Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bleeding Summary
Bleeding Summary
Uploaded by
neeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bleeding Summary
Bleeding Summary
Uploaded by
neeCopyright:
Available Formats
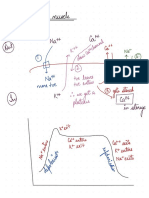
# PT: same as INR, used for extrinsic factors and # warfarin patients:
warfarin
- Vitamin K antagonist
# PTT: used for intrinsic factors and heparin - Effect start after 8-12 hours
- Maximal at 36 hours
# Haemophilia A: - Lasts for 72 hours
- Most common blood coagulation hereditary - Prolonged INR
condition - INR should be measured within 24 hours and
- Sex linked so males >females should not exceed 2.5 for surgical procedures
- Disease is characterised by excessive bleeding - Post op. bleeding is controlled by local
that starts after blood clot is formed measures, antifibrinolytics, fresh frozen
- Deficiency of factor VIII plasma, vitamin K if a haematologist decides
- Most cases are severe so.
- Lab test will show: low VIII levels, normal PT, - Can interact with prolonger antibiotic therapy,
prolonged PTT, normal bleeding time. Ritovavir, Miconazole, Aspirin
- Treated by: fresh frozen factor, dried factor
# Heparin patients:
VIII, Desmopressin, Tranexemic acid.
- Immediate action
# Haemophilia B: - Lasts for 4-6 hours
- Chirstmas disease - Test using APTT
- Factor IX - If more that 5 days use monitor for
- Trated by replacing IX factor thrombocytopenia
- Prolonged PTT and low IX - If dialysis patient on heparin treat patient
one day after procedure.
# Haemophilia C: - Protamine sulphate IV is the antidote
- Rare # Antiplatelet disorders:
- Deficiency of facto XI
- Fresh frozen plasma treatment - Superficial effect
- Aspirin most common acquired cause
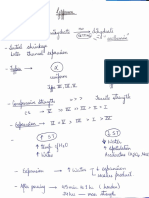
# Dental management of haemophilia: - vWF disease included
- if ID block 25*10^9 platelet count
- Preventive dentistry
- If Minor OS 50*10^9 platelet count
- Caution with endo
- IF Major OS 75*10^9 platelet count
- Avoid ID block and IM injections
- Can be managed by local measures,
- Involve a hospital setting in surgeries
tranexamic acid and platelet transfusion (
# von Willbrand disease: within 6-24h)
- Pseudohaemphilia # Aspirin patients:
- Most common inherited bleeding disorder
- Irreversible effect
- V.W factor deficiency
- For effective stop of aspirin effect it should be
- Males = females
stopped for about 10 days, this will cause to
- Decreased factor VIII and vWF, normal PT,
put the patient at risk, so DO NOT STOP
prolonged PTT, prolonged Bleeding time
ASPIRIN
- Type 1 can be controlled by desmopressin
spray # Clopidogrel patients:
- Type II and III needs replacement therapy
- Don’t stop unless patient is on both aspirin
# Notes: and Plavix, in this case we stop Plavix.
- Vitamin K is important for the synthesis of
factor (X, IX, VII and II)
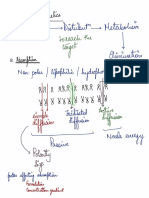
# Anemia:
- Should test MCV, normal range is 79-100
- Microcytic: iron deficiency is the most
common cause. Thalassemia is another cause
- Normocytic: anemia of chronic disease
- Macrocytic: common cause is B12 or low
folate
- Sickle cell anemia: causes to lessen RBCs in
the blood, and vasculopathy
- Can be homozygous or heterozygous
# Thalassemia:
- Caused by abnormal rate of synthesis of
globin chains
- Has two types: alpha and beta
- Can lead to pallor and jaundice,
splenomegaly, and skeletal deformity
- Lab tests shows: low haemoglobin, microcytic
pattern, normal or elevated RBCs
Done by: Raneem Malkawi.
