Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab Report 07
Lab Report 07
Uploaded by
Mohammad SubhanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Introduction - To.microelectronic - Fabrication R.C.jaegerDocument328 pagesIntroduction - To.microelectronic - Fabrication R.C.jaegerdugash692% (50)
- Portable Air Conditioner ReportDocument37 pagesPortable Air Conditioner ReportWilliam Clarke100% (2)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab NewDocument86 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits Lab NewleevasusanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines EE-260: Instructor: DR Mehmood AlamDocument30 pagesElectrical Machines EE-260: Instructor: DR Mehmood AlamSaif Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document6 pagesUnit 2ShanilDayalanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 05Document5 pagesLab Report 05Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Pe Lab 8-200708Document21 pagesPe Lab 8-200708Omar JanjuaNo ratings yet
- PDC Lab ManualDocument33 pagesPDC Lab ManualBhanu SriNo ratings yet
- Static Characteristics of SCR Experiment 1 Aim: To Study The Static Characteristics of SCR Apparatus: Multism Theory: SCR Works in Three ModesDocument9 pagesStatic Characteristics of SCR Experiment 1 Aim: To Study The Static Characteristics of SCR Apparatus: Multism Theory: SCR Works in Three ModesHoward TimbangNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document4 pagesExperiment 2Emre YavuzNo ratings yet
- Scientech 2708Document53 pagesScientech 2708Chandan Sambhaji KambleNo ratings yet
- Power Converters Lab Manual - M.Tech (PE&ED) - Prepared by Dr.T.DevarajuDocument50 pagesPower Converters Lab Manual - M.Tech (PE&ED) - Prepared by Dr.T.DevarajuhodeeesvcetNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital Ic'S Short Questions With AnswersDocument41 pagesAnalog and Digital Ic'S Short Questions With Answerspriya adhavanNo ratings yet
- AC PotentiometerDocument20 pagesAC PotentiometerKevin HaleNo ratings yet
- Single Phase ControlledDocument39 pagesSingle Phase Controlledchandan Goswami50% (2)
- Power Electronics Laboratory Nitt B.Tech EeeDocument11 pagesPower Electronics Laboratory Nitt B.Tech EeeHahahNo ratings yet
- Course Work 2.1Document7 pagesCourse Work 2.1Ranu GamesNo ratings yet
- SCR Triggering MethodsDocument17 pagesSCR Triggering MethodssriNo ratings yet
- PDC Lab Updated 1Document63 pagesPDC Lab Updated 1deepa reddyNo ratings yet
- L8 Controlled Rectifier (Part1)Document12 pagesL8 Controlled Rectifier (Part1)mohamedsamy9878No ratings yet
- Silicon Controlled RectifierDocument8 pagesSilicon Controlled RectifierTrisha Camille NerieNo ratings yet
- Bs-El-344 - Lecture-05 - P2Document13 pagesBs-El-344 - Lecture-05 - P2Bushra IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1 Title History of Electronics: Student: Prof: Talangan, Trinidad Engr. Norlan SantosDocument8 pagesAssignment No. 1 Title History of Electronics: Student: Prof: Talangan, Trinidad Engr. Norlan SantosTrinidad TalanganNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Experiment-No. 6 Single-Phase Full and Half Wave Controlled SCR Rectifier Aim: To Study and Analyze The Properties and The Characteristics of A Single-PhaseDocument6 pagesPower Electronics Lab Experiment-No. 6 Single-Phase Full and Half Wave Controlled SCR Rectifier Aim: To Study and Analyze The Properties and The Characteristics of A Single-Phaseحسن علي جاسمNo ratings yet
- Electronics Devices & Circuit Lab ManualDocument53 pagesElectronics Devices & Circuit Lab Manualbiswajit7sarkar100% (1)
- SCRDocument4 pagesSCRJoshua Amiel javines100% (1)
- Scientech 2708Document40 pagesScientech 2708sarikapravinNo ratings yet
- Linear Integrated Circuits 70 Interview Questions and Solutions 2 - DivyumDocument14 pagesLinear Integrated Circuits 70 Interview Questions and Solutions 2 - Divyumbalu56kvNo ratings yet
- 17eel37 Eml Lab ManualDocument64 pages17eel37 Eml Lab ManualpriyaNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Full Wavecontrolled RectifierDocument2 pagesSingle Phase Full Wavecontrolled Rectifierjosebijo17No ratings yet
