Professional Documents
Culture Documents
04 Handout 03 Transformations
04 Handout 03 Transformations
Uploaded by
wrfe0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pages1. The document describes various transformations of functions including:
- Reflecting the graph of a function f(x) across the x-axis to obtain the graph of y=-f(x).
- Shifting the graph of f(x) right 3 units to obtain the graph of g(x)=f(x+3).
- Shifting the graph of a function f(x) left 1 unit and up 2 units to obtain the graph of g(x)=f(x-1)+2.
- Stretching the graph of a function f(x) vertically by a factor of 2 to obtain the graph of g(x)=2f(x-1).
- Ref
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document describes various transformations of functions including:
- Reflecting the graph of a function f(x) across the x-axis to obtain the graph of y=-f(x).
- Shifting the graph of f(x) right 3 units to obtain the graph of g(x)=f(x+3).
- Shifting the graph of a function f(x) left 1 unit and up 2 units to obtain the graph of g(x)=f(x-1)+2.
- Stretching the graph of a function f(x) vertically by a factor of 2 to obtain the graph of g(x)=2f(x-1).
- Ref
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pages04 Handout 03 Transformations
04 Handout 03 Transformations
Uploaded by
wrfe1. The document describes various transformations of functions including:
- Reflecting the graph of a function f(x) across the x-axis to obtain the graph of y=-f(x).
- Shifting the graph of f(x) right 3 units to obtain the graph of g(x)=f(x+3).
- Shifting the graph of a function f(x) left 1 unit and up 2 units to obtain the graph of g(x)=f(x-1)+2.
- Stretching the graph of a function f(x) vertically by a factor of 2 to obtain the graph of g(x)=2f(x-1).
- Ref
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
AASL1 U4 Lesson 04 Handout 03 Transformation
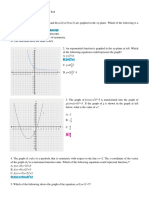
1. Part of the graph of a function f is shown in the diagram below.
a) On the same diagram sketch
the graph of y = − f (x) .
b) Let g(x) = f (x + 3) ,
i. Find g(−3) .
ii. Describe fully the transformation
that maps the graph of f to the
graph of g.
( )
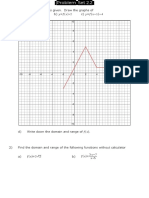
2. The graph of a function f is shown in the diagram below. The point −1, 1 is on
the graph and y = −1 is a horizontal asymptote.
a) Let g(x) = f (x − 1) + 2 . On the diagram,
sketch the graph of g.
b) Write down the equation of the
horizontal asymptote of g.
c) Let A′ be the point on the graph of g
corresponding to point A. Write down
the coordinates of A′
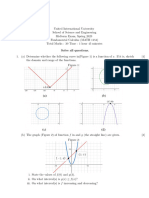
3. The sketch shows part of the graph of y = f (x) which passes through the points
A( −1, 3) , B ( 0, 2 ) , C (1, 0 ) , D ( 2, 1) and E ( 3, 4 ) .
A second function is defined by g(x) = 2 f x − 1 . ( )
a) Calculate g(0), g(1), g(2) and g(3) .
b) On the same axes, sketch the graph of
the function g(x) . Clearly indicate the
position of the given points using
A′, B′, C ′, D′ and E ′ .
4. A function f (x) is transformed to the function g(x) = − f (−x) .
a) Describe the nature of the transformation.
( )
b) If 3, − 7 lies on y = f (x) , find the transformed point on y = g(x) .
c) Find the point on f (x) that transforms to the point −5, − 1 . ( )
5. ( )
The point a, b lies on the function y = f (x) , what point lies on y = 13 f (x − 2) − 4 ?