You might also like
- Miscellaneous For FinalsDocument30 pagesMiscellaneous For Finalsjames.a.blairNo ratings yet
- Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument5 pagesDeep Vein Thrombosisampogison08No ratings yet
- Pharm Final Exam NotesDocument26 pagesPharm Final Exam Noteskatiana louis100% (1)
- Approach To A Bleeding NeonateDocument51 pagesApproach To A Bleeding NeonateJosmy JosephNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingFrom EverandOrthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingNo ratings yet
- McLeod Heme Tovee ClassDocument131 pagesMcLeod Heme Tovee ClassSimone Reis100% (1)
- AnticoagulantDocument47 pagesAnticoagulantasma barhoomNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis/Thrombosis Ii: Congenital/Acquired Hemorrhagic Disorders & Their TreatmentDocument43 pagesHemostasis/Thrombosis Ii: Congenital/Acquired Hemorrhagic Disorders & Their TreatmentBiniyam AsratNo ratings yet
- HemophiliaDocument60 pagesHemophiliavibhurocksNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulants ParamedDocument20 pagesAnticoagulants ParamedManikanta GupthaNo ratings yet
- Issues in The Diagnosis and Management of Thombocytopenic DisordersDocument45 pagesIssues in The Diagnosis and Management of Thombocytopenic Disorderspeter_mrNo ratings yet
- Blood NursingDocument34 pagesBlood NursingManikanta GupthaNo ratings yet
- 7.hemostasis, Surgical BleedingDocument61 pages7.hemostasis, Surgical Bleedingoliyad alemayehuNo ratings yet
- Platelet, FFP and Cryoprecipitate Transfusion in Emergency Room by DR Riaz AhamedDocument31 pagesPlatelet, FFP and Cryoprecipitate Transfusion in Emergency Room by DR Riaz AhamedAETCM Emergency medicineNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulant PresentationDocument29 pagesAnticoagulant Presentationrozha100% (2)
- Overview of HemostasisDocument21 pagesOverview of Hemostasis黄資元100% (1)
- Bleeding Clotting DisordersDocument80 pagesBleeding Clotting DisordersDMnDLNo ratings yet
- Bleeding Disorders: Dr. Vishal Saxena MBBS, MD (Path), FicmrDocument59 pagesBleeding Disorders: Dr. Vishal Saxena MBBS, MD (Path), Ficmrmus zaharaNo ratings yet
- High Risk Patients inDocument16 pagesHigh Risk Patients inWafa AbdurahmanNo ratings yet
- Medication AdultDocument40 pagesMedication AdultFarah HusseinNo ratings yet
- 14-Coagulation DisorderDocument51 pages14-Coagulation Disorderqjf7p2pstdNo ratings yet
- Bleeding DisordersDocument26 pagesBleeding DisordersChelleyOllitroNo ratings yet
- Dissiminated Intravascular Coagulation PathoDocument2 pagesDissiminated Intravascular Coagulation Pathoapi-341263362No ratings yet
- Anaesthesia For A Patient With Coagulation DisorderDocument33 pagesAnaesthesia For A Patient With Coagulation DisorderNdenwaneku OkuwaNo ratings yet
- Antiplatelet, Thrombolitik, Antikoagulan, Vasodilator Referat VaskularDocument23 pagesAntiplatelet, Thrombolitik, Antikoagulan, Vasodilator Referat Vaskularmonyet65No ratings yet
- Anticoagulants Drdhriti 131109120033 Phpapp01Document18 pagesAnticoagulants Drdhriti 131109120033 Phpapp01Munazza QuraishiNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulants: Julene FunkDocument25 pagesAnticoagulants: Julene FunkJulieNo ratings yet