- Power Electronics - Basic MCQDocument14 pagesPower Electronics - Basic MCQDinesh SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document38 pagesChapter 5Markos NiguseNo ratings yet
- Pe Lab ManualDocument53 pagesPe Lab ManualKada JashNo ratings yet
- Slides Lec 1-2Document26 pagesSlides Lec 1-2ali tariqNo ratings yet
- MID Lecture-Thyristors 2Document39 pagesMID Lecture-Thyristors 2kazi AlviNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics & Drives: Unit: 1 Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument24 pagesPower Electronics & Drives: Unit: 1 Power Semiconductor DevicesTapobroto ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- B23CS1044 (Neeraj Kumar) Lab 2Document8 pagesB23CS1044 (Neeraj Kumar) Lab 2b23cs1044No ratings yet
- 1.5 ThyristorDocument15 pages1.5 ThyristorKhairul NaimNo ratings yet
- Other Members of The Thyristor FamilyDocument7 pagesOther Members of The Thyristor Familynisha sharmsNo ratings yet
- Batangas State University Alangilan - Main Campus Ii Electrical and Computer Engineering DepartmentDocument15 pagesBatangas State University Alangilan - Main Campus Ii Electrical and Computer Engineering DepartmentKarenMacalaladTanangNo ratings yet
- Slides Lec 5 RectifierDocument18 pagesSlides Lec 5 RectifierAijaz HussainNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDocument47 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manualshaan_patil100% (1)
- Three Phase Half and Full Wave Bridge RectifierDocument9 pagesThree Phase Half and Full Wave Bridge RectifierSHANKARNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Report: Submitted by Group Members Submitted To Date of Submission Grade/ PointsDocument23 pagesBasic Electronics Report: Submitted by Group Members Submitted To Date of Submission Grade/ PointsMahnam Nasir Nasir NaeemNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - NewDocument61 pagesUnit 2 - NewMonster AmanNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuits and Simulation LabDocument77 pagesAnalog Circuits and Simulation LableevasusanNo ratings yet
- شيت مختبر الكترونيك القدرة 2 PDFDocument21 pagesشيت مختبر الكترونيك القدرة 2 PDFMustafa MhmoodNo ratings yet
- Circuitos Sujetadores Con DiodosDocument50 pagesCircuitos Sujetadores Con DiodosrobertoNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Lab ManualsDocument31 pagesBasic Electronics Lab ManualsMirza Umar Farooq BaigNo ratings yet
- SCR, Traic, Diac ReportDocument19 pagesSCR, Traic, Diac ReportPravin Gareta60% (5)
- UntitledDocument165 pagesUntitledmenakadevieceNo ratings yet
- Analysis of An RC Phase Shifter Circuit:: ObjectiveDocument7 pagesAnalysis of An RC Phase Shifter Circuit:: Objectiveayesha amjadNo ratings yet
- Electrical BasicsDocument24 pagesElectrical BasicsSnehal Mane100% (1)
- Department of Electrical & Electronics Engg.: BEV Sem (Ex) Experiment No - 1 Aim: Apparatus RequiredDocument44 pagesDepartment of Electrical & Electronics Engg.: BEV Sem (Ex) Experiment No - 1 Aim: Apparatus Requiredvkdkris75% (4)
- Schuler Electronics Instructor CH14 Electronics ComtrolDocument30 pagesSchuler Electronics Instructor CH14 Electronics ComtrolRíõ EscanillaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document10 pagesExperiment 2Mark ArominNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Power ElectronicsDocument39 pagesLab Manual Power ElectronicsZainab AnwarNo ratings yet
- Electronic Components Circuits: (Diode Characteristies - Rectifier - Clipper)Document14 pagesElectronic Components Circuits: (Diode Characteristies - Rectifier - Clipper)em2200139No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Application Cover LetterDocument1 pageApplication Cover LetterMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Fa22 Hum102 A4Document1 pageFa22 Hum102 A4Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- FA22 HUM102 A3 - ProjectDocument4 pagesFA22 HUM102 A3 - ProjectMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Terminal Paper NCDocument3 pagesTerminal Paper NCMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- My Design of Front PageDocument2 pagesMy Design of Front PageMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- FP Ass 03Document1 pageFP Ass 03Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- NC All LabsDocument1 pageNC All LabsMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 Report Writing SkillsDocument3 pagesAssignment 4 Report Writing SkillsMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- FP Ass 04Document1 pageFP Ass 04Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 04Document3 pagesAssignment 04Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- NC LabsDocument1 pageNC LabsMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 7thDocument4 pagesLab Report 7thMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 03Document9 pagesLab Report 03Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Application Cover LetterDocument2 pagesApplication Cover LetterMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Lab NO 06 CompletedDocument5 pagesLab NO 06 CompletedMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 05Document5 pagesLab Report 05Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- 5 Examples of Process ControlDocument3 pages5 Examples of Process ControlMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- HUM102 Handouts Lecture22Document12 pagesHUM102 Handouts Lecture22Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of Feedback Control System For Robotic ArmDocument3 pagesBlock Diagram of Feedback Control System For Robotic ArmMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- FIFA World Cup 2022 Full Schedule PDFDocument4 pagesFIFA World Cup 2022 Full Schedule PDFMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 02Document10 pagesLab Report 02Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04Document55 pagesChapter 04Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Complete SlidesDocument81 pagesChapter 02 Complete SlidesMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05Document40 pagesChapter 05Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Pspice Simulation of SPIMDocument7 pagesPspice Simulation of SPIMMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- PWM AC ChopperDocument88 pagesPWM AC ChopperMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03completeDocument56 pagesChapter 03completeMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Wa0047Document1 pageWa0047Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Bahir Dar Institute of Technology: Faculty of Electrical Engineering ArduinoDocument44 pagesBahir Dar Institute of Technology: Faculty of Electrical Engineering ArduinoGech ManNo ratings yet
- DiodeModeling Tesi Gustavo 12gen2006 PDFDocument102 pagesDiodeModeling Tesi Gustavo 12gen2006 PDFhitec92407No ratings yet
- I.mx BSP Porting GuideDocument61 pagesI.mx BSP Porting GuideKishore ChilakalaNo ratings yet
- FM ReceiverDocument26 pagesFM ReceiverVs Varun Sardana100% (4)
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocument8 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationdombipinNo ratings yet
- 2N2608 MotorolaDocument1 page2N2608 MotorolaLuis Carlos OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Transmission LinesDocument12 pagesTransmission Linesacestrider1023No ratings yet
- Halbach Array MotorDocument8 pagesHalbach Array MotoralexsurenderNo ratings yet
- Activity 1.1.6 Component Identification: Digital: Combinational LogicDocument7 pagesActivity 1.1.6 Component Identification: Digital: Combinational LogicLuke PierNo ratings yet
- Application Note: Tda 16888: Multioutput Single Transistor Forward Converter 150W / 100KhzDocument20 pagesApplication Note: Tda 16888: Multioutput Single Transistor Forward Converter 150W / 100KhzManuel Alejandro Espinosa FarfanNo ratings yet
- Downlight Series: Lights Your LifeDocument7 pagesDownlight Series: Lights Your LifeKenari UtamiNo ratings yet
- L-132XYD (Ver 17B)Document5 pagesL-132XYD (Ver 17B)yafix34669No ratings yet