You might also like
- Math 30-1 Review PackageDocument28 pagesMath 30-1 Review PackageMarc Lambert100% (1)
- BLM 1-14 Section 1.4 PractiDocument2 pagesBLM 1-14 Section 1.4 PractiRenier Palma CruzNo ratings yet
- IB REVIEW Functions and QuadraticsDocument17 pagesIB REVIEW Functions and QuadraticsPiotr MazurNo ratings yet
- TutorialDocument2 pagesTutorialewansallehNo ratings yet
- IB Qns Functions Composite InvesrseDocument2 pagesIB Qns Functions Composite InvesrseDevNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Worksheet-BornotyDocument3 pages2.4 Worksheet-Bornoty조민성No ratings yet
- Functions - WorksheetDocument2 pagesFunctions - WorksheetEkaterinNo ratings yet
- MTH101 Lec#2Document29 pagesMTH101 Lec#2Omar HaroonNo ratings yet
- Fungsi InversDocument26 pagesFungsi InversBilly ArokhmanNo ratings yet
- PS Linear and Quadratic FunctionsDocument7 pagesPS Linear and Quadratic FunctionsQuinn VelascoNo ratings yet
- Name - Chapter 4 - Functions Review 1Document4 pagesName - Chapter 4 - Functions Review 1Terence AnquandahNo ratings yet
- Worksheet FunctionsDocument4 pagesWorksheet FunctionsvalerieNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Lower Ability Activity SheetDocument4 pagesLesson 4 - Lower Ability Activity SheetLaundry VendingNo ratings yet
- Leccion Inversa Composicion RacionalesDocument9 pagesLeccion Inversa Composicion RacionalesWilliam Yunda T.No ratings yet
- 1.2 Operations On Functions and Types of FunctionsDocument17 pages1.2 Operations On Functions and Types of FunctionsIsiahTanEdquibanNo ratings yet
- Differentiation RevisionDocument9 pagesDifferentiation RevisionZero AnonymousNo ratings yet
- IB Mathematics HL-Year 1 Unit 6: Worksheet-IB Style Questions (Core Topic 7)Document8 pagesIB Mathematics HL-Year 1 Unit 6: Worksheet-IB Style Questions (Core Topic 7)boostoberoiNo ratings yet
- Math 1151 Practice Problems For Final Exam Spring 2024Document7 pagesMath 1151 Practice Problems For Final Exam Spring 2024bruhshazzNo ratings yet
- Math 1151 Practice Problems For Final Exam Spring 2024Document7 pagesMath 1151 Practice Problems For Final Exam Spring 2024farhadfaruq78No ratings yet
- Math 141 E1 Review SolnsDocument4 pagesMath 141 E1 Review SolnsPrashidiNo ratings yet
- Math 1151 Sample Questions For MID Exam Summer 2023Document8 pagesMath 1151 Sample Questions For MID Exam Summer 2023Shurav DasNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Equation Graphs - Level 3-4Document10 pagesNonlinear Equation Graphs - Level 3-4baobinh341102No ratings yet
- 1 2 Functions MediumDocument27 pages1 2 Functions MediumShanayaNo ratings yet
- DP 1 Test Aa 002Document8 pagesDP 1 Test Aa 002gulsafar.sadonshoevaNo ratings yet
- Math-1151, Homework-1 Spring 2023Document3 pagesMath-1151, Homework-1 Spring 2023Mahbog AfhgNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions For FINAL ExamDocument8 pagesSample Questions For FINAL ExamTausif AhmedNo ratings yet
- WS 11 Rational FunctionsDocument7 pagesWS 11 Rational FunctionsZeynep İYİGÜNNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Calculus Assignment 03 CSE Spring 2023Document3 pagesFundamental Calculus Assignment 03 CSE Spring 2023Shurav DasNo ratings yet
- Function NotationDocument17 pagesFunction NotationJohnNo ratings yet
- CEMC's Open Courseware - All ExercisesDocument28 pagesCEMC's Open Courseware - All ExercisesMr. Math & ScienceNo ratings yet
- Math 1151 Practice Problems For MID ExamDocument8 pagesMath 1151 Practice Problems For MID ExamMohammad Akter HossainNo ratings yet