- 5 Bleeding Disorders PPT EditedDocument87 pages5 Bleeding Disorders PPT EditedFrances Isabella OlasimanNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Cancer Patients: Mona Shrestha MN (Adult Nursing)Document77 pagesDrugs For Cancer Patients: Mona Shrestha MN (Adult Nursing)sushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Indications For Plasma Products and CryoprecipitateDocument4 pagesIndications For Plasma Products and Cryoprecipitateraul sinatoNo ratings yet
- Medical Disorder Considerations in Orthodontic Patients NDocument115 pagesMedical Disorder Considerations in Orthodontic Patients Nshubhangi_jain_10No ratings yet
- Table 4Document1 pageTable 4Walter JuniorNo ratings yet
- CCF InrDocument10 pagesCCF Inravid_No ratings yet
- BDS4081 - Bleeding Disorders 2Document37 pagesBDS4081 - Bleeding Disorders 2NouraHabiba28No ratings yet
- Hemostasis, Surgical Bleeding and TransfusionDocument15 pagesHemostasis, Surgical Bleeding and TransfusionJenneylyn AbieraNo ratings yet
- ITP LectureDocument20 pagesITP LectureReza MajidiNo ratings yet
- Bleeding Disorder: Agustin, Justine Helena Avila, Jed Naziel Bacani, Mitchzel Andrea Bacud, HoneyletteDocument45 pagesBleeding Disorder: Agustin, Justine Helena Avila, Jed Naziel Bacani, Mitchzel Andrea Bacud, HoneyletteJulius FrondaNo ratings yet
- Anti CoagulantsDocument25 pagesAnti Coagulantsshoaib106muhammadNo ratings yet
- Disorders of HemostasisDocument21 pagesDisorders of HemostasisGreg SabinoNo ratings yet
- HaemostasisDocument34 pagesHaemostasiskgzyvqqr4jNo ratings yet
- AnticoagulantsDocument47 pagesAnticoagulantsKeerthana KNo ratings yet
- WarfarinDocument3 pagesWarfarinJustine CastilloNo ratings yet
- Fibrinolytic and Antiplatelet Drugs 2020 BDS BSCN Online (Compatibility Mode)Document7 pagesFibrinolytic and Antiplatelet Drugs 2020 BDS BSCN Online (Compatibility Mode)ireneNo ratings yet
- Child Health Departement Medical School - University of Sumatera UtaraDocument18 pagesChild Health Departement Medical School - University of Sumatera UtaraEga FlorenceNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Case of Bleeding DisorderDocument26 pagesApproach To A Case of Bleeding DisorderSachidanand ShahNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 4: Blood DisorderDocument27 pagesACTIVITY 4: Blood DisorderMarjoNo ratings yet
- Coagulation DisordersDocument40 pagesCoagulation DisordersDr. Shatdal Chaudhary100% (6)
- PATH - Clotting Disorders (3p)Document3 pagesPATH - Clotting Disorders (3p)Omar HamwiNo ratings yet
- Cogulation Profile: Bleeding Time, Clotting Time, PT, and PTTDocument49 pagesCogulation Profile: Bleeding Time, Clotting Time, PT, and PTTDorin PathakNo ratings yet
- Coagulation Disorders 1.1Document67 pagesCoagulation Disorders 1.1Mridula DevadigaNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulantele Si Explorarile Invazive 2021Document33 pagesAnticoagulantele Si Explorarile Invazive 2021GabrielaOaneNo ratings yet
- Disorders of HemostasisDocument50 pagesDisorders of HemostasisAri_Ariel_896100% (1)
- HEMOPHILIADocument27 pagesHEMOPHILIAr DNo ratings yet
- Bleeding Disorders in Children: Abdulhadi Alzaben, MD Pediatric Hematology Oncology and Stem Cell TransplantDocument51 pagesBleeding Disorders in Children: Abdulhadi Alzaben, MD Pediatric Hematology Oncology and Stem Cell TransplantRasha Al MousaNo ratings yet