- Ieee 1459Document8 pagesIeee 1459Michael SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Pedais ResumoDocument15 pagesPedais ResumoAilson Tavares FerreiraNo ratings yet
- 6 Hydroxyhexyl 4 E 4 Alkoxy Halostyryl Benzoates Synthesis Characterisation and Study of Mesomorphic and Fluorescent PropertiesDocument16 pages6 Hydroxyhexyl 4 E 4 Alkoxy Halostyryl Benzoates Synthesis Characterisation and Study of Mesomorphic and Fluorescent PropertiesKhushi MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Reactive Power Compensation For Transmission and Distribution SystemsDocument4 pagesReactive Power Compensation For Transmission and Distribution SystemsSuranjana DasNo ratings yet
- Sensors: An Integrated Low-Power Lock-In Amplifier and Its Application To Gas DetectionDocument20 pagesSensors: An Integrated Low-Power Lock-In Amplifier and Its Application To Gas DetectionFrank PatricioNo ratings yet
- The Cathode-Ray TubeDocument4 pagesThe Cathode-Ray TubeJoseGarciaRuizNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Kinetics BasheerDocument9 pagesCorrosion Kinetics Basheerchenabeel0% (1)
- Electrical Machines DC MotorDocument5 pagesElectrical Machines DC MotorKitkay NivramNo ratings yet
- SCT 013Document1 pageSCT 013SilvioNo ratings yet
- Pioneer Avh-P5000dvd SM 1 (ET)Document201 pagesPioneer Avh-P5000dvd SM 1 (ET)Jesus LopezNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 61 PDFDocument14 pagesUnit 3 61 PDFDeepankumar Athiyannan100% (1)
- 74HC04 Rev1Document7 pages74HC04 Rev1PUMASNYNo ratings yet
- CMOS AmplifiersDocument39 pagesCMOS AmplifiersLaura MendozaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Folio Form 4Document45 pagesChemistry-Folio Form 4Ahmad Izzat Mohd HanafiNo ratings yet
- Simd Instruction Set X86 Intel Pentium Iii Amd 3dnow! Single Precision Floating PointDocument1 pageSimd Instruction Set X86 Intel Pentium Iii Amd 3dnow! Single Precision Floating PointMarasigan RyanNo ratings yet
- 1977 Motorola M2900 TTL Processor Family 2edDocument70 pages1977 Motorola M2900 TTL Processor Family 2edLovely DilipNo ratings yet
Lab Report 07
Lab Report 07
Uploaded by
Mohammad SubhanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab Report 07
Lab Report 07
Uploaded by
Mohammad SubhanCopyright:
Available Formats
Thyristor Signal Phase Full Wave Controlled Rectifier
Lab Title
Design Power Thyristor Signal-Phase full-wave Controlled Rectifier
Lab Safety Rules:
Some rules and regulation should be necessary to follow during entering or performing lab
that are given below.
o Be sure of the condition of the equipment.
o Never rely on safety devices.
o Grounding should be done.
o Circuit should be clean avoid cluttered environment.
o Floor should not be wet.
o Use if possible one hand for practically performing.
o Never use ring etc.
o Never talk during the performing.
o Be slowly or cool and calm in lab.
o Resistors can burn your skin be aware of it.
Objectives:
When we have completed this lab, we will know about these things given below.
o Application of Thyristor
o The full-wave Thyristor rectifier using bridge Network
o Waveforms of voltages and currents present in these rectifiers for various load
conditions.
o How to calculate the average dc voltages provided by the bridge network.
o How to calculate the performance parameters of rectifier.
o Able to Analysis harmonic contents present in output waveform.
Introduction:
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current, which periodically reverses
direction, to direct current, which flows in only one direction. The process is known as
Rectification, since it “straightens” the direction of current. Physically, rectifiers take a
number of forms, including vacuum tube diodes, mercury arc valves, stacks of copper and
selenium oxide plates, semiconductor diodes, silicon controlled rectifiers and other silicon
based semiconductors have been used. Early radio synchronous electromechanical switches
and motors have been used a “cat’s whisker” of fine wire pressing on a crystal of galena(load
sulfide) to serve as a point contact rectifier or “crystal detector”.
