo ratings yet
- Merge Sort: Merge Sort Is Defined As A: Sorting AlgorithmDocument12 pagesMerge Sort: Merge Sort Is Defined As A: Sorting AlgorithmBharti PatelNo ratings yet
- Searching AlgorithmsDocument22 pagesSearching AlgorithmsEvertonNo ratings yet
- Power Point Presentation On-: Array Based Applications in C LanguageDocument20 pagesPower Point Presentation On-: Array Based Applications in C LanguageTanmay SharmaNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmDocument28 pagesAlgorithmJustine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Sorting DetailDocument134 pagesSorting DetailGet InsightNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cs 1Document2 pagesIntroduction To Cs 1תאמר קדמאניNo ratings yet
- Searching and SortingDocument12 pagesSearching and Sortingabc defNo ratings yet
- Dsa ch3 ArraysDocument55 pagesDsa ch3 Arraysapi-394738731No ratings yet
- Computational Thinking NotesDocument49 pagesComputational Thinking NotesCarl MhongweiNo ratings yet
- Sorting Algorithms: Searching AlgorithmDocument7 pagesSorting Algorithms: Searching AlgorithmLatera GonfaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Searching and Sorting AlgorithmDocument47 pagesChapter Three Searching and Sorting AlgorithmAbeya Taye100% (1)
- AOA Viva QuestionDocument8 pagesAOA Viva QuestionJay MhatreNo ratings yet
- Data Structures and Algorithms Analysis: ArraysDocument19 pagesData Structures and Algorithms Analysis: ArraysJobenilita CunadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 - Array Searching and SortingDocument21 pagesChapter-2 - Array Searching and SortingKartik TyagiNo ratings yet
- Insertion Sort: What Are The Boundary Cases of Insertion Sort Algorithm?Document5 pagesInsertion Sort: What Are The Boundary Cases of Insertion Sort Algorithm?Masood MughalNo ratings yet
- Unit1 ADTDocument27 pagesUnit1 ADTjhaa98676No ratings yet
- Lecture16 Arrays&Pointers (Part II)Document107 pagesLecture16 Arrays&Pointers (Part II)Arya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Part-A: Searching: Searching Refers To The Operation of Finding Locations of ADocument8 pagesPart-A: Searching: Searching Refers To The Operation of Finding Locations of AShekhar TiwariNo ratings yet
- List Data Structures: and Doubly) Linked List Search, Adding New NodesDocument86 pagesList Data Structures: and Doubly) Linked List Search, Adding New NodesMessay DamtewNo ratings yet
- Python Programming: Recursion, Recursive Function Searching, Sorting and MergingDocument35 pagesPython Programming: Recursion, Recursive Function Searching, Sorting and MergingA's Was UnlikedNo ratings yet
- DsDocument5 pagesDsmanimic023No ratings yet
- CollectionsDocument24 pagesCollectionsAjayNo ratings yet
- 8 - 19UITPC301 - A - 7 - 28unit - 5 FundamentalsDocument2 pages8 - 19UITPC301 - A - 7 - 28unit - 5 FundamentalsKISHORE ANTHONYNo ratings yet
- DSA RTU 2022 PaperDocument15 pagesDSA RTU 2022 PaperAmaan KhokarNo ratings yet
- Day 5 - Basic AlgorithmsDocument46 pagesDay 5 - Basic Algorithmsloarifse16No ratings yet
- 2B SortsDocument28 pages2B SortsNatalia HassanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: University of Engineering and Technology, TaxilaDocument7 pagesExperiment 2: University of Engineering and Technology, TaxilaAfras AhmadNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document39 pagesUnit 3mimanshas28No ratings yet
- Daa Q&aDocument8 pagesDaa Q&aAryan PrasadNo ratings yet
- 1.what Is A Data Structure? What Are The Types of Data Structures?Document13 pages1.what Is A Data Structure? What Are The Types of Data Structures?ali_afzal89No ratings yet
- 1 Intro DSDocument23 pages1 Intro DSYash JogiNo ratings yet
- VivaDocument32 pagesVivaAbhishek RaiNo ratings yet
- Cracking The Placement TestsDocument11 pagesCracking The Placement TestsafdsaNo ratings yet
- DSA and Algo For InterviewDocument15 pagesDSA and Algo For Interviewmuhammadibrarw4No ratings yet
- Read AnswerDocument12 pagesRead AnswerchitraNo ratings yet
- Sorting Hashing: Sam Dominic B. Antonio March 15, 2017 Ms - Jovy Ruth Obliosca IS211Document6 pagesSorting Hashing: Sam Dominic B. Antonio March 15, 2017 Ms - Jovy Ruth Obliosca IS211Sam antonioNo ratings yet
- Search AlgoDocument33 pagesSearch Algomonica11cssNo ratings yet
- Ds Unit2Document84 pagesDs Unit2Shrikant SardaNo ratings yet
- Pricelist Nehru PlaceDocument8 pagesPricelist Nehru Placesahil vermaNo ratings yet
- BCS 012 Previous Year Question Papers by IgnouassignmentguruDocument75 pagesBCS 012 Previous Year Question Papers by Ignouassignmentgurusahil vermaNo ratings yet
- BCSL44 Short NotesDocument2 pagesBCSL44 Short Notessahil vermaNo ratings yet
- MCS 014 Previous Year Question Papers by IgnouassignmentguruDocument55 pagesMCS 014 Previous Year Question Papers by Ignouassignmentgurusahil vermaNo ratings yet
- BCA Notes FinalDocument150 pagesBCA Notes Finalsahil vermaNo ratings yet
- BCSL43Document2 pagesBCSL43sahil vermaNo ratings yet
- MCSL16 VivaDocument1 pageMCSL16 Vivasahil vermaNo ratings yet
- MCSL16 (Short Notes For Viva)Document1 pageMCSL16 (Short Notes For Viva)sahil vermaNo ratings yet
- BCA 3rd Semester Schedule Jul-Dec 2021Document2 pagesBCA 3rd Semester Schedule Jul-Dec 2021sahil vermaNo ratings yet
- Semester - IIDocument20 pagesSemester - IIsahil vermaNo ratings yet
- Eco-02 2020-21Document10 pagesEco-02 2020-21sahil vermaNo ratings yet