- Emtiyaz 2020Document10 pagesEmtiyaz 2020leenamro1999No ratings yet
- Snake Bite 1234Document23 pagesSnake Bite 1234awais ahmedNo ratings yet
- Bleeding & CoagulationDocument72 pagesBleeding & CoagulationSowmya ManthaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of CoagulationDocument27 pagesDisorders of CoagulationRishikesh HukeriNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Drugs 2Document23 pagesCritical Care Drugs 2Asri Ernadi100% (1)
- Prep Doctors Internationally Trained Dentists Upskilling ProgramDocument20 pagesPrep Doctors Internationally Trained Dentists Upskilling ProgramneeNo ratings yet
- CSV 34488726Document2 pagesCSV 34488726neeNo ratings yet
- FS ChildhoodToothDecay ENDocument2 pagesFS ChildhoodToothDecay ENneeNo ratings yet
- HIGHLIGHTER Article #10Document13 pagesHIGHLIGHTER Article #10neeNo ratings yet
- RCDSO COVID19 Managing in Person CareDocument13 pagesRCDSO COVID19 Managing in Person CareneeNo ratings yet
- HIGHLITYRT CA8 Informed ConsentDocument4 pagesHIGHLITYRT CA8 Informed ConsentneeNo ratings yet
- HIGHLIGHTER Reviewed Article 19-Prevention of Infective EndocarditisDocument5 pagesHIGHLIGHTER Reviewed Article 19-Prevention of Infective EndocarditisneeNo ratings yet
- Highlighter Info Consent 2 Art.17Document3 pagesHighlighter Info Consent 2 Art.17neeNo ratings yet
- Oral SurgeryDocument34 pagesOral SurgeryneeNo ratings yet
- Immune CellsDocument4 pagesImmune CellsneeNo ratings yet
- Medical Compromise SummeryDocument4 pagesMedical Compromise SummeryneeNo ratings yet
- A9 Anaesthesia OutpatientDocument7 pagesA9 Anaesthesia OutpatientneeNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument32 pagesAnatomyneeNo ratings yet
- Prostho - Occlusion & RPDDocument12 pagesProstho - Occlusion & RPDneeNo ratings yet
- EmbryologyDocument10 pagesEmbryologyneeNo ratings yet
- Ferrule and BleachingDocument6 pagesFerrule and BleachingneeNo ratings yet
- Tooth Preparation - Cavities, Indirect Restoration and CrownDocument9 pagesTooth Preparation - Cavities, Indirect Restoration and CrownneeNo ratings yet
- Anti - HypertensivesDocument8 pagesAnti - HypertensivesneeNo ratings yet
- Resto - Non Carious Lesions, Enamel & Dentinal CariesDocument28 pagesResto - Non Carious Lesions, Enamel & Dentinal CariesneeNo ratings yet
- Endodontic DiagnosisDocument7 pagesEndodontic DiagnosisneeNo ratings yet
- Pharma - MiscellaneousDocument9 pagesPharma - MiscellaneousneeNo ratings yet
- Principles of Pharma + ANS PharmacologyDocument25 pagesPrinciples of Pharma + ANS PharmacologyneeNo ratings yet
- CNS PharmacologyDocument8 pagesCNS PharmacologyneeNo ratings yet
- Endodontic MicrobiologyDocument2 pagesEndodontic MicrobiologyneeNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument16 pagesAntibioticsneeNo ratings yet
- Gypsum + Alloys ClassificationDocument6 pagesGypsum + Alloys ClassificationneeNo ratings yet
- Prostho Materials - Alooys, Porcelain & CeramicsDocument13 pagesProstho Materials - Alooys, Porcelain & CeramicsneeNo ratings yet
- Prostho - CD and FPDDocument13 pagesProstho - CD and FPDneeNo ratings yet
- Prosthodontics 9Document20 pagesProsthodontics 9neeNo ratings yet
- (DR - Anas #3) Elastic-Impression-MaterialsDocument36 pages(DR - Anas #3) Elastic-Impression-MaterialsneeNo ratings yet