Power Electronics Lab Report 6th
Thyristor Signal Phase Full Wave Controlled Rectifier
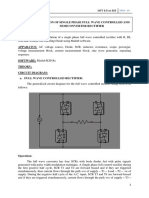
Circuit Diagram:
Anode Anode
Gate Gate
Cathode
Cathode
Load
Anode Gate Anode
Gate
Cathode Cathode
Simulation of Full Wave Controlled Rectifier:
For Resistive Load:
Circuit Diagram:
Power Electronics Lab Report 6th
Thyristor Signal Phase Full Wave Controlled Rectifier
Waveform Results:
For Inductive Load:
Waveform Results:
Power Electronics Lab Report 6th
Thyristor Signal Phase Full Wave Controlled Rectifier
Practical Implementation and Analysis Results
For Resistive Load:
For Inductive Load:
Power Electronics Lab Report 6th
Thyristor Signal Phase Full Wave Controlled Rectifier
Performance Parameter of Full Wave Controlled Rectifier:
𝑽𝒅𝒄 = 𝑉𝑚/𝜋(1 + 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝛼)
𝑰𝒅𝒄 = 𝑉𝑚/𝑅𝜋(1 + 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝛼)
𝑽𝒓𝒎𝒔 = 𝑉𝑚 √𝜋 − 𝛼/2𝜋 + 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝛼/4𝜋
𝑰𝒓𝒎𝒔 = 𝑉𝑚/𝑅 √𝜋 − 𝛼/2𝜋 + 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝛼/4𝜋
𝑭𝒐𝒓𝒎 𝑭𝒂𝒄𝒕𝒐𝒓 = 𝑉𝑟𝑚𝑠/𝑉𝑑𝑐
𝑹𝒊𝒑𝒑𝒍𝒆 𝑭𝒂𝒄𝒕𝒐𝒓 = 𝑉𝑎𝑐/𝑉𝑑𝑐
𝑻𝒓𝒂𝒏𝒇𝒐𝒓𝒎𝒆𝒓 𝑼𝒕𝒊𝒍𝒊𝒛𝒂𝒕𝒊𝒐𝒏 𝑭𝒂𝒄𝒕𝒐𝒓:
𝑻𝑼𝑭 = 𝑃𝑑𝑐/ 𝑉𝑠𝐼𝑠
Here Vs is secondary RMS voltages of Transformer and Is is secondary RMS current of
Transformer.
Effect of inductive Load
When we will use inductor in the circuit the voltages will go in negative because of changing
the polarities of the inductor in negative cycle or in second cycle if we use free wheeling
diode then it will stop the voltages to go into negative region.
Conclusion:
In this lab we learn about full wave controlled Rectifiers we see what are the impact of load
on the output voltages of Rectifier and we also see the performance parameters of full wave
controlled rectifier.
Power Electronics Lab Report 6th
You might also like
- Introduction - To.microelectronic - Fabrication R.C.jaegerDocument328 pagesIntroduction - To.microelectronic - Fabrication R.C.jaegerdugash692% (50)
- Portable Air Conditioner ReportDocument37 pagesPortable Air Conditioner ReportWilliam Clarke100% (2)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab NewDocument86 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits Lab NewleevasusanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines EE-260: Instructor: DR Mehmood AlamDocument30 pagesElectrical Machines EE-260: Instructor: DR Mehmood AlamSaif Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document6 pagesUnit 2ShanilDayalanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 05Document5 pagesLab Report 05Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Pe Lab 8-200708Document21 pagesPe Lab 8-200708Omar JanjuaNo ratings yet
- PDC Lab ManualDocument33 pagesPDC Lab ManualBhanu SriNo ratings yet
- Static Characteristics of SCR Experiment 1 Aim: To Study The Static Characteristics of SCR Apparatus: Multism Theory: SCR Works in Three ModesDocument9 pagesStatic Characteristics of SCR Experiment 1 Aim: To Study The Static Characteristics of SCR Apparatus: Multism Theory: SCR Works in Three ModesHoward TimbangNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document4 pagesExperiment 2Emre YavuzNo ratings yet
- Scientech 2708Document53 pagesScientech 2708Chandan Sambhaji KambleNo ratings yet
- Power Converters Lab Manual - M.Tech (PE&ED) - Prepared by Dr.T.DevarajuDocument50 pagesPower Converters Lab Manual - M.Tech (PE&ED) - Prepared by Dr.T.DevarajuhodeeesvcetNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital Ic'S Short Questions With AnswersDocument41 pagesAnalog and Digital Ic'S Short Questions With Answerspriya adhavanNo ratings yet
- AC PotentiometerDocument20 pagesAC PotentiometerKevin HaleNo ratings yet
- Single Phase ControlledDocument39 pagesSingle Phase Controlledchandan Goswami50% (2)
- Power Electronics Laboratory Nitt B.Tech EeeDocument11 pagesPower Electronics Laboratory Nitt B.Tech EeeHahahNo ratings yet
- Course Work 2.1Document7 pagesCourse Work 2.1Ranu GamesNo ratings yet