- Problemset3 BADocument2 pagesProblemset3 BAAlaina JeyabalanNo ratings yet
- Math 1151 Sample Questions For MID Exam Summer 2023Document7 pagesMath 1151 Sample Questions For MID Exam Summer 2023Shurav DasNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document6 pagesTutorial 1Muhd HafidzNo ratings yet
- Set 1Document4 pagesSet 1Ka Ho WongNo ratings yet
- APPCU08 WKSTF AnswersDocument7 pagesAPPCU08 WKSTF Answerspausean20708No ratings yet
- The Graph of y F (X) Is Stretched Vertically About The X-AxisDocument15 pagesThe Graph of y F (X) Is Stretched Vertically About The X-Axissunita agreyNo ratings yet
- Functions ReviewDocument2 pagesFunctions ReviewJacob WindoverNo ratings yet
- 2 - Problem Set 2.2Document3 pages2 - Problem Set 2.2ed boNo ratings yet
- Functions and EqationsDocument25 pagesFunctions and EqationsPavlos StavropoulosNo ratings yet
- AQA Core 3 Revision BookletDocument20 pagesAQA Core 3 Revision Bookletjake1731No ratings yet
- 100 Ways To Motivate OthersDocument38 pages100 Ways To Motivate OthersonyejekweNo ratings yet
- 9426 - Some Suggestions For Review For Test2-PMT0101 (T3-1415)Document10 pages9426 - Some Suggestions For Review For Test2-PMT0101 (T3-1415)YoongHong ChoyNo ratings yet
- Course End Review: Polynomial FunctionsDocument6 pagesCourse End Review: Polynomial FunctionsRoland CardinalNo ratings yet
- GTK Mathematics2 04 HandoutDocument54 pagesGTK Mathematics2 04 Handoutgraczerfanni19No ratings yet
- Focus U1 T1Document2 pagesFocus U1 T1NOOR AKMARNo ratings yet
- Inbound 6153025579738585635Document65 pagesInbound 6153025579738585635Justin Ralph GanzonNo ratings yet
- Transformations Transformations (Calculator)Document11 pagesTransformations Transformations (Calculator)Praggu SwarnkarNo ratings yet
- Day 4 Combined Transformations WKSHTDocument2 pagesDay 4 Combined Transformations WKSHTjiwanjotmann26No ratings yet
- Lesson 3.3 Finding The Derivative of An Inverse Function-1Document5 pagesLesson 3.3 Finding The Derivative of An Inverse Function-1Hazen D'AuroraNo ratings yet
- AA SL IB2 Calculus 1 File Tutoring PDFDocument8 pagesAA SL IB2 Calculus 1 File Tutoring PDFchelsNo ratings yet
- Math 102 Worksheet1Document2 pagesMath 102 Worksheet1charmaineNo ratings yet
- Seminar 2 - Questions (7,10)Document2 pagesSeminar 2 - Questions (7,10)armaansinghgill05No ratings yet
- Chapter 5-6Document47 pagesChapter 5-6lipapak687No ratings yet
- M106 Worktext Ch2.Lesson 3Document8 pagesM106 Worktext Ch2.Lesson 3Raymond GarciaNo ratings yet
- 2.8 - CHP 2 Test ReviewDocument2 pages2.8 - CHP 2 Test ReviewDalokohsNo ratings yet
- Math 1151 Midterm Question Spring 2023 Edit Nasrina-1Document3 pagesMath 1151 Midterm Question Spring 2023 Edit Nasrina-1Shurav DasNo ratings yet
- IB Questionbank Mathematical Studies 3rd Edition 1Document7 pagesIB Questionbank Mathematical Studies 3rd Edition 1capo007No ratings yet
- Quadratic Function Exam QuestionsDocument20 pagesQuadratic Function Exam QuestionsCho Ah YoungNo ratings yet
- Functional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)From EverandFunctional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)No ratings yet
- Intro To Economics 2022Document32 pagesIntro To Economics 2022wrfeNo ratings yet
- 04 Handout 01 Deductive Proof Practice SolutionsDocument3 pages04 Handout 01 Deductive Proof Practice SolutionswrfeNo ratings yet
- 04 TransformationsDocument7 pages04 TransformationswrfeNo ratings yet
- Rehaan Matthew GOYAL - EE Student ContractDocument2 pagesRehaan Matthew GOYAL - EE Student ContractwrfeNo ratings yet