- SCR Triggering MethodsDocument17 pagesSCR Triggering MethodssriNo ratings yet
- PDC Lab Updated 1Document63 pagesPDC Lab Updated 1deepa reddyNo ratings yet
- L8 Controlled Rectifier (Part1)Document12 pagesL8 Controlled Rectifier (Part1)mohamedsamy9878No ratings yet
- Silicon Controlled RectifierDocument8 pagesSilicon Controlled RectifierTrisha Camille NerieNo ratings yet
- Bs-El-344 - Lecture-05 - P2Document13 pagesBs-El-344 - Lecture-05 - P2Bushra IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1 Title History of Electronics: Student: Prof: Talangan, Trinidad Engr. Norlan SantosDocument8 pagesAssignment No. 1 Title History of Electronics: Student: Prof: Talangan, Trinidad Engr. Norlan SantosTrinidad TalanganNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Experiment-No. 6 Single-Phase Full and Half Wave Controlled SCR Rectifier Aim: To Study and Analyze The Properties and The Characteristics of A Single-PhaseDocument6 pagesPower Electronics Lab Experiment-No. 6 Single-Phase Full and Half Wave Controlled SCR Rectifier Aim: To Study and Analyze The Properties and The Characteristics of A Single-Phaseحسن علي جاسمNo ratings yet
- Electronics Devices & Circuit Lab ManualDocument53 pagesElectronics Devices & Circuit Lab Manualbiswajit7sarkar100% (1)
- SCRDocument4 pagesSCRJoshua Amiel javines100% (1)
- Scientech 2708Document40 pagesScientech 2708sarikapravinNo ratings yet
- Linear Integrated Circuits 70 Interview Questions and Solutions 2 - DivyumDocument14 pagesLinear Integrated Circuits 70 Interview Questions and Solutions 2 - Divyumbalu56kvNo ratings yet
- 17eel37 Eml Lab ManualDocument64 pages17eel37 Eml Lab ManualpriyaNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Full Wavecontrolled RectifierDocument2 pagesSingle Phase Full Wavecontrolled Rectifierjosebijo17No ratings yet
- Power Electronics - Basic MCQDocument14 pagesPower Electronics - Basic MCQDinesh SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document38 pagesChapter 5Markos NiguseNo ratings yet
- Pe Lab ManualDocument53 pagesPe Lab ManualKada JashNo ratings yet
- Slides Lec 1-2Document26 pagesSlides Lec 1-2ali tariqNo ratings yet
- MID Lecture-Thyristors 2Document39 pagesMID Lecture-Thyristors 2kazi AlviNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics & Drives: Unit: 1 Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument24 pagesPower Electronics & Drives: Unit: 1 Power Semiconductor DevicesTapobroto ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- B23CS1044 (Neeraj Kumar) Lab 2Document8 pagesB23CS1044 (Neeraj Kumar) Lab 2b23cs1044No ratings yet
- 1.5 ThyristorDocument15 pages1.5 ThyristorKhairul NaimNo ratings yet
- Other Members of The Thyristor FamilyDocument7 pagesOther Members of The Thyristor Familynisha sharmsNo ratings yet
- Batangas State University Alangilan - Main Campus Ii Electrical and Computer Engineering DepartmentDocument15 pagesBatangas State University Alangilan - Main Campus Ii Electrical and Computer Engineering DepartmentKarenMacalaladTanangNo ratings yet
- Slides Lec 5 RectifierDocument18 pagesSlides Lec 5 RectifierAijaz HussainNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDocument47 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manualshaan_patil100% (1)
- Three Phase Half and Full Wave Bridge RectifierDocument9 pagesThree Phase Half and Full Wave Bridge RectifierSHANKARNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Report: Submitted by Group Members Submitted To Date of Submission Grade/ PointsDocument23 pagesBasic Electronics Report: Submitted by Group Members Submitted To Date of Submission Grade/ PointsMahnam Nasir Nasir NaeemNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - NewDocument61 pagesUnit 2 - NewMonster AmanNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuits and Simulation LabDocument77 pagesAnalog Circuits and Simulation LableevasusanNo ratings yet
- شيت مختبر الكترونيك القدرة 2 PDFDocument21 pagesشيت مختبر الكترونيك القدرة 2 PDFMustafa MhmoodNo ratings yet
- Circuitos Sujetadores Con DiodosDocument50 pagesCircuitos Sujetadores Con DiodosrobertoNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Lab ManualsDocument31 pagesBasic Electronics Lab ManualsMirza Umar Farooq BaigNo ratings yet
- SCR, Traic, Diac ReportDocument19 pagesSCR, Traic, Diac ReportPravin Gareta60% (5)
- UntitledDocument165 pagesUntitledmenakadevieceNo ratings yet
- Analysis of An RC Phase Shifter Circuit:: ObjectiveDocument7 pagesAnalysis of An RC Phase Shifter Circuit:: Objectiveayesha amjadNo ratings yet
- Electrical BasicsDocument24 pagesElectrical BasicsSnehal Mane100% (1)
- Department of Electrical & Electronics Engg.: BEV Sem (Ex) Experiment No - 1 Aim: Apparatus RequiredDocument44 pagesDepartment of Electrical & Electronics Engg.: BEV Sem (Ex) Experiment No - 1 Aim: Apparatus Requiredvkdkris75% (4)
- Schuler Electronics Instructor CH14 Electronics ComtrolDocument30 pagesSchuler Electronics Instructor CH14 Electronics ComtrolRíõ EscanillaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document10 pagesExperiment 2Mark ArominNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Power ElectronicsDocument39 pagesLab Manual Power ElectronicsZainab AnwarNo ratings yet
- Electronic Components Circuits: (Diode Characteristies - Rectifier - Clipper)Document14 pagesElectronic Components Circuits: (Diode Characteristies - Rectifier - Clipper)em2200139No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Application Cover LetterDocument1 pageApplication Cover LetterMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Fa22 Hum102 A4Document1 pageFa22 Hum102 A4Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- FA22 HUM102 A3 - ProjectDocument4 pagesFA22 HUM102 A3 - ProjectMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Terminal Paper NCDocument3 pagesTerminal Paper NCMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- My Design of Front PageDocument2 pagesMy Design of Front PageMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- FP Ass 03Document1 pageFP Ass 03Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- NC All LabsDocument1 pageNC All LabsMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 Report Writing SkillsDocument3 pagesAssignment 4 Report Writing SkillsMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- FP Ass 04Document1 pageFP Ass 04Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 04Document3 pagesAssignment 04Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- NC LabsDocument1 pageNC LabsMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 7thDocument4 pagesLab Report 7thMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 03Document9 pagesLab Report 03Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Application Cover LetterDocument2 pagesApplication Cover LetterMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Lab NO 06 CompletedDocument5 pagesLab NO 06 CompletedMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 05Document5 pagesLab Report 05Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- 5 Examples of Process ControlDocument3 pages5 Examples of Process ControlMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- HUM102 Handouts Lecture22Document12 pagesHUM102 Handouts Lecture22Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of Feedback Control System For Robotic ArmDocument3 pagesBlock Diagram of Feedback Control System For Robotic ArmMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- FIFA World Cup 2022 Full Schedule PDFDocument4 pagesFIFA World Cup 2022 Full Schedule PDFMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 02Document10 pagesLab Report 02Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04Document55 pagesChapter 04Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Complete SlidesDocument81 pagesChapter 02 Complete SlidesMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05Document40 pagesChapter 05Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Pspice Simulation of SPIMDocument7 pagesPspice Simulation of SPIMMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- PWM AC ChopperDocument88 pagesPWM AC ChopperMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03completeDocument56 pagesChapter 03completeMohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Wa0047Document1 pageWa0047Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Bahir Dar Institute of Technology: Faculty of Electrical Engineering ArduinoDocument44 pagesBahir Dar Institute of Technology: Faculty of Electrical Engineering ArduinoGech ManNo ratings yet
- DiodeModeling Tesi Gustavo 12gen2006 PDFDocument102 pagesDiodeModeling Tesi Gustavo 12gen2006 PDFhitec92407No ratings yet
- I.mx BSP Porting GuideDocument61 pagesI.mx BSP Porting GuideKishore ChilakalaNo ratings yet
- FM ReceiverDocument26 pagesFM ReceiverVs Varun Sardana100% (4)
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocument8 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationdombipinNo ratings yet
- 2N2608 MotorolaDocument1 page2N2608 MotorolaLuis Carlos OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Transmission LinesDocument12 pagesTransmission Linesacestrider1023No ratings yet
- Halbach Array MotorDocument8 pagesHalbach Array MotoralexsurenderNo ratings yet
- Activity 1.1.6 Component Identification: Digital: Combinational LogicDocument7 pagesActivity 1.1.6 Component Identification: Digital: Combinational LogicLuke PierNo ratings yet
- Application Note: Tda 16888: Multioutput Single Transistor Forward Converter 150W / 100KhzDocument20 pagesApplication Note: Tda 16888: Multioutput Single Transistor Forward Converter 150W / 100KhzManuel Alejandro Espinosa FarfanNo ratings yet
- Downlight Series: Lights Your LifeDocument7 pagesDownlight Series: Lights Your LifeKenari UtamiNo ratings yet
- L-132XYD (Ver 17B)Document5 pagesL-132XYD (Ver 17B)yafix34669No ratings yet
- Ieee 1459Document8 pagesIeee 1459Michael SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Pedais ResumoDocument15 pagesPedais ResumoAilson Tavares FerreiraNo ratings yet
- 6 Hydroxyhexyl 4 E 4 Alkoxy Halostyryl Benzoates Synthesis Characterisation and Study of Mesomorphic and Fluorescent PropertiesDocument16 pages6 Hydroxyhexyl 4 E 4 Alkoxy Halostyryl Benzoates Synthesis Characterisation and Study of Mesomorphic and Fluorescent PropertiesKhushi MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Reactive Power Compensation For Transmission and Distribution SystemsDocument4 pagesReactive Power Compensation For Transmission and Distribution SystemsSuranjana DasNo ratings yet
- Sensors: An Integrated Low-Power Lock-In Amplifier and Its Application To Gas DetectionDocument20 pagesSensors: An Integrated Low-Power Lock-In Amplifier and Its Application To Gas DetectionFrank PatricioNo ratings yet
- The Cathode-Ray TubeDocument4 pagesThe Cathode-Ray TubeJoseGarciaRuizNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Kinetics BasheerDocument9 pagesCorrosion Kinetics Basheerchenabeel0% (1)
- Electrical Machines DC MotorDocument5 pagesElectrical Machines DC MotorKitkay NivramNo ratings yet
- SCT 013Document1 pageSCT 013SilvioNo ratings yet
- Pioneer Avh-P5000dvd SM 1 (ET)Document201 pagesPioneer Avh-P5000dvd SM 1 (ET)Jesus LopezNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 61 PDFDocument14 pagesUnit 3 61 PDFDeepankumar Athiyannan100% (1)
- 74HC04 Rev1Document7 pages74HC04 Rev1PUMASNYNo ratings yet
- CMOS AmplifiersDocument39 pagesCMOS AmplifiersLaura MendozaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Folio Form 4Document45 pagesChemistry-Folio Form 4Ahmad Izzat Mohd HanafiNo ratings yet
- Simd Instruction Set X86 Intel Pentium Iii Amd 3dnow! Single Precision Floating PointDocument1 pageSimd Instruction Set X86 Intel Pentium Iii Amd 3dnow! Single Precision Floating PointMarasigan RyanNo ratings yet
- 1977 Motorola M2900 TTL Processor Family 2edDocument70 pages1977 Motorola M2900 TTL Processor Family 2edLovely DilipNo ratings yet